Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Histopathology ETAS
Загружено:
Dr.Tawheed75%(4)75% нашли этот документ полезным (4 голоса)
1K просмотров89 страницETAS MCQ with explanation
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документETAS MCQ with explanation
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
75%(4)75% нашли этот документ полезным (4 голоса)
1K просмотров89 страницHistopathology ETAS
Загружено:
Dr.TawheedETAS MCQ with explanation
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 89
1
What is the neoplasm in this biopsy?
1
Chondroid syringoma
2
Papillary eccrine adenoma
3
Tubular apocrine adenoma
4
Eccrine acrospiroma
5
Trichoblastoma
Q/Q(M)-482088 Report a Problem
Chondroid syringoma
Chondroid Syringoma: Most commonly occurs in middle age males on the head and neck.
Histologically this is a well circumscribed dermal tumor composed of dilated ducts, hyaline or
plasmacytoid cells (myoepithelial cells), keratinous cysts, +/- cells that show hair matricial
differentiation occasionally with some areas of mature fat. All elements arise within a homogenous
bluish chondromyxoid matrix (+ Type II collagen, + acid MPS stains with Alcian blue/green (stains at
high and low PH) consistent with chondroitin sulfate). Focal calcification may occur.
Q/Q(M)-482088 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Osteoclast-like giant cells are characteristic of:
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Osteoclast-like giant cells are characteristic of:
4
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath
1
Giant cell fibroblastoma
2
Reticulohistiocytoma
3
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum
4
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath
5
Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma
Q/Q(M)-474383 Report a Problem
2
Osteoclast-like giant cells are seen in giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath. Osteoclast-like giant cells
have eosinophilic cytoplasm with haphazardly arranged nuclei. Reticulohistiocytoma is characterized by
giant cells with an oncocytic glassy pink cytoplasm.
Q/Q(M)-474383 Report a Problem
biopsy of a 54-year-old female with suspected lichen planopilaris would likely reveal inflammation
around which portion of the hair follicle:
5
Infundibulum
On biopsy, alopecia areata exhibits a peribulbar lymphocytic swarm of bees. Discoid lupus
typically exhibits inflammation surrounding the isthmus, along with a perivascular dermatitis and
vacuolar interface changes. Lichen planopilaris exhibits inflammation most densely concentrated about
the infundibulum.
Q/Q(M)-
Which of the following is sometimes used to stain BCC during Mohs micrographic surgery?
1
Carcinoembryonic Antigen
2
Factor 13A
3
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
4
Desmin
5
Toluidine Blue
Q/Q(M)-482560
Which of the following is sometimes used to stain BCC during Mohs micrographic surgery?
5
Toluidine Blue
The correct answer is toluidine blue. Toluidine blue staining shows dark blue BCC tumor cells and a
magenta-colored stroma around the tumor cells. CEA is used to stain adenocarcinoma, extramammary
Paget\'s disease, and eccrine neoplasms. Desmin stains muscle. GFAP stains neurologic cells including
astrocytes and Schwann cells. Factor 13A is used to stain dermatofibroma.
Q/Q(M)-482560
What substance is found histologically in talon noir to be the source of the pigment seen clinically?
1
Hemoglobin
2
Hemosiderin
3
Melanin
4
Carbon
5
Keratin
Q/Q(M)-482223
What substance is found histologically in talon noir to be the source of the pigment seen clinically?
1
Hemoglobin
Talon noir is caused by trauma and hemorrhage trapped in the stratum corneum. It can clinically appear
pigmented and is often biopsied to rule out melanoma. Because phagocytosis of extravascular RBCs and
subsequent degradation of hemoglobin to hemosiderin does not occur in the stratum corneum, traditional
iron stains do not work and histochemical stains must be directed toward hemoglobin.
Q/Q(M)-482223
What is the diagnosis?
1
Calciphylaxis
3
2
Polyarteritis nodosa
3
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
4
Erythema nodosum
5
Cryoglobulinemia
Q/Q(M)-482086
1
Calciphylaxis
Calciphylaxis: seen in patients with elevated Ca-PO4 product and secondary hyperparathyroidism most
commonly patients in renal failure. Calcification occurs within the media of vessels in the lower dermis
resulting in intimal hyperplasia and secondary intraluminal thrombi. Vascular occlusion then results in
epidermal/dermal infarction.
Q/Q(M)-482086 Report a Problem
1
Sclerotic fibroma
2
Angiofibroma
3
Keloid
4
Neurofibroma
5
Dermatofibroma
Q/Q(M)-482096 Report a Problem
4
1
Sclerotic fibroma
Sclerotic Fibroma (circumscribed storiform collagenoma): This can occur as an isolated lesion n the
head or neck or upper extremities, but multiple lesions are associated with Cowden's disease which is an
AD disorder linked to a mutation of PTEN on chromosome 10p. Histology: Dome shaped papule with
an overlying attenuated epidermis. A well-circumscribed nodule composed of thickened homogenous
collagen that is arranged in whorls with a thumbprint or grains of wood appearance is seen in the dermis.
Overall the lesion exhibits low cellularity and the elastic fibers are absent. The tumor stains positively
with vimentin, Factor XIIIA and focally for CD34.
Q/Q(M)-482096 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The histologic finding of "shoulder parakaratosis", parakeratosis with prediliection for the follicular
ostia, is characteristic of pityriasis rubra pilaris as well as:
1
Stasis dermatitis
2
Atopic dermatitis
3
Seborrheic dermatitis
4
Nummular dermatitis
5
Allergic contact dermatitis
Q/Q(M)-479629 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The histologic finding of "shoulder parakaratosis", parakeratosis with prediliection for the follicular
ostia, is characteristic of pityriasis rubra pilaris as well as:
3
Seborrheic dermatitis
Parakeratosis refers to pyknotic keratinocyte nuclei in the stratum corneum, where nuclei are not usually
present. It is common in diseases with changes in the epidermis. Histologically seborrheic dermatitis can
shows "shoulder parakeratosis" with epidermal spongiosis. Histologically atopic, nummular and contact
dermatitis present with spongiosis with or without vesicles. Stasis dermatitis presents with more dilated
papillary dermal small blood vessels and hemosiderin.
Q/Q(M)-479629 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is characteristic of Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome?
1
Autosomal recessive mode of inheritance
5
2
Multiple trichoepitheliomas
3
Caused by mutation in hamartin
4
Multiple trichodiscomas
5
Colon cancer common
Q/Q(M)-478645 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is characteristic of Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome?
4
Multiple trichodiscomas
Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome (BHD) characterized by multiple small harartomas of mesodermal
component of hair discs, which were indentified as trichodiscromas. It is an autosomal dominant disease
caused by mutations in folliculin. Patients with multiple fibrofolliculomas may also have acrochordons,
collagenomas, lipomas, and/or oral fibromas. BHDS recently has been reported in association with
various types of renal tumors, such as oncocytoma and a variant of papillary renal cell carcinoma. There
are no trichoepitheliomas in BHD syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-478645 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Psoriasis has been shown to be genetically linked to:
1
Pityriasis rubra pilaris
2
Clear cell acanthomas
3
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis
4
Verruciform xanthomas
5
Poromas
Q/Q(M)-474391 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Psoriasis has been shown to be genetically linked to:
3
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis
Mutations have been found in the EVER1 and EVER2 genes in epidermodysplasia verruciformis; these
genes are on 17q25, the location of the PSORS2 gene (one of the genes implicated in the inheritance of
psoriasis).
6
Q/Q(M)-474391 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The predominant cleft in dermatitis herpetiformis is:
1
Dermal
2
Basement membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Suprabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479695 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The predominant cleft in dermatitis herpetiformis is:
2
Basement membrane zone
Dermatitis herpetiformis or Duhring's disease, presents with very pruritic vesicles symmetrically on
extensor surfaces. On histology it presents as suprapapillary vesicles with mostly neutrophils and
inflammatory destruction of the basement membrane zone. Direct immunoflourescence shows granular
deposition of IgA in the dermal papillae and along the basement membrane zone. The cleft in dermatitis
herpetiformis is most commonly found in the basement membrane zone/subepidermal. The antigen is
transglutaminase.
Q/Q(M)-479695 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following lesions demonstrates a pseudo-Dariers sign?
1
Mastocytoma
2
Spitz nevus
3
Smooth muscle hamartoma
4
Pilomatricoma
5
Bullous pemphigoid
Q/Q(M)-477141 Report a Problem
7
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following lesions demonstrates a pseudo-Dariers sign?
3
Smooth muscle hamartoma
Smooth muscle hamartomas are benign tumors which arise from smooth muscle of the dermis. Pseudo-
Darier's sign may be elicited due to transient piloerection after rubbing. Histologically, red-orange
bundles and fascicles are present with blunt-ended nuclei.
Q/Q(M)-477141 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Eosinophilia-Myalgia syndrome is caused by:
1
Norwegian salt-petter
2
Unadultered Spanish grapeseed oil
3
Pb intoxication
4
L-Tryptophan
5
Excessive anaerobic exercise
Q/Q(M)-477421 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Eosinophilia-Myalgia syndrome is caused by:
4
L-Tryptophan
The eosinophilia myalgia syndrome is characterized by marked peripheral eosinophilia with a clinical
spectrum of signs and symptoms, including generalized myalgias, pneumonitis, myocarditis,
neuropathy, encephalopathy and fibrosis. Many patients progress to a clinical picture clinically
indistinguishable from eosinophilic fasciitis. The disease is caused by the ingestion of certain lots of L-
tryptophan.
Q/Q(M)-477421 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A patient with a blue-red discoloration of the nail plate reports that the same finger becomes very tender
when exposed to the cold. You suspect a:
8
1
Periungual verruca
2
Glomus tumor
3
Pterygium
4
Mucous cyst
5
Pyogenic granuloma
Q/Q(M)-477215 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A patient with a blue-red discoloration of the nail plate reports that the same finger becomes very tender
when exposed to the cold. You suspect a:
2
Glomus tumor
Glomus tumors are tumors of the arterio-venous anastamosis of the digital dermis. They occur most
frequently in the nail bed. The commonly have a bluish-red discoloration and may be tender or painful
with exposure to heat or cold.
Q/Q(M)-477215 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following have been found within a nevus sebaceous?
1
Squamous cell carcinoma
2
Merkel cell carcinoma
3
Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum
4
Verruca vulgaris
5
Hidradenoma Papilliferum
Q/Q(M)-482624 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following have been found within a nevus sebaceous?
3
Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum
Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma, trichoblastoma, syringocystadenoma papilliferum and basal cell carcinomas
have all been reported to be found within a nevus sebaceous.
9
Q/Q(M)-482624 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following immunohistochemical stains can help distinguish basal cell carcinomas and
trichoepitheliomas from microcystic adnexal carcinomas?
1
Pro-collagen 1
2
CD34
3
Peanut agglutinin
4
TTF-1
5
Ber-Ep4
Q/Q(M)-482495 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following immunohistochemical stains can help distinguish basal cell carcinomas and
trichoepitheliomas from microcystic adnexal carcinomas?
5
Ber-Ep4
Ber-Ep4 helps distinguish between BCCs/Trichoepitheliomas and microcystic adnexal carcinomas.
Morpheaform BCC and desmoplastic trichoepithelioma are Ber-Ep4 positive where as microcystic
adnexal carcinomas (MAC) are Ber-Ep4 negative. Other markers that help distinguish between BCCs
and trichoepitheliomas are peanut agglutinin and CD34. Peanut agglutinin is positive in BCC and
negative in trichoepithelioma vs CD34 which is negative in BCC and positive in the peritumoral
fibroblasts of trichoepitheliomas.
Q/Q(M)-482495 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Mulberry cells contain increased:
1
Phagolysosomes
2
Mitochondria
3
Golgi
4
Ribosomes
5
Phagolysosomes and mitochondria
10
Q/Q(M)-474345 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Mulberry cells contain increased:
2
Mitochondria
Hibernomas commonly arise in the neck, axillae, and posterior shoulder. The cells are multivacuolated
and resemble mulberries; the cells are filled with mitochondria, as are the cells in normal brown fat.
Q/Q(M)-474345 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following drugs has been known to cause pyogenic granuloma?
1
Daunorubicin
2
Mithramycin
3
Isosfamide
4
Capecitabine
5
Paclitaxel
Q/Q(M)-477495 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following drugs has been known to cause pyogenic granuloma?
4
Capecitabine
Systemic retinoids, indinavir and capecitabine have all been describe to cause pyogenic granulomas.
Q/Q(M)-477495 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following immunohistochemical staining profiles of a non-breast skin lesion best
characterizes extra-mammary Pagets disease secondary to an underlying visceral malignancy?
1
MART-1 positive/cytokeratin 20 negative/cytokeratin 7 negative/gross cystic fluid disease
protein-15 negative
11
2
MART-1 negative/pankeratin positive/cytokeratin 7 positive/cytokeratin 20 positive/gross cystic
fluid disease protein-15 negative
3
MART-1 negative/pankerative positive/cytokeratin 7 negative
4
MART-1 negative/pankeratin positive/cytokeratin 7 positive/cytokeratin 20 negative/gross cystic
fluid disease protein-15 positive
5
CD34 positive, Factor XIIIa negative
Q/Q(M)-482838 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following immunohistochemical staining profiles of a non-breast skin lesion best
characterizes extra-mammary Pagets disease secondary to an underlying visceral malignancy?
2
MART-1 negative/pankeratin positive/cytokeratin 7 positive/cytokeratin 20 positive/gross
cystic fluid disease protein-15 negative
The differential for Pagetoid cells in the epidermis includes melanoma in situ, Pagets disease of the
breast, extra-mammary Pagets disease, squamous cell carcinoma in situ, sebaceous carcinoma, and
others. MART-1 positivity in the setting of pagetoid spread suggests melanoma in situ. The combination
of MART-1 negativity, pankeratin positivity, and cytokeratin 7 negativity suggests squamous cell
carcinoma in situ. Both Pagets disease of the breast and extra-mammary Pagets disease are
characterized by pankeratin positivity and cytokeratin 7 positivity. Extra-mammary Pagets is defined
clinically by its location outside of the breast. Extra-mammary Pagets disease arising secondary to a
visceral malignancy is further characterized by cytokeratin 20 positivity and gross cystic fluid disease
protein-15 negativity, whereas primary extra-mammary Pagets disease is cytokeratin 20 negative and
gross cystic fluid disease protein-15 positive.
Q/Q(M) Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is characteristic of lichen planus histopathologically?
1
Wedge-shaped parakeratosis
2
Irregular acanthosis
3
Absent interface changes
4
Parakeratosis
5
Absent granular layer
Q/Q(M)-478638 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is characteristic of lichen planus histopathologically?
12
2
Irregular acanthosis
Histopathology of lichen planus: Acanthosis with wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, irregular (sawtooth
acanthosis), hyperkeratosis without significant parakeratosis, and basal vacuolization (interface
changes).
Q/Q(M)-478638 Report a Problem
-482838 RPrevious
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn has been associated with:
1
Hypocalcemia
2
Hypercalcemia
3
Hypokalemia
4
Hyperkalemia
5
Hyponatremia
Q/Q(M)-474390 Report a Problem
eport a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn has been associated with:
2
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia has been noted in some cases of subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn.
Q/Q(M)-474390 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A healthy 6 month old girl has a subcutaneous nodule above her right eyebrow. A skin biopsy
demonstrates a cystic lesion with adnexal structures in the wall. Your diagnosis is:
1
Steatocystoma
2
Pilar cyst
3
Nevus sebaceous
4
Epidermal inclusion cyst
5
Dermoid cyst
13
Q/Q(M)-477193 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A healthy 6 month old girl has a subcutaneous nodule above her right eyebrow. A skin biopsy
demonstrates a cystic lesion with adnexal structures in the wall. Your diagnosis is:
5
Dermoid cyst
Dermoid cysts present along lines of embryonic closure. The are most commonly found on the head
(around the eyes) and the neck. They are lined by an epidermis that contains various epidermal
appendages that are usually fully matured.
Q/Q(M)-477193 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This biopsy was obtained from an annular pigmented plaque on the trunk, what is this neoplasm?
1
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma
2
Glomeruloid hemangioma
3
Angiosarcoma
4
Kaposi's sarcoma
5
Tufted hemangioma
Q/Q(M)-482108 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This biopsy was obtained from an annular pigmented plaque on the trunk, what is this neoplasm?
