Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Reproductive and Respiratory Systems NAT Test
Загружено:
Kristine Barredo0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
371 просмотров11 страницparallel test for grade 6 NAT takers
Оригинальное название
Science Nat Parallel Test2
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документparallel test for grade 6 NAT takers
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
371 просмотров11 страницReproductive and Respiratory Systems NAT Test
Загружено:
Kristine Barredoparallel test for grade 6 NAT takers
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 11
4
Division of City Schools
City of Muntinlupa
District of Muntinlupa I
Tunasan Elementary School
PARALLEL TEST in NAT SCIENCE VI
SY 2012-2013
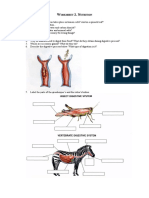
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Identify major parts of male and female reproductive system/ and their functions.
1. The union of egg cell from female organ and the sperm cell from the male organ is known as fertilization. Life
begins when fertilization takes place. In which part of the drawing below does fertilization happen?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
2. Which reproductive organ produces the hormone that develops the secondary characteristics of human female?
a. Uterus b. testes c. scrotum d. ovary
3. What hormone produced by the testes is responsible for the changes experienced by boys at the onset of
puberty?
a. estrogen b. progesterone c. testosterone d. semen
4. Which is NOT a function of the female reproductive system?
a. Produce eggs c. house an unborn baby
b. Deliver sperm d. give birth
5. When does fertilization happens?
a. When the testes release sperm
b. When the ovary releases an egg
c. When a sperm cell enters the fallopian tube
d. When a sperm cell unites with an egg cell
OBJECTIVE: Explain how the respiratory system works.
1. Why are the lungs also considered as organs of excretion?
a. They remove nitrogenous waste from the blood.
b. They remove salts from the blood.
c. They remove carbon dioxide from the blood.
d. They remove oxygen from the blood.
2. How do respiratory and circulatory system work together?
a. Respiratory system brings in the oxygen and the circulatory
system transport it through the body.
b. Transport nutrients and oxygen and remove wastes from the cells.
c. Bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide.
d. Carry nutrients and oxygen to the veins.
3. What happens when you breathe in?
a. The diaphragm expands and ribcage contracts
b. The diaphragm contracts and ribcage expands
c. The diaphragm explodes and ribcage contracts.
d. The diaphragm contracts and expands.
1
2
3
4. Which of these doesnt occur when air flows into the lungs?
a. The air is filtered.
b. The air is cooled.
c. The air is humidified.
d. The air is heated.
5. How does the respiratory system deliver oxygen to the different parts of the body?
a. Breathing
b. Circulation
c. Inhale carbon dioxide
d. Exhalation
OBJECTIVE: Identify parts of the urinary system and their function.
1. What is the function of the kidney?
a. It stores urine.
b. It carries urine out of the body.
c. It removes wastes from the blood.
d. It gives signal to the brain to expel urine from the blood.
2. What happens when the urethra is removed from the excretory system?
a. Amount of salts, minerals and vitamins in the blood will be regulated.
b. Urine will continue flowing.
c. Urine will not be formed.
d. Blood cannot be filtered.
3. Which is the correct pathway for the elimination of urine?
a. Kidneysbladderurethraureters
b. Kidneysurethrabladderureters
c. Kidneysuretersbladderurethra
d. Kidneysuretersurethrabladder
4. Justine felt that he needed to urinate, but somebody was in the comfort room. The person said, Please wait for
a while. Which part of the urinary system holds the liquid waste?
a. ureter b. bladder c. kidney d. urethra
5. The baby boy urinated in his shorts. Then he cried out loud! In which part of the urinary system did the urine
come out?
a. ureter b. bladder c. kidney d. urethra
OBJECTIVE: Classify vertebrate into: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians or fishes.
1. Which among the vertebrate animals are mammals?
I II III
IV V VI
a. I and IV b. II and III c. II and IV d. V and VI
2. A sea horse is a fish, not a horse or mammal. Why?
a. It lives and swims in deep sea.
b. It reproduces in water.
c. It has gills and fins.
d. It has gills and scales.
3. How do mammals different from other group of animals?
a. They are animals covered with feathers.
b. They feed their young with milk.
c. They spend part of their life in water and part on land.
crocodile whale snake
monkey shark chameleon
d. They are cold blooded animals with dry and scaly skin.
4. Platypus is different from other mammals. What is its distinct characteristic?
a. A duck-billed mammal that lays eggs.
b. It feeds its young with milk.
c. It has mammary glands.
d. It has hair or fur as its body covering.
