Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Research Activity
Загружено:
Khizer SikanderАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Research Activity
Загружено:
Khizer SikanderАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
Research the below terminologies, and prepare for discussion in next weeks lecture
Terminology Definition Source
Data Data is raw fact or observation, typically about physical
phenomenon or business transactions. More specifically,
data is the obective measurement of the attributes of
entities, such as people, places, things, and events. !e can
think of data as a "raw material" # it needs to be processed
before it can be turned into something useful.
$adomski, %dam Maria&
'())*+ ,-nformation,
.references and
/nowledge, %n -nteresting
0volution in 1hought2.
-nformation -nformation is data that has been given meaning by way of
relational connection. 1his "meaning" can be useful, but
does not have to be. -n computer parlance, a relational
database makes information from the data stored within it.
3harma, 4ikhil& '())*+ ,1he
5rigin of the Data
-nformation
/nowledge !isdom
6ierarchy2.
/nowledge /nowledge is information that is contextual, relevant, and
actionable. 7or example, a map giving detailed driving
directions from one location to another could be considered
data. %n up#to#the#minute traf8c bulletin along the freeway
that indicates a traf8c slowdown due to construction several
miles ahead could be considered information. %wareness of
an alternative, back#roads route could be considered as
knowledge.
Rasmus, D. !.& '()))+
,/nowledge Management9
More than %- :ut ;ess
!ithout -t,2 <ol. 1*, 4o. (.
1
3ystem % system is a group of interrelated components working
together toward a common goal by accepting inputs and
producing outputs in an organi=ed transformation process. %
system 'sometimes called a dynamic system+ has three
basic interacting components or functions. 1hese include9
-nput involves capturing and assembling elements that
enter the system to be processed.
.rocessing involves transformation processes that convert
input into output.
5utput involves transferring elements that have been
produced by a transformation process to their ultimate
destination.
1wo additional components of the system concept include
feedback and control. % system with feedback and control
components is sometimes called a cybernetic system, that
is, a self#monitoring, self#regulating system.
7eedback is data about the performance of a system.
>ontrol involves monitoring and evaluating feedback to
determine whether a system is moving toward the
achievement of its goals.
%shish /. Dixit& '%ugust 1?,
()11+ ,3ystem %nalysis9
Data, -nformation @
-nformation 3ystems2 <ol
(.1.
2
-nformation system -nformation system has been defined in terms of two
perspectives9 one relating to its function& the other relating to
its structure. 7rom a functional perspective& an information
system is a technologically implemented medium for the
purpose of recording, storing, and disseminating linguistic
expressions as well as for the supporting of decision making.
7rom a structural perspective& an information system
consists of a collection of people, processes, data, models,
technology and partly formali=ed language, forming a
cohesive structure which serves some organi=ational
purpose or function.
5A:rien, B %. '())C+
,-ntroduction to information
systems9 essentials for the
e#business enterprise2.
Mc$raw#6ill, :oston, M%
1ype of information
system
% typical organi=ation has six of information systems with
each supporting a specific organi=ational level. 1hese
systems include transaction processing systems '1.3+ at
the operational level, office automation systems '5%3+ and
knowledge work systems '/!3+ at the knowledge level,
management information systems 'M-3+ and decision
support 3ystems 'D33+ at the management level, and the
executive support systems '033+ at the strategic level.