1
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma
Targetoid Hemosiderotic Hemangioma: Occurs most commonly on young adult males on the trunk and
14
named for its clinical appearance. The lesion typically appears as a plaque with concentric rings, there is
violaceous central region surrounded by a ring of pallor which is then surrounded by an erythematous or
brown rim. Histologically in the superficial dermis there are dilated blood vessels, some of which have
plump hobnailed endothelial cells. In the deeper dermis the vessels have a narrower lumen and dissect
between the collagen bundles. Often within the lesion there are extravasated red blood cells and
hemosiderin.
Q/Q(M)-482108 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This is a plakin:
1
BPAg1
2
Plakoglobin
3
Plakophilin
4
Desmocollin
5
Beta-catenin
Q/Q(M)-474370 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This is a plakin:
1
BPAg1
Desmoplakins include desmoplakin 1, BPAg1, envoplakin, and periplakin.
Q/Q(M)-474370 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Multiple pilomatricomas are seen in:
1
Myotonic dystrophy
2
Cowden's
3
Turner's
4
Gorlin's
5
Myotonic dystrophy and Turner's
Q/Q(M)-474371 Report a Problem
15
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Multiple pilomatricomas are seen in:
5
Myotonic dystrophy and Turner's
Multiple pilomatricomas are seen in Rubinstein-Taybi, Gardner's (cyst-like pilomatricomas), myotonic
dystrophy, Turner's, sarcoidosis, sternal cleft and coagulation defects.
Q/Q(M)-474371 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Mantle cell lymphoma is characteristically positive for which of the following?
1
CD10
2
CD23
3
CD138
4
Bcl-1
5
bcl-6
Q/Q(M)-474342 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Mantle cell lymphoma is characteristically positive for which of the following?
4
Bcl-1
Bcl-1 (Cyclin D1) is a marker for mantle cell lymphoma. CD10, bcl-6, and bcl-2 are markers for
follicular cell lymphoma. Bcl-2 also stains normal T cells. CD23 is a marker for CLL/SLL and is
negative in mantle cell lymphoma. CD138 is a marker for plasma cells.
Q/Q(M)-474342 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The mutated product in Dariers disease is:
1
SPINK5
2
SERCA2
3
ATP2A2
16
4
ATP2C1
5
SPINK5 and ATP2A2
Q/Q(M)-474378 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The mutated product in Dariers disease is:
2
SERCA2
In Dariers disease, the ATP2A2 gene encoding the SERCA2 Ca(2+)-ATPase is mutated in some
patients. SPINK5 is the gene that is mutated in some patients with Nethertons syndrome, and this
gene the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI. ATP2C1 is the gene mutated in some patients with Hailey-
Hailey disease.
Q/Q(M)-474378 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The predominant location of the cleft in erythema toxicorum neonatorum is:
1
Dermal
2
Basement membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Suprabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479631 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The predominant location of the cleft in erythema toxicorum neonatorum is:
5
Subcorneal/granular
Erythema toxicorum neonatorum is an idiopathic vesiculopustular eruption on the face and trunk of
neonates that often resolves in a few weeks. Histologically it presents with subcorneal eosinophil rich
pustules.
Q/Q(M)-479631 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
17
Show Answer
Histologically, adenoma sebaceum represent which of the following lesions?
1
Neurofibromas
2
Angiofibromas
3
Collagenomas
4
Angiokeratomas
5
Smooth muscle hamartomas
Q/Q(M)-477342 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Histologically, adenoma sebaceum represent which of the following lesions?
2
Angiofibromas
Adenoma sebaceum, fibrous papules and pearly penile papules all have similar features histologically,
presenting as angiofibromas. Features include atrophic epidermis with patchy melanocytic hyperplasia
and hyperkeratosis, vertically oriented collagen, increased fibroblasts and blood vessels.
Q/Q(M)-477342 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following stains Natural Killer Cells?
1
CD1a
2
CD11
3
CD30
4
CD56
5
CD68
Q/Q(M)-476789 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following stains Natural Killer Cells?
4
CD56
CD56 stain Natural Killer Cells and angiocentric lymphomas.
Q/Q(M)-476789 Report a Problem
18
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following body contains calcium:
1
Negri body
2
Lipschutz body
3
Michaelis-Gutman body
4
Guarnieri body
5
Negri body and Michaelis-Gutman body
Q/Q(M)-474381 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following body contains calcium:
3
Michaelis-Gutman body
The Michaelis-Gutman body is a concentrically laminated spherical inclusion that contains calcium that
is seen within macrophages in malakoplakia. Other inclusion bodies that contain calcium are Schaumann
bodies and psammoma bodies. The Negri body is seen in rabies. The Lipschutz body is an intranuclear
inclusion seen in herpes. It is considered synonymous with the Cowdry A body. The Guarnieri body is
seen in smallpox.
Q/Q(M)-474381 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This tumor was excised from the scalp of an older woman, what is this neoplasm?
1
Cylindroma
2
Sebaceous carcinoma
3
Pilomatricoma
4
Basal cell carcinoma
5
Spiradenoma
Q/Q(M)-482110 Report a Problem
19
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This tumor was excised from the scalp of an older woman, what is this neoplasm?
1
Cylindroma
Cylindroma: Most often seen in middle age females on the scalp. Multiple lesions can be associated with
trichoepitheliomas, spiradenoma and adenomas of parotid gland in Brooke Spieler syndrome.
Histologically this is a poorly circumscribed dermal tumor with multiple small irregularly shaped
basophilic islands often likened to puzzle pieces composed of a peripheral layer of smaller darker cells,
with cells that have increased eosinophilic cytoplasm centrally. Each island is surrounded by a thick
eosinophilic cuticle (type IV and VII collagen), with similar eosinophilic hyaline droplets seen within
the island.
Q/Q(M)-482110 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The inclusions in infantile digital fibromatosis stain for trichrome and:
1
Phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin
2
Osmium tetroxide
3
Thioflavin T
4
Bodian
5
Pentahydroxy flavanol
Q/Q(M)-474349 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The inclusions in infantile digital fibromatosis stain for trichrome and:
1
Phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin
Osmium tetroxide stains fat. Thioflavin T stains amyloid. The Bodian stain is for nerves. Pentahydroxy
20
flavanol is a fluorescent stain for calcium.
Q/Q(M)-474349 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Goblet cells are seen in:
1
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
2
Endometriosis
3
Dermoid cyst
4
Bronchogenic cyst
5
Steatocystoma
Q/Q(M)-474387 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Goblet cells are seen in:
4
Bronchogenic cyst
Bronchogenic cysts have a pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar lining that is ciliated; goblet cells are
found in the lining as well.
Q/Q(M)-474387 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Lipomembranous change is seen in:
1
Hibernoma
2
Cystic sebaceous adenoma
3
Sebaceous carcinoma
4
Mucocele
5
Sclerosing panniculitis
Q/Q(M)-474368 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
21
Finish
Show Answer
Lipomembranous change is seen in:
5
Sclerosing panniculitis
Lipomembranous change is a non-specific histologic pattern that is most commonly seen in
lipodermatosclerosis, which is also known as sclerosing panniculitis; this condition may be secondary to
venous stasis.
Q/Q(M)-474368 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Histologic examination of cutaneous metastases from breast cancer is likely to demonstrate:
1
Dense lymphocytic infiltration
2
Tumors cells perivascularly
3
Eosinophilia
4
Tumor cells in the lymphatics
5
Band-like dermal infiltrate
Q/Q(M)-477149 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Histologic examination of cutaneous metastases from breast cancer is likely to demonstrate:
4
Tumor cells in the lymphatics
Histologic appearance of metastatic breast carcinoma to the skin typically shows tumor cells in linear
arrangement in so-called "Indian-filing" pattern. These tend to occur in the dermis and
subcutaneous lymphatics. Extensive lymphatic dissemination may be caused by retrograde lymphatic
spread. The tumor cells are large, pleomorphic with hyperchromatic nuclei.
Q/Q(M)-477149 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is this neoplasm?
1
Pilomatricoma
22
2
Proliferating pilar tumor
3
Trichoepithelioma
4
Basal cell carcinoma
5
Eccrine acrospiroma
Q/Q(M)-482109 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is this neoplasm?
1
Pilomatricoma
Pilomatrixoma (Calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe): Found on the head, neck and upper extremities in
the first 2 decades of life. Typically solitary but multiple pilomatricomas arise in several syndromes.
Even in isolation these tumors may arise due to activating mutations in the beta-catenin gene.
Histologically: This tumor consists of two major cell types plus an intermediate or transitional cell type.
Initially the tumor is more cystic with the cells at the periphery of the tumor that are more basophilic
with indistinct cell borders and little cytoplasm. The cells have hyperchromatic nuclei and often normal
mitoses can be appreciated. Centrally there are eosinophilic ghost or shadow cells which are
cells that have undergone terminal differentiation. These cells have more distinct borders, increased
cytoplasm but only a ghost of a nucleus. Then there are cells that reside somewhere in between these
two cell types. The proportion of these cells varies depending on the stage of the lesion; i.e younger
lesions have more basophilic cells and appear more cystic, older lesions have a greater component of
ghost cells and up to 20% of lesions on removal are completely composed of ghost cells.
Q/Q(M)-482109 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This is associated with MEN IIa:
1
Neurothekeoma
2
Macular amyloidosis
3
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
4
Chondroid syringoma
23
5
Mucocele
Q/Q(M)-474375 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This is associated with MEN IIa:
2
Macular amyloidosis
Macular amyloidosis is associated with MEN IIa.
Q/Q(M)-474375 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is true regarding S-100 Protein?
1
S-100 protein is an basic protein that binds Ca2+ and Zn2+
2
It is not soluble in 100% ammonium sulfate at neutral pH
3
Can be detected in melanocytes and in Schwann cells
4
It is not useful in diagnosing of spindle cell melanoma & desmoplastic melanoma
5
It is not useful in diagnosing poorly differentiated cutaneous metastases
Q/Q(M)-475945 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is true regarding S-100 Protein?
3
Can be detected in melanocytes and in Schwann cells
S-100 protein is an acidic protein that binds Ca2+ and Zn2+. At a neutral pH, it is soluble in 100%
ammonium sulfate. It is useful in diagnosing both spindle cell melanomas, desmoplastic melanomas, as
well as poorly differentiated cutaneous metastases. It also stains positively in neurofibromas and
schwannomas.
Q/Q(M)-475945 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
24
Which of the following sets of special immunohistochemical stains would help differentiate an atypical
fibroxanthoma (AFX) from a malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH)?
1
CD74 and CD99
2
CD34 and Stromelysin-3
3
HMB45 and p75NPR
4
CK20 and TTF-1
5
CK20 and GCDFP-15
Q/Q(M)-482502 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following sets of special immunohistochemical stains would help differentiate an atypical
fibroxanthoma (AFX) from a malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH)?
1
CD74 and CD99
CD74 (LN2) and CD99 help differentiate an AFX from an MFH where an AFX is CD74-,CD99+ and an
MFH stains weakly from CD99 and is CD74 negative. CD34 and Stromelysin-3 differentiate
dermatofibromas and DFSPs. HMB45 and p75NPR are stains helping to differentiate melanomas from
desmoplastic melanomas. CK20 and TTF-1 staining differentiates a merkel cell carcinoma and
metastatic small cell lung carcinoma. CK20 and GCDFP-15 staining helps distinguish primary and
secondary (assoc with underlying neoplasm) Paget\'s disease.
Q/Q(M)-482502 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following regarding stains is true?
1
A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain is used to stain elastic fibers red.
2
A methanamine silver stain is used to identify bacteria.
3
A fite stain is used to identify spirochetes.
4
A Von Kossa stain is used to identify calcium.
5
A giesma stain is used to identify eosinophil granules.
Q/Q(M)-478635 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following regarding stains is true?
25
4
A Von Kossa stain is used to identify calcium.
Stains/Application/Result Van Gieson - Elastic fibers - Black Methanamine-silver - Fungi, parasites -
Black AFB/Fite - Acid-fast bacilli - Red Von Kossa - Calcium - Black Giesma - Mast cells -
Metachromatically purple
Q/Q(M)-478635 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is the best diagnosis?
1
Psoriasiform
2
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
3
Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia
4
Lichen Nitidus
5
Ochronosis
Q/Q(M)-482129 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is the best diagnosis?
3
Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia
Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia(EPITHELIOID HEMANGIOMA) consists of solitary or
multiple benign cutaneous nodules comprised of immature and mature vascular structures intermingled
with endothelial cells and a varied infiltrate of eosinophils, histiocytes, lymphocytes, and mast cells.
Q/Q(M)-482129 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
26
Show Answer
Which of the following is true of Rosai-Dorfman disease?
1
S-100 negative, CD1a positive, not characterized by emperipolesis
2
S-100 positive, CD1a positive, not characterized by emperipolesis
3
S-100 positive, CD1a negative, characterized by emperipolesis
4
S-100 positive, CD1a positive, characterized by emperipolesis
5
S-100 negative, CD1a negative, characterized by emperipolesis
Q/Q(M)-482198 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is true of Rosai-Dorfman disease?
3
S-100 positive, CD1a negative, characterized by emperipolesis
Rosai-Dofrman disease (also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy) is
characterized by large "fluffy" histiocytes that are S-100 positive but CD1a negative, multinucleated
giant cells, plasma cells, aggregates of lymphocytes, and emperipolesis. There is debate as to whether
the condition is related to herpes type 6.
Q/Q(M)-482198 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A 30-year old male presents with clustered, painful plaques on his shoulder. Histopathology showed
interlacing bundles of cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and no mitoses. Desmin and SMA stains were
positive. What gene defect is associated with the development of these lesions?
1
Fumarate Hydratase
2
Endoglin
3
ERCC8
4
RECQL2
5
GJB3
Q/Q(M)-482251 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
27
A 30-year old male presents with clustered, painful plaques on his shoulder. Histopathology showed
interlacing bundles of cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and no mitoses. Desmin and SMA stains were
positive. What gene defect is associated with the development of these lesions?
1
Fumarate Hydratase
The patient has multiple cutaneous leiomyomas. Hereditary leiomyomatosis is an inherited defect of
fumarate hydratase. These patients develop multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and have an increased
incidence of renal cell carcinoma. Female patients will usually also develop significant uterine
leiomyomatosis resulting in hysterectomy.
Q/Q(M)-482251 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This lesion was excised from the face, what is this neoplasm?
1
Clear cell syringoma
2
Sebaceous carcinoma
3
Microcystic adenocarcinoma
4
Renal cell carcinoma
5
Clear cell hidradenoma
Q/Q(M)-482091 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This lesion was excised from the face, what is this neoplasm?
1
Clear cell syringoma
Syringoma: Multiple eyelids, cheeks, chests, can be eruptive and increased numbers in Down's
syndrome and a clear cell change has been associated with Diabetes. Histologically this is a dermal
tumor consisting of eccrine ducts, lined by two cell layers sometimes creating a tad pole appearance,
there can also be small basaloid islands or strands of cells. Within the lumens of the ducts is eosinophilic
material, the lumens are CEA+. The tumor is located superficially and fails to display perineural
extension as is seen in MAC. The glands are associated with a fibrous sclerotic stroma, usually no (or
minimal) keratin cysts or foreign body granulomas as seen in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma.
28
Enlargement of the glandular cells more of a clear or vacuolated cytoplasm can be seen in patients with
diabetes.
Q/Q(M)-482091 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Sebaceous carcinomas commonly arise on the eyelid. A biopsy of an ocular sebaceous carcinoma
typically reveals:
1
uniform, eosinophilic cells with rare atypia
2
pagetoid cells in the epidermis
3
negative staining with Androgen Receptor (AR)
4
positive staining with Ber-Ep4
5
may be associated with overexpression of MLH-1 and MSH-2
Q/Q(M)-482553 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Sebaceous carcinomas commonly arise on the eyelid. A biopsy of an ocular sebaceous carcinoma
typically reveals:
2
pagetoid cells in the epidermis
Periocular sebaceous carcinomas are histologically composed of lobules of cell that extend deep in the
dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The cells are pleomorphic, with vacuolated cytoplasm with moderate
atypia. A characteristic feature in ocular tumors is the pagetoid spread of the tumor in the overlying
epidermis. Immunostaining for the androgen receptor has been reported as a method to determine
sebaceous differentiation, and it is helpful in diagnosing poorly differentiated sebaceous carcinomas,
which may lack staining for EMA and other markers. Basal cell carcinomas, nodular-type are typically
positive for Ber-Ep4 while sebaceous tumors are almost always negative for this marker. Sebaceous
carcinomas may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome, which is characterized with loss of expression
of MLH-1 and MSH-2
Q/Q(M)-482553 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A skin biopsy shows numerous fibroblasts with fibrosis and thickening of the dermis. There is sparse
mucin deposition and on low power the biopsy appears square. Which of the following paraproteins
would you expect to find in this patient?
