Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
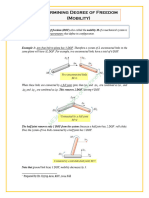
Degree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Загружено:
Vamsi Krishna0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров17 страницK&D
Оригинальное название
Lecture 2
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документK&D
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров17 страницDegree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Загружено:
Vamsi KrishnaK&D
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 17
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Degr ee of Fr eedom
No. of independent coordinates needed to define position of body
How many DOF does a body in three-space (3-D) have?
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Definitions
All of the above contain linkages which consist of:
Links
J oints
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Links
A link is a nominally rigid body that
possess at least 2 nodes.
A node is an attachment point to other
links via joints.
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Links
- The order of a link indicates the number of
joints to which the link is connected (or the
number of nodes per link).
There are binary (2 nodes), ternary (3 nodes),
and quaternary (4 nodes) links.
- Can be any shape (not just those shown)
-Link order = number of nodes
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Links
- Are assumed to be rigid bodies
- Have nodes for attachment
- Can be any shape (not just those shown)
-Link order = number of nodes
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
J oints
allow
DOF
between
links
J OINTS
A joint is a connection between
two or more links at their nodes,
which allows
motion to occur between the
links.
A pivot is a joint that allows
rotary motion,
A slider is a joint that allows
linear motion.
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
J oints
allow
DOF
between
links
J OINTS
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
J oi nt s Reduc e
Syst em DOF
2.5: Det er mi ni ng DOF or Mobi l i t y
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
J oi nt s Reduc e
Syst em DOF
2.5: Det er mi ni ng DOF or Mobi l i t y
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Kinematics Diagrams
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
Grueblers
Equation is the
most commonly
used equation
for evaluating
simple
linkages.
Kutzbachs equation
is modified
Grueblers Equation
that takes into
consideration full (1
DOF) and half (2
DOF) joints.
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Grubler & Kutzbach Equations
Lower pairs (first order joints) or full-joints (counts as J = 1 in
Grueblers Equation) have one degree of freedom (only one motion can
occur):
- Revolute (R): Also called a pin joint or a pivot, take care to ensure that the
axle member is firmly anchored in one link, and bearing clearance is present
in the other link , washers make great thrust bearings, snap rings keep it all
together
A rolling contact joint also counts as a one-degree-of-freedom revolute
joint
- Prismatic (P): Also called a slider or sliding joint, beware Saint-Venant!
- Helical (H): Also called a screw, beware of thread strength, friction and
efficiency
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
Joints: Multiple Degree-of-Freedom
Lower Pair joints with multiple degrees of freedom:
Cylindrical (C) 2 DOF
A multiple-joint (J = 2)
Spherical (S) 3 DOF
A multiple-joint not used in planar mechanisms (J = 3)
Planar (F) 3 DOF
A multiple-joint (J = 3)
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
J oints: Higher Pair Multiple Degree-of-Freedom
Higher Pair joints with multiple degrees of freedom:
Link against a plane and a force is required to keep the joint closed
(force closed)
A half-joint (J 2 = 1 in Kutzbachs equation)
The link may also be pressed against a rotating cam to create
oscillating motion
Pin-in-slot
Geometry keeps the joint closed (form closed) (Slide and pin)
A multiple-joint (J = 2 in Grueblers equation)
Second order pin joint, 3 links joined, 2-DOF
A multiple-joint (J = 2 in Grueblers equation)
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Kinematics Diagrams
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Appl yi ng Mobi l i t y Equat i ons - 1
M = 3 (L-1) 2(J 1) J 2 = 3(8-1) 2(10) 0 = 1
Uni on Col l ege
Mec hani c al Engi neer i ng
MER 312: Dynami c s and Ki nemat i c s
(of Mec hani sms) / AT
Appl yi ng Mobi l i t y Equat i ons - 2
M = 3 (L-1) 2(J 1) J 2 = 3(6-1) 2(7) 1 = 0
Вам также может понравиться
- Determining Degrees of Freedom and Mobility of MechanismsДокумент26 страницDetermining Degrees of Freedom and Mobility of Mechanismsxrx91765Оценок пока нет
- Cume213 L2Документ80 страницCume213 L2irvinvongiОценок пока нет
- M 1B Degrees of Freedom, InversionДокумент32 страницыM 1B Degrees of Freedom, InversionRimti BhowmikОценок пока нет
- Mode-Matching Analysis of Large Aperture Coupling and Its Applications To The Design of Waveguide Directional CouplersДокумент7 страницMode-Matching Analysis of Large Aperture Coupling and Its Applications To The Design of Waveguide Directional CouplersTinhVoОценок пока нет
