Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biomass Energy
Загружено:
pradian_dian0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
52 просмотров2 страницыbiomass energy.
Оригинальное название
Biomass energy
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документbiomass energy.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
52 просмотров2 страницыBiomass Energy
Загружено:
pradian_dianbiomass energy.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
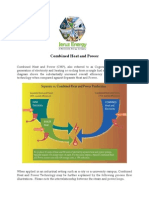
Biomass Energy
freecall 1800 303 116 | www.stanwell.com
Biomass refers to renewable energy
sources from plant material.
The conversion of biomass energy to
electrical and mechanical energy is
part of a process called cogeneration.
CONVERTING BIOMASS ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
Other agricultural industries use the plant waste of their industry as
the biomass energy source, such as rice husks in the rice industry.
Green waste is another source of biomass energy consisting of
council garden waste and wood waste left over from pruning trees.
This type of biomass is usually transported to a processing plant,
where it passes through a grinding machine and over screens to
sift out any dirt and other contaminants.
The different types of biomass can also be blended to create a
fuel blend, and then placed in a fuel storage bin where it is then
supplied to the boiler.
The processed
biomass fuel is burnt
producing heat
energy, which turns
the feedwater into
superheated steam.
The steam drives a
steam turbine, which
is connected to an
electrical generator.
The electrical
generator produces
high voltage
electricity.
The electricity is sent
out to consumers via
the electricity grid.
In the sugar mill,
the bagasse is
conveyed directly
to the cogeneration
plants boiler.
In sugar mills, the
biomass energy source
is called bagasse and
is the bre from the
sugar cane after it has
been milled to extract
the sugar.
energy smart education
Steam to Mill
Turbine Generator
Surplus Electricity
to Power Grid Electricity
to Mill
Boiler Steam
Bagasse
Biomass
Secondary Fuel Source
Bulk Sugar
Storage
Mill
Sugar
Cane
SUGAR MILL COGENERATION PROCESS
Biomass facts:
freecall 1800 303 116 | www.stanwell.com
energy smart education
What is cogeneration?
Cogeneration involves the combustion of fuel sources
to produce two forms of energy, usually steam for
both heat energy and electricity generation.
Cogeneration can be used to reduce energy costs for
the host industry, such as a sugar mill, because the
mill uses some of the steam produced for heat energy
and electricity to operate the mill. The surplus steam
produced is used to generate electricity for export to
the grid.
There are currently more than 100 cogeneration
plants operating in Australia. Most of these are small
sized plants that generate less than 10 MW
of electricity.
Biomass cogeneration plants make better use of
waste biomass, which would otherwise be dumped or
burnt as waste.
Biomass and sugarmills
As the sugar cane season occurs for only part of the year,
green waste can be used in some cases for the rest of the
year, to ensure a continuous supply of electricity.
On average, one tonne of sugar cane yields 250 kg of bagasse.
The ash, which forms from non-combustible material in the
biomass, is removed from the sugar mill to be used as a soil
conditioner in landscaping work or added to cane farms to
supplement fertiliser.
The waste water from the cogeneration facility cooling system
is passed through treatment systems before being utilised off
site, such as for irrigation water for local cane farms.
Some sugar mills have their own distillery, where alcohol
(particularly fuel alcohol or ethanol) is produced from molasses.
Ethanol is a renewable energy fuel, which has potential in
Australia as a vehicle fuel. This provides another use for
molasses, which was considered a waste product used
only as stockfeed for cattle.
Carbon dioxide (C0
2
) is released
and reabsorbed by plants
SUGAR MI LL
A percentage of the energy
is sent back to the mill
Steam and electricity are produced
Oxygen in
COGENERATI ON PLANT
BI OMASS
Oxygen out
Sunlight in
As plants grow they consume C0
2
and sunlight and release oxygen
Biomass is used to fuel
cogeneration plant boilers
Electricity fed into
local network
C0
2
in
Biomass energy and other agricultural industries
Any industry which produces large amounts of waste plant material during its process is suitable for cogeneration.
Apart from the sugar industry, other suitable industries include the rice industry (rice husk) and macadamia nut industry (nut shells).
