Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Leadership Study Guide Quiz 1
Загружено:
mistasockaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Leadership Study Guide Quiz 1
Загружено:
mistasockaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Leadership Study Guide
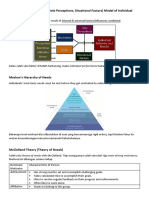
5 Leadership Practices Model the Way, Encourage the Heart, Enable Others to Act, Challenge the
Process and Inspire a Shared Vision.
Haidt Haidts work discusses the multiple aspects of the self that drives the individual. He draws upon
Platos metaphor of the charioteer controlling one horse by the whip (the horse that behaves on his
desires) and the other one with words (the horse that behaves in accordance to the mission). He also
mentions Freuds Id, Ego and Super Ego. He then uses his own metaphor of a rider on an elephant.
Though the rider works to control the elephant, whatever the elephant wants to do it will ultimately do.
This is to say that there are two main parts of you that you must be aware of, your upper level-goal
driven ideals and your impulsive and emotional side.
Heifetz Heifetz talks about authority and how authority does not equate to leadership. He starts with
a summary of authority in other primate cultures /groups including Gorillas (silverback male) and
Chimpanzees, but they do not have direct carry over to humans because of complexities in human
interaction, potential for larger groups and because of social Darwinism (someone should lead and
dominate so those that do were more fit to). However Authority should not be confused with
dominance which is an environmental control but not necessarily institutionally appointed (like an
authority is). People grow up within a society that is run based on authoritative control and they tend to
abhor authority later. However, the flipside is that those same authority roles can be used simply as a
mean to set social norms. Especially during times of stress where a new authority is likely to be needed,
charisma is a big key to acquiring such a role.
Authorities and their subordinates depend on each other out of necessity. If one does not abide to their
expectations their relationship breaks down. This is especially the case when the authority does not
have the solution and thus we perpetuate the cycle and look for another authority to replace the
current one (who we tend to blindly believe in more due to charisma effects). He also goes on to discuss
3 types of problems Type 1 being technical ones that have a specific solution, Type 2 being an adaptive
one that is definable but doesnt have a clear solution and Type 3 which isnt definable at all. It is in this
3 case that leadership is required to define the problem and find its potential solutions. You must be
able to recognize the difference btwn adaptive and technical problems because each requires a different
response.
Creative Tension This relates to visions (be them organizational or personal) in saying that there is a
current reality and an idealized image of the future. If they are un-tethered then it doesnt allow for
growth because there is no clear path to achieve it. If they are too close and muddled then it becomes
difficult to distinguish from the current and is hard to energize and stimulate. But if they are far enough
apart it can energize you (or the org) and understand the gap in going from the current to the future
that will allow for more results, thus producing more energy etc.
Leadership Challenge In chapter 4 it is all about Modeling the way and setting the example. It is
important to lead by example because it shows your seriousness, builds credibility and helps to inspire
others. This includes showing others the importance of self improvement (asking questions and looking
for feedback to improve). Modeling the way makes it more accessible for identification and for
understanding that it is possible.
In chapter 5 the topic of envisioning a future is highlighted. To do this you must 1) Imagine the
possibilities (including looking backwards to think ahead AKA Janus Effect) and 2) Find a common
purpose (this means listening to others, determining what is important and asking for others to commit)
Positive Leadership the prospect of positive leadership is to focus on improving the capabilities of
human performance. This is done through 3 means, focusing on positive deviant performance (ie stuff
way above the norm), affirmative bias (focusing on current strengths and growth as much as on
impediments and obstacles) and focusing on being virtuous. Instilling this positive leadership should be
done through creating a positive environment that promotes the growth mindset and positive thinking.
The bad is stronger than the good is a known psychological effect that it is easier to focus on negative
things because they are detrimental. Positive leaders though shine because they are able to address the
negativity but do not dwell on it and bring in positivity to brighten it. 3 things to set this climate are
compassion, gratitude and forgiveness. These things should all be modeled and encouraged.