5. Which of the following group of animals is a reptile, a fish and an amphibian respectively?
a. Snake, whale, crocodile
b. Turtle, dolphin, frog
c. Monkey, milkfish, eagle
d. Monitor lizard, shark, toad
OBJECTIVE: Describe characteristics that enable animals to survive in an environment.
1. Animals have adaptations that help them to survive. One example of this is the giraffes long neck. What primary
purpose does this adaptation serve?
a. Protection from heat c. protection from predators
b. Gathering of food d. increased speed
2. In some fishes, baby fishes are seen to come out of the males mouth. Which of the following explains this
observation?
a. Fertilization happens in the males body.
b. The male fish changes to female as it matures.
c. The male has male and female reproductive organs.
d. The male keeps the fertilized eggs in its mouth until they hatch.
3. The veins in a dragonflys wings provide both rigidity and flexibility, which are necessary for flight.
The veins in a dragonflys wings most likely provide
a. Propulsion for the dragonfly in flight
b. Streamlining of the dragonfly wing
c. Stability for the dragonfly wing
d. Lift for the dragonfly wing
4. Which of the following phrases best describes adaptation of organism?
a. Thick covering to conserve water.
b. Fast movements to escape its enemies.
c. Blending of color so that it cannot be easily seen by its enemies
d. Structure of behavior of an organism to help it survive in its environment.
5. Here are the different beaks of birds
Which are best for catching food from the water?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
OBJECTIVE: Describe characteristics of different kinds of plants.
1. Two leafy branches I and II were covered, one with clear plastic bag and the other with a paper bag.
After two weeks, the two leafy branches were wilted and dying. What are missing in I and II that caused the
leafy branches to wilt and die?
A. Sunlight in I, air in II c. Air in I, air in II
B. Sunlight in I, sunlight in II d. Sunlight and Air in I and II
2. What special structures do pomelo and camachile trees have that keep animals away from them?
a. They have hooks c. They have sharp thorns.
b. They have pleasant smell d. They have sticky juice.
3. Rose, cactus and makahiya plants cannot be easily touched and eaten by some animals because of
their________.
a. Unpleasant smell c. thorns
b. Hard stems d. needle like leaves
4. What characteristics does cactus have to survive the long,, hot dry summer months?
a. Long roots c. short roots
b. Watery stem d. thin leaves
5. Here are the two groups of living things.
With what group will you put a mushroom and why?
a. I, because it is a plant.
b. I, because it can make food.
c. II, because it has no chlorophyll.
d. II, because it has roots, stems and leaves.
OBJECTIVE: Differentiate physical from chemical changes/ processes by giving examples.
1. Which of these processes brings about a physical change?
a. Rusting of knife c. melting butter
b. Cooking adobo d. bread becomes stale
2. In which process is heat removed from the material undergoing a change in state?
a. Changing water to ice (freezing)
b. Changing ice to water (melting)
c. Changing water to water vapor (evaporating)
d. Changing water to steam (vaporizing)
3. Which of these processes brings about a chemical change?
a. Grinding cacao seeds c. drilling holes
b. Exploding a firecracker d. pounding rice
4. Aling Teresita brought kilo raw mangoes from the market. She placed them in a basket. After 3 days, the green
mangoes turned yellowish in color. What change took place?
a. Physical change c. energy change
b. Chemical change d. electrical change
5. A child pours water into a plastic container in the freezer. After an hour it turned into ice. What change took
place?
a. Physical change c. energy change
b. Chemical change d. electrical change
OBJECTIVE: Describe the distinctive characteristics of planets in the solar system.
1. Which of the following statements can be made based on the data in the chart?
a. Mercury is the closest planet to Venus.
b. Earth is the coldest of the inner planets.
c. Mars has the shortest day of the inner planets.
d. Venus is the closest planet in diameter to Earth.
2. Which of the following statements is TRUE about the orbits of planets around the sun?
a. The orbits are in the form of a circle.
b. Some planets revolve in a clockwise direction.
c. The planets move in a counterclockwise direction.
d. The planets move around the Sun at the same speed.
3. After many space explorations and using space satellites, many studies have been made. Which of the following
members of the solar system can be considered geologically alive?
a. Venus, Mercury, Mars c. Jupiter, Saturn, Mars
b. Mercury, Neptune, Pluto d. Saturn, Venus, Earth
4. Which description is TRUE about some planets?
a. Earth and Mars have almost the same mass.
b. Venus and Earth are almost of the same size.
c. Uranus is bigger and heavier than Neptune.
d. Jupiter is the biggest planet but lesser in mass than Saturn.
