Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
FICHT-5243627-Presentation Feasibility CSP China Oct2010 PDF
Загружено:
fran013340 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
29 просмотров24 страницыCost figures in the left bar were initially based on real CSP plants without storage commissioned by 2009. The range of possible cost reductions through local Chinese manufacturing is still pivotal. Specific investment costs are expected to decrease substantially in the future.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
FICHT-5243627-Presentation_Feasibility_CSP_China_Oct2010.pdf
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCost figures in the left bar were initially based on real CSP plants without storage commissioned by 2009. The range of possible cost reductions through local Chinese manufacturing is still pivotal. Specific investment costs are expected to decrease substantially in the future.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
29 просмотров24 страницыFICHT-5243627-Presentation Feasibility CSP China Oct2010 PDF
Загружено:
fran01334Cost figures in the left bar were initially based on real CSP plants without storage commissioned by 2009. The range of possible cost reductions through local Chinese manufacturing is still pivotal. Specific investment costs are expected to decrease substantially in the future.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 24
Concentrating Solar Power Plants
- Status and Costs -
Wen Zhang, Dr. Ole Langniss
October 2010
Content
Concentrated solar thermal power
Cost reduction potential
Case study China
Conclusion Conclusion
Concentrated Solar Thermal Power
Cost reduction potential through Chinese manufacturing
Using services, labor and plant components from domestic Chinese market
significant cost reduction relative to EU
Example: Parabolic trough example-plant with storage: 41 MW
e
8000
10000
12000
Steel support structure
Power Block
Source: Fichtner
The cost figures in the left bar were initially based on real CSP plants without storage commissioned by
2009. To simulate the cost with storage, the power plant capacity was decreased so that the storage could
be fuelled with the same area of mirrors. Specific investment costs are expected to decrease substantially
in the future. Still, the range of possible cost reductions through local Chinese manufacturing is still pivotal.
0
2000
4000
6000
EU China
$
/
k
W
e
Site development
Heat Collection Elements
Mirrors
Thermal storage
Solar BoP
Total savings: ~ 40%
Future cost reduction potential due to technology development
Several aspects may lead to a substantial cost reduction in CSP technology
Projection for 2020
Scale up plants
Technology
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60%
Total
Volume production
& competition
Scale up plants
beyond 50 MW
relative cost reduction
Source: Deutsche Bank Research
Cost reduction prospects
Cost of CSP
Technology advancement
Economics of scale
Competition
100MW 1000 MW
split up into the plants components (technology development)
15%
20%
25%
30%
0%
5%
10%
15%
Mirror Heat
collecting
element
Storage Power block Others
Source: Deutsche Bank Research
Case study China
Case I: 100MW Solar trough, today, Chinese market benefits
Case II: 1000MW Solar trough, today, Chinese market benefits, cost reduction by economics of
scale
Case III: 1000MW Solar trough, 2020, Chinese market benefits, cost reduction by economics of
scale and learning factors
These case studies are based on expected costs of new CSP plants with economically viable sizes
Electricity costs at generation site:
Source: Fichtner
0.12
0.16
0.14
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15
Case III
Case II
Case I
$/kWhe
Electricity costs at load centers
New power lines have to be built (200-2000km)
Electricity costs at power line outlet
Source: Fichtner
0.16
0.14
0.17
0.12
0.14
0.19
0.12
0.14
0.16
0.18
0.20
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
Case I Case I Case II Case II Case III Case III
200 2,000 200 2,000 200 2,000
$
/
k
W
h
e
Present
Future
Grid Inter-connection location
Distance between the plant and the grid between 200 km (Location A) and 2000
km (Location C); resources in Location C better than in the other locations; cost
analysis shows that even with transmission expenditure, plants at location C can
be economically competitive with plants at location A
Hami
Gobi
desert
(Location C)
(Location A)
Locations are geologically viable to install large CSP
Badanjilin
desert
desert
Lanzhou
(Location B)
Conclusion
Bigger plants are more cost effective than small plants
Better solar resources in remote areas may justify extra costs of
transmission so that they are competitive with plants at locations less
remote but with a poorer solar resource
Large saving potential in Chinese manufacturing and service
Good future prospects of CSP due to:
Sizeable resource potential in China Sizeable resource potential in China
Technology advancement potential
Opportunities for low-cost technology and construction in China
Opportunities for integrated energy storage
Annex: Detailed Cost Analysis of CSP
Parabolic Trough Investment cost
Broken down into 6 major cost components from 3 different data sources
Trough Unit Sargent & Lundy Fichtner
2003 2008 2008
Power Plant
SEGS VI
Trough
100
Trough
100
Trough
100
Trough
100
Hybrid Storage No Storage Storage Hybrid
Support Structure $/m 67 67 171 172 160
Receivers $/m 43 43 53 53 60
Comparison of costs disclosed. Realised projects in the year 2008 have
substantially higher costs than originally expected.