Вам также может понравиться
- Six Styles of LeadershipДокумент3 страницыSix Styles of LeadershipJulio César Rodríguez RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Top 10 Division Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент16 страницTop 10 Division Interview Questions and AnswersyawjonhsОценок пока нет
- Leadership My MydinДокумент28 страницLeadership My Mydinrudie_slurp100% (1)
- Music of The Medieval PeriodДокумент33 страницыMusic of The Medieval PeriodEric Jordan ManuevoОценок пока нет
- 8th Habit Book Review FinalДокумент18 страниц8th Habit Book Review FinalCatherine Fabilona DumalaogОценок пока нет
- Organizational LeadershipДокумент7 страницOrganizational LeadershipRafisah OsmanОценок пока нет
- The Benevolent Dictator: Gaining Competitive Advantage Through Enlightened LeadershipОт EverandThe Benevolent Dictator: Gaining Competitive Advantage Through Enlightened LeadershipОценок пока нет
- Revolutionize Teamwork: How to Create and Lead Accountable TeamsОт EverandRevolutionize Teamwork: How to Create and Lead Accountable TeamsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Resumen 7 Habitos de La Gente Altamente EfectivaДокумент20 страницResumen 7 Habitos de La Gente Altamente Efectivapapa_tigreОценок пока нет
- Star Wars Canon Timeline MythBankДокумент25 страницStar Wars Canon Timeline MythBankJonathan Carson100% (1)
- Fullan - Leading in A Culture of Change PDFДокумент15 страницFullan - Leading in A Culture of Change PDFapi-262786958Оценок пока нет
- Mastering Psychology: Discover the Science behind Motivation, Productivity and Success (Overcome Procrastination and Laziness)От EverandMastering Psychology: Discover the Science behind Motivation, Productivity and Success (Overcome Procrastination and Laziness)Оценок пока нет
- GCTAДокумент5 страницGCTAPatty CabañaОценок пока нет
- Heifetz Leadership Without Easy AnswersДокумент18 страницHeifetz Leadership Without Easy AnswersKilusang Ilagan Para Punong-Bayan100% (2)
- 1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Документ39 страниц1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Pratik TagwaleОценок пока нет
- TS4F01-1 Unit 3 - Master DataДокумент59 страницTS4F01-1 Unit 3 - Master DataLuki1233332100% (1)
- Organizational LeadershipДокумент15 страницOrganizational LeadershipBrenda Amondi100% (1)
- Test Present Simple TenseДокумент2 страницыTest Present Simple TenseSuchadaОценок пока нет
- Principles and Practice of ManagementДокумент22 страницыPrinciples and Practice of ManagementShilpa N. Lende100% (4)
- Edm 608 - Finals - Arnel CopinaДокумент5 страницEdm 608 - Finals - Arnel CopinaArnel CopinaОценок пока нет
- Module Two:: Leadership SkillsДокумент17 страницModule Two:: Leadership SkillsKapil ChoubisaОценок пока нет
- What Is Your Definition of LeadershipДокумент6 страницWhat Is Your Definition of LeadershipTessa ShasriniОценок пока нет
- Chapter One Management SkillsДокумент15 страницChapter One Management SkillsChuma Chumzee EnwezorОценок пока нет
- Orgbev 1Документ3 страницыOrgbev 1Jonabelle Lising0% (2)
- MB0038 - Management Process and Organizational Behaviour - 4 Credits (Book ID:B1127)Документ33 страницыMB0038 - Management Process and Organizational Behaviour - 4 Credits (Book ID:B1127)Kanika GargОценок пока нет
- Creating & Managing Groups and TeamsДокумент5 страницCreating & Managing Groups and TeamsSamin Yasar Rahman 2211843030Оценок пока нет
- Leading: Presented By: GROUP 4Документ40 страницLeading: Presented By: GROUP 4Mariel AriolaОценок пока нет
- Notes UTSДокумент7 страницNotes UTSdigitize.rf9Оценок пока нет
- Contemporary Leadership Styles - 3 CesДокумент8 страницContemporary Leadership Styles - 3 CesJericson San JoseОценок пока нет
