Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Microbiology Lab Manual
Загружено:
GuruKPO100%(3)100% нашли этот документ полезным (3 голоса)
770 просмотров23 страницыMicrobiology Lab Manual
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMicrobiology Lab Manual
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(3)100% нашли этот документ полезным (3 голоса)
770 просмотров23 страницыMicrobiology Lab Manual
Загружено:
GuruKPOMicrobiology Lab Manual
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 23
Biyani's Think Tank
Concept based notes
Zoology Lab Manual
Microbiology
B.Sc(Bio tech)
Alka Dadeech
(Lab In-charge)
Department of Biotechnology,
Biyani Girls College, Jaipur
2
Published by :
Think Tanks
Biyani Group of Colleges
Concept & Copyright :
Biyani Shikshan Samiti
Sector-3, Vidhyadhar Nagar,
Jaipur-302 023 (Rajasthan)
Ph : 0141-2338371, 2338591-95 Fax : 0141-2338007
E-mail : acad@biyanicolleges.org
Website :www.gurukpo.com; www.biyanicolleges.org
Edition: 2011
Price:
While every effort is taken to avoid errors or omissions in this Publication, any
mistake or omission that may have crept in is not intentional. It may be taken note of
that neither the publisher nor the author will be responsible for any damage or loss of
any kind arising to anyone in any manner on account of such errors and omissions.
Zoology Lab Manual 3
Leaser Type Setted by :
Biyani College Printing Department
4
Preface
I am glad to present this book, especially designed to serve the needs of the
students. The book has been written keeping in mind the general weakness in
understanding the fundamental concepts of the topics. The book is self-explanatory
and adopts the Teach Yourself style. It is based on question-answer pattern. The
language of book is quite easy and understandable based on scientific approach.
Any further improvement in the contents of the book by making corrections,
omission and inclusion is keen to be achieved based on suggestions from the
readers for which the author shall be obliged.
I acknowledge special thanks to Mr. Rajeev Biyani, Chairman & Dr. Sanjay
Biyani, Director (Acad.) Biyani Group of Colleges, who are the backbones and main
concept provider and also have been constant source of motivation throughout this
Endeavour. They played an active role in coordinating the various stages of this
Endeavour and spearheaded the publishing work.
I look forward to receiving valuable suggestions from professors of various
educational institutions, other faculty members and students for improvement of the
quality of the book. The reader may feel free to send in their comments and
suggestions to the under mentioned address.
Author
Zoology Lab Manual 5
Index
Topic
1. Introduction of Microbiology
2 Instruments
3.Sterilization
4.Culture
5.Stains
6
MICROBIOLOGY
(PRACTICAL)
Introduction of Microbiology
Q.1. What is Microbiology?
Ans.: Microbiology is a branch of science that deals with the study of various
morphological, physiological as well as genetic aspects of microorganisms
along with their activities. This field is divided in number of diversities as
Bacteriology, Virology, Protozoology, Physiology, and Mycology. It can be
employed in various fields as pharmaceutical, food, agriculture, waste
treatment, industrial microbiology etc. There are many applied aspect of
microbiology that convey the variety and significance of microbial activities.
Microbiology : The study of microscopic organism its name is derived from
three Greek words Mikros Means small, Bio means life and Logos mean to
study.
Q.2. Who is the father of Industrial Microbiology?
Ans.: Louis Pasteur
Q.3 Who is the father of Microbiology?
Ans.: Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
Q.4 What is Disinfection?
Ans.: It is complete destruction of pathogenic organisms or organisms capable of
giving rise to infection.
Zoology Lab Manual 7
Q.5. What is Pasteurization?
Ans.: It is a technique of sterilizing milk by heating at specific temperature for
specific duration and then followed by cooling.
Q.6. What is Incineration?
Ans.: It involves killing of micro-organisms by using flame.
Q.7. What is Clone?
Ans.: Clone is referring to as a colony that is derived from single parent cell; all the
cells of a clone are identical genetically and constitute a homogeneous
population.
Q.8. What is Contamination?
Ans.: The contamination is unwanted growth of microbes alongwith useful
microbes.
Q.9. What is Inoculums and Inoculation?
Ans.: Inoculums is the minimum amount of micro-organism required for its
propagation.
Inoculation is the transfer of inoculation on the fresh medium.
Q.10. What is Incubation?
Ans.: Allowing the micro-organism to grow in the specific set of optimal conditions
as temperature, light, humidity, duration etc.