1
IgG lambda
2
IgA
29
3
IgM
4
IgG kappa
5
IgA gamma
Q/Q(M)-480133 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A skin biopsy shows numerous fibroblasts with fibrosis and thickening of the dermis. There is sparse
mucin deposition and on low power the biopsy appears square. Which of the following paraproteins
would you expect to find in this patient?
1
IgG lambda
The description of the biopsy above is that of scleromyxedema. These patients have an associated IgG
lambda paraprotein. Other IgG subtypes may occur but lambda is most common. Scleromyxedema is a
subset of lichen myxedematosus (papular mucinosis). It will present with coalescent erythematous to
yellow papules and plaques. The most common location is the face, but will occur in many other
locations. The surrounding skin is usually sclerodermoid in appearance. (Bolognia, p648-9)
Q/Q(M)-480133 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following does not stain for mucopolysaccharides (mucin)?
1
Periodic-acid Schiff (PAS)
2
Trichome
3
Alcian blue
4
Colloidal iron
5
Mucicarmine
Q/Q(M)-482153 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following does not stain for mucopolysaccharides (mucin)?
2
Trichome
Trichome does not stain acid mucopolysaccharides. Trichome stains collagen blue or green and muscle
red depending on reagents used. PAS stains mucopolysaccharides red, alcian blue stains
mucopolysaccharides blue, colloidal iron stains mucin blue and mucicarmine stains mucin red.
Q/Q(M)-482153 Report a Problem
30
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
All of the following markers can be helpful in differentiating basal cell carcinoma from
trichoepithelioma except
1
CD10
2
CD31
3
CD34
4
Bcl-2
5
Stromelysin-3
Q/Q(M)-482113 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
All of the following markers can be helpful in differentiating basal cell carcinoma from
trichoepithelioma except
2
CD31
The histopathologic discrimination of trichoepithelioma and BCC often presents a diagnostic challenge.
The distinction is of clinical significance due to the differences in prognosis and treatment of these
tumors. Thus, a large number of ancillary laboratory techniques have been investigated as an aid in this
differential, include CD10, CD34, BCL-2, Stromelysin-3 and Ki-67. CD31 is a vascular marker that
stains positive in angiosarcoma and Kaposi sarcoma.
Q/Q(M)-482113 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following can be seen in dermatofibromas?
1
Hypopigmentation of the basal layer
2
Infiltration into the fat with a honeycomb pattern
3
Hypoplasia of the epidermis
4
S-100 positivity
5
Vimentin positivity
Q/Q(M)-478642 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
31
Show Answer
Which of the following can be seen in dermatofibromas?
5
Vimentin positivity
Dermatofibromas have characteristic features that can include collagen trapping, hyperplasia of
epidermis, hyperpigmentation of basal layer, dermal spindle cells, and whorls of fibrous tissue with
keloidal collagen. It stains with factor XIIIa(+) but not MAC 387 (-), S-100(-), or CD34 (-). DFSP
infiltrates the fat with a honeycomb pattern.
Q/Q(M)-478642 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
You examine a biopsy that is square on low power. The clinical history reports an IgG paraproteinemia
and the presence of a "doughnut sign". Which of the following conditions would you think of without
looking on higher power?
1
Scleromyxedema
2
Scleroderma
3
Scleredema
4
Localized Morphea
5
Pretibial myxedema
Q/Q(M)-480134 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
You examine a biopsy that is square on low power. The clinical history reports an IgG paraproteinemia
and the presence of a "doughnut sign". Which of the following conditions would you think of without
looking on higher power?
1
Scleromyxedema
The doughnut sign is seen on proximal interphalangeal joints where a central depression surrounded by
an elevated rim can be seen (Bolognia p649). This is a feature of the skin thickening seen in
Scleromyxedema. The other options will have a square appearance on low power microscopic
examination and scleredema can have an IgG paraprotein. Other microscopic findings in
scleromyxedema include incrased fibroblasts with fibrosis/increased collagen and thickening of the
dermis. Mucin may be scant or absent. This bx is more cellular than pretibial myxedema.
Q/Q(M)-480134 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
32
Show Answer
This was excised from the face, what is this neoplasm ?
1
Syringoma
2
Trichoadenoma
3
Basal cell carcinoma
4
Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma
5
Microcystic adenocarcinoma
Q/Q(M)-482092 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This was excised from the face, what is this neoplasm ?
1
Syringoma
Syringomas on the eyelids, cheeks, chests and can be eruptive and increased numbers in Down's
syndrome and a clear cell change has been associated with diabetes. Histologically this is a dermal
tumor consisting of eccrine ducts, lined by two cell layers sometimes creating a tad pole appearance,
there can also be small basaloid islands or strands of cells. Within the lumens of the ducts is eosinophilic
material, the lumens are CEA+. The tumor is located superficially and fails to display perineural
extension as is seen in MAC. The glands are associated with a fibrous sclerotic stroma, usually no (or
minimal) keratin cysts or foreign body granulomas as seen in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma.
Enlargement of the glandular cells more of a clear or vacuolated cytoplasm can be seen in patients with
diabetes.
Q/Q(M)-482092 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Caterpillar bodies are seen in:
1
Lipoid proteinosis
2
Amyloidosis
3
Porphyria cutanea tarda
4
Mucocele
5
Dyskeratosis congenital
33
Q/Q(M)-474377 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Caterpillar bodies are seen in:
3
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Caterpillar bodies are thought to be type IV collagen.
Q/Q(M)-474377 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A deposition of what substances leads to these deposits?
1
Homogentisic acid
2
Amyloid
3
Fungal organisms
4
Colloid
5
Tattoo
Q/Q(M)-482106 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
A deposition of what substances leads to these deposits?
1
Homogentisic acid
Ochronosis: can be either endogenous or exogenous. The endogenous form is due to an AR defect in
homogentisic acid oxidase, which prevents tyrosine and phenylalanine from being degraded beyond
homogentisic acid. The exogenous form of ochronosis, on the other hand, occurs from topical
34
hydroquinone, mercury resorcinol, phenol, picric acid or benzene, or systemic quinine or chloroquine
which all inhibits homogentisic oxidase and leads to a focal accumulation of homogentisic acid. Within
the superficial dermis there are irregular shaped elongated yellow deposits which have been described as
as bananas in the dermis that occur due to deposition of homogentisic acid on the collagen.
Q/Q(M)-482106 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is your best diagnosis?
1
Sebaceous Glands
2
Sebaceum
3
Lichen Planus
4
Atopic Eczema
5
Angiofibroma
Q/Q(M)-482132 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is your best diagnosis?
5
Angiofibroma
Angiofibroma is a small reddish spot or bump that consists of fibrous tissue and blood vessels. They are
most commonly found around the nose, cheeks, and chin, often combining to form a distinctive
butterfly-shaped pattern. Previously known as adenoma sebaceum.
Q/Q(M)-482132 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
35
Multiple trichoepitheliomas are seen in all except:
1
Bazex's syndrome
2
Brooke-Fordyce syndrome
3
Brooke-Spiegler syndrome
4
Gorlin's syndrome
5
Rombo syndrome
Q/Q(M)-474388 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Multiple trichoepitheliomas are seen in all except:
4
Gorlin's syndrome
Gorlin's syndrome is nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome; multiple trichoepitheliomas are not seen.
Several syndromes have been associated with multiple trichoepitheliomas: Basex, Brooke-Fordyce,
Brooke-Spiegler, Rombo, and possibly Rasmussen. (Rasmussen described one family in 1975 with
autosomal dominant inheritance of multiple trichoepitheliomas, milia, and cylindromas.) Basex
syndrome (follicular atrophoderma, hypotrichosis, occasional trichoepitheliomas, basal cell carcinomas,
and localized or generalized hypohidrosis) is inherited in an X-linked dominant manner. Brooke and
Fordyce both described multiple trichoepitheliomas concurrently in 1892, and therefore multiple familial
trichoepitheliomas are sometimes called Brooke-Fordyce sydrome. Spiegler described patients with
multiple cylindromas in 1899 and also noted that many of these patients had mutiple trichoepitheliomas;
more recently it has been noted that multiple spiradenomas may be seen in patients with multiple
trichoepitheliomas and cylinidromas; this co-occurrence of tumors has been referred to as Brooke-
Spiegler syndrome. (Brooke-Fordyce and Brooke-Spiegler are likely the same syndrome.) Rombo
syndrome is characterized by vermiculate atrophoderma, multiple BCCs, multiple trichoepitheliomas,
cyanosis and peripheral vasodilation.
Q/Q(Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is the best diagnosis for this vesiculobullous disorder?
1
Bullous Pemphigoid
2
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
3
Pemphigus vulgaris
4
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
5
Arthropod Bite
Q/Q(M)-482085 Report a Problem
36
M)-474388 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is the best diagnosis for this vesiculobullous disorder?
1
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous Pemphigoid: Most common subepidermal blistering disease that frequently occurs on abdomen,
groin, flexor surface of arms and legs of the elderly. In men an association with HLA-DQ7 has been
seen. Often eosinophilia and elevated IgE is seen in the serum. The pathogenesis of this blistering
disorder is due to binding of antibodies, IgG1 and 4 or IgE and rarely IgA, to BPAg I (230kd) and less
commonly BP Ag II (180kd) in the hemidesmosome. Histologically there is a unilocular subepidermal
blister with eosinophils. Early lesions may show eosinophilic spongiosis with papillary dermal edema.
Within the dermis there is a lymphocytic eosinophilic infiltrate that is both perivascular and interstitial.
DIF shows linear deposits of C3> IgG along the DEJ. Salt split skin show localization of
immunoreactants in the vesicle roof. Circulating anti-BMZ antibodies are seen in 60-80% of patients but
do not correlate to disease activity.
Q/Q(M)-482085 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Cicatricial pemphigoid antibodies directed against this are associated with high frequency of
malignancy:
1
Laminin 5
2
Laminin 6
3
Beta4-integrin
4
BPAg2
5
All of these answers are correct
Q/Q(M)-474374 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
37
Cicatricial pemphigoid antibodies directed against this are associated with high frequency of
malignancy:
1
Laminin 5
Anti-laminin 5 cicatricial pemphigoid (CP) is also known as anti-epiligrin CP. Anti-epiligrin CP is
associated with an increased frequency of internal adenocarcinomas. Laminin 5 is composed of three
chains (heterotrimer), alpha3, beta3, gamma2. Antibodies are frequently directed against the alpha3
chain, and so cross-reactivity can be observed with laminin 6, as laminin 6 (alpha3beta1gamma1) has
the alpha3 chain as well. Beta4-integrin antibodies have been associated with ocular CP. BPAg2
antibodies are seen in CP patients that have mucosal as well as skin disease.
Q/Q(M)-474374 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Acantholysis is not a prominent histopathologic feature of which disease?
1
Dermatitis herpetiformis
2
Darier's disease
3
Grover's disease
4
Pemphigus vulgaris
5
Hailey-Hailey diesease
Q/Q(M)-479628 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Acantholysis is not a prominent histopathologic feature of which disease?
1
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a bullous disease that on histology shows neutrophils in the dermal papillae.
On direct immunoflourescence IgA is seen in a granular depostion pattern. Acantholysis is seen
histologicaly in Darier's disease, Grover's disease, Pemphigus vulgaris, Hailey-Hailey disease and warty
dyskeratoma.
Q/Q(M)-479628 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Multiple dermatofibromas are seen in:
1
Cowden's
2
Lobomycosis
3
Incontinentia pigmenti
38
4
Lupus erythematosus
5
Reticulohistiocytosis
Q/Q(M)-474353 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Multiple dermatofibromas are seen in:
4
Lupus erythematosus
Multiple dermatofibromas are seen in lupus erythematosus and immunosuppression/HIV.
Q/Q(M)-474353 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The organisms highlighted by this GMS stain are?
1
Blastomycosis
2
Coccidioidomycosis
3
Mucormycosis
4
Candida albicans
5
Histoplasmosis capsulatum
Q/Q(M)-482082 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The organisms highlighted by this GMS stain are?
1
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis: Gilchrist disease, Bird droppings or spores on wood along Mississippi basin, incubation
33-44 days. Most infections develop in previously healthy people. In patients with HIV, 46% will get
39
CNS symptoms, which is 5-10x greater than non-HIV pts. 4 forms, pulmonary, disseminated (CNS,
bone, skin and GU) with secondary cutaneous lesions and primary inoculation (rare-1-2 weeks after
exposure-sporotrichoid pattern- mixed infiltrate numerous budding organisms). Lesions more typically
are verrucous or ulcerated plaques in males on exposed skin-face. Histology: Pseudoepitheliomatosis
hyperplasia overlying acute dermal inflammation usually only a few organisms in center of abscess with
thick walled 7-15 microns, single broad based bud, has a WI-1 adhesion protein and are best seen with
PAS or GMS.
Q/Q(M)-482082 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This tumor is vimentin+ and cytokeratin+:
1
Angiosarcoma
2
Neurothekeoma
3
Nodular fasciitis
4
Dermatofibroma
5
Epithelioid sarcoma
Q/Q(M)-474376 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This tumor is vimentin+ and cytokeratin+:
5
Epithelioid sarcoma
Characteristic immunohistochemistry of epithelioid sarcoma is vimentin- and cytokeratin- positivity.
Q/Q(M)-474376 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Paraproteinemia is associated with all except:
1
Scleromyxedema
2
Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma
3
Scleredema
4
Sclerosing panniculitis
5
Plane xanthoma
Q/Q(M)-474389 Report a Problem
40
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Paraproteinemia is associated with all except:
4
Sclerosing panniculitis
Sclerosing panniculitis (lipodermatosclerosis) displays characteristic changes in the fat
(lipomembranous change); it is not associated with paraproteinemia. Generalized plane xanthomas,
scleromyxedema, necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, scleredema, erythema elevatum diutinum, xanthoma
disseminatum, and pyoderma gangrenosum have all been associated with a paraproteinemia.
Q/Q(M)-474389 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is more commonly seen in lichen sclerosus et atrophicus compared to morphea?
1
Inflammation and fibrosis in the subcutis
2
Marked edema in the papillary dermis
3
Minimal hydropic degeneration noted at the dermaldermal-epidermal junction
4
Epidermis relatively normal with no thinning of the rete ridges
5
No follicular plugging
Q/Q(M)-478655 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is more commonly seen in lichen sclerosus et atrophicus compared to morphea?
2
Marked edema in the papillary dermis
Morphea vs. Lichen schlerosus et atrophicus: Morphea has a relatively normal epidermis without
follicular plugging. Interface changes are rare. In the dermis, the collagen fibers appear homogenized.
Elastic fibers are preserved. The inflammation and sclerosis can extend into the subcutaneous fat. LS&A
has an atrophic epidermis with follicular plugging. There is often prominent hydropic changes with
clefting. There is often edema of the papillary dermis and elastic fibers are often absent. The subcutis is
uninvolved.
Q/Q(M)-478655 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The organism on this slide stained with Warthin-Starry is responsible for what disease?
41
1
Bacillary Angiomatosis
2
Cellulitis
3
Madura foot
4
Pyoderma gangrenosum
5
Pyogenic granuloma
Q/Q(M)-482081 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
The organism on this slide stained with Warthin-Starry is responsible for what disease?
1
Bacillary Angiomatosis
Bacillary (epithelioid) angiomatosis is caused by Bartonella Henselae or Bartonella quintana (trench
fever- from body louse). Clinically resembles PG but multiple lesions and in a HIV+ patient, usually
with history of exposure to cats. Histologically there is dome shaped lesion with an epidermal collarette
with a proliferation of reactive plump blood vessels similar to a PG, but the lesion is less lobular and
there is PMNs and dust throughout the lesion along with extracellular clumps of purplish gram
bacilli. The organism is + for Warthin-Starry, which highlights the organisms in a characteristic Chinese
letter configuration.
Q/Q(M)-482081 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Stromelysin 3 is a negative marker for which of the following?
1
Dermatofibroma
2
Basal cell carcinoma
3
Dermatofibromasarcoma protuberans
4
Squamous cell carcinoma
5
Breast carcinoma
Q/Q(M)-477313 Report a Problem
42
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Stromelysin 3 is a negative marker for which of the following?