- SCDL - Pgdba - Finance - Sem 1 - Ob&OcДокумент35 страницSCDL - Pgdba - Finance - Sem 1 - Ob&Ocapi-3762419100% (1)
- Moral & Group Processes: AssignmentДокумент6 страницMoral & Group Processes: AssignmentRayhan SakinОценок пока нет
- Module 8 Motivation in Industry 1Документ13 страницModule 8 Motivation in Industry 1punzalanalvin526Оценок пока нет
- Community Power Max Weber Defined Power AsДокумент6 страницCommunity Power Max Weber Defined Power AsRamil Bagil LangkunoОценок пока нет
- Adl 5Документ14 страницAdl 5Anu GuptaОценок пока нет
- L BodyДокумент7 страницL BodyzoyahaiderzaidiОценок пока нет
- ROLL531110359 Assignment Set-1 Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1Документ16 страницROLL531110359 Assignment Set-1 Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1magbool1294Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 MotivationДокумент16 страницChapter 6 MotivationYosef TsegayeОценок пока нет
- Solved Organisational BehaviourДокумент10 страницSolved Organisational BehaviourSolve AssignmentОценок пока нет
- Leadership Traits and LeadershipДокумент11 страницLeadership Traits and LeadershipDiana ȘtefanețОценок пока нет
- Assignment B1127 MB0038Документ9 страницAssignment B1127 MB0038soniya_anthonyОценок пока нет
- Informal Authority in The WorkplaceДокумент7 страницInformal Authority in The WorkplaceADB Knowledge SolutionsОценок пока нет
- Q. What Are The Consequences of Conflict in Organisations?: AnswerДокумент15 страницQ. What Are The Consequences of Conflict in Organisations?: AnswerAbhijith IyengarОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Theories of MotivationДокумент10 страницContemporary Theories of MotivationAbdiel AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Leadership and Motivation: Unit 11Документ15 страницLeadership and Motivation: Unit 11nivas_mechОценок пока нет
- EDUC. 208 Development Administration and Educational LeadershipДокумент10 страницEDUC. 208 Development Administration and Educational LeadershipLourdes Tricia Iquiran DelorinoОценок пока нет
- Assignmenset-Master of Business Administration-Mba Semester 1 Mb0038 - Management Process and Organization Behavior Q.1 Write A Note On The Managerial Roles and Skills?Документ361 страницаAssignmenset-Master of Business Administration-Mba Semester 1 Mb0038 - Management Process and Organization Behavior Q.1 Write A Note On The Managerial Roles and Skills?منتصر الكريلОценок пока нет
- A00460017 Miguel Cruz Final+Exam RU+4003+Документ13 страницA00460017 Miguel Cruz Final+Exam RU+4003+Miguel CruzОценок пока нет
- PortfolioДокумент9 страницPortfolioapi-316813663Оценок пока нет
- Organizational Behavior Directed StudyДокумент37 страницOrganizational Behavior Directed StudyBrenda Williams PughОценок пока нет
- Power Tool: Suman Rudra Power vs. InfluenceДокумент10 страницPower Tool: Suman Rudra Power vs. InfluenceCoach CampusОценок пока нет
- Asignment Sem1Документ50 страницAsignment Sem1Ankit SahuОценок пока нет
- Learning Report: How To Manage People (Mooc Course)Документ7 страницLearning Report: How To Manage People (Mooc Course)Neeraj VermaОценок пока нет
- The Psychology of Power and Influence - JAGOДокумент2 страницыThe Psychology of Power and Influence - JAGOFrancis Perry ZafeОценок пока нет
- Organizational Theory NotesДокумент253 страницыOrganizational Theory NotesFausta BukontaitėОценок пока нет
- Smu Assignment Semester 1 Complete 2Документ134 страницыSmu Assignment Semester 1 Complete 2Subhransu PandaОценок пока нет
- Topic Group Present (Week 9) Chapter 4: Leadership and OrganizationДокумент3 страницыTopic Group Present (Week 9) Chapter 4: Leadership and OrganizationLEE LEE LAUОценок пока нет
- This Content Has Been Compiled by Tanay Sir For Personal Use Only. Visit For MoreДокумент5 страницThis Content Has Been Compiled by Tanay Sir For Personal Use Only. Visit For MoreTanay Kumar DasОценок пока нет