Q.11. What is Lyophillization?
Ans.: In this process, water is removed by evaporation, sublimation from the per
frozen sample. After drying the strains are stared under vacuum in in
dividual vialsor
8
Ampoules. This process is widely used to prescribe bacteria tests, fungi and
some viruses.
Q.12. What is Buffer Solution?
Ans.: Buffer solution is a solution that is resistant to change in pH
on the addition of
small amounts of acid/alkali.
Q.13. What is Floatation Method?
Ans.: In these method different concentrations of sucrose is used in which VAM
stores float. The spores can be separated out and examined under the
microscope.
Q.14 What is Micrometry?
Ans.: Micrometry is the measurement of micro-organisms. Micro-organism are
small. The dimensions of these are usually expressed in units smaller than
millimeters. The micrometer (m) is 10
-3
of a millimeter, one millionth (10
-6
) of
a meter and 1/25400 of an inch.
A Nanometer 10
-9
of a meter.
An Angstrom 10
-10
of a meter.
Q.15. Explain the following :
(i) Protozoology
(ii) Algology or Physiology
(iii) Microbial Ecology
(iv) Microbial Taxonomy
(v) Air Microbiology
(vi) Exomicrobiology
Zoology Lab Manual 9
(vii) Immunology
(viii) Bio-technology
Ans.: (i) Protozoology : It is the study of protozoananimal-like and mostly
single-celled, encaryotic organisms.
(ii) Algology or Psychology : It is the study of algaesimple aquatic
organisms ranging from single-celled forms to large sea weeds.
(iii) Microbial Ecology : It is the study of inter-relationships between
microbes and environment.
(iv) Microbial Taxonomy : It is concerned with the classification, naming
and identification of microorganism.
(v) Air Microbiology : It deals with the role of aerospora in contamination
and spoilage of food and dissemation of plant and animal disease
through air
(v) Exomicrobiology : It deals with the exploration for microbial life in
outer space.
(i) Immunology : It deals with the immune system that protects against
infections and helps us to understand the phenomena for both acquired
and innate, immunity, in addition to the study of antibodyanti-gen
reactions in the laboratory.
(ii) Biotechnology : It is the scientific manipulation of living organisms
especially at the monocular and genetic level to produce useful
products.
Q.16. What is the use of Hanging Drop Technique?
Ans.: Hanging drop preparation is useful for microscopic examination of living
micro-organisms, especially bacteria without staining them to see their
mobility due to flagella.
10
Q.17. What is Viruses?
Ans.: Viruses are non cellular biological entities compounds solely of a nucleic acid
surrounded by a protein coat, the cap Sid.
Q.18. What means the Microphotograph?
Ans.: The microphotograph means a small photograph, the details of which can be
seen clearly only with the help of optical enlargement.
Q.19. Why we store micro-organism in liquid nitrogen?
Ans.: Liquid nitrogen is the only suitable method for long term preservation of
micro-organism that do not survive freeze-drying. Some microbes do not
show the effect of cooling and warming. Such loss is reduced by the use of
cryoprotectant such as glycerol and dim ethyl suphoxide (DMSO) and the
adjustment of growth conditions, rate of cooling and warming.
Q.20. What are the basic requirements of a Microbiological Laboratory?
Ans.: Basic requirements of a Microbiological Laboratory is :
(1) Common Glassware : Test Tubes, Culture Tubes, Petridis, Pipette,
Erlenmeyer Flasks (Conical, Round Bottom etc.), Volumetric Flask,
Beaker, Measuring Cylinder, Stirrer/Glass Rod, Funnel, Dropping
Bottle, Microscopic Slide, Cavity Slide, Cover Slip etc.
(2) Tools/Apparatus : Glass Spreader, Inoculation Needle & Inoculation Loop,
Bunsen Burner, Spirit Lamp), Water Bath, Autoclave, Laminar, Airflow,
Incubator, Hot Air Oven, Quebec Colony Counter, pH Meter,
Spectrophotometer (Colorimeter), Centrifuges, Haemocytometer &
Microscope.
Zoology Lab Manual 11
Instruments
Q.1 What is Glass Spreader & its use.
Ans.: Bending L shaped glass rod called spreader. It is used to spread evenly the
microorganism on agar surface present in liquid medium.
Q.2. What is Inoculation Needle & Inoculation Loop?