3
Dermatofibromasarcoma protuberans
Stromelysin 3 is a negative marker which helps to distinguish dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans from
dermatofibromas. Stromelysin 3 is a metalloproteinase which is expressed tissue remodeling. In a study
performed by Cribier et.al. 100% of dermatofibromas stained positive Stromelysin 3 (ST3) is a member
of the metalloproteinase family, which is expressed in tissue remodeling processes such as scarring,
embryogenesis, or tumoral invasion.
Q/Q(M)-477313 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Scalp biopsy of a 14-year-old female with suspected alopecia areata would likely reveal inflammation
around which portion of the hair follicle:
1
Dermal papilla
2
Hair bulb
3
Inner root sheath
4
Isthmus
5
Infundibulum
Q/Q(M)-482939 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Scalp biopsy of a 14-year-old female with suspected alopecia areata would likely reveal inflammation
around which portion of the hair follicle:
2
Hair bulb
On biopsy, alopecia areata exhibits a peribulbar lymphocytic swarm of bees. Discoid lupus
typically exhibits inflammation surrounding the isthmus, along with a perivascular dermatitis and
vacuolar interface changes. Lichen planopilaris exhibits inflammation most densely concentrated about
the infundibulum.
Q/Q(M)-482939 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
43
Apocrine hidrocystoma may be associated with which of the following syndromes?
1
Downs syndrome
2
Schopf-Schulz-Passarge
3
Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome
4
Cowdens Disease
5
Osteogensis Imperfecta
Q/Q(M)-482600 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Apocrine hidrocystoma may be associated with which of the following syndromes?
2
Schopf-Schulz-Passarge
Schopf-Schulz-Passarge is a syndrome of ectodermal dysplasia which presents with keratosis
palmoplantaris with hypodontia, hypotrichosis, and cysts of the eyelids. The other answer choices have
not been associated with apocrine hidrocystomas.
Q/Q(M)-482600 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian can be found associated with which of the following conditions?
1
Granular cell tumor
2
Leishmaniasis
3
Schwannoma
4
Chromomycosis
5
Rhinoscleroma
Q/Q(M)-482844 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian can be found associated with which of the following conditions?
1
Granular cell tumor
Pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian can be seen in association with granular cell tumors. They appear as
relatively large and eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions with a surrounding clear halo. These
inclusions characteristically stain positive with PAS and are diastase resistant. Leishmaniasis is
associated with Donovan bodies, which are intracytoplasmic basophilic organismal (amastigotes)
inclusions found in parasitized histiocytes. Verocay bodies may be seen in schwannomas, which appear
44
as pallisaded nuclei in rows. Medlar bodies (copper pennies) can be seen in cutaneous infectious of
chromomycosis and appear as grouped ovoid spores measuring 6 to 12 micrometers both within
histiocytes as well as interstitially. Russell bodies are associated with rhinoscleroma and are elliptical
basophilic inclusions found in plasma cells and are comprised of immunoglobulins.
Q/Q(M)-482844 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is this neoplasm?
1
Trichoadenoma
2
Trichoblastoma
3
Trichoepithelioma
4
Basal cell carcinoma
5
Nevus comedonicus
Q/Q(M)-482093 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
What is this neoplasm?
1
Trichoadenoma
Trichoadenoma: A nodule on the face or butt that is slightly depressed. Typically confined to the upper
dermis and composed of multiple milia or infundibular-like cysts that have a squamous epithelial lining
associated with a granular layer and central flakey keratin in the lumen. The stroma can be sclerotic. The
lesion is composed primary of cysts with a few thin strands of basaloid cells; if basaloid strands
predominate with only a few cysts then lesion is a trichoepithelioma.
Q/Q(M)-482093 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
45
This is a culture of a fungus what is it?
1
Rhizopus
2
Phaeohyphomycosis
3
Aspergillosis
4
Mucor
5
Absidia
Q/Q(M)-482099 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
This is a culture of a fungus what is it?
1
Rhizopus
Mucormycosis: Rhizopus the roots are directly under sporangia. This is # 1 cause of localized and
systemic disease due to mucormycosis. Absidia the roots are on either side or the sporangia. Causes
localized infections such as in burns, under dressings and also seen in IV drug users. Mucor the roots are
absent. Mucor more frequently causes disseminated lesions such as rhinocerebral infections in diabetics
with ketoacidosis or in patients with leukemia or neutropenia. These organisms result in a necrotizing
cellulitis or a plaque or nodule with a necrotic eschar. The organisms invade the wall of blood vessels
resulting in thrombosis and infarction. The organism in tissue displays irregular branching at 90 degree
(right angle) and the hyphae are broad ribbon-like with no septae. The organism can be seen on H & E,
but better with GMS
Q/Q(M)-482099 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is commonly seen histopathologically in pityriasis rosea?
1
Absent spongiosis
46
2
Full thickness necrosis
3
Exravasated erythrocytes in the subcutaneous fat
4
Lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate
5
Focal parakeratosis
Q/Q(M)-478637 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Which of the following is commonly seen histopathologically in pityriasis rosea?
5
Focal parakeratosis
Histopathological features of Pityriasis Rosea: Mild subacute spongiotic dermatitis, focal parakeratosis
(corresponds to cigarette paper-like scale), perviascular lymphocytic infiltrate, hemorrhage in papillary
dermis, and sometimes a few necrotic keratinocytes.
Q/Q(M)-478637 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
All of the following are true regarding smooth muscle hamartomas except:
1
Hyperpigmentation
2
Transient piloerection
3
Hypertrichosis
4
Association with Michelin tire baby in females
5
Beckers nevus is an example
Q/Q(M)-477122 Report a Problem
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
All of the following are true regarding smooth muscle hamartomas except:
4
Association with Michelin tire baby in females
Smooth muscle hamartomas of the skin may develop from three locations: the arrector pili muscles,
blood vessel walls, and genital/areolar skin. The have been associated with hyperpigmentation, tranisent
piloerection ("pseudo-Darier's sign") and hypertrichosis. It is thought to be the underlying lesion in
"Michelin tire baby" syndrome in boys, not girls.
Q/Q(M)-477122 Report a Problem
47
Previous
Next
Finish
Show Answer
Comma-shaped bodies are seen in:
1
Benign cephalic histiocytosis
2
Malakoplakia
3
Sarcoidosis
4
Lipoid proteinosis
5
Gauchers
Q/Q(M)-474364 Report a Problem
Comma-shaped bodies are seen in:
1
Benign cephalic histiocytosis
Comma-shaped bodies and worm-shaped bodies can be seen in a variety of histiocytoses and are non-
specific. The most common association is with benign cephalic histiocytosis.
Q/Q(M)-474364 Report a Problem
This biopsy was obtained from a Filipino woman who lives in Southern California, what is this
organism?
1
Coccidioidomycosis
2
Rhinosporidium
3
Prototheca wickerhamii
4
Histoplasmosis capsulatum
5
Cryptococcus neoformans
Q/Q(M)-482084 Report a Problem
This biopsy was obtained from a Filipino woman who lives in Southern California, what is this
organism?
1
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis: Found in nature in the soil of desert areas of the South West, also known as
Valley Fever . Usually presents as a self-limited lung infection, but in less 1% of people
dissemination can occur. The risk is highest in immunocompromised people, and there is a higher risk in
Mexicans, Filipinos, African Americans, American Indians, and in pregnancy. Systemic illness can be
48
associated with eosinophilia, arthritis and rarely hypercalcemia. Disseminated cutaneous lesions present
as papulopustules on nasolabial fold or verrucous plaque on face. Approximately 20% of patients with
pulmonary infections develop a hypersensitivity reaction to the infection resulting in erythema nodosum.
Primary inoculation is rare and usually occurs in farmers and can present with a sporotrichoid pattern.
Histology: Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis overlying a suppurative granulomatous
dermatitis that often contains numerous eosinophils in the inflammatory infiltrate. Within the
granulomas are thin walled sporangia measuring 10-80 microns that often contain multiple endospores.
The organism can usually be easily seen on H & E, but use of PAS and Congo red stains highlights the
spores. The classic appearance on culture is alternating light and dark chains of organisms with a box
car-like appearance.
Q/Q(M)-482084 Report a Problem
Turk cells are found in what infection?
1
Roseola
2
Mumps
3
Rubella
4
Syphilis
5
Rubeola
Q/Q(M)-477474 Report a Problem
Turk cells are found in what infection?
3
Rubella
Turk cells are atypical lymphocytes found in rubella.
Q/Q(M)-477474 Report a Problem
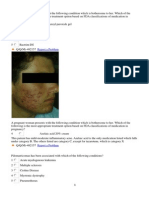
A pregnant patient presents complaining of a worsening skin eruption for the duration of the past three
years. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Seborrheic dermatitis
2
Tinea versicolor
3
Tinea corporis
4
Prurigo of pregnancy
5
Pityriasis rosea
Q/Q(M)-482879 Report a Problem
A pregnant patient presents complaining of a worsening skin eruption for the duration of the past three
years. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor presents as hyper or hypopigmented coalescing scaly macules on the trunk and upper
extremities. It is more common during the summer and favors oily areas of skin. Mild pruritus may be
present. It is caused by Malassezia furfur. Pityrosporum orbiculare is the yeast phase of the organism.
This patient had tinea versicolor for several years and apparently got worse during her pregnancy. A
study in Italy, revealed the frequency of tinea versicolor during pregnancy (5.7%) does not seem
different from that reported in general population living in temperate climates (2-5%). However, higher
degree of colonization by Malassezia resulted at the end of pregnancy and postpartum.
49
Q/Q(M)-482879 Report a Problem
Clinically, a nondescript hyperkeratotic papule on the ulnar side of the base of the fifth finger is most
likely:
1
Acquired digital fibrokeratoma
2
Accessory digit
3
Cutaneous horn
4
Digital fibromatosis
5
Glomus tumor
Q/Q(M)-474362 Report a Problem
Clinically, a nondescript hyperkeratotic papule on the ulnar side of the base of the fifth finger is most
likely:
2
Accessory digit
Accessory digits (supernumerary digits) are usually found at the base of the fifth finger, often bilaterally.
Q/Q(M)-474362 Report a Problem
Using the salt-split skin technique with direct immunofluorescence, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita will
show linear deposition of complement in what position?
1
Roof of the split
2
Roof and floor of the split
3
Floor of the split
4
Neither the roof or floor of the split since IgA is the most common reactant
5
None of the above since the pattern is not linear
Q/Q(M)-479626 Report a Problem
Using the salt-split skin technique with direct immunofluorescence, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita will
show linear deposition of complement in what position?
3
Floor of the split
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a bullous disease of adults in which minor trauma (usually on
the hands and feet) leads to blisters that heal with scaring. On histology there is classically a
noninflammatory subepidermal split. The blister will immunostain with IgG on the floor of salt-split
skin, as the antigen is type VII collagen.
Q/Q(M)-479626 Report a Problem
What are these organisms?
1
Leishmania
2
Trichosporon beigelii
3
Sporothrix schenckii
4
Penicillium marneffei
5
Histoplasmosis capsulatum
50
Q/Q(M)-482098 Report a Problem
What are these organisms?
1
Leishmania
Leishmaniasis: Three main types: cutaneous (L tropica and mexicana), mucocutaneous (L. brasiliensis)
and visceral/kala-azar (L donovani). Old world Leishmania (L tropica-major, minor and aethiopica)
transmitted by Phlebotomus sandfly, new world (L mexicana, brasiliensis) transmitted by Lutzomyia
sandfly. The promastigote lies in the sandfly is transmitted to humans and the amastigote infects
macrophages. Macrophages become engorged with the organisms, but there is abnormal intracellular
killing. Histology: Epidermis may display PEH and there is a dense dermal infiltrate consisting of foamy
histiocytes, aka Leishman-Donovan bodies, with intracellular amastigotes along with epithelioid
monocytes, giant cells, plasma cells and lymphocytes, variable eosinophils and PMNs. Organisms stain
better with Giemsa, have a paranuclear kinetoplast and typically are located at periphery of macrophage,
i.e. the Marquee sign. Can also see organism on skin slit smear. Older lesions show decreased organisms
and tuberculoid granulomas may form.
Q/Q(M)-482098 Report a Problem
Blue-gray pigmentation on the legs secondary to minocycline on biopsy stains with:
1
Fontana Masson
2
Perls
3
Sudan black
4
Fontana Masson and Perls
5
All of these answers are correct
Q/Q(M)-474350 Report a Problem
Blue-gray pigmentation on the legs secondary to minocycline on biopsy stains with:
4
Fontana Masson and Perls
There are three types of pigmentary change that are caused by minocycline. The blue-gray pigmentation
on the legs and the blue pigment in scars is thought to be secondary to a drug-protein complex deposited
in the dermis. The blue-gray pigment on the legs stains with Perls and Fontana-Masson. The blue in
scars (often on the face) stains with Perls. The muddy-brown discoloration on sun-exposed areas shows
increased basilar pigment and melanin incontinence on biopsy. It is likely secondary to phototoxicity.
Q/Q(M)-474350 Report a Problem
Which marker stains melanosomes?
1
S-100
51
2
Mart-1/Melan-A
3
MITF
4
HMB-45
5
Fontana-Masson
Q/Q(M)-482680 Report a Problem
Which marker stains melanosomes?
4
HMB-45
HMB-45 is a melanosome immunostain targeting glycoprotein. S-100 is a melanocyte immunostain, but
it has low specificity also staining Langerhans cells, smooth and skeletal muscle, adipocytes, and eccrine
coils. MITF is a melanocyte nuclear stain. Fontana-Masson is a melanin stain.
Q/Q(M)-482680 Report a Problem
Weibel-Palade bodies are seen in:
1
Endothelial cells
2
Spitz Nevi
3
Cells infected with MCV
4
Plasmacytoid Cells
5
Malakoplakia
Q/Q(M)-474380 Report a Problem
Weibel-Palade bodies are seen in:
1
Endothelial cells
Weibel-Palade bodies are seen in endothelial cells and are therefore found in vascular lesions. Kamino
bodies are found in Spitz nevi. Henderson Patterson bodies are seen in molluscum. Dutcher bodies are
intranuclear inclusions seen in plasmacytoid cells. Michaelis Gutmann bodies are partially digested
bacteria seen in malakoplakia.
Q/Q(M)-474380 Report a Problem
CK20 is useful in the diagnosis of:
1
Dermatofibrosarcoma
2
Dermatofibroma
3
Epitheloid sarcoma
4
Merkel cell carcinoma
5
Plasmacytoma
Q/Q(M)-478653 Report a Problem
CK20 is useful in the diagnosis of:
4
Merkel cell carcinoma
CK20 is useful in diagnosis of Merkel Cell Ca. Dermatofibrosarcoma would stain CD34+.
Dermatofibroma would stain CD68 +. Plasmacytoma would stain CD138 + and CEDa. Epithelioid
52
sarcoma would stain CD34+.
Q/Q(M)-478653 Report a Problem
Cellular neurothekeoma stains with:
1
Stromelysin-3
2
Desmin
3
S-100
4
PGP-9.5
5
Low molecular weight keratin
Q/Q(M)-474347 Report a Problem
Cellular neurothekeoma stains with:
4
PGP-9.5
PGP-9.5 and S100-a6 stains cellular neurothekeoma. Stromelysin-3 is positive in dermatofibromas and
negative in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Desmin stains rhabdomyosarcoma. S-100 stains neural
tumors and melanocytic tumors among other things, but cellular neurothekeomas are generally S100-
negative.
Q/Q(M)-474347 Report a Problem
Positive staining with Gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) suggests:
1
An apocrine origin
2
An eccrine origin
3
A sebaceous origin
4
A follicular origin
5
None of these answers are correct
Q/Q(M)-474351 Report a Problem
Positive staining with Gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) suggests:
1
An apocrine origin
Gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 (GCDFP-15) is a commonly used apocrine marker.
Q/Q(M)-474351 Report a Problem
Dorf balls are seen in which tumor?
1
Kaposi's sarcoma
2
Angiosarcoma
3
Tufted angioma
4
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
5
Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans
Q/Q(M)-477442 Report a Problem
Dorf balls are seen in which tumor?
53
1
Kaposi's sarcoma
Dorf balls are pink amorphous globules seen in vessels in Kaposi's sarcoma. Typical histologic findings
include proliferation of spindle cells, prominent slitlike vascular spaces, and extravasated red blood
cells.