5. What could be TRUE of Earths characteristics as compared to other planets?
I. It has a temperature lower than Mars.
II. It has presence of water
III. It has atmosphere that supports life.
IV. Its atmosphere has clouds of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid.
a. I and II b. II and III c. I and IV d. III and IV
OBJECTIVE: Identify major parts of the nervous system and their functions.
Refer to the diagram of the brain below to answer questions 1 to 2.
1. A basketball player dribbles the ball while walking. Which part of the brain enables him to coordinate his
movements?
a. I b. II c. III d. IV
2. The baby is sleeping, still he is breathing, and his heart is beating. Which part of the brain is responsible for this?
a. I b. II c. III d. IV
3. Trace the normal path of message form the stimuli to the interpreter.
a. Sense organspinal cordbrain
b. Spinal cordbrainsense organ
c. Brainspinal cordsense organ
d. Sense organnervesbrain
4. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT
a. senses changes c. predict changes
b. analyzes changes d. respond to changes
5. What is most important function of the nerves?
a. They are all over the body.
b. They carry messages from one part of the body to another.
c. They are connected to the spinal cord.
d. They are connected to the brain.
OBJECTIVE: Identify major parts of the circulatory system and their functions.
1. Based on the diagram of the circulatory system, which of the following statement is correct?
A. From the intestine, digested food flows first to the heart for
distribution to all parts of the body.
B. From the intestine, digested food goes to all parts of the body
where it is needed.
C. The right ventricle pumps blood to the head.
D. The left ventricle pumps blood to the lungs.
2. How does the blood flow from the heart through the blood vessels?
a. Arterycapillaryvein
b. Veinarterycapillary
c. Capillaryveinartery
d. Arteryveincapillary
3. How does the circulation of the blood help the cells?
a. It brings food and oxygen to the cells.
b. It collects carbon dioxide from the cells.
c. It contains WBCs that attract microbes that may harm the cells.
d. It does a, b and c.
1
2
3 4
4. How does the body react, when germs enter the body through an open wound?
a. The red blood cells kill the harmful microorganisms.
b. The platelets tend to clot and engulf the harmful microorganisms.
c. The white blood cells engulf or kill harmful microorganism.
d. The plasma thickens and surrounds the harmful microorganisms.
5. Mr. Barredo is a very fat and an overweight man. What might happen to his heart?
a. The heart will work harder.
b. The heart will pump blood.
c. The heart is heavy.
d. The heart is big, so the person is big.
OBJECTIVE: Present through a diagram the feeding interrelationship among living organisms
1. Shown above is a simple food web in a grassy community. The arrow symbol ( ) means eaten by.
What would happen if all snakes are killed?
a. Grasshopper population would increase.
b. Bird and frog population would increase.
c. Grasshopper and bird population would increase.
d. Grass population would decrease.
2. Here is a simple food web in a lake.
Which animals feed on algae and another animal?
a. Duck and big fish c. small fish and big fish
b. Snail and duck d. snail and small fish
3. Along a food chain, the role of __________________________ is to help return or recycle the primary chemical
compounds of organisms back to the chain: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and other minor compounds.
A) decomposers (bacteria, fungus)
B) consumers (lions, tigers)
C) prey (deer, water buffaloes)
D) producers (plants, trees)
4. Which of the following shows energy transfer in a food chain?
a. Energy is lost in the air.
b. Energy is transferred from producer to consumer.
c. Energy is transferred from consumer to producer.
d. Energy is increased from one consumer to another consumer.
5. What will happen if there is overpopulation of organism in a habitat?
a. It will help the ecosystem.
b. It will harm the ecosystem.
c. It will not affect the habitat.
d. It will not affect the ecosystem.
OBJECTIVE: Illustrate the interdependence of plants and animals for gases through the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
1. Study the flow of gases in the aquarium during the day.
What gas does I represent? What gas does II represent?
a. I- oxygen, II- carbon dioxide
b. I- carbon dioxide, II-oxygen
c. I- carbon dioxide, II other gases in the atmosphere
d. I-other gases in the atmosphere, II-carbon dioxide
2. Using the diagram, what would happen if the gas in arrow 1 is not released by the fish?
I- Decrease of oxygen
II- Decrease of food production
III- Increase of oxygen
IV- Increase of food production
a. 1 and 2 b. 1 and 4 c. 2 and 3 d. 3 and 4
3. Tropical rainforests have many trees and other plants that photosynthesize. What happens when huge areas of
tropical rainforests are destroyed?
a. Oxygen increases and carbon dioxide increases.
b. Oxygen increases and carbon dioxide decreases.
c. Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases.
d. Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases.