Ans.: Inoculation needle loop is made up of a long platinum wire fixed in to a
metallic rod. A wire loop has a handle with steel screw shaft in which
nichrome or platinum wire is to be fitted. The loop should be such so as to
retain a small circular film in it by dipping in solution for this proper size (5-
7cm) of the wire is recommended.
The loop and wire used for picking small quantities of solid materials from a
microbial colony, and can be used to inoculated either a liquid or a solid
medium. Both the loop and straight wire must be flamed immediately after
uswed so that contamination is avoided.
Q.3. What is Water Bath & its use?
Ans.: Water bath is an instrument that is used to provide constant temperature to a
sample. It consists of an insulating box made up of steel fitted with electrode
heating coil. The temperature is controlled through a thermostat. The main
use of water bath is the incubation of samples at a desired & constant
temperature.
12
Q.4. What is Autoclave?
Ans.: The killing action of heat on the organisms can be done by using increase in
the steam in a closed system. The water molecules become aggregated
resulting in increase in their penetration. The water boils at 100C and the
steam accumulates in a closed container result ion in increase in pressure.
The autoclave is usually of pressure cooker type made up of gunmetal sheet
that is supported in an iron case. It is based on moist heat sterilization. It
usually operates at 15 lb/inch
2
steam pressure and 121C kmp for 30 min. This
temperature for 30 minutes is enough to kill all the spores and call of
microorganisms.
Q.5. What is Laminar Airflow.
Ans.: Laminar flow is an apparatus consists of an air blower in the rear side of the
chamber that can produce airflow with uniform velocity along patroller flow
lines. There is a special filter system of high efficiency particulate air filter
HEPA that can remove particles as small as 0.3mm. It uses is all the work
related to pouring, plating streaking etc. are to be carried out in the flame zone
of the burner or spirit lamp.
Q.6. Write name of Filter present in Laminar Air Flow?
Ans.: High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are present in laminer air
flow.
Q.7. What is Haemocytometer?
Ans.: Heamocytometer is the name given to a device used to measure the blood
cells. This is also used for counting the other cells viz. spores, bacteria etc.
Q.8. What is pH Meter?
Ans.: The electrode system for measurement of pH
is called pH
meter. A standard
pH meter has two electrodes - one glass electrode and the second Mercury
Zoology Lab Manual 13
Miraculous Chloride (Calomel) or silver silver chloride reference electrode.
The reference electrode is emerging in saturated KCl solution.
P
H
can be defined as a negative log of hydrogen ions.
(H
+
) concentration pH
= -log10H
+
=7.
pH is the degree of acidity alkalinity of a solution on a scale 1 to 14.
Q9. How many types of Centrifuge are there?
Ans.: There are three types of centrifuge :
(1) Small Bench Centrifuge : The maximum speed of these centrifuges vary
from 4000 to 6000 rpm (round per minute) related with 3000 to 7000 gm.
(2) High Speed Refrigerated Centrifuge : Its maximum rotor speeds of
25000 rpm related with 60000 gm with a range of interchangeable fixed
angle and swinging bucket rotors are available.
(3) Ultracentrifuge : The preparative ultracentrifuges have spinning rotors
that can attain 80000 rpm with a relative centrifugal field of up to
600000 gm.
14
Sterilization
Q.1. What is Sterilization
Ans.: Sterilization is a process of making an article, surface or medium free from any
type of microorganisms. Through sterilization, any kind of micro-organisms
are killed.
Q.2. Which method we use for Sterilization.
Ans: Method of Sterilization:
(1) Physical Method of Sterilization :
(a) Moist Heat: It is done through autoclaving.
Dry Heat: Dry heat is produced by an hot air oven, glass syringe,
forceps, scalpel, flasks, Petri dishes etc sterilized in an oven at
150
o
C for 30 minutes.
(b) Radiation: Ultra Violet (UV) radiation is used in inoculation
chamber or laminar air flow.
(c) Sterilization by Membrane Filtration: Certain substances like
enzymes, antibiotics, amino acids, vitamins, etc. are heat
sensitive; hence their sterilization is not possible by autoclaving.
Such heat-sensitive substances are sterilized through various
types of filters which may retain the bacteria. Millipore
membrane filters are commonly used.
(2) Chemical Method of Sterilization :
(a) Alcohol: 70% ethanol or 70% isopropanol is used to sterilize the
working table top, inoculation chamber etc.
(b) Aldehyde : Laboratory is fumigated with formaldehyde when
the number of contaminants gets increased.