Mirrors $/m 43 40 63 63 60
Solar BOP $/m 234 250 141 141 150
Power Block/BOP $/kWe 527 306 1183 1183 2500
Thermal Storage $/kWe - 958 - 765 -
Total
Investment
cost
M$ 92 254 447 671 559
$/kWe 3052 5073 4471 6708 5594
Operating & Maintenance Cost of Parabolic Trough
Levelized Energy Cost of Parabolic Trough
Internal Rate of Return: 8%
LEC for project Andasol 1
An example of the first commercial CSP project in Europe
Cost Reduction Prospects for Parabolic Trough
Technological Advancements
Improve the efficiency of the solar field,
the reflectivity of mirror and the
absorber
Advanced structural design with lower
weight and costs
Application of advanced heat transfer Application of advanced heat transfer
fluid
Adapt turbine design for the CSP
power-plant to night-time operation
Source ESTELA report
Solar Power Tower Investment Cost
Broken down in 7 major cost components
Tower Unit Sargent & Lundy Fichtner
2003 2008 2008
Powe Plant Solar Tres
13.65 MW
Solar Tres
13.65 MW
Tower
47.25
Storage Storage Solar-Only
Site development / Infrastructure
$/m 11.6 - 25.3 $/m 11.6 - 25.3
Heliostat field
$/m 160 230.6 191.2
Receiver
280m 280m 155MWth
57,143$/m 12,1680$/m 151.5$/kWth
Tower & Piping $/m 11.6 21.99 18.9
Power Bolck & Balance of Plant $/kWe 1,397.7 4,719.6 1,556.6
Thermal storage $/kWt 49 24.9 -
Total
investment cost
M$ 119 219 214
$/kWe 8,753 16,905 4,534
Levelized Energy Cost of Solar Power Tower
Internal Rate of Return: 8%
LEC for Project PS 10
An example of the first commercial solar power tower project in
Europe
Cost Reduction Prospect of Solar Power Tower
The parabolic trough plant with storage is about 28.6% lower than solar tower
plant with storage
It is expected that the costs of solar power tower will decrease more than for the
parabolic trough technology.
