Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ch1 3 Campbell
Загружено:
Jaime BerryИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ch1 3 Campbell
Загружено:
Jaime BerryАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
C b ll Di C b ll Di Campbell Diagram Campbell Diagram
Waterfall Plot Waterfall Plot
Spring Semester, 2010
Chong-Won Lee
Center for Noise and Vibration Control
Department of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST
Campbell diagram Campbell diagram
Whirl speed chart (map)
Frequency-speed diagram
Natural frequency-speed map
Damped natural frequency map
Inte fe ence map Interference map
Frequency interference diagram
2
Typical Campbell diagram: Typical Campbell diagram: twin spool engine
300
HP
=
OP
200
100
W
h
i
r
l
S
p
e
e
d
,
H
z
CMF56 J et Engine
LP
=
146( )
HP LP
Hz = +
1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000
Rotational Speed, rpm
0
M. Lalanne and G. Ferraris, Rotordynamic
Predictions in Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, 1990
32 Bladed Fan Vibration 32 Bladed Fan Vibration
3
32 Bladed Fan Vibration 32 Bladed Fan Vibration
Frequency Frequency- -speed diagram by Campbell (1924) speed diagram by Campbell (1924)
Determination of
Critical ( ),
minor ( ) and
3 nodal
diameter mode
minor ( ) , and
sub-minor ( )
resonant speeds
from
forward/backward
traveling wave modes
of rotating disk of rotating disk
4
Frequency Frequency- -speed diagram by Campbell (1924) speed diagram by Campbell (1924)
Steam turbine
disk wheel
Walking into
w/
n nodal diameter
modes
a mine field?
All mines are
dangerous?
Campbell diagram: turbine blade w/ 24 nozzles Campbell diagram: turbine blade w/ 24 nozzles
IV NPF
V NPF VI NPF
7000
6000
z
Not a possibility,
but a realization
II NPF
III NPF
IV NPF
6000
5000
4000
3000
e
N
a
t
u
r
a
l
F
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
,
H
z
Coupled Mode II
Coupled Mode III
-40
but a realization
I NPF
0 1000 2000 3000
Rotor Speed, rpm
2000
1000
0
B
l
a
d
e
Coupled Mode I
0 -20
J. S. Rao, Turbomachine Blade
Vibration, John Wiley & Sons, 1991
M. J. Goodwin, Dynamics of Rotor-bearing
Systems, Unwin Hyman Ltd., 1989, p275
5
Campbell diagram
exhibits frequency
margins for
Commercial S/W: SwRI Commercial S/W: SwRI
fundamental stair
and flow
distortion
excitations. Rising
frequencies are
caused by
centrifugal
stiffening;
d di
Thi i
descending
frequencies are
caused by rising
temperature.
This is a
Campbell
diagram.
But too many
possible
resonances.
Rotating Circular Plate: Stationary Coordinates
2
2
2
2
2
2
4
2
v v v
f r + + + = ( , , )
2 2
f ( , , )
w
W
b
R
b
t
D
hb
hb
D
s
= = = = , ,
)
, , r D=
Eh
( -
3
2
12 1
4
4
( , , ):dimensionless transverse deflection of
isotropic, homogeneous, uniform in thickness, disk
v r
( , , ) : dimensionless excitation force f r
s
: mass density, h : thickness, E : elastic modulus
: Poisson's ratio, : rotational speed
6
Rotating Circular Plate : Stationary Coordinates
[ ]
v r c e c e R r
mn
jm
mn
jm
m n
mn
( , , ) ( ) ( ) ( )
,
= +
1
2
0
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) c jm c m c f
mn mn mn mn mn
+ = 2
2 2 2
f f r e R r rdrd
mn
jm
mn
( ) ( , , ) ( )
=
1
0
2
( ) 0 : forward traveling wave
( ) 0 for : backward traveling wave
F
mn mn
B mn
mn mn
m
m
m
= + >
= < <
: dimensionless ( , ) modal frequency at =0
: complex wave coordinate
: complex wave force
mn
mn
mn
m n
c
f
m
Chladni Figures (1787)
7
Wafer Cutting Machine w/o Initial Tension Wafer Cutting Machine w/o Initial Tension
a
t
u
t
a
l
f
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
forward
rotational speed,
n
a
backward
flutter instability
Wafer Cutting Maching w/ Initial Tension Wafer Cutting Maching w/ Initial Tension
a
t
u
t
a
l
f
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
forward
backward
rotational speed,
n
a
8
Waterfall: conventional spectrum
1X 2X
1B,1F
2BF
2X
3X
2BF
Waterfall: Waterfall: directional spectrum directional spectrum
1X 2X
2F
2B
2X
3X
2F
9
Three-disks HDD spindle system
Three Three- -disks HDD spindle system disks HDD spindle system
100
(1,0)
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
(3.0)
(2,0)
(rps)
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600
0
30
20
conical
Frequency (Hz)
10
Three Three- -disks HDD spindle system disks HDD spindle system
528 Hz
677 Hz
677 Hz
1st : in-phase unbalanced mode
2nd & 3rd : balanced modes (uncoupled disk
modes)
2239 Hz
3885 Hz
4th : out-of-phase unbalanced mode
5th : bouncing mode
Fan Blade Vibration Fan Blade Vibration
11
Campbells vision in 1924 Campbells vision in 1924
One of the most important features in the
design and manufacture of a steam turbine
is the elimination of the possibility of
vibration occurrence at the various natural
frequencies of its disk wheels and buckets.