(c) Inorganic Chemicals : There are certain heavy metals which are
toxic to any organisms such as salts of copper mercury etc. HgCl2
Zoology Lab Manual 15
solution (0.1%) is most commonly used as disinfectants for seeds,
explants or any materials.
16
Culture
Q.1. What is Culture? Define the different types of Culture Media?
Ans.: The growth of an organism on a medium is called culture. The food base that
supports the growth of an organism is called culture medium.
The culture media are devised in such a way that the organism should get the
entire nutritional requirement. Basically, the culture media are of three types.
(i) Natural Medium : Ex diluted blood, urine, milk, vegetable, juices,
peptone or animal cells/tissues/organs.
(ii) Semi-synthetic Medium : Ex potato dextrose agar, czapek-dax agar,
nutrient agar, beef extract agar, media etc.
(iii) Synthetic Medium : The synthetic medium will be of different types as
(a) General purpose medium Ex-for routine microbiological work.
(b) Differential medium Ex-differentiate the groups of
microorganisms by opting such media that contain dyes and
colour indicators to give biochemical response Ex-mac-monkey
and eosin ethylene blue agar.
(c) Selective Medium : Contains compounds found in differential
media and certain agents that further inhibit growth of most of
the micro-organism and promote growth of the required ones.
(d) One Purpose Medium : Highly selective medium used to isolate
specific micro-organizers ex-brilliant green agar for isolation of
salmonella from faces.
(e) Assay Medium : Assay antibiotics, amino acid, vitamins etc.
Q.2 What is the preparation of liquid media or Broth?
Ans.: Components
Nutrient Broth Medium
Zoology Lab Manual 17
HCL (1 N)
Controlled the pH
NaOH (1 N)
NaCl 5.0 gm.
Beef Extract - 3.0 gm.
Distilled Water - 1 ltr.
pH - 7.0
Procedure : Weigh the chemical ingredients of the nutrient broth and transfer
them into a beaker containing 500 ml distilled water neat on hot plate and
dissolve the ingredients. Add more distilled water to make the volume to 1
litre. Measure the pH by pH meter. Adjust the pH
to 7.0 by adding drops of
either HCl or NaOH solution. Prepare cotton plugs and apply them into the
mouth of flask. Tightly cover the mouth of cotton plugs with aluminum foil
and tie with a rubber band. Place the flask in side the autoclave sterilises at
121C for 30 minutes. Use the broth when required or store room temperature
for further use.
Q.3. Write the composition of media.
(i) PDA (ii) Nutrient Agar Media
Ans.: (i) PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar)
Potato Tubers - 200 gms.
Dextrose - 20 gms.
Agar - 15 gms.
Distilled Water - 1 litre
pH - 5.6
(ii) Nutrient Agar Media :
Peptone 5.0 gms.
Beef Extract 3.0 gms.
18
Agar 15 gms.
pH - 7.0
Distilled Water - 1 ltr.
NaCl - 5.0 gms.
Q.4. Explain the quality control of media?
Ans.: (i) The media are sterile exfree from microbes.
(ii) It has stable and shelf life.
(iii) It has effectiveness.
(iv) If required, it also has selectiveness.
Q.5. What is the technique for pure culture of Microorganisms?
Ans.: Bacteria exist in mixed population. It is very rare to get a single and pure form
for studying the cultural, morphological, and physiological characters of
individual species. It is essential to separate them from the others to get in the
form called pure culture. There are many important methods for isolating
pure culture from mixed culture.
(iii) Streak plate method from culture to pure culture.
(iv) Pour plate method for pure culture.
(v) Spread plate method.
(vi) Serial dilution agar plate method (or viable plate count method).
Q.6. Write the methods of culture preservation and maintenance.
Ans.: The methods of preservation are :
(i) Freeze drying or Lyophilization Ex-bacteria, yeasts, fungi and some
viruses.
Zoology Lab Manual 19
(ii) Storage in liquid nitrogen.
(iii) Storage of strains at 70
0
C.
(iv) Storage on glass beads at 60 to 70
0
C.
(v) Storage in gelatin discs.
(vi) Storage in mineral oils.
(vii) Storage in soil ex fungi aspergillums, rhizopur, alternara, penicillin.
(viii) Maintenance by sub culturing.
Q.7. What is Agar?