Q/Q(M)-477442 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of PLEVA?
1
Alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis
2
Red cell extravasation
3
Dermal mucin deposition
4
Fibrinoid necrosis of medium sized vessels
5
Numerous eosinophils and neutrophils
Q/Q(M)-478643 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of PLEVA?
2
Red cell extravasation
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta has characteristic findings. Parakeratosis, spongiosis with
vacuolar alteration, papillary dermal edema, wedge shaped infiltrate, and extravasated RBC's can all be
seen. Occasionally, the infiltrate can include atypical lymphoid cells. Eosinophils and neutrophils are
more frequently seen in LyP.
Q/Q(M)-478643 Report a Problem
Degeneration of cartilage in chondrodermatitis nodularis helices affects which type of collagen?
1
Type I collagen
2
Type II collagen
3
Type III collagen
4
Type IV collagen
5
Type VII collagen
Q/Q(M)-477206 Report a Problem
Degeneration of cartilage in chondrodermatitis nodularis helices affects which type of collagen?
2
Type II collagen
Chondrodermatitis nodularis helices presents as a tender nodule usually on the helix or antihelix of the
ear. It is thought to be a result of vascular insufficiency. Degeneration of the cartilage is seen on
histopathology which is primarily composed of type II collagen.
Q/Q(M)-477206 Report a Problem
Verruciform xanthoma is seen most commonly on:
1
Head and neck
2
Distal extremities
3
Oral mucosae and genital areas
4
Mucosal surfaces and trunk/proximal extremities
54
5
Nail bed and periungual areas
Q/Q(M)-474356 Report a Problem
Verruciform xanthoma is seen most commonly on:
3
Oral mucosae and genital areas
Verruciform xanthoma is an uncommon lesion that usually occurs on the oral mucosa of middle-aged
persons or on the scrotum of middle-aged to elderly Japanese men. The most common site for
verruciform xanthoma is the oral mucosa.
Q/Q(M)-474356 Report a Problem
Which of the following can be used to stain amyloid?
1
PAS
2
Eosin
3
Giemsa
4
Aldehyde fuchsin
5
Crystal violet
Q/Q(M)-478644 Report a Problem
Which of the following can be used to stain amyloid?
5
Crystal violet
Stains for amyloidosis: Congo Red, Thioflavin T, Crystal Violet, Methyl violet, Pagoda red no. 9, PAS
+ diastase, amyloid P-component antibody
Q/Q(M)-478644 Report a Problem
A biopsy was performed from the scalp of an elderly man what is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
2
Angiosarcoma
3
Carcinoid
4
Sebaceous Carcinoma
5
Clear cell hidradenoma
Q/Q(M)-482090 Report a Problem
A biopsy was performed from the scalp of an elderly man what is the most likely diagnosis?
55
1
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma: Metastatic lesions are commonly located on the scalp. The tumor itself is
composed of cells with clear to slightly granular cytoplasm secondary to increased glycogen and lipid.
The tumors typically forms abortive tubes/ducts, cords or sheets of cells. Immunohistochemical stains
are + for EMA and CD10. Typically the tumor is very vascular with scant stroma associated with
extravasated RBC and hemosiderin. The differential diagnosis includes clear cell hidroadenoma. This
latter tumor is usually composed of a mixture of components; solid areas composed of small poroid cells
often with duct formation admixed with clear cells and squamoid cells. The tumor can be solid or cystic
or a combination of the two. The large cystic spaces typically contain sialomucin. The stroma is delicate
fibrovascular. The tumor is + CAM 5.2, CEA, EMA, with glycogen and no lipid in the clear cells.
Q/Q(M)-482090 Report a Problem
The deficiency in familial multiple cutaneous leiomyomatosis is:
1
Arginase
2
Adenosine deaminase
3
Endoglin
4
MC1R
5
Fumarate hydratase
Q/Q(M)-474361 Report a Problem
The deficiency in familial multiple cutaneous leiomyomatosis is:
5
Fumarate hydratase
Fumarate hydratase is deficient in familial multiple cutaneous leiomyomatosis. This same enzyme is
deficient in familial uterine leiomyomatosis associated with renal cell cancer. Arginase is deficient in
arginemia. Adenosine deaminase is deficient in autosomal recessive severe combined immunodeficiency
disease (SCID). Endoglin is deficient in some patients with Osler-Weber-Rendu. MC1R (melanocortin 1
receptor) shows sequence variation in people with red hair.
Q/Q(M)-474361 Report a Problem
Langerhans cells express or are characterized by all of the following except:
1
Chromagranin
2
HLA-DR
3
CD1a
4
Birbeck granules
5
S-100
Q/Q(M)-476787 Report a Problem
Langerhans cells express or are characterized by all of the following except:
1
Chromagranin
Chromagranin stain neuroendocrine cells, Merkel cellcarcinomas and eccrine glands. They do not stain
Langerhans cells.
Q/Q(M)-476787 Report a Problem
The PDGF gene has been shown to be translocated into the collagen I gene in:
56
1
Angiofibroma
2
Dermatofibroma
3
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
4
Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
5
Solitary fibrous tumor
Q/Q(M)-474357 Report a Problem
The PDGF gene has been shown to be translocated into the collagen I gene in:
3
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
A translocation involving the PDGF gene and collagen I gene is found in dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans.
Q/Q(M)-474357 Report a Problem
Silver preferentially deposits in:
1
Eccrine glands
2
Apocrine glands
3
Hair follicles
4
Fat
5
Eccrine glands and apocrine glands
Q/Q(M)-474367 Report a Problem
Which of the following histologic features is seen in aging skin?
1
Thickened dermal-epidermal junction
2
Increased mast cells
3
Increased number of terminal hairs
4
Fewer Langerhans cells
5
Increased sebum production
Q/Q(M)-477144 Report a Problem
Which of the following histologic features is seen in aging skin?
4
Fewer Langerhans cells
Histologic features of aging epidermis include flattened dermo-epidermal junction, occasional nuclear
atypia, decrease in the number of melanocytes and Langerhans cells. Changes that are present in the
dermis include atrophy, decrease in fibroblasts, mast cells and blood vessels.
Q/Q(M)-477144 Report a Problem
What is the best diagnosis?
1
Cholesterol emboli
2
Masson's Tumor
3
Calciphylaxis
57
4
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
5
Processing Artifact
Q/Q(M)-482087 Report a Problem
What is the best diagnosis?
1
Cholesterol emboli
Cholesterol Emboli: Typically occurs after a vascular procedure but can occur spontaneously. Usually
presents as livedo reticularis of distal lower extremities, associated with eosinophilia and acute renal
failure. Often need multiple deeper levels on sectioning a punch biopsy to see the characteristic
cholesterol clefts and fibrin thrombi in the lower dermis or subcutis.
Q/Q(M)-482087 Report a Problem
Methyl-green pyronin stains RNA what color?
1
Pink
2
Green
3
Blue
4
Purple
5
Black
Q/Q(M)-474348 Report a Problem
Methyl-green pyronin stains RNA what color?
1
Pink
Methyl-green pyronin stains RNA pink and stain DNA green.
Q/Q(M)-474348 Report a Problem
Which immunohistochemical stain would be positive in eosinophilic granuloma?
1
HMB-45
2
Cytokeratin 20
3
Congo red
4
Mucin
5
CD1a
Q/Q(M)-477134 Report a Problem
58
Which immunohistochemical stain would be positive in eosinophilic granuloma?
5
CD1a
Eosinophilic granuloma is a form of Langerhans Cell Histocytosis (LCH), previously called
Histiocytosis X. Eosinophilic granuloma is a localized, benign form which is more common in males
and generally affects the bones. All forms of LCH are characterized by the infiltration of Langerhans
cells on pathology, which stains for S-100, CD1a and contain cytoplasmic birbeck granules.
Q/Q(M)-477134 Report a Problem
This tumor is best visualized using PAS stains with and without diastase what is it?
1
Clear cell acanthoma
2
Seborrheic keratosis
3
Bowen's disease
4
Tricholemmoma
5
Inverted follicular keratosis
Q/Q(M)-482089 Report a Problem
This tumor is best visualized using PAS stains with and without diastase what is it?
1
Clear cell acanthoma
Clear cell acanthoma is composed of pale staining keratinocytes that have increased glycogen content.
The increased glycogen in this tumor is due to a defect in phosphorylase. Histologically the
keratinocytes are mildly enlarged and pale and distinctly separated from the surrounding epidermis. The
epidermis appears focally expanded by an acanthotic plate like growth that spares the follicular
epithelium. Also associated with this tumor are PMNs that extend into the epidermis. There may be
edema of the papillary dermal and some telangiectasis. PAS stain with and without diastase highlights
the abundant glycogen.
Q/Q(M)-482089 Report a Problem
What infectious agent is most likely responsible for a reaction of fibrin and antibodies which help to
prevent phagocytosis?
1
Nocardia
2
Ricketsii species
3
Actinomycosis
4
Candida albicans
5
Anthrax
Q/Q(M)-476427 Report a Problem
59
What infectious agent is most likely responsible for a reaction of fibrin and antibodies which help to
prevent phagocytosis?
3
Actinomycosis
Hoeppli-Splendore reaction is characterized histologically by intensely eosinophilic material consisting
of fibrin and antibodies. Causes of the phenomenon include Actinomycosis israelii, Staph aureus,
Proteus, Pseudomonas and E. coli.
Q/Q(M)-476427 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains with Ulex europeus agglutinin I?
1
Smooth muscle
2
Eccrine glands
3
Endothelial cells
4
Macrophages
5
Melanocytes
Q/Q(M)-476788 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains with Ulex europeus agglutinin I?
3
Endothelial cells
Ulex europeus agglutinin I is a stain which identifies endothelial cells, keratinocytes, angiosarcomes and
Kaposi's sarcoma.
Q/Q(M)-476788 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains would be helpful in the diagnosis of cryptococcus?
1
Colloidal iron
2
Oil red O
3
Mucicarmine
4
Giemsa
5
Verhoeff von Gieson
Q/Q(M)-478652 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains would be helpful in the diagnosis of cryptococcus?
3
Mucicarmine
The yeast cytoplasm of Crytococcosis stains with PAS and methanamine silver while the the capsule
stains with Alcain blue and mucicarmine. Colloidal iron stains mucin; Oil red O stains fat; Giemsa stains
mast cells and leishmaniasis; Verhoeff von Gieson stains elastic tissue.
Q/Q(M)-478652 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains would be helpful in the diagnosis of cryptococcus?
3
Mucicarmine
The yeast cytoplasm of Crytococcosis stains with PAS and methanamine silver while the the capsule
stains with Alcain blue and mucicarmine. Colloidal iron stains mucin; Oil red O stains fat; Giemsa stains
mast cells and leishmaniasis; Verhoeff von Gieson stains elastic tissue.
Q/Q(M)-478652 Report a Problem
60
A 9 year-old girl presents for evaluation of alopecia. Physical examination reveals a bizarrely shaped
patch of hair loss in the vertex area, with broken hairs of varying lengths. Biopsy is most likely to
demonstrate:
4
Traumatized hair follicles with perifollicular hemorrhage, empty follicles, and deformed hair
shafts
Biopsy of trichotillomania, characterized by an abnormal urge to pull out the hair, reveals traumatized
hair follicles with perifollicular hemorrhage, empty anagen follicles, many catagen hairs, deformed hair
shafts (known as trichomalacia), and melanin casts within the follicular canal. Lymphoid inflammation
at the level of the hair bulb is a feature of alopecia areata. Mucin within follicular epithelium is
characteristic of follicular mucinosis. Tinea capitis demonstrates fungal spores within hair shafts.
Suppurative folliculitis may be seen in folliculitis decalvans.
Q/Q(M)-482565 Report a Problem
This tumor was excised from a verrucous yellow plaque on the scalp what is it?
1
Syringocystadenoma papilliferum
2
Eccrine acrospiroma
3
Hidradenoma Papilliferum
4
Tubular apocrine adenoma
5
Syringofibroadenoma
Q/Q(M)-482097 Report a Problem
This tumor was excised from a verrucous yellow plaque on the scalp what is it?
1
Syringocystadenoma papilliferum
Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum: 33% arise in association with a nevus sebaceous, 10% may coexist
with a BCC or trichoblastoma. A subset of cases has a deletion of 9q22 PTCH gene and 9q21 (p16).
Histologically they present as surface invagination of glandular cords composed of one to two layers of
cuboidal cells associated with a fibrovascular stroma with numerous plasma cells. Cystic spaces may
form within which are free floating islands which are peripherally lined by cuboidal cells with an inner
core composed of loose connective tissue, blood vessels and numerous plasma cells.
Q/Q(M)-482097 Report a Problem
All are sebaceous glands except:
1
Tyson
2
Moll
3
Wolf
61
4
Fordyce
5
Meibomian
Q/Q(M)-474382 Report a Problem
All are sebaceous glands except:
2
Moll
Molls glands are modified apocrine glands located on the eyelid. Sebaceous glands in certain
locations have an associated name (Tysons on the penis, Wolfs or Meibomian on the eyelid, and
Fordyce on the vermilion/oral mucosa).
Q/Q(M)-474382 Report a Problem
An increased number of miniaturized hairs are seen in:
1
Lichen planopilaris
2
Alopecia areata
3
Trichotillomania
4
Telogen effluvium
5
Lichen planopilaris and alopecia areata
Q/Q(M)-474379 Report a Problem
An increased number of miniaturized hairs are seen in:
2
Alopecia areata
In alopecia areata, especially early stages, increased miniaturized catagen hairs can be seen in addition
to the finding of peribulbar lymphocytes resembling a swarm of bees. Lichen planopilaris is a
scarring alopecia in which vertical tracts of fibrosis are seen in place of follicles. Trichotillomania
displays follicular plugging, trichomalacia, pigmented casts, hemorrhage, and increased catagen hairs on
biopsy. Telogen effluvium is characterized by an increased number of telogen hairs.
Q/Q(M)-474379 Report a ProblemBoth mesenchymal and epithelial elements may be found in this
tumor:
1
Cylindroma
2
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma
3
Chondroid syringoma
4
Bednar tumor
5
Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma
Q/Q(M)-478580 Report a Problem
Both mesenchymal and epithelial elements may be found in this tumor:
3
Chondroid syringoma
Cutaneous mixed tumor, also known as Chondroid syringoma, represents an acquired hamartoma with
folliculosebaceous-apocrine differentiation that has been generally interpreted as a form of adnexal
adenoma (neoplasm). It has both a mesenchymal and epithelial component.
Q/Q(M)-478580 Report a Problem
62
Which of the following is true regarding pilomatricomas?
1
Calcification is rarely seen
2
Poorly demarcated tumor
3
Comprised of shadow cells and basophilic cells
4
Mutations found in the APC gene
5
Frequent malignant degeneration
Q/Q(M)-478641 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true regarding pilomatricomas?
3
Comprised of shadow cells and basophilic cells
Pilomatricomas are well-defined lobular tumor in dermis or subcutis comprised of germinative-matrical
cells that are basaloid and transition to "ghost" or "shadow" cells. Calcifiation or ossification are
frequently seen. Mutations are found in beta catenin.
Q/Q(M)-478641 Report a Problem
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis can be seen in which condition?
1
Rheumatoid neutrophilic dermatosis
2
Erythema elevatum diutinum
3
Urticaria
4
Granuloma inguinale
5
Sweet's Syndrome
Q/Q(M)-478646 Report a Problem
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis can be seen in which condition?
2
Erythema elevatum diutinum
Rheumatoid neutrophilic dermatitis is seen in the setting of severe rheumatoid arthritis. The
pathogenesis is not understood, but in the few reports of this rare dermatosis, a true vasculitis has not
been seen. Sweet's syndrome also does not show evidence of a true vasculitis. Erythema elevatum
diutinum histologically shows a leukocytoclastic vaculitis, but with prominent interstitial neutrophils.
Other conditions with evidence of LCV include Henoch-Schonlein purpura, granuloma faciale,
urticarial vasculitis, and occasionally serum sickness.
Q/Q(M)-478646 Report a Problem
Clinically, this lesion often has a blue hue and usually occurs on the face:
1
Apocrine hidrocystoma
2
Epidermoid inclusion cyst
3
Bronchogenic cyst
4
Eccrine hidradenoma
5
Myxoid cyst
Q/Q(M)-476767 Report a Problem
63
Clinically, this lesion often has a blue hue and usually occurs on the face:
1
Apocrine hidrocystoma
apocrine hidrocystoma are usually solitary, tranlucent nodules which may have a bluish hue due to the
Tyndall effect. Histologically, they have one or several large cystic spaces with decapitation secretion.
