Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Asepsis and Antisepsis
Загружено:
angelmd830 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
214 просмотров7 страницchirurgie
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документchirurgie
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
214 просмотров7 страницAsepsis and Antisepsis
Загружено:
angelmd83chirurgie
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 7
THE ASEPSIS AND ANTISEPSIS
Asepsis and antisepsis are 2 fundamental notions in order to become a doctor.
I) The asepsis
= the state of germ- free or without infections (without microorganisms =
bacteria, virus, parasite or even fungus).
The asepsis (primary prevention) covers all those procedures designed to reduce the
risk of bacterial fungal viral contamination through the use of sterile
instruments and the gloved !no touch" techni#ue ($e% surgical gloves need to be
sterilised = be aseptic)
Asepsia or aseptic = total absence of germs on a surface, ob&ects, li#uid or in a
wound.
They include all of those prophylactic methods, working processes and behavioral
forms by which microorganisms (bactera, fungi or viruses) can be kept away from
the patient's organism and the surgical wound.
The goal of asepsis is to prevent contamination.
()amples%
*ur internal medium is aseptic meaning germ+free normally. Also the instruments
used for intervention or any surgical procedure must be aseptic because during
surgery the body's ma&or defense against organism (= the skin) is broken , inner
surface of the body are e)posed to the environment.
-hen we must operate it is vital to desinfect the skin before the operation using
betadine for e) before to proceed the incision.
The major method generating the aseptia is the sterilisation.
Sterilisation = method destroying completely all kind of pathogenic or apathogenic
organisms including viruses, bacteria and latent or resting forms such as spores.
This is achived by%
Physical method
echanical method
!hemical method
Sterility " microbiologically germ+free state of materials items.
#$ Physical methods
.oiling water (/0012 30minutes4/hour) = not e5cient on endospore
meaning that must be used in
e)treme conditions when no other
possibilities are availables.
6team at high temperature = A%toclaves% self locking machine that
sterili7es with steam under pressure%
the time needed for sterili7ation at /2/12 is
20 minutes and at /3812 is /0 minutes.
Disadvantage = unsuitable for heat sensitive ob&ects.
9ry heat at /:0+/;01c for respectively 2 and / hours.
*pen <ame of propane = !&laming'% common type of heat sterili7ation
consisting to !burn" microorganisms by
e)posing them to an open <ame of propane.
=rocess also known as !incineration"% ie% <aming of inoculating
needles and the tops of laboratory glassware before and
after sampling are e)amples of incineration.
Disadvantage = some say
that this method , creation of a thin bed
ofg carbon which is a focus for infection (must wipe the
carbon o> and clean with (T*?).
@adiation = AB or gamma% use for sterilise the needles, the drainage
tubes or even the surgicals gloves.
9isadvantage% it is forbiden to
combine it with another method because it generates
to)ic substances% ie% using ethylene o)ide after a gamma radiation ,
formation of ethylene chlorohydrin (cytoto)ic e)tremely irritating on
wound, less on skin inhibit cell growth).
($ !hemical methods
.y vapo%rs and ga), using%
+ &ormaline% 80C a#ueous solution of formaldehyde (2h2o) =
colorless, neutral and volatile li#uid with a pungent odor and
slightly irritating taste. Dormalin is e#ual in germicidal power
to corrosive sublimate and in large room a 2,E volume C of
formalin in the air destroyed all microorganisms in a #uarter
of hour.
?owF, when allowed to evaporate in the presence of wool,
gau7e+bandages or other dressing material, the vapors of
formalin condensed upon the fabrics in solid form
(paraformalin) and so desinfected them.and ethyleno)ide.
?ence dressing material impregnated with formalin become
perfectly sterile and can immediatly be used as antiseptic
dressing.Also the vapors from the spray by a steam atomi7er
above the patient's head has proven e5cient in whooping+
cough and chronic bronchitis.
+ Ethylene o*ide " ga) sterilisation% highly penetrative and
active against bacteria spores viruses.9isadvantage% it is
<ammable to)ic e)pensive leaves to)ic residues on
sterili7ed items (see above).