Ans.: It is that component of the medium that helps in the solidification of the liquid
medium (Broth). It is known as agar. It is a complex polysaccharide consists
of 3,6unhydro-L-Galactose & D-Galactopyranose.
Q.8. What is Sub-culturing?
Ans.: Sub-culturing is recommended for small collection centers. It has a draw back
that it is time consuming and labour intensive process.
20
Stains
Q.1. Explain the Grams Staining and difference between Grams Positive &
Grams Negative?
Ans.: Grams staining is most important differential technique used in bacteriology.
There are two groups - grams positive bacteria and gram negative bacteria.
S.No. Characteristics Negative Bacteria Positive Bacteria
1- Grams reaction Dark-violator purple Red or brown
2- Cell wall
composition
Low in liquids 1-4% High in lipids (11-
22%)
3- Susceptibility to
penicillin
More susceptible Less susceptible
4- Effect of basic dyes Marked inhibition Less inhibition
5- Resistance to
physical disruption
More resistant Less resistant
Ex.: Streptococci
Mycobacterium
leprae
Salmonella typhus
Neisseria
meningitides
Q. 2 Write components of following Stains :
Ans.: (i) Grams Stain
(ii) Fungal Stain
(iii) Acid Fast Stain
(iv) Haemapoxylin
(v) Negative stain
Ans.: (i) Grams Stain
Zoology Lab Manual 21
(a) Crystal Violet (Huckers)
Solution A
Crystal Violet (90% dye) 3 gm.
Ethanol (95%) 20 ml.
Solution B
Apmoi, Pxaate 0.8 gms.
Distilled Water - 80 ml.
Prepare solution A & B separately, then mix & keep in a brown
colour bottle.
(b) Grams Iodine
Iodine 1.0 gm.
Potassium Iodide 2.0 gm.
Distilled Water 300 ml.
(c) Ethanol (95%)
Ethand (100%) 95 ml.
Distilled Water 5 ml.
(d) Safrarin
Safranine (2.5% solution prepared in 95% ethanol) 10ml.
Distilled Water 100 ml.
(ii) Fungal Stain
(a) Latophenol + Cotton blue
Lactic Acid 20 ml.
Phenol Cry Stables 20 gm.
Glycerol (Glycerin) 40 ml.
Distilled Water - 20 ml.
Cotton Blue 2 ml.
22
(iii) Acid Fast Stain
Carbol functisin (Ziehls)
Solution A
Basic Fuchsia (90% dye content) - 3 gm.
Ethylalcohd (95%) - 10.0 ml.
Solution B
Phenol Crystals (CP) - 5.0 gm.
Distilled Water - 95.0 ml.
Acid Alcohol -
Ethyl Alcohol 95% - 97.0 ml.
HCl 37% - 3.0 ml.
Ethylene Blue
Methylene Blue
Methylene Blue (90% dye content) - 0.3 gm.
Distilled Water -100.0 ml.
(iv) Haematoxyline
Haematoxyline - 2.0 gm.
Glacial Acetic Acid - 10.0 ml.
Absolute Alcohol 100.0 ml.
Glycerol - 100.0 ml.
Potassium Alum - In excess
Distilled Water - 100.0 ml.
(vii) Negative Stain (Nigrosim)
Nigrosin (water solude) - 10.0 gm.
Distilled Water - 100 ml.
Zoology Lab Manual 23
Formation - 0.5 ml.