THE CYCLE OF CARBON DIOXIDE DURING THE SUGAR MILL COGENERATION PROCESS
Вам также может понравиться
- Biogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationОт EverandBiogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Conceptual and Related LiteratureДокумент9 страницConceptual and Related LiteratureAlyssa Clarizze MalaluanОценок пока нет
- Electrical Power GenerationДокумент20 страницElectrical Power GenerationTabassum SavanurОценок пока нет
- Biomass Energy: Types, Conversion Methods & AdvantagesДокумент4 страницыBiomass Energy: Types, Conversion Methods & AdvantagesMubashir ImdadОценок пока нет
- Biomass EnergyДокумент1 страницаBiomass EnergyrapОценок пока нет
- Solar Heat Energy StorageДокумент5 страницSolar Heat Energy StorageSanjna ThondapuОценок пока нет
- District Heating NorwayДокумент8 страницDistrict Heating Norwaymahmoud4871Оценок пока нет
- ANAEROBIC DIGESTION, GASIFICATION AND PYROLYSIS FOR MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTEДокумент22 страницыANAEROBIC DIGESTION, GASIFICATION AND PYROLYSIS FOR MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTEJoao Minho100% (1)
- Biogas Generation A Study: By: Madhav Mohan Bsc. Physics (Hons.) Ii Year Roll Number: 1815052Документ17 страницBiogas Generation A Study: By: Madhav Mohan Bsc. Physics (Hons.) Ii Year Roll Number: 1815052Madhav Mohan100% (1)
- FLASH PYROLYSIS FOR BIO-OIL PRODUCTIONДокумент19 страницFLASH PYROLYSIS FOR BIO-OIL PRODUCTIONerkiruthiraj100% (1)
- Customized Heat Transfer: For Effective Comfort Heating and District HeatingДокумент8 страницCustomized Heat Transfer: For Effective Comfort Heating and District HeatingKhizerОценок пока нет
- Biomass Resource Facilities and Biomass Conversion Processing For Fuels and Chemicals 2001 Energy Conversion and ManagementДокумент22 страницыBiomass Resource Facilities and Biomass Conversion Processing For Fuels and Chemicals 2001 Energy Conversion and ManagementhassanОценок пока нет
- Solar Energy Storage MethodsДокумент3 страницыSolar Energy Storage Methodsakshaybj4396Оценок пока нет
- Biomass - Power PlantДокумент16 страницBiomass - Power PlantVinay MishraОценок пока нет
- Nordic District HeatДокумент52 страницыNordic District HeatFan DiОценок пока нет
- Thermal Energy StorageДокумент15 страницThermal Energy StorageragaОценок пока нет
- Second and Third Generation BiofuelsДокумент13 страницSecond and Third Generation Biofuelsguru9anandОценок пока нет
- Biomass Energy Generation: By: Caluna, Michael Ducao, Joshua Reyes, ElmerДокумент44 страницыBiomass Energy Generation: By: Caluna, Michael Ducao, Joshua Reyes, ElmerVance NavalesОценок пока нет
- Biofuels-The Next Great Source of Energy?Документ4 страницыBiofuels-The Next Great Source of Energy?Rizwan NadeemОценок пока нет
- Naphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionДокумент9 страницNaphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionsatishchemengОценок пока нет
- Alternative Energy From BiomassДокумент25 страницAlternative Energy From BiomassJen Abbas LubisОценок пока нет
- Types of Thermal Energy StorageДокумент4 страницыTypes of Thermal Energy StorageVinayak MuleyОценок пока нет
- Biomass Energy ResourcesДокумент24 страницыBiomass Energy ResourcesDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyОценок пока нет
- BIOMASS GASIFICATION FOR TRANSPORTДокумент72 страницыBIOMASS GASIFICATION FOR TRANSPORTBruno NavarroОценок пока нет
- Combined Heat and PowerДокумент8 страницCombined Heat and Powerawhk2006Оценок пока нет
- Biomass Technology ReviewДокумент44 страницыBiomass Technology Reviewdavid.spiderweb396191% (11)
- Pyrolysis of Biomass: Presented By: Ritendra Kumar Presented To: Dr. A.N SawarkarДокумент15 страницPyrolysis of Biomass: Presented By: Ritendra Kumar Presented To: Dr. A.N SawarkarRajat AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Suntec Energy System - Heat Pump in IndiaДокумент15 страницSuntec Energy System - Heat Pump in IndiasuntecОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen and Geothermal Energy Report by Group 2Документ14 страницHydrogen and Geothermal Energy Report by Group 2sdgalaponОценок пока нет