The protection of steam turbine disk
wheels from axial vibration Trans ASME wheels from axial vibration, Trans. ASME,
1924, p31-160.
Commercial S/W: DSPCon (2) Commercial S/W: DSPCon (2)
This should be called This should be called
order analysis.
12
Damped natural frequency map Damped natural frequency map
log/ decrement
speed
nat. freq
Whirl speed map: root loci Whirl speed map: root loci
exc
n =
UNSTABLE
3
UNSTABLE
1 c
2 c
3 c
1 i
F. F. Ehrich (ed.), Handbook of rotordynamics, McGraw-Hill Inc., 1992, Chapter 2.,
Analytic Prediction of Rotordynamic Response by H.D. Nelson and S. H. Crandall.
13
true Campbell diagram by SD true Campbell diagram by SD
bearing vibration
This should be called order analysis or waterfall plot.
Rotating Machinery Analyzer
Campbell Diagram Analysis
Commercial S/W: DSPCon Commercial S/W: DSPCon
This should be called
order analysis
Displayed as a traditional
Campbell diagram or color-
intensity spectrogram.
Order lines may be
superimposed.
Maximum response
frequency/RPM is detected,
marked, and annotated.
order analysis.
Maximum spectral response is
plotted as a function of RPM.
The Envelope of Spectral
responses is plotted as a
function of frequency.
14
Campbell Diagram
A mathematically constructed diagram used
to check for coincidence of vibration sources
Science and Engineering Encyclopedia Science and Engineering Encyclopedia
This should be called
order analysis.
with natural resonances. The form of the
diagram is like a spectral map, but the
amplitude is represented by a circular or
rectangular plot, the larger the amplitude the
larger the circle or rectangle.
In this particular example, the even
engine orders are plotted from 1E
to 10E and a resonance is seen at
approximately 120Hz. There is a
resonance at 320Hz excited by 4E
and another at approximately and another at approximately
500Hz that is excited by 6E.
If this was a 4 cylinder 4 stroke
engine 2E would equate to the firing
frequency.
In this particular example, the
smallest circle equates to a sound
pressure level of 35dB(A) and the
largest to 65dB(A).
Dirac Delta Consultants Ltd, 2001-2005
This is a
C b ll di Campbell diagram.
15
Whats in Campbell diagram? Whats in Campbell diagram?