.y immersion, using%
+ ercasept% a#ueous solution of phenylmercuric borate
(topical antiseptic and desinfectant that is soluble in water
ethanol glycerol) with a concentration of 2C1.Ased in
surgery
+ erc%ry+rom% very e5cient desinfectant for the burns
+ ,l%taraldehyde (ie% 2$9(G )= very corosive for the
instrument , destruction of the metal instruments with time
but it is very usefull for surgery = 30 minutes to /hour of
immersion is necessary to destroy all germs e*ept hepatic
vir%ses " - and ! . to destroy these vir%ses an
immersion of (/h at least is necessary. .efore any
invasive operation we must ask the patient if he has hepatitis
. or 2 and if it is the case , sterilise again the instruments
after operation.
0$ echanical methods
+ .acterial Hlters for air sterilisation is used.
8. E*amples.
Dor%
+ Air 1 rooms = use %ltraviolet radiation +acterial 2lter or formalin
vapors
+ Instr%ments 1 other o+jects resistant to temperat%re (glass or metal
made)=use dry heat at /:0+/;012 for 30+80 minutes or immersion in
special solution.
+ Soft materials meaning most common tissues%
!otton 3ool
!otton s3a+s
Dressing
!ompresses
-e are using sterilisation by stream 4a%toclaves) at /8012 and /,E atm.
+ 5%++er or plastic materials which are not resistant to normal heat
sterili7ation we use method as%
Ethylene o*ide vapors in special device at temperature of
80+EE1c for I0 to 3:0 minutes depending on pressure or
previous sterili7ation by gamma radiation obtained from cobalt
:0 or 2elsium /3J in industrial environment.
II) Antisepsis
Kethod of destroying germs on biological structure such%
S6in
7o%nds
-ody cavities
-o3el
Asing the methods seen before for asepsia.
$n fact antisepsis relate to the momentarily removal of transient microorganisms
from living tissues reduction in the resident <ora by using antiseptic products.
$n a wider sense, antisepsis includes all those prophylactic procedures designed to
ensure surgical asepsis.
Kethods of antisepia are%
!hemical s%+tances = antiseptics with e)ternal application on either the
skin or mucous membranes.
Dor academic purpose they can be classiHed as%
7ea6 antiseptic%
/. Soap detergent (most common one) = wash hands E
minutes at least with water but today with the new special
solution it takes only 2 to 3 minute to desinfect.
S%rface antiseptics%
+ Alcool 89: concentration = germicid by coagulation of
germ's proteins
+ Iodine.
o In alcoolic sol%tion " tinct%re of iodine. is a
very good anti+bacterial4 fungal 4 viruses agent$
Iodine alcoolic sol%tion is
used for mycosis and is able to destroy fungus.
o In non alcoolic sol%tion where it is associated
with polyvinil pyrolidone = +etadine (here there is
no coagulation of the germ's proteins).
-etadine 4or non alcoolic iodine sol%tion) is
used for hands skin or wounds (the alcoolic one
cannot be used for wounds)% clean the hands with
betadine during 3 minutes at least.
!hlor eliminating s%+stance.
+ Sodi%m hypochrorite (DA;IN solution) is indicated
freasly diluted by continuous or simple irrigation of
wounds (post operative) = %sed in %rology
+ !hloramine sol%tion. 9<(-=> concentration is used
for pavement, material and glass ob&ects (it is a too high
concentration to be used on the wounds , chemical
burns) 1 9<# to 9<0> for 3o%nds
?*ygen eliminating s%+tance.
H(?(. sol%tion p%t on a 3o%nd, generate a e>ervescence and
remove the necrotic tissue remove the pus clean the area by
destroying even anaerobical germs 4e*. gangren or tetanos)
+ -oric acid. it is a white cristal with similar e>ect than
?2*2 (but no e>ervescence).
Heavy metal compo%nds%
+ erc%ry
+ Silver
A)oic dyes.
+ 5ivanol 4 ethacridine lactate or ethacridine monolactate
monohydrate)% yellow powder largely used in surgery for treating infective
wounds (similar fre#uency of use than betadine or ?2*2 in surgery).
+ ;n?/ (kalium permanganic acid)= violet cristalL solution /+8C
concentration used in surgery for cleaning mucous membrane (in case of an
infective wound in the buccal cavity in case of hemorroids or anal Hssure =
local bath).
+ Panestrine = green color powder used in surgery before (20+30 years ago)
to clean wounds as an alternative to betadine...it is not use anymore.
Phenol or phenol compo%nds%
Ased in dentistry as spray to desinfect the instruments because it is e)tremly
corrosive.
Detergents% can be anionic or cationic
Anti+iotics%
-ith internal adimistration (intraveinous intramuscular) or oral
administration
They can be applied locally or systematically$
9i>erent categories of antibiotic e)ist related to the area (like the stomach or the
lung ect...) the germ concerned but there is also more general one.