- 5.9 MWe biomass gasification cogen plantДокумент0 страниц5.9 MWe biomass gasification cogen plantApri ApriyantoОценок пока нет
- Development of An Efficient Solar Drying SystemДокумент73 страницыDevelopment of An Efficient Solar Drying SystemErond Perez100% (1)
- Productive Usage of BiomassДокумент6 страницProductive Usage of BiomassN. Sasidhar100% (1)
- System Simulation - Thermal Energy Storage PosterДокумент1 страницаSystem Simulation - Thermal Energy Storage PosterSaeed NazariОценок пока нет
- Europe's Growing Biomass Power Plant MarketДокумент13 страницEurope's Growing Biomass Power Plant MarketBaris SamirОценок пока нет
- Energy Efficiency Improvement BreweriesДокумент74 страницыEnergy Efficiency Improvement BreweriesJaime CalmetОценок пока нет
- Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO)Документ8 страницPressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO)vitileeОценок пока нет
- Biomass A New Source of Energy: Famous For Using and Under Research?Документ12 страницBiomass A New Source of Energy: Famous For Using and Under Research?e_nurОценок пока нет
- Green Carbon Dioxide: Advances in CO2 UtilizationОт EverandGreen Carbon Dioxide: Advances in CO2 UtilizationGabriele CentiОценок пока нет
- Biomass For H&P - Lecture 2-2006Документ51 страницаBiomass For H&P - Lecture 2-2006Leonardo Nanjar100% (1)
- Physical Conversion TechnologiesДокумент89 страницPhysical Conversion TechnologiesIttihad KhanОценок пока нет
- Hidrogeno Revision PDFДокумент6 страницHidrogeno Revision PDFtunja1Оценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy Resourses PPT-1Документ51 страницаRenewable Energy Resourses PPT-1Dhanashree JagtapОценок пока нет
- Group 9 (Bio-Oil Pyrolysis) - HandoutДокумент15 страницGroup 9 (Bio-Oil Pyrolysis) - HandoutShimme7Оценок пока нет
- BiodieselДокумент20 страницBiodieseldschnitzelОценок пока нет
- Biomass GasificationДокумент84 страницыBiomass Gasificationkalyanimotghare100% (4)
- Thermal Gasification For Power and FuelsДокумент105 страницThermal Gasification For Power and FuelsRodolfo Barbosa YoungОценок пока нет
- Chapter No. 1: Catalytic Steam Gasification of MSWДокумент79 страницChapter No. 1: Catalytic Steam Gasification of MSWMUh Ammar100% (1)
- Schematic Process Diagram For The Production of Biochar by Slow Pyrolysis ProcessДокумент2 страницыSchematic Process Diagram For The Production of Biochar by Slow Pyrolysis ProcessVince CastilloОценок пока нет
- CFD Modeling of A Downdraft Gasifier WitДокумент18 страницCFD Modeling of A Downdraft Gasifier Witray mayyerОценок пока нет
- Biomass Pellet MillsДокумент4 страницыBiomass Pellet MillsRadmila BlagojevicОценок пока нет
- Effect of Temperature On The Anaerobic Digestion of Palm Oil Mill EffluentДокумент10 страницEffect of Temperature On The Anaerobic Digestion of Palm Oil Mill Effluentbalajit7835Оценок пока нет
- Biomass, Biodiesel & Ethanol Energy Sources ExplainedДокумент36 страницBiomass, Biodiesel & Ethanol Energy Sources ExplainedveenaОценок пока нет
- Waste Biorefinery Models Towards Sustainable Circular Bioeconomy Critical Review and Future Perspectives2016bioresource Technology PDFДокумент11 страницWaste Biorefinery Models Towards Sustainable Circular Bioeconomy Critical Review and Future Perspectives2016bioresource Technology PDFdatinov100% (1)
- Types of BiofuelДокумент27 страницTypes of Biofuelsimysarvepalli100% (1)
- Typha Charcoal SenegalДокумент31 страницаTypha Charcoal SenegalGraschopf2Оценок пока нет
- Calibration ISO IEC 17025 Application DocumentДокумент60 страницCalibration ISO IEC 17025 Application Documentpradian_dianОценок пока нет
- Guide To Taxonomies of Learning OutcomesДокумент6 страницGuide To Taxonomies of Learning Outcomespradian_dianОценок пока нет
- Protein StructureДокумент52 страницыProtein Structurepradian_dianОценок пока нет