Missing information
Evaluation of possible
Existing information
Modal frequency Evaluation of possible
resonances in order of
importance
Modal damping
/logarithmic decrement
/stability
Modal frequency
Excitation order lines
Possible resonances
Input-output relation
/gain
Modal response
/modal vector
Whirl speed chart Whirl speed chart (1 quadrant plot)
2F
+1X
F
2B
1B
1F
16
3
4
2F
2B
Whirl speed chart Whirl speed chart (2 quadrant plot)
-1
0
1
2
w
h
i
r
l
s
p
e
e
d
Dimentberg
2B
1B
1F
1B
-4 -2 0 2 4
-4
-3
-2
speed
Lee
2B
F. M. Dimentberg F. M. Dimentberg
1950 1978
17
DyRoBeS DyRoBeS
http://www.dyrobes.com/index.htm
DyRoBeS DyRoBeS
18
Turbine Generator FEM: Turbine Generator FEM: DyRoBeS DyRoBeS
Вам также может понравиться
- Solucion Cap 4 ChapmanДокумент6 страницSolucion Cap 4 ChapmanEduardo Llanos CruzОценок пока нет
- Tesla Symp06 CorumДокумент7 страницTesla Symp06 CorumNO,NO,NO 2 status QUOОценок пока нет
- Frequencies of Multiple Systems and System DynamicsДокумент4 страницыFrequencies of Multiple Systems and System DynamicstylerdurdaneОценок пока нет
- A. - B. Derive The Expression For Pitch Factore. CДокумент8 страницA. - B. Derive The Expression For Pitch Factore. CStream MarkusОценок пока нет
- Garland Dynamic TestingДокумент27 страницGarland Dynamic TestingmarcvenzОценок пока нет
- Journal of Fluid MechanicsДокумент20 страницJournal of Fluid MechanicsShezan KanjiyaniОценок пока нет
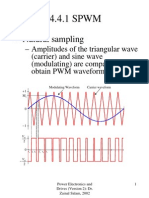
- SPWMДокумент30 страницSPWMRicky LesmanaОценок пока нет
- Eywords: Analytical Models ImpellerДокумент11 страницEywords: Analytical Models ImpellerbaubaumihaiОценок пока нет
- A Slip Factor Calculation in Centrifugal Impellers Based On Linear Cascade DataДокумент21 страницаA Slip Factor Calculation in Centrifugal Impellers Based On Linear Cascade DatajavadamniОценок пока нет
- Acoustic Radiation From Cylindrical ArraysДокумент2 страницыAcoustic Radiation From Cylindrical Arraysd00brightОценок пока нет
- Probabilistic Approach To Allow For Maximum Admissible Loss of Tensile StrengthДокумент9 страницProbabilistic Approach To Allow For Maximum Admissible Loss of Tensile Strengthalenyxcv3217Оценок пока нет
- Quest Tutorials Head Office: E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439Документ6 страницQuest Tutorials Head Office: E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439ChennaiSuperkingsОценок пока нет
- A Disk Monopole AntennaДокумент4 страницыA Disk Monopole AntennaAgra GautamaОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Performance Assessment of 6-Pulse Inverter-Fed 3 Phase and 6-Phase Induction MachinesДокумент8 страницAnalysis and Performance Assessment of 6-Pulse Inverter-Fed 3 Phase and 6-Phase Induction MachinesEmmanuel Esteban SebanstianОценок пока нет
- Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsДокумент13 страницEc2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsSumathy SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Iahr 2006 2Документ15 страницIahr 2006 2Pixing ZuoОценок пока нет
- Electronotes AN-348, July 1998Документ9 страницElectronotes AN-348, July 1998Kevin HaworthОценок пока нет
- Practical Formula Cable TensionДокумент6 страницPractical Formula Cable TensionAlma M. LaraОценок пока нет
- Assistant Eng Elect HPPSC Hpseb PaperДокумент12 страницAssistant Eng Elect HPPSC Hpseb Paperबिपन गुलेरिया100% (5)
- Lec2 VIVДокумент44 страницыLec2 VIVroulement_justeОценок пока нет
- Matrix Analysis Techniques in Cage Induction Machines: David G. DorrellДокумент7 страницMatrix Analysis Techniques in Cage Induction Machines: David G. Dorrellni60Оценок пока нет
- Free Vibration Analysis of FGM Sandwich Beam RestingДокумент39 страницFree Vibration Analysis of FGM Sandwich Beam RestingLaksh ManОценок пока нет
- 083 Martin RotorДокумент60 страниц083 Martin RotormarintraianОценок пока нет
- Vibration EngineeringДокумент37 страницVibration EngineeringAlen Benguit II0% (1)
- Carsten Klempt Et Al - Direct Observation of Vacuum Fluctuations in Spinor Bose-Einstein CondensatesДокумент33 страницыCarsten Klempt Et Al - Direct Observation of Vacuum Fluctuations in Spinor Bose-Einstein CondensatesPomac232Оценок пока нет
- School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical EngineeringДокумент13 страницSchool of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical EngineeringJeff HardyОценок пока нет