Site Selection
Requirements
Solar Resource
CSP Power plant is only economical for locations >1,800 kWh/ (ma)
Land Requirement
20,000 40,000m per megawatt of electricity generation
Infrastructure
Proximity to transmission line corridor, natural gas pipeline and rail
transportation
Water Availability Water Availability
Adequate supply, otherwise dry cooling
Location
System Design
A 41 MW Project
Location: Badanjilin Inner Mongolia
Solar resource of 5 to 5.5 kWh/(mday)
Satisfied distance to local centre
Low Wind speed
High Temperature in Summer
Cost Status of CSP Project in China
Investment Cost
Specific investment cost ($/kWe) in China is 6,810 $/kWe (two
thirds of the price in Europe)
O & M Cost
1.25% of the total investment cost per year in China ( 2%/yr in
Europe )
Levelized Energy Cost Levelized Energy Cost
The electricity cost of a 41 MW parabolic trough power plant in
China is 44% lower than that in Europe
Вам также может понравиться
- 2011-03 EarthworkAndMassDiagrams PDFДокумент42 страницы2011-03 EarthworkAndMassDiagrams PDFSushmit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Recent Process Developments at The Phu Kham Concentrator PDFДокумент16 страницRecent Process Developments at The Phu Kham Concentrator PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Multi ObjectДокумент5 страницMulti ObjectEmir IkanovićОценок пока нет
- DRC1200 - Hard Rock Sizer A Twin Roll Sizer Designed For Mobility PDFДокумент2 страницыDRC1200 - Hard Rock Sizer A Twin Roll Sizer Designed For Mobility PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- HPGR Faq PDFДокумент9 страницHPGR Faq PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Use of Excavated Excess Soils in Earth Works: Akiomi ShimazuДокумент14 страницUse of Excavated Excess Soils in Earth Works: Akiomi Shimazufran01334Оценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S2095268614000895 Main PDFДокумент5 страниц1 s2.0 S2095268614000895 Main PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S089268750300178X Main PDFДокумент7 страниц1 s2.0 S089268750300178X Main PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- The Metals and Mining Industry Under Structural Changes: Singapore March 24, 2009Документ41 страницаThe Metals and Mining Industry Under Structural Changes: Singapore March 24, 2009fran01334Оценок пока нет
- 06 10028 - Solar Energy The Basics PDFДокумент2 страницы06 10028 - Solar Energy The Basics PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Icl7660 PDFДокумент11 страницIcl7660 PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Saramak PDFДокумент14 страницSaramak PDFsempatik721Оценок пока нет
- CarmeliteДокумент3 страницыCarmeliteNicandroPorcelliОценок пока нет
- Planning, Simulation and Yield Calculation of Solar Power PlantsДокумент39 страницPlanning, Simulation and Yield Calculation of Solar Power Plantsfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Grinding Operations DesignДокумент50 страницGrinding Operations DesignLe Hoang LongОценок пока нет
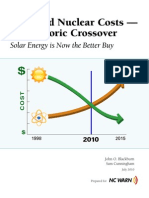
- Solar and Nuclear Costs-The Historic Crossover-Solar Energy Is Now The Better BuyДокумент18 страницSolar and Nuclear Costs-The Historic Crossover-Solar Energy Is Now The Better BuyYoudont CareatallОценок пока нет
- Cicme08 20 PDFДокумент7 страницCicme08 20 PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- CSP Brochure PDFДокумент4 страницыCSP Brochure PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Multiphysics SimulationДокумент32 страницыMultiphysics Simulationminutiae100% (1)
- CSP Review Design Methodology 2013 PDFДокумент16 страницCSP Review Design Methodology 2013 PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Concentrating Solar Power: Clean Energy For The Electric GridДокумент14 страницConcentrating Solar Power: Clean Energy For The Electric Gridfran01334Оценок пока нет
- 02 Cont AttritorsДокумент4 страницы02 Cont Attritorsfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Diagram 08Документ2 страницыDiagram 08fran01334Оценок пока нет