- MACHINES AND MECHANISMSДокумент97 страницMACHINES AND MECHANISMSCorey TaylorОценок пока нет
- Me 555 Degrees of FreedomДокумент2 страницыMe 555 Degrees of FreedomkrishОценок пока нет
- Lect Degrees of FreedomДокумент111 страницLect Degrees of FreedomZeeshan Rafiq100% (1)
- Transmission Line Parameter CalculationДокумент12 страницTransmission Line Parameter Calculationksg9731100% (4)
- Lecture 2 Degrees of FreedomДокумент105 страницLecture 2 Degrees of FreedombourneОценок пока нет
- MatlabДокумент5 страницMatlabhimanshuОценок пока нет
- FEM - 1 Introduction PDFДокумент23 страницыFEM - 1 Introduction PDFwiyorejesend22u.infoОценок пока нет
- An Integrated Inverter Output Passive Sinewave Filter For Eliminating Both Common and Differential Mode PWM Motor Drive ProblemsДокумент7 страницAn Integrated Inverter Output Passive Sinewave Filter For Eliminating Both Common and Differential Mode PWM Motor Drive ProblemsdavialacerdaОценок пока нет
- Fem Short AnswersДокумент8 страницFem Short Answers21k95a0324Оценок пока нет
- Trask Tem TutorialДокумент5 страницTrask Tem TutorialbangntsuОценок пока нет
- Mechanics Guide: Statics, Dynamics, Kinematics, KineticsДокумент47 страницMechanics Guide: Statics, Dynamics, Kinematics, Kineticsanon_672293409Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ13 страницLecture 3Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniОценок пока нет
- Mechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionДокумент10 страницMechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionAHMED ghribiОценок пока нет
- Joints DOF Kinematic Pairs Mechanism Mobility: TodayДокумент26 страницJoints DOF Kinematic Pairs Mechanism Mobility: TodayMaya VargheseОценок пока нет
- 4 Mobility 1Документ10 страниц4 Mobility 1praiselovesscienceОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ28 страницChapter 1uccs1Оценок пока нет
- Three Moment EquationДокумент13 страницThree Moment EquationHan WuОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachineryДокумент65 страницKinematics of Machinerykumaravel07Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahДокумент29 страниц2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahHaroonОценок пока нет
- 4 BarsДокумент49 страниц4 BarsTalha Naeem RaoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 MechanismДокумент44 страницыLecture 9 Mechanismaku_la100% (8)
- Design of Members with Intermediate RestraintsДокумент8 страницDesign of Members with Intermediate RestraintsszalaijaОценок пока нет
- Mechatronics Modeling With Bond Graphs by Kevin Craig PDFДокумент125 страницMechatronics Modeling With Bond Graphs by Kevin Craig PDFAhmed H El ShaerОценок пока нет
- Kinematics and DynamicsДокумент48 страницKinematics and Dynamicsakhilesh120Оценок пока нет
- RF and Microwave Systems IntroductionДокумент38 страницRF and Microwave Systems IntroductionAbdul Hafiz AnuarОценок пока нет
- MunjaДокумент6 страницMunjaBat MojОценок пока нет
- Traceable Loop Antenna Calibration Methods Using A VNAДокумент25 страницTraceable Loop Antenna Calibration Methods Using A VNAAton LuanОценок пока нет
- RVS College EC Circuit Theory QuestionsДокумент11 страницRVS College EC Circuit Theory QuestionsJoshua DuffyОценок пока нет
- Yoo1994 HybridДокумент18 страницYoo1994 HybridBrendon MenezesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Structure of MechanismsДокумент35 страницChapter 1 Structure of MechanismsHuỳnh BảoОценок пока нет
- Subject: Theory of Machines and Mechanisms (ME-403)Документ79 страницSubject: Theory of Machines and Mechanisms (ME-403)amitОценок пока нет
- Theory of MachinesДокумент83 страницыTheory of MachinesVijay AnandОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms and Kinematics ConceptsДокумент68 страницMechanisms and Kinematics ConceptselangandhiОценок пока нет
- CH 2: Fundamentals of Kinematics: - Topic OutlineДокумент36 страницCH 2: Fundamentals of Kinematics: - Topic OutlineJohn FiveОценок пока нет
- Jeroen J. de Jonge, Mark A. Ratner and Simon W. de Leeuw - Local Field Controlled Switching in A One-Dimensional Dipolar ArrayДокумент8 страницJeroen J. de Jonge, Mark A. Ratner and Simon W. de Leeuw - Local Field Controlled Switching in A One-Dimensional Dipolar ArrayHumdsОценок пока нет
- Machine DesigningДокумент147 страницMachine DesigningSiddharth VatsОценок пока нет
- Progress in Studies of Transients Analysis Method of Multiconductor Transmission LinesДокумент5 страницProgress in Studies of Transients Analysis Method of Multiconductor Transmission LinesKushtrim MalaОценок пока нет
- W - 1 - Mce 3513 - Lo1Документ19 страницW - 1 - Mce 3513 - Lo1Ajay SambojuОценок пока нет
- Transmission Characteristics of SMS Fiber Optic Sensor Structures 2003 Optics CommunicationsДокумент5 страницTransmission Characteristics of SMS Fiber Optic Sensor Structures 2003 Optics CommunicationsRahul KumarОценок пока нет
- Plot displacement curves from position diagramsДокумент9 страницPlot displacement curves from position diagramsReyner LozaОценок пока нет
- Kinamatic FundamentalsДокумент49 страницKinamatic FundamentalsFaisal IrfanОценок пока нет
- 2009 ICNDENuclear Dupond SCCCiva-Athena ENДокумент8 страниц2009 ICNDENuclear Dupond SCCCiva-Athena ENHyujeii MceОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: Simple Link Compound LinkДокумент9 страницChapter One: Simple Link Compound Linkusman yimerОценок пока нет