- Core Leadership TheoriesДокумент6 страницCore Leadership TheoriesjacobR9BОценок пока нет
- Thesis On Autocratic Leadership StyleДокумент6 страницThesis On Autocratic Leadership Stylejuliasolembellevue100% (1)
- Organizational BehaviourДокумент4 страницыOrganizational Behaviourmd. mohabbat aliОценок пока нет
- What Makes Leader - HBR - GolemanДокумент3 страницыWhat Makes Leader - HBR - GolemanMurat YücekuşОценок пока нет
- Leadership Final DraftДокумент8 страницLeadership Final Draftkartik aryОценок пока нет
- Community-Led Leadership : How Shared Leadership Is Created and What Its Requirements AreОт EverandCommunity-Led Leadership : How Shared Leadership Is Created and What Its Requirements AreОценок пока нет
- Courageous Relationship in Uncertain Times: Leadership in Uncertainty, #2От EverandCourageous Relationship in Uncertain Times: Leadership in Uncertainty, #2Оценок пока нет
- Scupin and DeCorse Chapter 20Документ29 страницScupin and DeCorse Chapter 20Sana FarshbafiОценок пока нет
- Information Security NotesДокумент15 страницInformation Security NotesSulaimanОценок пока нет
- Modules 1-8 Answer To Guides QuestionsДокумент15 страницModules 1-8 Answer To Guides QuestionsBlackblight •Оценок пока нет
- Grammar For Ielts - Worksheet: Module 1 - Lesson 9: Past Simple & Past ContinuousДокумент11 страницGrammar For Ielts - Worksheet: Module 1 - Lesson 9: Past Simple & Past ContinuousNguyễn Như QuỳnhОценок пока нет
- Edgeworth, Matt. 2018. Rivers As Material Infrastructure: A Legacy From The Past To The FutureДокумент14 страницEdgeworth, Matt. 2018. Rivers As Material Infrastructure: A Legacy From The Past To The FutureMauro FernandezОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Problem Set # 2Документ4 страницыRunning Head: Problem Set # 2aksОценок пока нет
- Beaconhouse National University Fee Structure - Per Semester Year 2017-18Документ1 страницаBeaconhouse National University Fee Structure - Per Semester Year 2017-18usman ghaniОценок пока нет
- ACR Format Assisstant and ClerkДокумент3 страницыACR Format Assisstant and ClerkJalil badnasebОценок пока нет
- Quiz On Cash and Cash EquivalentДокумент5 страницQuiz On Cash and Cash EquivalentJomel BaptistaОценок пока нет
- EA FRM HR 01 03 JobApplicationДокумент6 страницEA FRM HR 01 03 JobApplicationBatyОценок пока нет
- Simao Toko Reincarnated Black JesusДокумент25 страницSimao Toko Reincarnated Black JesusMartin konoОценок пока нет
- Opec Asb - 2010-11Документ108 страницOpec Asb - 2010-11nishant bhushanОценок пока нет
- Projections GuideДокумент28 страницProjections GuidemkmattaОценок пока нет
- BPI Lesson 1 - Surveys & Investigation PDFДокумент60 страницBPI Lesson 1 - Surveys & Investigation PDFMayОценок пока нет
- War and Peace NTДокумент2 882 страницыWar and Peace NTAMBОценок пока нет
- Mt-Requirement-01 - Feu CalendarДокумент18 страницMt-Requirement-01 - Feu CalendarGreen ArcОценок пока нет
- Fare Matrix: "No Face Mask, No Ride" "Two Passengers Only"Документ4 страницыFare Matrix: "No Face Mask, No Ride" "Two Passengers Only"Joshua G NacarioОценок пока нет
- Biology ProjectДокумент7 страницBiology ProjectChitwan GuptaОценок пока нет
- I.T. Past Papers Section IДокумент3 страницыI.T. Past Papers Section IMarcia ClarkeОценок пока нет
- Suggested Answer: Business Strategy May-June 2018Документ10 страницSuggested Answer: Business Strategy May-June 2018Towhidul IslamОценок пока нет
- CEAT PresentationДокумент41 страницаCEAT PresentationRAJNTU7aОценок пока нет
- Gwinnett Schools Calendar 2017-18Документ1 страницаGwinnett Schools Calendar 2017-18bernardepatchОценок пока нет
- Use Case NarrativeДокумент2 страницыUse Case NarrativePrajwol Sangat100% (1)