4. Study the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
Here are the statements from pupils about the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
I. During the day, plants produce oxygen and use carbon dioxide.
II. At night, animals use oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
III. At night, plants use oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
Which statement is correct?
a. I and II only b. I and III only c. II and III only d. I, II, III
5. During daytime, plants manufacture their food. The raw materials are sunlight, water, soil minerals, and carbon
dioxide. In this process, what is the by-product?
a. Nitrate c. nitrogen
b. Oxygen d. carbon dioxide
OBJECTIVE: Explain the effects of change in materials on health and the environment.
1. A lake was thickly covered with waste materials. Then, many dead fish were found floating on the water. What
could have caused the death of the fish?
a. Waste materials blocked sunlight.
b. Waste materials lessened the amount of water in the lake.
c. Decaying waste materials produced a foul smell.
d. Decaying waste materials used up most of the oxygen dissolved in the water.
2. Why do oil wastes kill aquatic organisms?
a. The oil is absorbed by the leaves and it affects photosynthesis.
b. The oil covers the surface preventing oxygen to get into the river.
c. The oil mixes with the liquid in the bodies of living organism.
d. The oil poisons the cell of the plants and animals living in the water.
3. Naphthalene or mothballs decrease in size when placed inside the closet. This illustrates ______.
a. Condensation c. evaporation
b. Deposition d. sublimation
4. Copper is used in making electrical wires because it can drawn into wires of very small diameters without
breaking. This property of copper is called ______.
a. Conductivity c. ductility
b. Density d. malleability
5. Acid rain is caused by certain gases emitted into the air when fossil fuels are burned. Which gases cause acid
rain?
a. Carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide
b. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide
c. Sulfur dioxide and ozone
d. Carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and hydrocarbons
OBJECTIVE: Identify energy forms and their uses.
1. Why is nuclear fusion less harmful than nuclear fission?
a. Nuclear fusion produces very little radioactivity and less dangerous waste products.
b. Nuclear fusion has an abundant supply of radioactive wastes.
c. Nuclear fusion can supply energy to homes.
d. None of the above.
2. What is always produced when there is energy transformation?
a. Heat b. chemical c. electrical d. radiant
3. What form of energy do muscles, wind and running water show when they do work?
a. Mechanical energy c. nuclear energy
b. Sound energy d. potential energy
4. A big mango fruit is on the edge of a table. What kind of energy does it have?
a. Mechanical energy c. nuclear energy
b. Sound energy d. potential energy
5. Which sequence of energy transformation takes place when you switch on an electric bulb?
a. Lightheatelectrical
b. Electricalheatlight
c. Electricallightheat
d. Heatelectricallight
OBJECTIVE: Identify factors that affect the motion of an object
1. What force causes a ball that rolls on a level surface to slow down and stop?
a. Friction b. inertia c. gravity d. electricity
2. The speed of a ball thrown upward decreases until it stops and moves downward. What force acts on the
moving ball?
a. Friction b. inertia c. gravity d. electricity
3. Why does a bus going uphill travel more slowly than one going downhill?
a. It is helped by gravity.
b. It is moving against gravity.
c. There is more friction going up.
d. The cold wind pulls it down
4. You see a flag waving on a pole. A force is acting on the flag. What is exerting that force?
a. Wind b. water c. gravity d. magnet
5. Truck A is loaded with good, while truck B is empty. Which truck can accelerate faster?
a. Truck A b. Truck B c. Truck A and B d. none
OBJECTIVE: Describe characteristics of the earths interior layers
1. Men have explored the moon and space. Can we explore the interior of the Earth?
a. No, because the interior of the Earth is very far away and very hot.
b. Yes, because the interior of the Earth is solid.
c. No, because it is liquid.
d. Yes, because the interior of the Earth is very cold.
2. People and other living things live here. They build their houses, buildings and even do most of their activities in
this part of the Earth. Which is it?
a. Crust b. mantle c. core d. guttenberg discontinuity
3. Which region of the Earth
consists primarily of solid iron and nickel?
a. Region A
b. Region B
c. Region C
d. Region D
4. Which of the following statements about the Moho (Mohovoricic discontinuity) is false?
a. Seismic waves speed up as they pass down through the Moho.
b. The Moho separates denser rocks below from less dense rocks above.
c. The Moho separates the crust from the mantle.
d. The Moho separates the crust from the mantle.