Q/Q(M)-476767 Report a Problem
The promontory sign is seen in:
1
Tufted angioma
2
Glomeruloid hemangioma
3
Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma
4
Acroangiodermatitis of Mali
5
Kaposis sarcoma
Q/Q(M)-474355 Report a Problem
The promontory sign is seen in:
5
Kaposis sarcoma
The promontory sign refers to the formation of new vessels around existing vessels and adnexal
structures. This is seen in Kaposis.
Q/Q(M)-474355 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Hibernoma
2
Malakoplakia
3
Myospherulosis
4
Liposarcoma
5
Pleomorphic lipoma
Q/Q(M)-482103 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Hibernoma
Hibernoma: This is a rare neoplasm that typically occurs in 30-40 year old males as a slowly enlarging
warm mass on scapular region, trunk, axilla or thigh. There are also myxoid & spindle cell variants that
occur on the posterior neck/shoulder. The lesion enhances with contrast on CT and MRI fails to reveal
fat septations which differs for that seen with other lipomas. Abnormalities in 11q13 and loss of MEN1
64
gene on 10q22 have been noted. Histologically: The lesion is composed of large polygonal adipocytes
that have with multiple vacuoles and an eosinophilic granular cytoplasm with a central nucleus and
prominent nucleolus. These cells are referred to as Mulberry cells . Admixed among these
larger adipocytes are smaller cells with a granular cytoplasm, mature white fat and some times spindle
cells.
Q/Q(M)-482103 Report a Problem
Guarnieri bodies can be found associated with which of the following viral infections?
1
Variola
2
HHV6
3
HHV8
4
Rubeola
5
Rubella
Q/Q(M)-482845 Report a Problem
Guarnieri bodies can be found associated with which of the following viral infections?
1
Variola
Guarnieri bodies are eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions associated with variola infection
(smallpox), however they can also be seen in infections with other pox viridae, including vaccinia,
cowpox, and parapox. These inclusions represent aggregates of viral particles.
Q/Q(M)-482845 Report a Problem
Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is associated with all except:
1
Rothmund-Thompson
2
Scleredema
3
Ehlers-Danlos
4
Acrogeria
5
Downs
Q/Q(M)-474384 Report a Problem
Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is associated with all except:
2
Scleredema
Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is associated with Downs syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos type IV,
Osteogenesis imperfecta, Rothmund Thompson, Marfans, Werners, acrogeria, and penicillamine
therapy.
Q/Q(M)-474384 Report a Problem
Eccrine glands are found on the:
1
Labia majora
2
Labia minora
3
Glans
4
Prepuce
65
5
Vermilion
Q/Q(M)-474365 Report a Problem
Eccrine glands are found on the:
1
Labia majora
Eccrine glands are present all over the body except on the vermilion of lips, glans, labia minora, nail
beds, and inner prepuce.
Q/Q(M)-474365 Report a Problem
The most common cause of a longitudinal groove of the nail plate is:
1
Myxoid cyst
2
Verruca vulgaris
3
Psoriasis
4
Onychomycosis
5
Paronychia
Q/Q(M)-477126 Report a Problem
The most common cause of a longitudinal groove of the nail plate is:
1
Myxoid cyst
A myxoid cyst is not a true cyst as it is devoid of cyst lining. They usually occur in an acral location
and are the most common cause of a longitudinal groove of a nail plate.
Q/Q(M)-477126 Report a Problem
Histopathologically, a swiss cheese type appearance is characteristic to which of the following?
1
Silica
2
Tattoos
3
Liquid silicone
4
Sea urchin spines
5
Zirconium
Q/Q(M)-478649 Report a Problem
Histopathologically, a swiss cheese type appearance is characteristic to which of the following?
3
Liquid silicone
Parafinoma and silicone granuloma both have a swiss cheese type appearance in the dermis to
subcutaneous fat. The remaining options typically appear sarcoidal.
Q/Q(M)-478649 Report a Problem
Diffuse staining with this marker is suggestive of BCC rather than trichoepithelioma:
1
CAM 5.2
2
Bcl-2
3
PTAH
66
4
CEA
5
Cytokeratin 8
Q/Q(M)-474358 Report a Problem
Diffuse staining with this marker is suggestive of BCC rather than trichoepithelioma:
2
Bcl-2
Trichoepitheliomas stain with bcl-2 on the periphery of individual tumor islands.
Q/Q(M)-474358 Report a Problem
Treatment of postmenopausal women with systemic conjugated estrogens has demonstrated:
1
Increased cellular atypia
2
Decreased mitotic activity of keratinocytes
3
Increased dermal collagen content
4
Decreased sebaceous gland activity
5
Increased skin laxity
Q/Q(M)-477159 Report a Problem
Treatment of postmenopausal women with systemic conjugated estrogens has demonstrated:
3
Increased dermal collagen content
Systemic use of conjugated estrogens in postmenopausal women increases total skin thickness, dermal
collagen content and mitotic activity of keratinocytes. In addition, there is a reduction of dry skin,
slackness and increased hydration.
Q/Q(M)-477159 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of pleomorphic lipoma?
1
Foreign body giant cells
2
Floret giant cells
3
Frequent mitoses
4
Exocytosis of lymphocytes
5
Virchow bodies
Q/Q(M)-478647 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of pleomorphic lipoma?
2
Floret giant cells
Pleomorphic lipomas characteristically have a mixture of variably sized fat cells with a varying number
of pleomorphic enlarged cells. These cells contain nuclei arranged in a circumferential pattern that has
been termed floret cells. Rare lipoblasts are found. Focal collections of lymphocytes and plasma cells
within the tumor are seen.
Q/Q(M)-478647 Report a Problem
What is the most common location of a verruciform xanthoma?
67
1
Mouth
2
Lower leg
3
Face
4
Hand
5
Thigh
Q/Q(M)-482850 Report a Problem
What is the most common location of a verruciform xanthoma?
1
Mouth
The oral mucosa is the most common location of a verruciform xanthoma. It is also seen in CHILD
syndrome, EBA, GVHD, and lymphedema syndromes.
Q/Q(M)-482850 Report a Problem
Psoriasis vulgaris may demonstrate all except one of the following histopathologic changes.
1
Munro microabscesses
2
Clubbing of the rete ridges
3
Spongiform pustules of Kogoj
4
Hypergranulosis
5
Suprapapillary thinning
Q/Q(M)-478634 Report a Problem
Psoriasis vulgaris may demonstrate all except one of the following histopathologic changes.
4
Hypergranulosis
Histopathological features of psoriasis: Hyperkeratosis with confluent parakertosis associated with a
thin to absent granular layer, Uniform elongation of rete ridges and they are expanded at their tips
(Clubbing of rete ridges), papillary dermal edema with dilated toruous capillaries, thinned
suprapapillary plates, neutrophils within stratum corneum (Munro's micorabscesses), neutrophils within
the spinous layer (spongiform pustule of Kogoj), and superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
Q/Q(M)-478634 Report a Problem
Multiple clear cell acanthomas are associated with:
1
Ichthyosis
2
Cowden's
3
Immunosuppression
4
Gastrointestinal polyps
5
Breast cancer
Q/Q(M)-474354 Report a Problem
Multiple clear cell acanthomas are associated with:
1
Ichthyosis
Clear cell acanthoma is associated with ichthyosis.
68
Q/Q(M)-474354 Report a Problem
All have been associated with increased risk of breast cancer except:
1
Cowdens
2
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
3
Peutz-Jeghers
4
Birt-Hogg-Dube
5
ataxia telangiectasia
Q/Q(M)-474369 Report a Problem
All have been associated with increased risk of breast cancer except:
4
Birt-Hogg-Dube
Birt-Hogg-Dube is associated with renal cancer and thyroid cancer. Female carriers of a mutated ATM
(homozygous mutations ATM cause ataxia telangiectasia) have an increased risk of breast cancer.
Q/Q(M)-474369 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in cicatricial pemphigoid is:
1
Dermal
2
Basment membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Supra basal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479694 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in cicatricial pemphigoid is:
2
Basment membrane zone
Cicatricial pemphigoid is an autoimmune blistering disease that presents with ulcers, blisters and
erosions of mucosal surfaces, especially the eyes and mouth. The cleft in cicatricial pemphigoid is
found in the basement membrane zone/subepidermal as the antigens are usually BPAg2,laminin 5 and
alpha-6-beta-4 integrin. Direct immunoflourescence is identical to that of bullous pemphigoid showing
linear IgG and complement deposits in the basement membrane zone.
Q/Q(M)-479694 Report a Problem
Which of the following shows granular deposition of IgA in the dermal papillae and along the basement
membrane zone on direct immunoflourescence:
1
IgA pemphigus
2
Bullous pemphigoid
3
Linear IgA dermatosis
4
Dematitis herpetiformis
5
Herpes gestationalis
Q/Q(M)-479627 Report a Problem
69
Which of the following shows granular deposition of IgA in the dermal papillae and along the basement
membrane zone on direct immunoflourescence:
4
Dematitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis or Duhring's disease, presents with very pruritic vesicles symmetrically on
extensor surfaces. On histology it presents as suprapapillary vesicles with mostly neutrophils and
inflammatory destruction of the basement membrane zone. Direct immunoflourescence shows granular
deposition of IgA in the dermal papillae and along the basement membrane zone.
Q/Q(M)-479627 Report a Problem
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with an indolent course is positive for which of the
following?
1
CD4
2
CD8
3
CD10
4
CD45
5
CD57
Q/Q(M)-474343 Report a Problem
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with an indolent course is positive for which of the
following?
2
CD8
There seems to be two subsets of subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma. One has an indolent
course, and is often CD8-positive and is positive for the alpha-beta T-cell receptor. The other has an
aggressive course, sometimes with evidence of systemic hemophagocytosis and high mortality. This
subset is CD56-positive and positive for the gamma-delta T-cell receptor.
Q/Q(M)-474343 Report a Problem
The green color in chloroma is secondary to:
1
Stromelysin
2
Chloracetate
3
Fumarase
4
Myeloperoxidase
5
Alkaline phosphatase
Q/Q(M)-474360 Report a Problem
The green color in chloroma is secondary to:
4
Myeloperoxidase
Chloromas are greenish tumor grossly secondary to involvement of the skin in acute granulocytic
leukemia. The green color is secondary to myeloperoxidase.
Q/Q(M)-474360 Report a Problem
What is the best diagnosis?
70
1
Keloid
2
Ochronosis
3
Lichen Nitidus
4
Compound Spitz Nevus
5
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Q/Q(M)-482130 Report a Problem
What is the best diagnosis?
1
Keloid
Distinguishing hypertrophic scar (HS) from keloid histopathologically is sometimes difficult because
thickened hyalinized collagen (keloidal collagen), the hallmark of keloid, is not always detectable and
[alpha]-smooth muscle actin ([alpha]-SMA), a differentiating marker of HS, is variably expressed in
both forms of scar.
Q/Q(M)-482130 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Poroma
2
Eccrine acrospiroma
3
Sebaceous adenoma
4
Basal Cell Carcinoma
5
Trichoblastoma
Q/Q(M)-482094 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Poroma
Poroma: Palmar/plantar skin, trunk and lower extremities. Named based upon location, If purely
intraepidermal called a hidroacanthoma simplex, if only in the dermis it is a dermal duct tumor, but
more commonly seen both in the epidermis and dermis and then it is given general classification as
poroma. Associated with Schopf-Schultz-Passarge syndrome and Clouston's syndrome. Histologically
composed of a proliferation of small uniform cuboidal basaloid cells that are PAS+DS (i.e. contains
glycogen). The cells are smaller than neighboring keratinocytes. The tumors can be pigmented and
there can be necrosis en mass. The latter finding is an exception to the general rule that benign tumors
71
do not show necrosis en mass.
Q/Q(M)-482094 Report a Problem
Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoide:
1
Occurs in older patient populations rather than Classical MF
2
Occurs in women more commonly than men
3
Is more likely to occur on the face
4
Does not differ from classic MF in terms of those affected
5
Is more likely to occur in patients with skin types V and VI.
Q/Q(M)-482867 Report a Problem
Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoide:
5
Is more likely to occur in patients with skin types V and VI.
Hypopigmented MF occurs more commonly in younger patients and patients with darker skin types.
Q/Q(M)-482867 Report a Problem
A biopsy was obtained from the nasal mucosa, what are the organisms in this biopsy?
1
Rhinosporidium
2
Coccidioidomycosis
3
Prototheca wickerhamii
4
Histoplasmosis capsulatum
5
Cryptococcus neoformans
Q/Q(M)-482083 Report a Problem
A biopsy was obtained from the nasal mucosa, what are the organisms in this biopsy?
1
Rhinosporidium
Rhinosporidiosis originally thought to be due to a fungus Rhinosporidium seeberi, now believed to be
caused by an aquatic protistan parasite or Cyanobacteria, Microcystics aeruginosa. Sri Lanka & South
America polypoid nasal/mucosal lesions in males and conjunctival lesions in females. Obtained from
water or soil. Histology: granulomatous dermatitis with mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate with large
thick walled birefringent sporangia which mature toward the center of a cyst, the organism measures
10-200 microns contain 7-8 micron endospores which contain eosinophilic globules. Watery
environments causes cyst to rupture.
Q/Q(M)-482083 Report a Problem
72
An aquarium owner presents with an erythematous, indurated nodule on the right hand that is tender and
warm. The patient has a history of drug induced lupus when he used minocycline for acne. What is the
most serious adverse effect associated with the first line alternative treatment?
1
Sudden cardiac death
2
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
3
Systemic lupus erythematosus
4
Acute renal failure
5
Pulmonary embolism
Q/Q(M)-482860 Report a Problem
An aquarium owner presents with an erythematous, indurated nodule on the right hand that is tender and
warm. The patient has a history of drug induced lupus when he used minocycline for acne. What is the
most serious adverse effect associated with the first line alternative treatment?
1
Sudden cardiac death
In a patient with exposure to marine environments, M. marinum is a common cause of an infection that
presents with an erythematous, indurated nodule on the extremities. First list treatment is minocycline.
Second line treatment is clarithromycin. A serious adverse effect of clarithromycin is sudden cardiac
death, as shown in the CLARICOR trial.
Q/Q(M)-482860 Report a Problem
This was a deep seated large tumor in the thigh, what is it?
1
Liposarcoma
2
Nodular fascitis
3
Hibernoma
4
Spindle cell lipoma
5
Pleomorphic lipoma
Q/Q(M)-482104 Report a Problem
This was a deep seated large tumor in the thigh, what is it?
1
Liposarcoma
A liposarcoma is one of the most common sarcomas to occur in adults, 50-70yos. Those that occur in
resectable regions (like the thigh) have a good prognosis; those that occur in retroperitoneum,
mediastinum or spermatic cord recur repeatedly and have a risk to dedifferentiate with a mortality
approaching 80% over the following 10-20 years. It has a characteristic supernumerary ring with
amplification of 12q14 MDM2 region. Histologically The adipocytes vary in size throughout the tumor.
Pleomorphism is variable depending upon the degree of differentiation that the tumor displays. The
73
nuclei of the more well-differentiated adipocytes, as well as, the spindled cells are hyperchromatic with
nuclear atypia. The presence of lipoblasts, i.e. either mono-vacuolated signet ring type of lipoblast as is
more commonly seen in myxoid liposarcoma and/or multi-vacuolated lipoblasts with central nuclei
scalloped by vacuoles, are characteristic of a liposarcoma, but are not necessary to make the diagnosis.
There is often a plexiform proliferation of blood vessels, with an appearance that has been likened to
crow's feet or chicken wire. The stroma can be loose and delicate, fibrous or myxoid. Thick ropey
fibrous septae are common in liposarcoma and in lipoblastoma.
Q/Q(M)-482104 Report a Problem
Biopsy of a mucosal neuroma from a patient with MEN IIb looks histologically like a:
1
Neurilemmoma
2
Neurofibroma
3
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma
4
Traumatic neuroma
5
Neurothekeoma
Q/Q(M)-474359 Report a Problem
Biopsy of a mucosal neuroma from a patient with MEN IIb looks histologically like a:
3
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma
Mucosal neuromas in MEN IIb often look histologically like PENs. Occasionally mucosal neuromas
display thickened nerves/perineurium.