-e reali7e an antibiogram to know.
Example of questions for the exam:
En%marating the chemical antiseptic
Descri+e s%rface antiseptic
Вам также может понравиться
- Pancreatic Cancer, Cystic Neoplasms and Endocrine Tumors: Diagnosis and ManagementОт EverandPancreatic Cancer, Cystic Neoplasms and Endocrine Tumors: Diagnosis and ManagementОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingОт EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováОценок пока нет
- Noninvasive Airway Management Techniques How and When To Use ThemДокумент16 страницNoninvasive Airway Management Techniques How and When To Use ThemBulborea MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Orthopedic EmergenciesДокумент63 страницыOrthopedic EmergenciesNasser AlQadhibОценок пока нет
- Choice of Mesh For Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia RepairДокумент12 страницChoice of Mesh For Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repairdr_592470553Оценок пока нет
- Topical Hemostatic Agents in Surgery PDFДокумент10 страницTopical Hemostatic Agents in Surgery PDFFernanda SouzaОценок пока нет
- Asepsis and AntisepsisДокумент22 страницыAsepsis and AntisepsisNdor BariboloОценок пока нет
- ESWL For Pancreatic StonesДокумент7 страницESWL For Pancreatic StonesOana TimofteОценок пока нет
- AnaphylaxisДокумент37 страницAnaphylaxisDenis Qosja100% (1)
- Revarsate PleuraleДокумент55 страницRevarsate PleuraleBogdan NiculaeОценок пока нет
- Pancreatitis Research PDFДокумент400 страницPancreatitis Research PDFNMSYED100% (1)
- Spleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementДокумент53 страницыSpleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementMuhammad SaadОценок пока нет
- Departator ThompsonДокумент52 страницыDepartator ThompsonMinnossОценок пока нет
- Presented By: Melissa PeartДокумент20 страницPresented By: Melissa PeartMelissa Monique Peart-YatesОценок пока нет
- Soc TraumaticДокумент39 страницSoc TraumaticAnca Toma100% (1)
- Liver Segments Explained With MnemonicДокумент13 страницLiver Segments Explained With Mnemonicmyat252100% (1)
- ImpetigoДокумент31 страницаImpetigoUmmu Insyirah100% (1)
- Ultrasonografia Splinei: Dr. Petru Adrian Mircea Clinica Medicala IДокумент38 страницUltrasonografia Splinei: Dr. Petru Adrian Mircea Clinica Medicala IOana Pop100% (1)
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Staging by CT and MRIДокумент134 страницыNasopharyngeal Carcinoma Staging by CT and MRIإسلام الجزيريОценок пока нет
- Mesentric IschemiaДокумент27 страницMesentric Ischemiawalid ganodОценок пока нет
- Ludwig AnginaДокумент3 страницыLudwig AnginaWellyAnggaraniОценок пока нет
- DR - Abeidi's Review FinalДокумент157 страницDR - Abeidi's Review FinalSandra AbboudОценок пока нет
- US Gall Bl. Biliary TreeДокумент20 страницUS Gall Bl. Biliary TreeNenad V. DjokicОценок пока нет
- Revision Sinus Surgery-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2008)Документ349 страницRevision Sinus Surgery-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2008)Javier Gutiérrez CastilloОценок пока нет
- 1.rationale of Use of Antibiotic in Surgical Patients CДокумент22 страницы1.rationale of Use of Antibiotic in Surgical Patients CPanna SahaОценок пока нет
- Boala Polichistica Hepato-RenalaДокумент1 страницаBoala Polichistica Hepato-RenaladoinaОценок пока нет
- Thoracentesis NEJMДокумент4 страницыThoracentesis NEJMKTNBОценок пока нет
- Staged Abdominal Re-Operation For Abdominal TraumaДокумент7 страницStaged Abdominal Re-Operation For Abdominal TraumaNovrianda Eka PutraОценок пока нет
- Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars - UpToDateДокумент23 страницыKeloids and Hypertrophic Scars - UpToDateAnna LopezОценок пока нет
- Parasitic Infections in SurgeryДокумент24 страницыParasitic Infections in SurgerykhadzxОценок пока нет