5. Which of the following statements about the Earths core is TRUE?
a. The inner core and the outer core are both liquid.
b. The inner core and the outer core are both solid.
c. The inner core is liquid and the outer core is solid.
d. The inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid.
OBJECTIVE: Describe characteristics of stars and how group of stars are useful to people
1. Which of the following lists orders the components of the universe from the component with the largest
diameter to the component with the smallest diameter?
a. Galaxies, stars, comets, planets
b. Galaxies, stars, planets, comets
c. Planets, comets, stars, galaxies
d. Comets, planets, stars, galaxies
2. Why stars dont twinkle but as seen in the sky seems to twinkle? It is because of the ________.
a
OBJECTIVE: Differentiate the different theories about the Universe.
1. The following statements explain the Big Bang Theory EXCEPT
a. All matter in the galaxies were once packed into one big ball.
b. The stars moved so far that they could not be seen anymore.
c. The universe expanded and would soon expand over again.
d. The stars came from the materials that exploded and thrown outward and moved farther away from each
other.
2. What would happen to the universe in the future according to the Big Bang theory?
a. New galaxies will form.
b. The universe will come to an end.
c. Galaxies will continue moving away from each other.
d. Galaxies will move forward each other then form a single galaxy.
3.
Вам также может понравиться
- Nat Reviewer ScienceДокумент41 страницаNat Reviewer SciencebrenttОценок пока нет
- Grade 1 EasyДокумент4 страницыGrade 1 EasyJosephine TabajondaОценок пока нет
- Q2 Scie 4 PTДокумент6 страницQ2 Scie 4 PTMauna Kea HexaОценок пока нет
- Science Quiz 2017: Easy, Average and Difficult RoundsДокумент4 страницыScience Quiz 2017: Easy, Average and Difficult RoundsNouiea Bernardelle AcabalОценок пока нет
- General Science ElementaryДокумент12 страницGeneral Science ElementaryShan Taleah RealОценок пока нет
- Sciquest Questions Grade Three Easy RoundДокумент2 страницыSciquest Questions Grade Three Easy RoundMyrna Andal TorratoОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Test-MATH SCIДокумент8 страницDiagnostic Test-MATH SCImayolynОценок пока нет
- Science 5 Quarter 1 Module 3 Week 3Документ6 страницScience 5 Quarter 1 Module 3 Week 3Vhacie TorresОценок пока нет
- Released ItemsДокумент8 страницReleased Itemsapi-299499242Оценок пока нет
- Science Grade 3: NamaДокумент2 страницыScience Grade 3: NamaAstika RahayuОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Sheet No.1 in Science 2: Key ConceptДокумент25 страницLearning Activity Sheet No.1 in Science 2: Key ConceptMary Grace BaldozaОценок пока нет
- Q2 - Summative Test No 3 - ELSДокумент2 страницыQ2 - Summative Test No 3 - ELSMARIZA MAPALOОценок пока нет
- GR 4 3rd QTR SCIENCE REVIEWER SY 2019-2020Документ24 страницыGR 4 3rd QTR SCIENCE REVIEWER SY 2019-2020ZacОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 Science 3rd QuarterДокумент2 страницыGrade 8 Science 3rd QuarterAiza AbdОценок пока нет
- English ReviewerДокумент4 страницыEnglish ReviewerCarol GelbolingoОценок пока нет
- Light Refraction Explains Straw in WaterДокумент6 страницLight Refraction Explains Straw in WaterMariel GregoreОценок пока нет
- Nursing Quiz Bee Elimination RoundДокумент80 страницNursing Quiz Bee Elimination RoundPrince Rener Velasco PeraОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Quarterly ExamДокумент6 страницScience 7 Quarterly Examjoan marie PeliasОценок пока нет
- Science 8 Exam 3rd QuarterДокумент3 страницыScience 8 Exam 3rd QuarterSandie Bergonia FajardoОценок пока нет
- Science and Math Quiz GuideДокумент7 страницScience and Math Quiz GuideMa. Joy JocosolОценок пока нет
- Achievement Test Science 5Документ6 страницAchievement Test Science 5charlotte castroОценок пока нет
- 3rd Periodical Test in English 2011-2012.docx2Документ30 страниц3rd Periodical Test in English 2011-2012.docx2Rosemarie LumbresОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarterly Assessment Science 5Документ6 страниц2nd Quarterly Assessment Science 5ARIEL JAY CHICOОценок пока нет