Вам также может понравиться
- Immediate Life Support PDFДокумент128 страницImmediate Life Support PDFShilin-Kamalei Llewelyn100% (2)
- Lab Manual Microbiology 251Документ115 страницLab Manual Microbiology 251Gilberto Gonzalez100% (1)
- Wastewater Microbiology, Filamentous Bacteria Morphotype Identification Techniques, and Process Control Troubleshooting StrategiesОт EverandWastewater Microbiology, Filamentous Bacteria Morphotype Identification Techniques, and Process Control Troubleshooting StrategiesОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology: A Laboratory ManualОт EverandPharmaceutical Microbiology: A Laboratory ManualРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesДокумент49 страницBiyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesGuruKPO71% (7)
- Christianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONДокумент64 страницыChristianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONWorld Religion NewsОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Lab ManualДокумент52 страницыMicrobiology Lab ManualHà Anh Minh LêОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Laboratory Manual (2016-17)Документ40 страницMicrobiology Laboratory Manual (2016-17)Vikrant SinghОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual For BiotechnologyДокумент42 страницыLaboratory Manual For BiotechnologySanjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Culture Media & Culture MethodsДокумент60 страницCulture Media & Culture MethodsGretchen Quimno Ayuson100% (2)
- Laboratory Manual: BTY351 Plant Biotechnology LaboratoryДокумент40 страницLaboratory Manual: BTY351 Plant Biotechnology LaboratoryRetik KoulОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Lab ManualДокумент61 страницаMicrobiology Lab ManualMadhu ShaliniОценок пока нет
- The Microbiology Manual PDFДокумент136 страницThe Microbiology Manual PDFMohammad Yasir100% (1)
- 5 Classification of MicroorganismsДокумент4 страницы5 Classification of MicroorganismsMaeve Ylain SeanОценок пока нет
- SOP078 Use and Mainteance of The 5L BioreactorДокумент40 страницSOP078 Use and Mainteance of The 5L Bioreactor김수경KOREAPENОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Lab SafetyДокумент5 страницMicrobiology Lab SafetyvpnarashimmanОценок пока нет
- Tissue Culture Lab PDFДокумент13 страницTissue Culture Lab PDFTimothy Dalingay Jr.100% (2)
- Microbiology - Introduction 2012Документ47 страницMicrobiology - Introduction 2012Linlinelin AvianiОценок пока нет
- Analytical Methods For The Determination of ChlorohexidineДокумент14 страницAnalytical Methods For The Determination of ChlorohexidineSanthi KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Microbiology PDFДокумент79 страницChapter 1 Microbiology PDFpizza100% (1)
- Draft: Manual of Methods OF Analysis of FoodsДокумент105 страницDraft: Manual of Methods OF Analysis of FoodsDhanushka WarnakulasooriyaОценок пока нет
- Microbial Contamination-A Regulatory Perspective.Документ8 страницMicrobial Contamination-A Regulatory Perspective.Sameer PanditОценок пока нет
- Wave BioreactorsДокумент16 страницWave BioreactorsSirsha PattanayakОценок пока нет
- Molecular Laboratory Design QAQC ConsiderationsДокумент46 страницMolecular Laboratory Design QAQC Considerationspunit mauryaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology: Laboratory ManualДокумент23 страницыMicrobiology: Laboratory ManualDevindraPrptОценок пока нет
- SBT413 Environmental MicrobiologyДокумент9 страницSBT413 Environmental MicrobiologyKiel Lee Dawn BurgeyОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Culture Media ManualДокумент222 страницыMicrobiology Culture Media ManualDavid García V.100% (6)
- Secondary MetabolliteДокумент20 страницSecondary MetabolliteChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology Lab Manual FinalДокумент19 страницMolecular Biology Lab Manual FinalAnupriyaОценок пока нет
- Food Spoilage: Dr. Rafat AminДокумент55 страницFood Spoilage: Dr. Rafat AminSbahat FatimaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology PDFДокумент40 страницMicrobiology PDFputri tyas100% (1)
- SterilizationДокумент33 страницыSterilizationFitri AnggraeniОценок пока нет
- Determin of Aero Anaerobic Spore FormersДокумент6 страницDetermin of Aero Anaerobic Spore FormersbhaleshОценок пока нет
- BSL-3 Training-1Документ22 страницыBSL-3 Training-1Dayanandhi ElangovanОценок пока нет
- Biosafety LevelДокумент13 страницBiosafety LevelSunil Bhavsar100% (2)
- Industrial MicrobiologyДокумент18 страницIndustrial MicrobiologyRajini hc100% (2)
- Sterilization and DisinfectionДокумент10 страницSterilization and DisinfectiondrugdrugОценок пока нет
- Antimicrobial AgentДокумент432 страницыAntimicrobial AgentdesosanОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 - Intro To Principles of EcologyДокумент58 страницTopic 1 - Intro To Principles of EcologyayuОценок пока нет
- Isolation and Characterization of Fungi Associated With Spoiled TomatoesДокумент5 страницIsolation and Characterization of Fungi Associated With Spoiled TomatoesJimoh Jamal100% (1)