Q/Q(M)-474359 Report a Problem
Immunohistochemical staining with neuron-specific enolase is positive in:
1
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
2
Malignant firbroushistiocytoma
3
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
4
Merkel cell carcinoma
5
Sebaceous carcinoma
Q/Q(M)-477164 Report a Problem
Immunohistochemical staining with neuron-specific enolase is positive in:
4
Merkel cell carcinoma
Neuron-specific enolase is a cytoplasmic product produced by Schwann cells and neurons. This
enzyme is present in neuroendocrine cells, neurons and tumors derived from them. Positive staining for
74
neuron-specific enolase is found in Merkel cell carcinomas, carcinoid tumors, and malignant
melanoma.
Q/Q(M)-477164 Report a Problem
This is an H and E stained slide, what is the organism?
1
Exophiala jeanselmei
2
Chromomycosis
3
Nocardia
4
Zygomycosis
5
Mucormycosis
Q/Q(M)-482100 Report a Problem
This is an H and E stained slide, what is the organism?
1
Exophiala jeanselmei
Phaeohyphomycotic cyst: Typically the result of an opportunist infection caused by being impaled by a
splinter contaminated with a dematiaceous or pigmented fungus. Most commonly seen on distal
extremities and results in a dermal abscess with fibrous tissue and granulomas within which are
pigmented hyphae and yeast. The most common organism is Exophiala jeanselmei (yellow-brown
septae hypha) and Wangiella dermatitidis. Histology: Circumscribed cyst with a fibrous wall within
which is a chronic granulomatous reaction or dermal abscess, a splinter is sometimes seen along with
the brown filamentous hyphae and yeast.
Q/Q(M)-482100 Report a Problem
Which disease process best describes Texier's disease?
1
Neutrophilic dermatosis
2
Deposition disorder
3
Infectious process
4
Panniculitis
5
Granulomatous disease
Q/Q(M)-477475 Report a Problem
Which disease process best describes Texier's disease?
4
Panniculitis
Texier's disease is a panniculitis secondary to vitamin K injections causing sclerotic lesions with lilac
75
borders on the buttocks and thighs resembling a cowboy belt and holster.
Q/Q(M)-477475 Report a Problem
What is your best diagnosis?
1
Lichen Trichophyticus
2
Secondary Lues
3
Lichen Nitidus
4
Scabies
5
Acral Hyperkeratosis
Q/Q(M)-482131 Report a Problem
What is your best diagnosis?
3
Lichen Nitidus
A chronic inflammatory disease characterized by shiny, flat-topped, usually flesh-coloured
micropapules no larger than the head of a pin. Lesions are localized in the early stages, found chiefly on
the lower abdomen, penis, and inner surface of the thighs. Distribution may become generalized as the
disease progresses.
Q/Q(M)-482131 Report a Problem
This biopsy was obtained from an immunosuppressed patient with multiple bruise like lesions on arms
and legs. What is this neoplasm?
1
Kaposi's sarcoma
2
Lobular hemangioma
3
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma
4
Tufted hemangioma
5
Angiosarcoma
Q/Q(M)-482107 Report a Problem
76
This biopsy was obtained from an immunosuppressed patient with multiple bruise like lesions on arms
and legs. What is this neoplasm?
1
Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's Sarcoma: The vascular proliferation in all subtypes of Kaposi's sarcoma are associated with an
infection with HHV-8. Histologically early on there is a subtle proliferation of irregular angulated slit
like blood vessels in dermis that dissects the collagen. When these new blood vessels encase
preexisting blood vessels it's called a promontory sign. In the stroma there is a lymphoplasmacytic
infiltrate, extravasated red blood cells and hemosiderin.
Q/Q(M)-482107 Report a Problem
Granular cell tumors will stain positive for all of the following markers except:
1
S100
2
PAS
3
PTAH
4
HMB-45
5
Neuron specific enolase
Q/Q(M)-482485 Report a Problem
Granular cell tumors will stain positive for all of the following markers except:
4
HMB-45
Granular cell tumors are of neural origin, with the granules representing an accumulation of lysosomes
in the cytoplasm. Lesions present on the tongue in 25% of cases. The granules stain positive with
periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining and are resistant to diastase. Being of neural origin, lesions also
stain with S100 and neuron specific enolase. The cells would not react with melanocyte markers, such
as HMB-45.
Q/Q(M)-482485 Report a Problem
What is a test that can be used to help differentiate primary extramammary Paget's and pagetoid
metastasis to the skin from underlying colon cancer?
1
Extramammary Paget's disease is carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) positive.
2
Extramammary Paget's disease is carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) negative.
3
Extramammary Paget's disease is gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 positive.
4
Extramammary Paget's disease is gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 negative.
5
Extramammary Paget's disease is EMA positive.
Q/Q(M)-482287 Report a Problem
What is a test that can be used to help differentiate primary extramammary Paget's and pagetoid
metastasis to the skin from underlying colon cancer?
3
Extramammary Paget's disease is gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 positive.
Extramammary Paget's disease is gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 positive, whereas pagetoid
metastasis to the skin from underlying colon cancer is not. Extramammary Paget's disease also is CK7
positive. Pagetoid cells may often be stained positive with both CEA and EMA.
77
Q/Q(M)-482287 Report a Problem
What is this condition?
1
Gouty Tophus
2
Sarcoid
3
Keratin granuloma
4
Rheumatoid Nodule
5
Granuloma annulare
Q/Q(M)-482105 Report a Problem
What is this condition?
1
Gouty Tophus
Gouty Tophi occur due to an accumulation of monosodium urate in the tissues. Deposits in the dermis
act as a foreign body and granulomas form around these deposits. Unless the tissue is fixed with
alcohol (Carnoy's fixative), the yellow brown crystals of gout are not well visualized on H and E. When
the tissue is submitted in formalin the tophus appears pink and amorphous.
Q/Q(M)-482105 Report a Problem
This is considered to be the juvenile counterpart of DFSP:
1
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis
2
Giant cell fibroblastoma
3
Myxofibrosarcoma
4
Myofibromatosis
5
Plexiform fibrous histiocytoma
Q/Q(M)-474352 Report a Problem
This is considered to be the juvenile counterpart of DFSP:
2
Giant cell fibroblastoma
An entity called giant cell fibroblastoma is CD34-positive, is mostly seen in male children on the
neck/trunk, and is thought to be a juvenile counterpart of DFSP.
Q/Q(M)-474352 Report a Problem
62-year old female with history of acute myeloid leukemia presents with multiple edematous,
erythematous papules after starting G-CSF.
1
Sweet's syndrome
2
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
3
Bowel bypass dermatosis
78
4
Polymorphous light eruption
5
Erythema multiforme
Q/Q(M)-476771 Report a Problem
62-year old female with history of acute myeloid leukemia presents with multiple edematous,
erythematous papules after starting G-CSF.
1
Sweet's syndrome
Sweet's syndrome, or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatoses, is often associated with AML and G-CSF.
Histologically, there is marked dermal edema with a prominent infiltrate composed of neutrophils with
leukocytoclasia. There is an absence of extensive vascular damage.
Q/Q(M)-476771 Report a Problem
Granular cell tumors are derived from:
1
Connective tissue
2
Smooth muscle
3
Vascular tissue
4
Neural tissue
5
Adipose tissue
Q/Q(M)-477119 Report a Problem
Granular cell tumors are derived from:
4
Neural tissue
40% of granular cell tumors occur on the tongue. They appear well-circumscribed, raised, firm nodules.
Histologically, the cells are plump and polygonal arranged in nests and cords. Cells are filled with fine
granules representing lysozymes. The tumors are neurally derived and stain with S-100 and PAS.
Q/Q(M)-477119 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in transient neonatal pustular melanosis is:
1
Dermal
2
Basement membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Suprabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479632 Report a Problem
79
The predominant location of the cleft in transient neonatal pustular melanosis is:
5
Subcorneal/granular
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis is an idiopathic pustular eruption of newborns, mostly on the
chest, that heals with hyperpigmentation. It is most common on pigmented individuals. Histologically it
presents as subcorneal pustules with eosinophils and neutrophils.
Q/Q(M)-479632 Report a Problem
ultiple spiradenomas are seen in this syndrome:
1
Alagille
2
Brooke-Spiegler
3
Nicolau-Balus
4
Schopfs
5
Lhermitte-Duclos
Q/Q(M)-474373 Report a Problem
Multiple spiradenomas are seen in this syndrome:
2
Brooke-Spiegler
Brooke-Spiegler syndrome combines multiple cylindromas and multiple trichoepitheliomas, and
sometimes multiple spiradenomas can be seen as well. Alagille syndrome associates arteriohepatic
dysplasia and nevus comedonicus. Nicolau-Balus syndrome describes the constellation of multiple
eruptive syringomas, milia, and atrophoderma vermiculata. Schopfs syndrome combines multiple
apocrine hidrocystomas, palmar-plantar keratoderma, teeth abnormalities (hypodontia), and
onychodystrophy. Lhermitte-Duclos disease may be a manifestation of Cowdens. In Lhermitte-
Duclos, there is a proliferation in the cerebellum (dysplastic gangliocytoma) with macrocephaly.
Q/Q(M)-474373 Report a Problem
The diagnosis is:
1
Dermatofibrosarcoma
2
Nodular fasciitis
3
Angiolipoma
4
Epithelioid sarcoma
5
Liposarcoma
Q/Q(M)-475192 Report a Problem
80
The diagnosis is:
3
Angiolipoma
Angiolipomas are tumors of fat that are characteristically painful. Histopathologically, mature
adipocytes are seen with numerous vessels. Microthrombi are often present.
Q/Q(M)-475192 Report a Problem
All of the following are true of reticulohistiocytoma except:
1
Rare occurrence in children
2
Giant cells with ground-glass cytoplasm
3
Association with arthritis
4
Immunostaining is positive for OKM1
5
Trauma is precipitating factor
Q/Q(M)-477330 Report a Problem
All of the following are true of reticulohistiocytoma except:
3
Association with arthritis
Reticulohistiocytomas, also called giant cell reticulohistiocytomas, occur almost exclusively in adults.
They are generally solitary, and unlike the multicentric type, are not associated with mutilating arthritis
or predisposition for malignancy.
Q/Q(M)-477330 Report a Problem
The cytoplasmic granules seen in granular cell tumor are:
1
Phagolysosomes
2
Ribosomes
3
Mitochondria
4
Intermediate filaments
5
Vacuoles
Q/Q(M)-474346 Report a Problem
The cytoplasmic granules seen in granular cell tumor are:
1
Phagolysosomes
The granules in granular cell tumor are phagolysosomes. The granularity of the granular cell layer in
epidermodysplasia verruciformis may be secondary to increased ribosomes. Mitochondria fill the cells
in hibernoma.
Q/Q(M)-474346 Report a Problem
Which of the following would suggest a diagnosis of malignant lymphoma, B-cell type over
pseudolymphoma, B-cell type?
1
Mixed-cell infiltrate
2
Mitotic figures only in germinal centers
3
Histoicytic giant cells episodically
81
4
Larger lymphocytes predominate
5
Prominant vasculature with thick-walled blood vessels lined by plump endothelial cells
Q/Q(M)-478654 Report a Problem
Which of the following would suggest a diagnosis of malignant lymphoma, B-cell type over
pseudolymphoma, B-cell type?
4
Larger lymphocytes predominate
Histological findings in pseudolymphoma, B-cell type include a mixed-cell infiltrate (important
diagnostic criterion), small lymphocytes (that predominate), the presence of histiocytes and giant cells,
mitotic figures limited to the germinal centers and prominant vasculature.
Q/Q(M)-478654 Report a Problem
Which marker helps to differentiate extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma from cutaneous gamma delta
lymphoma?
1
CD56
2
MUM-1
3
EBV status
4
CD43
5
bcl-2
Q/Q(M)-482226 Report a Problem
Which marker helps to differentiate extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma from cutaneous gamma delta
lymphoma?
3
EBV status
Both cutaneous gamma delta lymphoma and extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma are CD56+. However,
only extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma is EBV + while cutaneous gamma delta lymphoma is EBV
negative. Both these lymphomas have a 5-year survival rate that approaches 0%.
Q/Q(M)-482226 Report a Problem
Which of the following histological features would be most helpful in differentiating lichenoid drug
eruption from lichen planus?
1
Civatte bodies
2
Parakeratosis and eosinophils
3
Squamatization of the basal layer
4
Presence of pruritus
5
Band-like infiltrate with Saw-tooth rete ridges
Q/Q(M)-477221 Report a Problem
Which of the following histological features would be most helpful in differentiating lichenoid drug
eruption from lichen planus?
2
Parakeratosis and eosinophils
Lichenoid drug eruptions share clinical and histopathologic features with lichen planus. Sometimes
82
differentiation is not possible; however, eosinophil, parakeratosis, and a deeper perivascular infiltrate is
more suggestive of lichenoid drug. Implicated medications include captopril, penicillamine, and
chloroquine.
Q/Q(M)-477221 Report a Problem
Which of the following regarding necrobiotic xanthogranuloma and normolipemic plane xanthomas is
FALSE:
1
Both can have an associate paraproteinemia
2
Both commonly have normal serum lipids
3
Both are most commonly distributed on the upper body
4
Normolipemic plane xanthomas lack the induration and ulceration commonly seen in necrobiotic
xanthogranuloma
5
Multiple myeloma is seen in 80% of necrobiotic xanthogranuloma but is rarely seen in
normolipemic plane xanthomas
Q/Q(M)-482920 Report a Problem
Which of the following regarding necrobiotic xanthogranuloma and normolipemic plane xanthomas is
FALSE:
5
Multiple myeloma is seen in 80% of necrobiotic xanthogranuloma but is rarely seen in
normolipemic plane xanthomas
Necrobiotic xanthogranulomas are closely related to normolipemic plane xanthomas: both have a
yellow hue, associated paraproteinemia, normal serum lipids, upper body distribution. However,
normolipemic plane xanthomas have a much stronger association with multiple myeloma, their plaques
lack induration and they rarely ulcerate. Treatment is usually directed at the paraproteinemia.
Q/Q(M)-482920 Report a Problem
Steatocystoma multiplex is associated with:
1
Jadassohn-Lewandowsky
2
Jackson-Lawler
3
Schaufer-Brunauer
4
Zinsser-Engman-Cole
5
Touraine-Solente-Gole
Q/Q(M)-474372 Report a Problem
Steatocystoma multiplex is associated with:
2
Jackson-Lawler
Jackson-Lawler (Jackson-Sertoli) is known as pachyonychia congenital type 2. Multiple steatocysts can
be seen in this condition.
Q/Q(M)-474372 Report a Problem
The pigment deposits in ochronosis are accentuated with:
1
Cresyl violet
2
Methyl-green pyronin
83
3
Silver nitrate
4
Bodian
5
Cresyl violet and silver nitrate
Q/Q(M)-474386 Report a Problem
The pigment deposits in ochronosis are accentuated with:
1
Cresyl violet
Cresyl violet stains the pigment deposits in ochronosis black. Methylene blue will also stain the
pigment black. This pigment does not stain with silver nitrate. The Bodian stain is for nerves. Methyl-
green pyronin stains RNA and DNA.
Q/Q(M)-474386 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in acropustulosis of infancy is:
1
Dermal
2
Basment mebrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Suprabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479693 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in acropustulosis of infancy is:
5
Subcorneal/granular
Acropustulosis of infancy presents as idiopathic pustules on acral skin. Diagnosis is made only after
other causes of pustules have been ruled out, and it usually resolves in a few years. The cleft in
acropustulosis of infancy is subcorneal/granular with neutrophils.
Q/Q(M)-479693 Report a Problem
Which fixative would best preserve the histologic features of a gout tophus?
1
Saline
2
Absolute ethanol
3
Formaldehyde
4
Michel's fixative
5
Tissue culture media
Q/Q(M)-476548 Report a Problem
Which fixative would best preserve the histologic features of a gout tophus?
2
Absolute ethanol
Gout tophi are caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Using absolute
ethanol to fix the biopsy specimen will preserve the crystalline architechture. In formaldehyde fixed
tissure, the crystals are less obvious.
Q/Q(M)-476548 Report a Problem
84
The predominant location of the cleft in linear IgA is:
1
Dermal
2
Basement membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Suprabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479697 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in linear IgA is:
2
Basement membrane zone
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is an autoimmune disorder that presents with tense blisters along red
annular rings (like a string of pearls). Antibodies are found in the lamina lucida against LAD-1 antigen
in anchoring filaments. The cleft in linear IgA would be found in the basement membrane
zone/subepidermal with direct immunostaining IgA in a linear pattern at the dermal-epidermal junction.