- 2011-07-23 Laboratory Safety Guide - Chemical Engineering ITB - Full - FinalДокумент31 страница2011-07-23 Laboratory Safety Guide - Chemical Engineering ITB - Full - FinalDendikaKurniawanОценок пока нет
- Power From Renewable Resources - Biomass: Ohio - Current and Future OutlookДокумент2 страницыPower From Renewable Resources - Biomass: Ohio - Current and Future Outlookpradian_dianОценок пока нет
- Prepared By: Eva Marie Demple Soliman Noted By: DR. MARILOU H. MELLA - DeanДокумент27 страницPrepared By: Eva Marie Demple Soliman Noted By: DR. MARILOU H. MELLA - DeanJonadel GeronaОценок пока нет
- Take Assessment: Exercise 1Документ11 страницTake Assessment: Exercise 1Sayatbek OrazbekovОценок пока нет
- Apple IphoneДокумент34 страницыApple IphoneShyrah SaiОценок пока нет
- Neptune Zanzibar Pwani Beach Resort and SpaДокумент5 страницNeptune Zanzibar Pwani Beach Resort and SpafebryzioОценок пока нет
- C-Data Epon Olt Fd1108s Cli User Manual v1.3Документ89 страницC-Data Epon Olt Fd1108s Cli User Manual v1.3sarasa100% (2)
- Strama Quiz 7Документ3 страницыStrama Quiz 7Yi ZaraОценок пока нет
- Reading Diagnostic Test n2Документ5 страницReading Diagnostic Test n2Cleo TokongОценок пока нет
- RAD Studio LiveBindings GuideДокумент63 страницыRAD Studio LiveBindings Guidewolfie002Оценок пока нет
- Supplier Appraisal - What To CheckДокумент6 страницSupplier Appraisal - What To CheckCosmos AfagachieОценок пока нет
- NVD0105DH 4KДокумент2 страницыNVD0105DH 4KThom SangaréОценок пока нет
- 1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotДокумент18 страниц1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotYi Wei OngОценок пока нет
- Training-Related Staffing: Judge Learning SolutionsДокумент1 страницаTraining-Related Staffing: Judge Learning Solutionsadarsh1110Оценок пока нет
- Laekemariam Haile PDFДокумент26 страницLaekemariam Haile PDFchiroОценок пока нет
- Appendix 12.7.0 Fortinet Corporate ProfileДокумент8 страницAppendix 12.7.0 Fortinet Corporate ProfileYan Naing ThwinОценок пока нет
- Diass Answer SheetДокумент4 страницыDiass Answer SheetMa rosario JaictinОценок пока нет
- Bitwise Operations in CДокумент18 страницBitwise Operations in CPriyam ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- SNR Digital Product Lead - Job DescriptionДокумент2 страницыSNR Digital Product Lead - Job DescriptionMatthew SlightОценок пока нет
- Bangalore Smes Business Owners Sample PDF FreeДокумент116 страницBangalore Smes Business Owners Sample PDF FreeSampath R67% (3)
- Health LeadsДокумент42 страницыHealth LeadsJohnОценок пока нет
- Simran Dholasania, A200 006 948 (BIA Aug. 19, 2015)Документ6 страницSimran Dholasania, A200 006 948 (BIA Aug. 19, 2015)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCОценок пока нет
- Tieng Anh 6 Friends Plus - Review Unit 5&6 Test 2 (Key)Документ6 страницTieng Anh 6 Friends Plus - Review Unit 5&6 Test 2 (Key)Bui The Dung (K16HCM)Оценок пока нет
- Portfolio Theory, CAPM, WACC and Optimal Capital Structure - 20072018 PDFДокумент50 страницPortfolio Theory, CAPM, WACC and Optimal Capital Structure - 20072018 PDFdevashnee100% (2)
- The Millennial Generation: A Comparative PerspectiveДокумент10 страницThe Millennial Generation: A Comparative Perspectiveapi-199155734Оценок пока нет
- The Setter - Edward Laverack - 1872Документ93 страницыThe Setter - Edward Laverack - 1872Antoan J. HlebarovОценок пока нет
- Tonight Tonight Smashing Pumpkins ChordsДокумент5 страницTonight Tonight Smashing Pumpkins ChordsZack InglisОценок пока нет
- Elementis Selector Chart AdditiveДокумент14 страницElementis Selector Chart AdditiveEugene Pai100% (1)
- Cirrus DwgsДокумент14 страницCirrus DwgsRowan BirchОценок пока нет
- Medical TerminologyДокумент6 страницMedical TerminologyMarhina Asarabi MukimОценок пока нет
- W10 Assignment Help 2 2023Документ25 страницW10 Assignment Help 2 2023OnghiddenОценок пока нет
- Medado and DacanayДокумент6 страницMedado and DacanayDatu TahilОценок пока нет