- Hanson Infectious Diseases - Anamneza I StatusДокумент33 страницыHanson Infectious Diseases - Anamneza I StatusSilvia KesegОценок пока нет
- 1Документ4 страницы1Mirla Castellanos JuradoОценок пока нет
- Mastoidectomy KT KHДокумент28 страницMastoidectomy KT KHKyaw HtetОценок пока нет
- C Difficile DiarrheaДокумент12 страницC Difficile DiarrheaSi vis pacem...Оценок пока нет
- Syllabus 1. Programme Details: Ministerul Educației NaționaleДокумент5 страницSyllabus 1. Programme Details: Ministerul Educației NaționaleSilviaОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis PDFДокумент4 страницыViral Hepatitis PDFNina BracyОценок пока нет
- Acute Limb IschaemiaДокумент32 страницыAcute Limb IschaemiaAnonymous 9wHscM100% (1)
- Pancoast TumorДокумент26 страницPancoast TumorDhanis HastinОценок пока нет
- Global Atlas of AsthmaДокумент196 страницGlobal Atlas of AsthmaMinerva Stanciu50% (2)
- OSCE For The Final FFICMДокумент318 страницOSCE For The Final FFICMMohd Saif KhanОценок пока нет
- Kod - S Guide On Final Professional Exam 1 PDFДокумент31 страницаKod - S Guide On Final Professional Exam 1 PDFHassanAbasОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulants 2019Документ11 страницAnticoagulants 2019Srijan VermaОценок пока нет
- In The Clinic - Acute PancreatitisДокумент16 страницIn The Clinic - Acute PancreatitisSurapon Nochaiwong100% (1)
- 03-Non-Fermentative Gram-Negative Bact Eria v1 - 3 2Документ56 страниц03-Non-Fermentative Gram-Negative Bact Eria v1 - 3 2Abiola Olumuyiwa OlaitanОценок пока нет
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: by DR Moustafa Kamal Eldin, MD Lecturer of Cardiology Faculty of Medicine Fayoum UniversityДокумент24 страницыAcute Coronary Syndrome: by DR Moustafa Kamal Eldin, MD Lecturer of Cardiology Faculty of Medicine Fayoum UniversityAbdulrahman Ahmed100% (1)
- Thoracic Decortication: Sabita Chalise Bns 3 YearДокумент32 страницыThoracic Decortication: Sabita Chalise Bns 3 YearRamchandra Chalise100% (1)
- DSTC 0309-Dcs & DCR UpdatedДокумент124 страницыDSTC 0309-Dcs & DCR UpdatedDenny TombengОценок пока нет
- Tracheostomy A Multi Professional HandbookДокумент404 страницыTracheostomy A Multi Professional HandbookDaniela ManriquezОценок пока нет
- Modified Radical MastoidectomyДокумент5 страницModified Radical MastoidectomyRaman BhavanaОценок пока нет
- SYLLABUS-2016 CT SurgeryДокумент8 страницSYLLABUS-2016 CT SurgeryGaetano Di GiovanniОценок пока нет
- Dermatoscopy and Skin Cancer, updated edition: A handbook for hunters of skin cancer and melanomaОт EverandDermatoscopy and Skin Cancer, updated edition: A handbook for hunters of skin cancer and melanomaОценок пока нет
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesОт EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodОценок пока нет
- Thrombectomy Procedures - Percutaneous Mechanical, Vascular Surgical, PharmaceuticalОт EverandThrombectomy Procedures - Percutaneous Mechanical, Vascular Surgical, PharmaceuticalОценок пока нет
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Bhutan Final BacteriologyДокумент56 страницBhutan Final Bacteriology99nonameОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Asepsis and AntisepsisДокумент47 страницLecture 1 Asepsis and AntisepsisAmir KhanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Surgical Asepsis and Antiseptic MeasuresДокумент2 страницыChapter 7 Surgical Asepsis and Antiseptic MeasuresAndrew BonusОценок пока нет
- Liver SegmentationДокумент24 страницыLiver Segmentationangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- Diviziunea CelularaДокумент7 страницDiviziunea Celularaelen0587Оценок пока нет
- Clavien Dindo ClassificationДокумент9 страницClavien Dindo Classificationangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Examination of The AbdomenДокумент13 страницClinical Examination of The Abdomenangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- MELD/PELD Calculator Documentation: The MELD Score Calculation UsesДокумент4 страницыMELD/PELD Calculator Documentation: The MELD Score Calculation Usesfrfrfr11Оценок пока нет