3helly, >ashman and
<ermaat& ' ()))+ ,>oncepts
for a >onnected !orld2
3
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- (Notes) Peak: Secrets From The New Science of ExpertiseДокумент10 страниц(Notes) Peak: Secrets From The New Science of ExpertiseSylvia Fine100% (1)
- LW 311 Business Law Chap5Документ35 страницLW 311 Business Law Chap5Khizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Cholla Academy Ela Grade 11 Curriculum MapДокумент22 страницыCholla Academy Ela Grade 11 Curriculum Mapapi-320980022100% (1)
- Work Shop Manual Top Lifter Kalmar - 152578161Документ838 страницWork Shop Manual Top Lifter Kalmar - 152578161emezib100% (2)
- MX-CPG - BIM Execution Plan Template - Rev0Документ23 страницыMX-CPG - BIM Execution Plan Template - Rev0vico1982Оценок пока нет
- Food Chain Management For Sustainable Food System DevelopmentДокумент24 страницыFood Chain Management For Sustainable Food System DevelopmentVictor Fraile SordiОценок пока нет
- 7.victoria and Albert Museum: 6. The Natural History Museum Cromwell Road London SW7 5BDДокумент1 страница7.victoria and Albert Museum: 6. The Natural History Museum Cromwell Road London SW7 5BDKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Literature Review: 2.1.1 The Competitiveness of NationsДокумент20 страницChapter 2: Literature Review: 2.1.1 The Competitiveness of NationsKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- 6 StakeholdersДокумент31 страница6 StakeholdersKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Executive Secretary RequiredДокумент1 страницаExecutive Secretary RequiredKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- v4 MKT3001 Assessment One S1 2014-15 Student ViewДокумент4 страницыv4 MKT3001 Assessment One S1 2014-15 Student ViewKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Group E, The Brewers: Didier Acevedo, Justin Martel, Daiskue Takesako & Jonas WongsriskulchaiДокумент12 страницGroup E, The Brewers: Didier Acevedo, Justin Martel, Daiskue Takesako & Jonas WongsriskulchaiKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- University of Bolton, Immigration and Welfare Officers Tier 4 Students Attendance CensusДокумент1 страницаUniversity of Bolton, Immigration and Welfare Officers Tier 4 Students Attendance CensusKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- The Concept of Marketing, Borden (1984)Документ7 страницThe Concept of Marketing, Borden (1984)cristiurseaОценок пока нет
- My Part of Assignment of Corporate Business StrategyДокумент9 страницMy Part of Assignment of Corporate Business StrategyRakesh RoshanОценок пока нет
- 282 688 1 SMДокумент5 страниц282 688 1 SMKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- 1 Full Annual Report 2013Документ154 страницы1 Full Annual Report 2013Jeferson LopesОценок пока нет
- v4 MKT3001 Assessment One S1 2014-15 Student ViewДокумент4 страницыv4 MKT3001 Assessment One S1 2014-15 Student ViewKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- ICT Lecture StudentsДокумент41 страницаICT Lecture StudentsKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Topic - 4 System Selection, Implementation and ReviewДокумент11 страницTopic - 4 System Selection, Implementation and ReviewKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Topic - 7 Security, System Control, and AuditДокумент14 страницTopic - 7 Security, System Control, and AuditKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Topic - 4 System Selection, Implementation and ReviewДокумент11 страницTopic - 4 System Selection, Implementation and ReviewKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- AaaДокумент5 страницAaaKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- L6 - Analytical Tools in Strategic ManagementДокумент12 страницL6 - Analytical Tools in Strategic ManagementKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0167739X10002554 MainДокумент10 страниц1 s2.0 S0167739X10002554 MainBRED_25Оценок пока нет