- Chandravati Group of Institutions, Bharatpur (Raj.) : Attempt Any Five Questions. Each Question Carries Equal MarksДокумент2 страницыChandravati Group of Institutions, Bharatpur (Raj.) : Attempt Any Five Questions. Each Question Carries Equal MarksbhuvneshОценок пока нет
- Phase Shift OscillatorДокумент31 страницаPhase Shift OscillatorArjob MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Campbell PDFДокумент25 страницCampbell PDFAnonymous d23gWCRQОценок пока нет
- 'GATE - 2001: M"'E: Mech IcalДокумент16 страниц'GATE - 2001: M"'E: Mech IcalNikhil BathamОценок пока нет
- Numerical Example 1.3: SolutionДокумент4 страницыNumerical Example 1.3: Solutionkeinhuat79Оценок пока нет
- HC138 SingingPropellersДокумент2 страницыHC138 SingingPropellerswendellОценок пока нет
- Shunjiro Shinohara and Konstantin Shamrai - Physics of High Pressure Helicon Plasma and Effect of Wavenumber SpectrumДокумент14 страницShunjiro Shinohara and Konstantin Shamrai - Physics of High Pressure Helicon Plasma and Effect of Wavenumber SpectrumHimaszОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineering 5Документ19 страницElectrical Engineering 5manikandaprabhuОценок пока нет
- Viscous Accretion Disks: Planet FormationДокумент50 страницViscous Accretion Disks: Planet FormationSharan SuryaОценок пока нет
- Vibration Midterm 2012Документ2 страницыVibration Midterm 2012Aravind KumarОценок пока нет
- Hmws Civil Final Key-2 - VG PDFДокумент54 страницыHmws Civil Final Key-2 - VG PDFMadhu KurmiОценок пока нет
- Effect of Compensation Factor On The Subsynchronous Resonance in Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemДокумент6 страницEffect of Compensation Factor On The Subsynchronous Resonance in Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemLong LeoОценок пока нет
- Digital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterДокумент9 страницDigital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterJennifer WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Near-Field Characteristics of Circular Piston RadiatorsДокумент8 страницNear-Field Characteristics of Circular Piston Radiatorsjperdigon9634Оценок пока нет
- Designing Electronics For High Vibration and ShockДокумент9 страницDesigning Electronics For High Vibration and ShocknicolasОценок пока нет
- Campbell Diagram: in RotordynamicsДокумент2 страницыCampbell Diagram: in RotordynamicslauracarrionОценок пока нет
- EMS Module 4-1 and 4-2Документ9 страницEMS Module 4-1 and 4-2Shiza ShakeelОценок пока нет
- Acdc - Ac Generator - Lecture Notes 7Документ53 страницыAcdc - Ac Generator - Lecture Notes 7Cllyan ReyesОценок пока нет
- International Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyДокумент11 страницInternational Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyLovely JuttОценок пока нет
- EE 340 Chap 1 Solutions Solucionario Tarea 1Документ18 страницEE 340 Chap 1 Solutions Solucionario Tarea 1Edward Abdiel MontenegroОценок пока нет
- EMT 212/4: Analogue Electronic IIДокумент41 страницаEMT 212/4: Analogue Electronic IIdev_mathanОценок пока нет
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceДокумент8 страницe = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaОценок пока нет
- EE 2257-Control Systems Lab ManualДокумент66 страницEE 2257-Control Systems Lab ManualRam KumarОценок пока нет
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksОт EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsОт EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricОценок пока нет
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryОт EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillОценок пока нет
- Characteristic Modes: Theory and Applications in Antenna EngineeringОт EverandCharacteristic Modes: Theory and Applications in Antenna EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignОт EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignОценок пока нет
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1От EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Abaqus/CAE Truss Tutorial: (Version 6.12)Документ23 страницыAbaqus/CAE Truss Tutorial: (Version 6.12)Jaime BerryОценок пока нет