- Surgical InstrumentsДокумент3 страницыSurgical Instrumentsangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- LP Surgery LaparotomyДокумент2 страницыLP Surgery Laparotomyangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- Acute PeritonitisДокумент11 страницAcute Peritonitisangelmd83100% (1)
- LP Surgery ChestДокумент6 страницLP Surgery Chestangelmd83Оценок пока нет
- Horizontal Steam Sterilizer V2Документ12 страницHorizontal Steam Sterilizer V2SujiОценок пока нет
- ISO 13408-6-2008-Aseptic Processing of HeДокумент24 страницыISO 13408-6-2008-Aseptic Processing of HeJOSEPHОценок пока нет
- 65705A Manual ConcentrixFX FB SXandSW 2Документ2 страницы65705A Manual ConcentrixFX FB SXandSW 2Nicoli RajcoomarОценок пока нет
- Thermal SolutionsДокумент14 страницThermal SolutionsManuel J. Vílchez FrancoОценок пока нет
- Food Losses During Food Processing As Food WasteДокумент20 страницFood Losses During Food Processing As Food WasteJyoti JhaОценок пока нет
- Effects of Gamma On Medical DevicesДокумент7 страницEffects of Gamma On Medical DevicesLin ZinОценок пока нет
- Quality Control in The Microbiology LaboratoryДокумент5 страницQuality Control in The Microbiology LaboratoryAnne CabreraОценок пока нет
- Seminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementДокумент24 страницыSeminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementTHONDYNALUОценок пока нет
- Las Tle Week2 Hand SpaДокумент21 страницаLas Tle Week2 Hand SpaCheiryl Dandoy100% (1)
- Esterilizacion Indicadores Biologicos 2Документ8 страницEsterilizacion Indicadores Biologicos 2adriana hernandezОценок пока нет
- Antibacterial For Plastics PDFДокумент24 страницыAntibacterial For Plastics PDFRiaОценок пока нет
- Auto So NixДокумент140 страницAuto So NixAlejandro CapizОценок пока нет
- Gamma IrradiationДокумент27 страницGamma Irradiationmuzammil21_adОценок пока нет
- Practical Uses and Applications of Gamma RaysДокумент4 страницыPractical Uses and Applications of Gamma RaysTaurus PearsonОценок пока нет
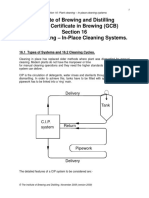
- GCB 2009 Sect16 CIP SystemsДокумент17 страницGCB 2009 Sect16 CIP SystemsRiyanОценок пока нет
- DeltaLAB Catalogue PDFДокумент320 страницDeltaLAB Catalogue PDFViktorija AvicenaОценок пока нет
- Reverberi Pratika B16-20 Sterilizer - Service ManualДокумент27 страницReverberi Pratika B16-20 Sterilizer - Service ManualMoyses MoyОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент429 страницPDFFilipa ChinêsОценок пока нет
- Manuf Sterility Testing GuidelinesДокумент36 страницManuf Sterility Testing GuidelinesAlief AnggaОценок пока нет
- GE Mac 400 - Quick GuideДокумент7 страницGE Mac 400 - Quick GuideEduard Stiven MarinОценок пока нет
- Cupping Presentation 1Документ69 страницCupping Presentation 1Said Halilovic100% (3)
- 3 Surgical Asepsis PDFДокумент32 страницы3 Surgical Asepsis PDFLimYiОценок пока нет
- The Membrane Selector Guide. MilliporeДокумент1 страницаThe Membrane Selector Guide. MilliporeClaudiaОценок пока нет
- Sterile Supplies Audit ToolsДокумент2 страницыSterile Supplies Audit ToolsAbdur Rashid KhanОценок пока нет
- MyRay-HyperioX9-Manual Del Usuario ESДокумент1 226 страницMyRay-HyperioX9-Manual Del Usuario ESmjidilaОценок пока нет
- Sensory Evaluation of Concentrated Milk Products FinalДокумент41 страницаSensory Evaluation of Concentrated Milk Products Finalhauvu75% (4)
- CHAPTER 1 Form 4 BIOLOGY SPMДокумент15 страницCHAPTER 1 Form 4 BIOLOGY SPMCrescentiaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology and Parasitology Unit IIДокумент15 страницMicrobiology and Parasitology Unit IIBrixValdrizОценок пока нет
- Incubadora de Muestras Attest 290 Manual de UsuarioДокумент12 страницIncubadora de Muestras Attest 290 Manual de UsuariowatisnaiОценок пока нет