- HPGR Faq PDFДокумент9 страницHPGR Faq PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- DAKOTA Reference 4.0 PDFДокумент150 страницDAKOTA Reference 4.0 PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Wire 311 January 2010 PDFДокумент100 страницWire 311 January 2010 PDFfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Evolution of Nonlinear Sloshing in A Tank Near Half The Fundamental ResonanceДокумент23 страницыEvolution of Nonlinear Sloshing in A Tank Near Half The Fundamental Resonancefran01334Оценок пока нет
- TX242 App DДокумент139 страницTX242 App Dfran01334Оценок пока нет
- Special Report: Global Water SecurityДокумент30 страницSpecial Report: Global Water SecurityAlfredo Jalife RahmeОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Met Coal MethodДокумент20 страницMet Coal MethodTjandra LiemОценок пока нет
- Achievement TestДокумент7 страницAchievement TestJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Infinity IT ParkДокумент9 страницInfinity IT ParkSaikiranОценок пока нет
- Material Handling Flow PatternДокумент20 страницMaterial Handling Flow PatternAli WarsiОценок пока нет
- Nellore SEZДокумент11 страницNellore SEZMunira JagannathОценок пока нет
- Asp List of PartnersДокумент6 страницAsp List of PartnersRiza GaquitОценок пока нет
- CV Hala N. Ballouz, P.E 1 / 8: Titles: EducationДокумент8 страницCV Hala N. Ballouz, P.E 1 / 8: Titles: EducationZahid MehmoodОценок пока нет
- IELTS Writing 1 Graph PracticeДокумент21 страницаIELTS Writing 1 Graph PracticevanekhОценок пока нет
- Business Profile 5Документ13 страницBusiness Profile 5jhonsonarmaniОценок пока нет
- Hitachi - AirExchange Instruction ManualДокумент36 страницHitachi - AirExchange Instruction ManualtheophiloОценок пока нет
- شركات اماراتية 2Документ2 страницыشركات اماراتية 2Basem Mansour100% (1)
- DOCC Project at AERFДокумент45 страницDOCC Project at AERFcutenikОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Judy-Li Ernst&Young enДокумент11 страниц5.3 Judy-Li Ernst&Young enaasgroupОценок пока нет
- Ratna Cement Production Report & CostДокумент8 страницRatna Cement Production Report & CostJCSОценок пока нет
- The Basic 10 For Boiler Tuning: Tip SheetДокумент2 страницыThe Basic 10 For Boiler Tuning: Tip SheetEliecer Romero MunozОценок пока нет
- Optimising Cost of 24x7 Quality Power - Energy ConnectДокумент36 страницOptimising Cost of 24x7 Quality Power - Energy ConnectDevasyrucОценок пока нет
- Green Product Management - Wistron - ENДокумент7 страницGreen Product Management - Wistron - ENxtrayangОценок пока нет
- Citadis Spirit - Brochure - enДокумент6 страницCitadis Spirit - Brochure - enLuca Marius CristianОценок пока нет
- JR PaperДокумент8 страницJR PaperManu KaushalОценок пока нет
- US Army Journal of Installation Management Fall 2010Документ95 страницUS Army Journal of Installation Management Fall 2010U.S. Army Installation Management CommandОценок пока нет
- For Pressure Vessels and Columns (Bidding Stage)Документ2 страницыFor Pressure Vessels and Columns (Bidding Stage)SYedZYnAleОценок пока нет
- Shell Capital Markets Day 2016 Analyst Webcast Presentation Slides 160607122448Документ80 страницShell Capital Markets Day 2016 Analyst Webcast Presentation Slides 160607122448kglorstad100% (1)
- Solar Advice: Buonassisi GroupДокумент10 страницSolar Advice: Buonassisi GroupsujithaprethiОценок пока нет
- Name of Co. For Industrial Training Source: ICAI WebsiteДокумент16 страницName of Co. For Industrial Training Source: ICAI Websitenikhil taksande100% (2)
- WelcomeLetterДокумент4 страницыWelcomeLetterIndrani RayОценок пока нет
- Bangladesh Power Development Board Electricity Bill: LT CONSUMER (Single Register)Документ1 страницаBangladesh Power Development Board Electricity Bill: LT CONSUMER (Single Register)adfaxfafaea0% (1)
- 19Документ15 страниц19KrisnaОценок пока нет
- Coupon 10% P.A. - 6 Months - Low Strike at 75% - USDДокумент1 страницаCoupon 10% P.A. - 6 Months - Low Strike at 75% - USDapi-25889552Оценок пока нет
- 04 BRCE 2017 Jens Kammann Bearing Maintenance and The Right ToolsДокумент36 страниц04 BRCE 2017 Jens Kammann Bearing Maintenance and The Right ToolsHojaAmarillaОценок пока нет
- Service DetailsДокумент1 страницаService DetailssabeerОценок пока нет