- SOP124 Use and Maintenance of The Galaxy 170R Co2 IncubatorДокумент7 страницSOP124 Use and Maintenance of The Galaxy 170R Co2 IncubatorAntonio PorchedduОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Lab ManualДокумент78 страницMicrobiology Lab ManualDrMd IdrisОценок пока нет
- 0707-0712 (1117) Microbiological Best Laboratory PracticesДокумент6 страниц0707-0712 (1117) Microbiological Best Laboratory PracticesoliveluvpopayОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Документ100 страницMicrobiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Arief NorddinОценок пока нет
- BiotechnologyДокумент15 страницBiotechnologyUpanyaaОценок пока нет
- Food Microbiology PDFДокумент20 страницFood Microbiology PDFbyagniОценок пока нет
- Scope of MicroДокумент32 страницыScope of MicroShehram QazafiОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmДокумент383 страницыPharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmkeyurОценок пока нет
- Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application S of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlДокумент50 страницPrinciple, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application S of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlAhmed ImranОценок пока нет
- Sterilization PDFДокумент6 страницSterilization PDFBMT100% (1)
- General MycologyДокумент28 страницGeneral MycologyShimelis Teshome AyalnehОценок пока нет
- SterilizationДокумент40 страницSterilizationRajib SarkarОценок пока нет
- The Importance of laboratory animal genetics Health, and the Environment in Biomedical ResearchОт EverandThe Importance of laboratory animal genetics Health, and the Environment in Biomedical ResearchEdward C. Jr. MelbyРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM): Microbiological, Clinical and Geographical DistributionОт EverandNontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM): Microbiological, Clinical and Geographical DistributionОценок пока нет
- Microbiological Assay: An Introduction to quantitative principles and EvaluationОт EverandMicrobiological Assay: An Introduction to quantitative principles and EvaluationОценок пока нет
- Techniques for Downstream process for Biologic Drugs and VaccinesОт EverandTechniques for Downstream process for Biologic Drugs and VaccinesОценок пока нет
- Micobiology Nov. 18Документ12 страницMicobiology Nov. 18JOANNA MARIE O. YOCAMPOОценок пока нет
- Think Tank - Advertising & Sales PromotionДокумент75 страницThink Tank - Advertising & Sales PromotionGuruKPO67% (3)
- Applied ElectronicsДокумент40 страницApplied ElectronicsGuruKPO75% (4)
- Abstract AlgebraДокумент111 страницAbstract AlgebraGuruKPO100% (5)
- OptimizationДокумент96 страницOptimizationGuruKPO67% (3)
- Advertising and Sales PromotionДокумент75 страницAdvertising and Sales PromotionGuruKPO100% (3)
- Applied ElectronicsДокумент37 страницApplied ElectronicsGuruKPO100% (2)
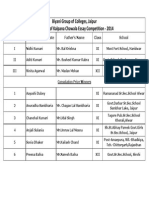
- Biyani Group of Colleges, Jaipur Merit List of Kalpana Chawala Essay Competition - 2014Документ1 страницаBiyani Group of Colleges, Jaipur Merit List of Kalpana Chawala Essay Competition - 2014GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Production and Material ManagementДокумент50 страницProduction and Material ManagementGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Data Communication & NetworkingДокумент138 страницData Communication & NetworkingGuruKPO80% (5)
- Computer Graphics & Image ProcessingДокумент117 страницComputer Graphics & Image ProcessingGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Business Ethics and EthosДокумент36 страницBusiness Ethics and EthosGuruKPO100% (3)
- Algorithms and Application ProgrammingДокумент114 страницAlgorithms and Application ProgrammingGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Algorithms and Application ProgrammingДокумент114 страницAlgorithms and Application ProgrammingGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Biological Science Paper I July 2013Документ1 страницаBiological Science Paper I July 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Phychology & Sociology Jan 2013Документ1 страницаPhychology & Sociology Jan 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Phychology & Sociology Jan 2013Документ1 страницаPhychology & Sociology Jan 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing I Nov 2013Документ1 страницаCommunity Health Nursing I Nov 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing Jan 2013Документ1 страницаCommunity Health Nursing Jan 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of Nursing Nov 2013Документ1 страницаFundamental of Nursing Nov 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Biological Science Paper 1 Nov 2013Документ1 страницаBiological Science Paper 1 Nov 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Biological Science Paper 1 Jan 2013Документ1 страницаBiological Science Paper 1 Jan 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Business LawДокумент112 страницBusiness LawDewanFoysalHaqueОценок пока нет