- Food Chain GameДокумент2 страницыFood Chain Gameapi-443327549Оценок пока нет
- Science and Physics Practice QuestionsДокумент2 страницыScience and Physics Practice QuestionsTbt-lion Cecilia Enriquez0% (1)
- Quiz Bee Answer KeyДокумент9 страницQuiz Bee Answer KeyPeter Jay CorrosОценок пока нет
- Second Quarter Summative Test Science 4Документ4 страницыSecond Quarter Summative Test Science 4Hazel Obena EneroОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Activity Sample QuestionnaireДокумент2 страницыReproductive Activity Sample Questionnairefull in loveОценок пока нет
- Vegetative Propagation WorksheetДокумент1 страницаVegetative Propagation WorksheetOrmie ChanОценок пока нет
- Gr4 Selected Response ItemsДокумент15 страницGr4 Selected Response ItemsKyo ToeyОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Worksheet Q3 Science 6 - Week 1Документ4 страницыLearning Activity Worksheet Q3 Science 6 - Week 1Prince Jallie Bien GuraОценок пока нет
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsДокумент27 страницScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsShawee Gucor SaquilabonОценок пока нет
- Science 8: Reviewer For The Monthly ExamДокумент4 страницыScience 8: Reviewer For The Monthly Examtwinckel mae bienesОценок пока нет
- Skeletal System FunctionsДокумент9 страницSkeletal System FunctionsAlvin JuaniteОценок пока нет
- I. Solve Each Item and Write The Answer On The Space.: MTAP Reviewer - GRADE 3Документ8 страницI. Solve Each Item and Write The Answer On The Space.: MTAP Reviewer - GRADE 3dianne agatepОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle Test - v1Документ5 страницCell Cycle Test - v1api-316239296Оценок пока нет
- Kinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingДокумент2 страницыKinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingMOHDFADZLY84Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Grading Periodical TestДокумент4 страницы2nd Grading Periodical TestEvelyn PabuaОценок пока нет
- S6 - Q2 - Week 4Документ10 страницS6 - Q2 - Week 4RANDY ALVAROОценок пока нет
- STEM Grade 12 Module on Work, Energy and PowerДокумент19 страницSTEM Grade 12 Module on Work, Energy and Powergregory jimenezОценок пока нет
- 7 Final English Grade 5 Week 7 Second QuarterДокумент10 страниц7 Final English Grade 5 Week 7 Second QuarterEugene PicazoОценок пока нет
- Grade 4 Science ReviewerДокумент2 страницыGrade 4 Science ReviewerLeciram Felipe DesalesОценок пока нет
- Science Grade 9: Quarter 4 - Module 6 Heat, Work and EnergyДокумент15 страницScience Grade 9: Quarter 4 - Module 6 Heat, Work and Energymaesheil computerОценок пока нет
- Directions: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple ChoiceДокумент4 страницыDirections: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple Choicejam syОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Examination: Assumption Montessori SchoolДокумент9 страницComprehensive Examination: Assumption Montessori Schoolshincee23Оценок пока нет
- Grade 4 Summative 5 THДокумент2 страницыGrade 4 Summative 5 THKristine Gallogo0% (1)
- Science 8: Second Quarter Unit TestДокумент3 страницыScience 8: Second Quarter Unit Testrionisah bastasaОценок пока нет
- 1st Summative Test in Mathematics VIДокумент3 страницы1st Summative Test in Mathematics VIMarilynPajonillanTagnepisОценок пока нет
- Science3 Q2 Mod11 LivingThingsAndTheirInvironment V4Документ30 страницScience3 Q2 Mod11 LivingThingsAndTheirInvironment V4Alzen GalaponОценок пока нет
- G5 Science Q1Документ7 страницG5 Science Q1Alfonso CaranguianОценок пока нет
- ALS A&E Science Test ReviewДокумент16 страницALS A&E Science Test ReviewMaricel MaapoyОценок пока нет
- MICROSCOPY PARTS AND FUNCTIONS - Desktop PPT (LOCAL DEMO)Документ34 страницыMICROSCOPY PARTS AND FUNCTIONS - Desktop PPT (LOCAL DEMO)Kristel Dela Torre100% (1)
- Physical Science Exam ReviewДокумент10 страницPhysical Science Exam ReviewEunice HolgadoОценок пока нет