- Digital Economy 1Документ11 страницDigital Economy 1Khizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementДокумент8 страницCloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Week 5 Recruitment and Selection Powerpoint FinalДокумент25 страницWeek 5 Recruitment and Selection Powerpoint FinalKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- MHR9 e PPT07Документ57 страницMHR9 e PPT07Khizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementДокумент8 страницCloud Computing For Education A New Dawn 2010 International Journal of Information ManagementKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Topic - 1 The Changing Role of The ComputerДокумент12 страницTopic - 1 The Changing Role of The ComputerKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Oral PresentationДокумент34 страницыOral PresentationKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Corse Time TableДокумент1 страницаCorse Time TableKhizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- LW 311 Business Law Chap18Документ30 страницLW 311 Business Law Chap18Khizer SikanderОценок пока нет
- Citizens' Budget Reports:: Improving Performance and Accountability in GovernmentДокумент4 страницыCitizens' Budget Reports:: Improving Performance and Accountability in GovernmentreasonorgОценок пока нет
- Approved CHSE - NCM 102n & ND 221 - SOLLANOДокумент43 страницыApproved CHSE - NCM 102n & ND 221 - SOLLANOCyrelle Heart YoshikawaОценок пока нет
- 3G KPI TroubleshootingДокумент134 страницы3G KPI TroubleshootingVivek Sharma100% (2)
- Defradar - GDPR Competence Development ProcedureДокумент14 страницDefradar - GDPR Competence Development ProcedureJakobović DomagojОценок пока нет
- PrE4 Module 1Документ8 страницPrE4 Module 1Galang, Princess T.Оценок пока нет
- Authorization Letterity IntelligenceДокумент1 страницаAuthorization Letterity Intelligencekancil121Оценок пока нет
- Research Trends in The Development of Information TechnologyДокумент3 страницыResearch Trends in The Development of Information TechnologyКарина КомароваОценок пока нет
- Principles of Effective Speech Writing Grade9aДокумент46 страницPrinciples of Effective Speech Writing Grade9aBC JoshОценок пока нет
- Typography, Color, and Information StructureДокумент18 страницTypography, Color, and Information StructureArual DnasОценок пока нет
- Operations Auditing ExplanationДокумент6 страницOperations Auditing ExplanationNiña Mae DiazОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Oral Communication and Written CommunicationДокумент5 страницDifference Between Oral Communication and Written CommunicationAaqibR100% (1)
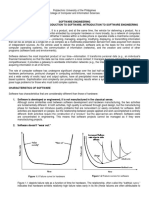
- Figure 1.1 Failure Curve For Hardware Figure 1.2 Failure Curves For SoftwareДокумент5 страницFigure 1.1 Failure Curve For Hardware Figure 1.2 Failure Curves For SoftwareJohn Dustin SaintsОценок пока нет
- MOST Work Measurement Systems (2002, CRC Press) Kjell B. ZandinДокумент548 страницMOST Work Measurement Systems (2002, CRC Press) Kjell B. ZandinPeash MredhaОценок пока нет
- Enterprise Systems and Ongoing Process Change: Thomas H. Davenport, Jeanne G. Harris and Susan CantrellДокумент11 страницEnterprise Systems and Ongoing Process Change: Thomas H. Davenport, Jeanne G. Harris and Susan CantrellVu NguyenОценок пока нет
- Outline: - Transmitters (Chapters 3 and 4, Source Coding and Modulation) (Week 1 and 2)Документ21 страницаOutline: - Transmitters (Chapters 3 and 4, Source Coding and Modulation) (Week 1 and 2)HarshaОценок пока нет
- Volunteer Manual Catholic Community Services of Western WashingtonДокумент42 страницыVolunteer Manual Catholic Community Services of Western WashingtonmpriceatccusaОценок пока нет
- Sample Cover Letter For Fresh Graduate Quantity SurveyorДокумент8 страницSample Cover Letter For Fresh Graduate Quantity Surveyorafllfsbxu100% (1)
- Consumer Law Tutorial Letter 101Документ15 страницConsumer Law Tutorial Letter 101OseameОценок пока нет
- Beckman Coulter DXC 700 AU Host ManualДокумент204 страницыBeckman Coulter DXC 700 AU Host ManualKinnari BhattОценок пока нет
- Finance ReflectionДокумент2 страницыFinance ReflectionCJ IbaleОценок пока нет
- ICT Lesson Notes 2nd Term 2022.23Документ9 страницICT Lesson Notes 2nd Term 2022.23Tolulope VictoriaОценок пока нет
- Rozayus Academy School Scheme of WorkДокумент14 страницRozayus Academy School Scheme of WorkSiti Lorena Binti EdmundОценок пока нет
- Primary Secondary and Tertiary Literature ReviewДокумент8 страницPrimary Secondary and Tertiary Literature ReviewjsmyxkvkgОценок пока нет
- Library Management System Project ReportДокумент33 страницыLibrary Management System Project ReportMafas Munawfar50% (2)
- Fabm 1 - CL Module Week 3Документ15 страницFabm 1 - CL Module Week 3Pamela Diane Varilla AndalОценок пока нет