- ReliabilityAnalysis PDFДокумент21 страницаReliabilityAnalysis PDFJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- Oil Debris Analysis For Condition Monitoring of An IC EngineДокумент3 страницыOil Debris Analysis For Condition Monitoring of An IC EngineJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- MIT Mathematics CoursesДокумент2 страницыMIT Mathematics CoursesJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- Certificate of MembershipДокумент2 страницыCertificate of MembershipJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- TandM Instruments Linesheet PDFДокумент2 страницыTandM Instruments Linesheet PDFJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Opencourseware 8.03Sc Fall 2012 Notes For Lecture #1: Periodic PhenomenaДокумент4 страницыMassachusetts Institute of Technology Opencourseware 8.03Sc Fall 2012 Notes For Lecture #1: Periodic PhenomenaJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- Top Six TacticsДокумент8 страницTop Six TacticsJaime BerryОценок пока нет
- Lecture5 (Amplifier Noise Etc)Документ5 страницLecture5 (Amplifier Noise Etc)Jaime BerryОценок пока нет
- 24a Fuel Injection-Motronic (1.8L)Документ14 страниц24a Fuel Injection-Motronic (1.8L)Sinisa Gale GacicОценок пока нет
- Cri:Iftzmiin: S - Ea/ SДокумент52 страницыCri:Iftzmiin: S - Ea/ SElliott KastnerОценок пока нет
- Pso Blaze 4TДокумент1 страницаPso Blaze 4TicrcgisОценок пока нет
- Pavc Series Variable Volume Piston Pump: Service Parts GuideДокумент10 страницPavc Series Variable Volume Piston Pump: Service Parts GuideRafael RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Quick Start Guide: Operating & Maintenance InstructionsДокумент20 страницQuick Start Guide: Operating & Maintenance InstructionsEnrique CaboОценок пока нет
- Sec 7Документ32 страницыSec 7Diego Castillo JaramilloОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Counterbalancing Force by Opposing Impellers Pressure 3rd Suc 3rd Dich 4th SucДокумент5 страницCalculation of Counterbalancing Force by Opposing Impellers Pressure 3rd Suc 3rd Dich 4th SucTusar KoleОценок пока нет
- EIT Masters Engineering MIA BrochureДокумент28 страницEIT Masters Engineering MIA BrochureRichard AnarfiОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/42Документ16 страницCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/42Huzaim SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Skenario VI MPU Smt. VIII DIVДокумент3 страницыSkenario VI MPU Smt. VIII DIVmonika retno gunartiОценок пока нет
- Shop Manual s225lc V 1 PDFДокумент670 страницShop Manual s225lc V 1 PDFEdgar Martinez Carmona67% (6)
- VRV HSДокумент17 страницVRV HSAnthony WoenarwanОценок пока нет
- Pre Tensioning SystemsДокумент19 страницPre Tensioning SystemsDiego H FernandezОценок пока нет
- Rolling PPT KalpakjianДокумент33 страницыRolling PPT Kalpakjianshourav2113Оценок пока нет
- TDI Injection and Glow Plug System 6-Cyl 3 0 LTR 4-Valve Common Rail Generation IIДокумент87 страницTDI Injection and Glow Plug System 6-Cyl 3 0 LTR 4-Valve Common Rail Generation IIergdegОценок пока нет
- Heavy Duty Flyer CatalogДокумент7 страницHeavy Duty Flyer CatalogJessie BechaydaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 1Документ69 страницThermodynamics 113670319Оценок пока нет
- AXC 800-9-4 (5,5KW) IE2: Item NoДокумент2 страницыAXC 800-9-4 (5,5KW) IE2: Item Nosiva ramakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Kitz PDFДокумент20 страницKitz PDFAde MustiaharjaОценок пока нет
- Thermostatic Mixing Valve Series 30 MR Installation and Maintenance InstructionsДокумент2 страницыThermostatic Mixing Valve Series 30 MR Installation and Maintenance InstructionsMartin McTaggartОценок пока нет
- Electrical SubstationДокумент19 страницElectrical SubstationMigueldelaTorreОценок пока нет
- Igit PB 2018-19Документ32 страницыIgit PB 2018-19Ipsita SahuОценок пока нет
- Evolution of MechatronicsДокумент9 страницEvolution of Mechatronicsnihal_ahmad2068Оценок пока нет
- Vetus Thruster SelectionДокумент1 страницаVetus Thruster SelectionKiky IchanafiОценок пока нет
- Physics 106 Set 2 Corrected Motion Along A Straight Line Algebra CalculusДокумент1 страницаPhysics 106 Set 2 Corrected Motion Along A Straight Line Algebra CalculusJPH EsguerraОценок пока нет
- 558 Servo Pneumatic Universal Testing Machine For Resilient ModulusДокумент6 страниц558 Servo Pneumatic Universal Testing Machine For Resilient ModulusRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- AerofoilAnalysisusingXFOIL ResearchGateДокумент16 страницAerofoilAnalysisusingXFOIL ResearchGatechigurla ajayОценок пока нет
- 6-4.11.2. Differential Pressure TestДокумент8 страниц6-4.11.2. Differential Pressure TestCharles PereiraОценок пока нет
- Power Plants Q and AДокумент39 страницPower Plants Q and AKaye Freyssinet Nermal AbangganОценок пока нет