Q/Q(M)-479697 Report a Problem
Clear cell syringomas are associated with:
1
Malignancy
2
Sarcoidosis
3
Argyria
4
Diabetes
5
Lichen myxedematosis
Q/Q(M)-474385 Report a Problem
Clear cell syringomas are associated with:
4
Diabetes
Clear cell syringomas are associated with diabetes. Syringomas are associated with Downs
syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-474385 Report a Problem
This keratin is associated with hair and nail:
1
Keratin 6
2
Keratin 8
3
Keratin 10
4
Keratin 16
5
Keratin 17
Q/Q(M)-474366 Report a Problem
This keratin is associated with hair and nail:
85
5
Keratin 17
Keratins 6 and 16 are found in the nail. Keratin 17 is seen in the nail as well as in the hair follicle, and
patients with pachyonychia congenital type 2, in which there is a mutation of keratins 6b and 17, have
nail findings as well as steatocysts.
Q/Q(M)-474366 Report a Problem
This keratin is associated with hair and nail:
5
Keratin 17
Keratins 6 and 16 are found in the nail. Keratin 17 is seen in the nail as well as in the hair follicle, and
patients with pachyonychia congenital type 2, in which there is a mutation of keratins 6b and 17, have
nail findings as well as steatocysts.
Q/Q(M)-474366 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains is specific for melanin?
3
Fontana-Masson
Fontana-Masson is a silver stain and stains melanin black. S-100, HMB 45, MART-1 (Melan-A) are
melanocyte stains. S-100 also decorates Langerhans cells, acrosyringium, and neural crest-derived
cells.
Q/Q(M)-478119 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in porphyria cutanea tarda is:
1
Dermal
2
Basement membrane zone
3
Basal keratinocytes
4
Subrabasal
5
Subcorneal/granular
Q/Q(M)-479696 Report a Problem
The predominant location of the cleft in porphyria cutanea tarda is:
2
Basement membrane zone
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is the most common porhyria. It is due to a deficiency of uroprophyrin
decarboxylase. Adults present with sun induced vesicles, papules, crusts and milia in areas of scaring.
On histology the cleft in porphyria cutanea tarda is subepidermal or in the basement membrane zone
with festooning of dermal papillae into the blister. Hyalinized material around blood vessels in the
papillary dermis may be seen, as well as caterpillar bodies (eosinophilic segemented basement
membrane) in the roof of the blister. PCT is associated with hepatitis C, alcohol abuse and liver disease.
Q/Q(M)-479696 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Mastocytoma
2
Poroma
86
3
Glomus tumor
4
Langerhans cell histocytosis
5
Nevus
Q/Q(M)-482102 Report a Problem
What is this neoplasm?
1
Mastocytoma
Approximately 10% cases of mastocytosis present as a solitary lesion, otherwise known as a mastocytoma.
Typically they present in childhood on trunk or wrist and usually are self limited and spontaneously resolve.
Histologically the epidermis overlying the mast cell proliferation is often hyperpigmented. Within the dermis
there are increased numbers of fried egg mast cells. Often the mast cells are primarily located in the
upper dermis where they fill and expand the dermal papillae. Frequently admixed among the mast cells there
are increased numbers of eosinophils.
Q/Q(M)-482102 Report a Problem
Birt-Hogg-Dube has been associated with increased risk of renal cancer and:
1
Spontaneous pneumothorax
2
Hepatic cysts
3
Adrenal hemorrhage
4
Cirrhosis
5
Gastrointestinal polyps
Q/Q(M)-474363 Report a Problem
Birt-Hogg-Dube has been associated with increased risk of renal cancer and:
87
1
Spontaneous pneumothorax
The gene defect in Birt-Hogg-Dube is folliculin.
Q/Q(M)-474363 Report a Problem
Birt-Hogg-Dube has been associated with increased risk of renal cancer and:
1
Spontaneous pneumothorax
The gene defect in Birt-Hogg-Dube is folliculin.
Q/Q(M)-474363 Report a Problem
In addition to psoriasis, all of the following dermatoses demonstrate regular psoriasiform hyperplasia except:
1
Lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus develops in areas of chronically rubbed skin. On histopathology, there is
hyperkeratosis with areas of parakeratosis, hypergranulosis, slight spongiosis, and a sparse superficial
perivascular infiltrate. The acanthosis in LSC is irregular. The other choices all have regular psoriasiform
hyperplasia.
Q/Q(M)-477207 Report a Problem
This presented as a papule with a tuft of hair on the face, what is this neoplasm?
1
Trichofolliculoma
2
Trichoepithelioma
3
Fibrous Papule
4
Acrochordon
5
Fibrofolliculoma
Q/Q(M)-482095 Report a Problem
88
This presented as a papule with a tuft of hair on the face, what is this neoplasm?
1
Trichofolliculoma
Trichofolliculoma: Most often occurs on the face as a papule with a tuft of hair. Histologically composed of a
central dilated large follicle (Mama hair), from which many secondary smaller hair follicles radiate (Baby hairs),
with the entire unit often enveloped in a vascularized fibrotic stroma. If sebaceous glands are associated with
the hair follicles then the term used is a sebaceous trichofolliculoma or a Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma.
Within the mesenchymal stroma there are increased CD34 and factor XIIIA fibroblasts and Merkel cells as is
seen in the ORS of the follicles.
Q/Q(M)-482095 Report a Problem
A lichenoid infiltrate that surrounds eccrine glands is seen in:
1
Lichenoid drug rection
2
Lichen striatus
3
Lichen planus
4
Lichenoid purpura
5
Lichen planopilaris
Q/Q(M)-475868 Report a Problem
A lichenoid infiltrate that surrounds eccrine glands is seen in:
2
Lichen striatus
Lichen striatus is an uncommon inflammatory dermatitis seen most commonly in children aged 5 to 15. It
presents unilaterally along Blaschko's lines as raised, slightly scaly, erythematous papules, which are often
89
pruritic. These lesions typically regress spontaneously within a year. The histopathologic features of lichen
striatus include a superficial perivascular inflammatory lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with rare plasma cells and
eosinophils. There is a focal lichenoid infiltrate in the papillary dermis with basilar vacuolar alteration and
necrotic keratinocytes. Spongiosis with exocytosis of lymphocytes can be seen in the epidermis. A specific and
distinctive feature of lichen striatus is the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate that surrounds hair follicles
and eccrine glands.
Q/Q(M)-475868 Report a Problem
Supporting evidence for the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is CD4+ lymphocytes with loss of CD7 as well as loss
of
1
CD2
2
CD3
3
CD5
4
CD20
5
CD30
Q/Q(M)-474344 Report a Problem
Supporting evidence for the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is CD4+ lymphocytes with loss of CD7 as well as loss
of
3
CD5
CD5 as well as CD7 are sometimes lost on the surface of epidermotropic T cells in mycosis fungoides. CD2, CD3,
and CD5 are T cell markers. CD20 is a B cell marker. CD30 is positive in anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells,
Hodgkins lymphoma, and lymphomatoid papulosis. Reactive infiltrates can also have some CD30-positive
cells.
Q/Q(M)-474344 Report a Problem
Вам также может понравиться
- General Dermatology MCQsДокумент197 страницGeneral Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed95% (19)
- General Dermatology MCQsДокумент197 страницGeneral Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed95% (19)
- MCQ DermatologyДокумент2 страницыMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- MCQ DermatologyДокумент2 страницыMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- Vesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsДокумент59 страницVesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Dermatology MCQ FRCPДокумент101 страницаDermatology MCQ FRCPhesham89% (19)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASДокумент183 страницыQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- Hair and Nail Disorders MCQsДокумент67 страницHair and Nail Disorders MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Hair and Nail Disorders MCQsДокумент67 страницHair and Nail Disorders MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASДокумент183 страницыQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- NEWS2 Chart 3 - NEWS Observation Chart - 0 PDFДокумент1 страницаNEWS2 Chart 3 - NEWS Observation Chart - 0 PDFKartini MedikalОценок пока нет
- Photodermatology MCQsДокумент53 страницыPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Skin Tumor MCQДокумент73 страницыSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Документ67 страницMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- Derma MCQ Ch01Документ20 страницDerma MCQ Ch01Rasha Dabbagh75% (4)
- Photodermatology MCQsДокумент53 страницыPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Skin Tumor MCQДокумент73 страницыSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Документ672 страницыETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- Genodermatosis MCQsДокумент152 страницыGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Dermatology QuizДокумент7 страницDermatology QuizFaddy OrahaОценок пока нет
- Dermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryДокумент77 страницDermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDr.Tawheed100% (3)
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsДокумент58 страницCutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Dermatology QuizДокумент10 страницDermatology QuizSyed Ali Haider0% (1)
- Dermatology MCQ 1700Документ45 страницDermatology MCQ 1700Dr-Jahanzaib Gondal100% (1)
- Oral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersДокумент29 страницOral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersMedo JTОценок пока нет
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsДокумент111 страницAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- Dermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryДокумент77 страницDermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDr.Tawheed100% (3)
- Mycology MCQsДокумент48 страницMycology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (11)
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsДокумент58 страницCutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsДокумент111 страницAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- Cholesterol Mortality Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаCholesterol Mortality Chart PDFTms Arn100% (1)
- Nursing Care OF A Family Experiencing A Pregnancy From A Preexisting OR Newly Acquired IllnessДокумент55 страницNursing Care OF A Family Experiencing A Pregnancy From A Preexisting OR Newly Acquired IllnessJohn Van Dave TaturoОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Dermatology MCQsДокумент53 страницыPediatric Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed89% (18)
- Dermatology QuestionsДокумент3 страницыDermatology QuestionsMuziki Wa KiafrikaОценок пока нет
- Geno MCQДокумент60 страницGeno MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Dermatopathology Q - AДокумент55 страницDermatopathology Q - AKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (7)
- Photo QuizДокумент21 страницаPhoto Quizabas_maytham1021100% (3)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsДокумент92 страницыBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (16)
- Dermatology MCQ With AnswersДокумент27 страницDermatology MCQ With Answershesham0% (1)
- Immunedermatology MCQsДокумент73 страницыImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyДокумент7 страницMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemОценок пока нет
- Dermatology MCQ With ExplinationsДокумент46 страницDermatology MCQ With ExplinationsheshamОценок пока нет
- Dermatology MCQДокумент9 страницDermatology MCQNiwashiny CnyОценок пока нет
- DermatologyДокумент121 страницаDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- DermatologyДокумент17 страницDermatologyEbn Seena75% (4)
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQДокумент9 страницPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzДокумент27 страницMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- 11Документ3 страницы11faresaltaii100% (2)
- DermatologyДокумент3 страницыDermatologyDrkhslid890% (1)
- Dermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3Документ42 страницыDermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3hifuka100% (1)
- Pics MCQSДокумент22 страницыPics MCQStania100% (1)
- MCQ DermatologyДокумент42 страницыMCQ Dermatologydraik71100% (5)
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsДокумент25 страниц101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhОценок пока нет
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionДокумент207 страницPrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (2)
- MCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)Документ17 страницMCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)R Ratheesh100% (9)
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationДокумент41 страница1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007Оценок пока нет
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Документ31 страницаMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavОценок пока нет
- Dermatology RecertificatДокумент8 страницDermatology RecertificatKhalifa AL-WishahiОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2Документ56 страницDermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2hesham50% (2)
- Dermatology QuestionsДокумент19 страницDermatology QuestionsBenjamin Nelson50% (2)
- Etas MCQ 2015..2Документ605 страницEtas MCQ 2015..2sajithaОценок пока нет
- Final Dermatology ExamДокумент37 страницFinal Dermatology ExamheshamОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Quiz 2015 AnswersДокумент40 страницDermatology Quiz 2015 Answerspoorva shahОценок пока нет
- Dermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizДокумент3 страницыDermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizheshamОценок пока нет
- Derma CD McqsДокумент22 страницыDerma CD McqsheshamОценок пока нет
- Prometric Exam March 2020Документ250 страницPrometric Exam March 2020Sally dossОценок пока нет
- Bollous MCQДокумент21 страницаBollous MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- KEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female CameДокумент8 страницKEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female Camefairodz salapudinОценок пока нет
- PEDIATRICS Dermatology MCQДокумент1 страницаPEDIATRICS Dermatology MCQcataztropher100% (1)
- Dermatology Essay QuestionsДокумент2 страницыDermatology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (1)
- Genetics 50qДокумент62 страницыGenetics 50qAnonymous 4txA8N8etОценок пока нет
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis in AdultsДокумент29 страницSeborrhoeic Dermatitis in AdultskdwazirОценок пока нет
- Alopecia AreataДокумент71 страницаAlopecia AreatadrbhaveshpОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology MCQsДокумент88 страницPharmacology MCQsDr.Tawheed86% (7)
- Plant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsДокумент50 страницPlant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (2)
- Immunedermatology MCQsДокумент73 страницыImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsДокумент92 страницыBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (16)
- Aceclofenac 100 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (eMC) PDFДокумент9 страницAceclofenac 100 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (eMC) PDFHabibОценок пока нет
- Use of Occipital Nerve BlocksДокумент5 страницUse of Occipital Nerve BlocksMilton quisbert paredesОценок пока нет
- Science 6 - Q2 - L4 - Parts and Function of Excretory SystemДокумент28 страницScience 6 - Q2 - L4 - Parts and Function of Excretory SystemSonny Matias100% (1)
- Eurican Technicalsheet 12-08-2019Документ2 страницыEurican Technicalsheet 12-08-2019dzulfikarfaizin romasОценок пока нет
- Maturity Onset Diabetes of The Young: Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis and ManagementДокумент10 страницMaturity Onset Diabetes of The Young: Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis and ManagementatikahanifahОценок пока нет
- WSES Jerusalem Guidelines For Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute AppendicitisДокумент25 страницWSES Jerusalem Guidelines For Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute AppendicitisRenatoMendozaОценок пока нет
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Документ5 страницImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthОценок пока нет
- Constipation NCPДокумент2 страницыConstipation NCPjudaperlОценок пока нет
- PT. Bina Mitra Jaya BersamaДокумент25 страницPT. Bina Mitra Jaya BersamaHADI PRAYITNOОценок пока нет
- 10a. HipoksiaДокумент21 страница10a. HipoksiaputrianitaОценок пока нет
- 5-Lump ExaminationДокумент4 страницы5-Lump Examinationdzidek7Оценок пока нет
- Soumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Документ24 страницыSoumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Salman HabeebОценок пока нет
- 6 Birth DefectsДокумент40 страниц6 Birth DefectsjulieОценок пока нет
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy With Bilateral SalpingoДокумент3 страницыTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy With Bilateral SalpingoReyniel Pablo ElumbaОценок пока нет
- ActinobacillosisДокумент17 страницActinobacillosisKhalid Gul100% (1)
- Basic Knee Arthroscopy Part 4Документ2 страницыBasic Knee Arthroscopy Part 4Diego BellingОценок пока нет
- Notes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessДокумент7 страницNotes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessjyzzadОценок пока нет
- GEFITINIBДокумент3 страницыGEFITINIBErza GenatrikaОценок пока нет
- Guided Notes 7Документ9 страницGuided Notes 7Desiree Denise Valle-DearОценок пока нет
- Sample: Reading Sub-Test - Text Booklet: Part AДокумент24 страницыSample: Reading Sub-Test - Text Booklet: Part AAlwin BrightОценок пока нет
- Ovarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFДокумент397 страницOvarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFnersitiulfahОценок пока нет
- Book 2Документ132 страницыBook 2siti fatimahОценок пока нет
- Bacte01 STREPTOCOCCUS ENTEROCOCCUSДокумент8 страницBacte01 STREPTOCOCCUS ENTEROCOCCUSAngelic AngelesОценок пока нет
- Skin Graft and Flap: Ibnu F Hantoro Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineДокумент11 страницSkin Graft and Flap: Ibnu F Hantoro Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineLuqman AlwiОценок пока нет
- ARTG Summary For Health NavigatorДокумент2 страницыARTG Summary For Health NavigatorinergetixОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of Antidiabetic DrugsДокумент6 страницDrug Study of Antidiabetic DrugsLorina Lynne ApelacioОценок пока нет
- Basic Life Support in Infants and ChildrenДокумент9 страницBasic Life Support in Infants and ChildrenMelissa Espinoza PeñaОценок пока нет