- Basic Elements of Control SystemДокумент36 страницBasic Elements of Control Systemeugeni madaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsДокумент34 страницыIntroduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsArif ZainОценок пока нет
- Degree of FreedomДокумент26 страницDegree of Freedomumair rasheedОценок пока нет
- Extended Composite Right/Left-Handed (E-CRLH) Metamaterial and Its Application As Quadband Quarter-Wavelength Transmission LineДокумент4 страницыExtended Composite Right/Left-Handed (E-CRLH) Metamaterial and Its Application As Quadband Quarter-Wavelength Transmission LineNgoc Lan NguyenОценок пока нет
- BEAM ANALYSIS PROGRAM for SINGLE & CONTINUOUS BEAMSДокумент4 страницыBEAM ANALYSIS PROGRAM for SINGLE & CONTINUOUS BEAMSRonald Rusbell Madera ArnaoОценок пока нет
- 3x3 Multimode Interference Optical Switches Using Electro-Optic Effects As Phase ShiftersДокумент6 страниц3x3 Multimode Interference Optical Switches Using Electro-Optic Effects As Phase ShiftersTran Tuan AnhОценок пока нет
- JMT000392 PDFДокумент7 страницJMT000392 PDFTadveer Singh HoraОценок пока нет
- 2marks With AnswerДокумент17 страниц2marks With AnswerMECH HODОценок пока нет
- INCOSE CSEP Certification Program BriefingДокумент35 страницINCOSE CSEP Certification Program BriefingIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Indranassgn3 v1Документ1 страницаIndranassgn3 v1Indran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Modelling and Simulation of Solar PV Array for Battery ChargingДокумент5 страницModelling and Simulation of Solar PV Array for Battery Chargingsrinureddy2014Оценок пока нет
- Pmbok 49 Processes Edition 6Документ19 страницPmbok 49 Processes Edition 6Love Love100% (5)
- UniMAP's Administrative Structure and Academic DepartmentsДокумент109 страницUniMAP's Administrative Structure and Academic DepartmentsIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Honeywell Engineering Manual of Automatic Control For Commercial BuildingsДокумент518 страницHoneywell Engineering Manual of Automatic Control For Commercial Buildingsmubashirhasan67% (3)
- Data InputДокумент2 страницыData InputIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Project Human Resource ManagementДокумент39 страницProject Human Resource ManagementblackghostОценок пока нет
- 4493 Lec 1Документ1 страница4493 Lec 1Indran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Ukulalalalalav 12Документ1 страницаUkulalalalalav 12Indran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- PMP ch5Документ42 страницыPMP ch5blackghostОценок пока нет
- Re TestДокумент1 страницаRe TestIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Ukulalalalalav 12Документ1 страницаUkulalalalalav 12Indran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- PM Chapter 1Документ31 страницаPM Chapter 1annexious1Оценок пока нет
- LolДокумент1 страницаLolIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- IEC White Paper - Electrical Energy Storage PDFДокумент78 страницIEC White Paper - Electrical Energy Storage PDFRizqi PriatnaОценок пока нет
- Commissioning of Mechanical Systems For Command, Control, Communications, Computer, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4Isr) FacilitiesДокумент102 страницыCommissioning of Mechanical Systems For Command, Control, Communications, Computer, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4Isr) FacilitiesIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Lecture I: Performance, Properties and Selection: Emergent Materials Workshop The Ecology of Construction MaterialsДокумент24 страницыLecture I: Performance, Properties and Selection: Emergent Materials Workshop The Ecology of Construction MaterialseemanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To CANDU and CANDU 9 Manual 2011.10Документ258 страницIntroduction To CANDU and CANDU 9 Manual 2011.10chupamythОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Bearing Loading Conditions in Rotating EquipmentДокумент1 страницаEvaluation of Bearing Loading Conditions in Rotating EquipmentIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- WordДокумент3 страницыWordIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7: Design and Operation of Steam-Assisted FlaresДокумент44 страницыChapter 7: Design and Operation of Steam-Assisted FlaresBre WirabumiОценок пока нет
- Cre Sample ExamДокумент16 страницCre Sample ExamJayjean KwakОценок пока нет
- Kern Method Heat ExchangerДокумент30 страницKern Method Heat ExchangerCS100% (3)
- Nuclear Power Plant Design CharacteristicsДокумент40 страницNuclear Power Plant Design Characteristicsankit407Оценок пока нет
- WordДокумент3 страницыWordIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Gas Turbine Performance: by Rainer KurzДокумент16 страницGas Turbine Performance: by Rainer Kurzthryee100% (1)
- MinutesДокумент1 страницаMinutesIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Got YeahДокумент1 страницаGot YeahIndran KunusilinОценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy HandbookДокумент89 страницRenewable Energy HandbookGovinda RajОценок пока нет