- Paediatric Nursing Sep 2013 PDFДокумент1 страницаPaediatric Nursing Sep 2013 PDFGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing I July 2013Документ1 страницаCommunity Health Nursing I July 2013GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Service MarketingДокумент60 страницService MarketingGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Banking Services OperationsДокумент134 страницыBanking Services OperationsGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Product and Brand ManagementДокумент129 страницProduct and Brand ManagementGuruKPOОценок пока нет
- BA II English (Paper II)Документ45 страницBA II English (Paper II)GuruKPOОценок пока нет
- Software Project ManagementДокумент41 страницаSoftware Project ManagementGuruKPO100% (1)
- Undertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Документ3 страницыUndertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Anuj ManglaОценок пока нет
- Caregiving Learning Activity Sheet 3Документ6 страницCaregiving Learning Activity Sheet 3Juvy Lyn CondaОценок пока нет
- Jaimini Astrology and MarriageДокумент3 страницыJaimini Astrology and MarriageTushar Kumar Bhowmik100% (1)
- KBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race ScheduleДокумент2 страницыKBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race SchedulezainОценок пока нет
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Документ37 страницNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonОценок пока нет
- An Etymological Dictionary of The Scottivol 2Документ737 страницAn Etymological Dictionary of The Scottivol 2vstrohmeОценок пока нет
- People Vs Felipe Santiago - FCДокумент2 страницыPeople Vs Felipe Santiago - FCBryle DrioОценок пока нет
- Harbin Institute of TechnologyДокумент7 страницHarbin Institute of TechnologyWei LeeОценок пока нет
- Information Security Policies & Procedures: Slide 4Документ33 страницыInformation Security Policies & Procedures: Slide 4jeypopОценок пока нет
- Michael M. Lombardo, Robert W. Eichinger - Preventing Derailmet - What To Do Before It's Too Late (Technical Report Series - No. 138g) - Center For Creative Leadership (1989)Документ55 страницMichael M. Lombardo, Robert W. Eichinger - Preventing Derailmet - What To Do Before It's Too Late (Technical Report Series - No. 138g) - Center For Creative Leadership (1989)Sosa VelazquezОценок пока нет
- Science Project FOLIO About Density KSSM Form 1Документ22 страницыScience Project FOLIO About Density KSSM Form 1SarveesshОценок пока нет
- W 26728Документ42 страницыW 26728Sebastián MoraОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Classrooms in An Architecture FacultyДокумент21 страницаDifferent Types of Classrooms in An Architecture FacultyLisseth GrandaОценок пока нет
- CHIR12007 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis Portfolio Exercises Week 5Документ4 страницыCHIR12007 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis Portfolio Exercises Week 5api-479849199Оценок пока нет
- CURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaДокумент13 страницCURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaHung LeОценок пока нет
- AnnulmentДокумент9 страницAnnulmentHumility Mae FrioОценок пока нет
- TN Vision 2023 PDFДокумент68 страницTN Vision 2023 PDFRajanbabu100% (1)
- Panera Bread Company: Case AnalysisДокумент9 страницPanera Bread Company: Case AnalysisJaclyn Novak FreemanОценок пока нет
- Effect of Added Sodium Sulphate On Colour Strength and Dye Fixation of Digital Printed Cellulosic FabricsДокумент21 страницаEffect of Added Sodium Sulphate On Colour Strength and Dye Fixation of Digital Printed Cellulosic FabricsSumaiya AltafОценок пока нет
- DLP No. 10 - Literary and Academic WritingДокумент2 страницыDLP No. 10 - Literary and Academic WritingPam Lordan83% (12)
- ISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCДокумент2 страницыISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCdevaprОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Diagram of Ways To Increase SalesДокумент1 страницаConceptual Diagram of Ways To Increase SalesO6U Pharmacy RecordingsОценок пока нет
- Lesson 73 Creating Problems Involving The Volume of A Rectangular PrismДокумент17 страницLesson 73 Creating Problems Involving The Volume of A Rectangular PrismJessy James CardinalОценок пока нет
- SULTANS OF SWING - Dire Straits (Impresión)Документ1 страницаSULTANS OF SWING - Dire Straits (Impresión)fabio.mattos.tkd100% (1)
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasДокумент30 страницNetwork Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasBaraa EsamОценок пока нет
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Документ336 страницNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaОценок пока нет
- Language Analysis - GRAMMAR/FUNCTIONS Context Anticipated ProblemsДокумент2 страницыLanguage Analysis - GRAMMAR/FUNCTIONS Context Anticipated Problemsshru_edgyОценок пока нет
- Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Документ11 страницAlice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Oğuz KarayemişОценок пока нет