- Quiz Bee ClassroomДокумент3 страницыQuiz Bee ClassroomMyra Ann AlforqueОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 TestДокумент9 страницChapter 1 TestShivali PatelОценок пока нет
- Sci 8, 4th Periodical ExamДокумент3 страницыSci 8, 4th Periodical ExamRutchie Lasque100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemДокумент8 страницThe Respiratory SystemHazel Jane Ambrona VillegasОценок пока нет
- Metrobank-MTAP Math Challenge Division FinalsДокумент8 страницMetrobank-MTAP Math Challenge Division FinalsAkai ShuichiОценок пока нет
- Baliwag South Central School: Blacken or Shade The Circle On A Separate Sheet For Your AnswersДокумент5 страницBaliwag South Central School: Blacken or Shade The Circle On A Separate Sheet For Your AnswersElainee SantosОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 2. NutritionДокумент6 страницWorksheet 2. NutritionrosaronceroОценок пока нет
- LAC gr3 9122022Документ16 страницLAC gr3 9122022Kristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- April PristineДокумент1 страницаApril PristineKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- 2012 Window CardsДокумент3 страницы2012 Window CardsKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Nutritional Status FormatДокумент1 страницаNutritional Status FormatKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- 1.1 LRMDS Specification and Guidelines For Intellectual Property Rights ManagementДокумент6 страниц1.1 LRMDS Specification and Guidelines For Intellectual Property Rights ManagementRohclem BacasenОценок пока нет
- GRADE 5 QUARTER 1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryДокумент7 страницGRADE 5 QUARTER 1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryKristine Barredo92% (26)
- IWAR-Week5 - Kristine Joan BarredoДокумент7 страницIWAR-Week5 - Kristine Joan BarredoKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Tunasan Elementary School FLAT Reading Assessment ToolДокумент2 страницыTunasan Elementary School FLAT Reading Assessment ToolKristine Barredo100% (2)
- DepEd Research GuideДокумент8 страницDepEd Research GuideKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : (Pakilagay Code From Melcs) ItoДокумент4 страницыMost Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : (Pakilagay Code From Melcs) ItoKristine Barredo82% (11)
- IWAR-Week3 - Kristine Joan BarredoДокумент4 страницыIWAR-Week3 - Kristine Joan BarredoKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Schools Division Office Muntinlupa CityДокумент1 страницаSchools Division Office Muntinlupa CityKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- IWAR-Week4 - Kristine Joan BarredoДокумент3 страницыIWAR-Week4 - Kristine Joan BarredoKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Tunas Elementary Workweek ReportДокумент9 страницTunas Elementary Workweek ReportKristine Barredo100% (2)
- Classifying Materials by PropertiesДокумент7 страницClassifying Materials by PropertiesKristine Barredo90% (41)
- Grade 6 Q1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryДокумент6 страницGrade 6 Q1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryKristine Barredo93% (45)
- RPMS-PPST SY 2020-2021 Capacity Building For Raters - Worksheets With COTДокумент132 страницыRPMS-PPST SY 2020-2021 Capacity Building For Raters - Worksheets With COTKristine Barredo100% (8)
- DepEd AWA Framework for Online MeetingДокумент28 страницDepEd AWA Framework for Online MeetingKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Science CG - With Tagged Sci Equipment - Revised PDFДокумент203 страницыScience CG - With Tagged Sci Equipment - Revised PDFRonnelMananganCorpuzОценок пока нет
- Arduino Project1Документ3 страницыArduino Project1Kristine Barredo0% (1)
- RPMS Tool For Proficient TeachersДокумент16 страницRPMS Tool For Proficient TeachersOdie PenafloridaОценок пока нет
- RPMS Tool For Proficient TeachersДокумент16 страницRPMS Tool For Proficient TeachersOdie PenafloridaОценок пока нет
- 08 - Appendices - RPMSTool - HP PDFДокумент18 страниц08 - Appendices - RPMSTool - HP PDFGener ToledoОценок пока нет
- GettingToKnowYou PDFДокумент1 страницаGettingToKnowYou PDFKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- TES-MES Questionnaire SSPFДокумент4 страницыTES-MES Questionnaire SSPFKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- The Learning Action Cell (LAC)Документ15 страницThe Learning Action Cell (LAC)Kristine Barredo75% (16)
- Muntinlupa Elementary Teacher IPCRF ReviewДокумент9 страницMuntinlupa Elementary Teacher IPCRF ReviewKristine Barredo86% (14)
- Basic Education Research AgendaДокумент41 страницаBasic Education Research AgendaKristine Barredo100% (1)
- Approaches For Teaching Social StudiesДокумент6 страницApproaches For Teaching Social StudiesKristine BarredoОценок пока нет
- Rock CycleДокумент2 страницыRock CycleKristine Barredo67% (3)
- Awakening:13 Steps To Love, Freedom, and PowerДокумент14 страницAwakening:13 Steps To Love, Freedom, and Poweruragreat125622100% (3)
- Glossary of Physics TermsДокумент33 страницыGlossary of Physics TermsDjoanna Joy Carandang100% (1)
- Outer Space LawДокумент42 страницыOuter Space LawmudassirОценок пока нет
- NASA Facts: Satellites - A Global View of EarthДокумент4 страницыNASA Facts: Satellites - A Global View of EarthNASAdocumentsОценок пока нет
- The Ailing PlanetДокумент8 страницThe Ailing PlanetNavin PandiyanОценок пока нет
- Trivias About EarthДокумент3 страницыTrivias About EarthJiblerОценок пока нет
- Planet EarthДокумент6 страницPlanet EarthJanus SalinasОценок пока нет
- Spheres of the EarthДокумент45 страницSpheres of the EarthKristine CantileroОценок пока нет
- Reading Course by ETSx TOEFLДокумент57 страницReading Course by ETSx TOEFLSteven situmorangОценок пока нет
- The Earth: Nama: Rouzan Abdurrahman Tsaqif Absen: 27Документ2 страницыThe Earth: Nama: Rouzan Abdurrahman Tsaqif Absen: 27DewantiОценок пока нет
- Worksheet BiosphereДокумент13 страницWorksheet Biosphererkv100% (1)
- Module 6Документ19 страницModule 6rodena sabadoОценок пока нет
- Disturbing The UniverseДокумент3 страницыDisturbing The UniverseSally MoremОценок пока нет
- FIL Celestial BodiesДокумент5 страницFIL Celestial BodiesRaimundo SousaОценок пока нет
- All Tests in This Single FileДокумент1 944 страницыAll Tests in This Single FileMohammed ShukkurОценок пока нет
- Possibility of Experimental Study of Properties of Time: N. A. KozyrevДокумент16 страницPossibility of Experimental Study of Properties of Time: N. A. KozyrevCfg SuvfyОценок пока нет
- Activity On Environmental ScienceДокумент2 страницыActivity On Environmental ScienceJohn Alexis CabolisОценок пока нет
- 17DX53QL3ZQV5Документ2 страницы17DX53QL3ZQV5Syeda SadiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture NotesДокумент92 страницыLecture NotesSharyl Plan SarominesОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент7 страницUntitledEdlyn KayОценок пока нет
- Layers of The Earth: Science NotesДокумент13 страницLayers of The Earth: Science NotesFrigid GreenОценок пока нет
- Since Plate Tectonic Processes Are Powered by Heat Energy Coming From Radio Active DecayДокумент2 страницыSince Plate Tectonic Processes Are Powered by Heat Energy Coming From Radio Active DecaySydney MagbuhosОценок пока нет
- Grade 6 END of Term 3 PracticeДокумент34 страницыGrade 6 END of Term 3 PracticeĤᾄmἄď ãκἱʆ ϟОценок пока нет
- NDA Complete World Geography English (New)Документ58 страницNDA Complete World Geography English (New)Nigam Chaudhary100% (1)
- Global warming causes and effectsДокумент10 страницGlobal warming causes and effectsZabbyyОценок пока нет
- Solar System Flash CardsДокумент11 страницSolar System Flash Cardsapi-215059920100% (1)
- Astrobiology Quiz With AnswersДокумент3 страницыAstrobiology Quiz With AnswersNaveen Jayawardena100% (1)
- Laboratory Manual For Introductory Geology PDFДокумент361 страницаLaboratory Manual For Introductory Geology PDFJhinsher TagleОценок пока нет
- DLL Earth & Life Science Week 2 - (September 4 - 8, 2023)Документ4 страницыDLL Earth & Life Science Week 2 - (September 4 - 8, 2023)JERRY, JR. JUGARОценок пока нет
- Marine Biology Thesis TopicsДокумент7 страницMarine Biology Thesis Topicsgjga9bey100% (1)