Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances
Загружено:
Taz NazОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances
Загружено:
Taz NazАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Latitude, Longitude, And Great Circle Distances
By Chip Pearson
www.cpearson.com/Excel/LatLong.aspx
!"#an"$%%&
'his wor(sheet contains )ormulas )or wor(ing with Latitude and Longitude *alues in Excel. +t also illustrates )ormulas )or
calculating the Great Circle Distance ,etween two points on Earth.
-aduis .) Earth /mean0 1iles 2&34.4$
5ilometers 62!.%
+nput )ields are in green.
Calculated )ields are in red.
Great Circle Distances
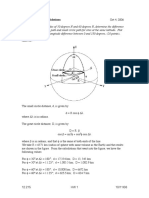
A Great Circle Distance is the shortest distance ,etween two points on a sphere. All lines o) Longitude are Great Circles.
'he only latitudinal Great Circle is the E7uator.
'he )unctions in this wor(sheet use the -AD+A89 )unction, which is part o) the Analysis 'ool Pa(, so the Analysis 'ool Pa( add"in must
,e loaded /'ools menu, Add"+ns item0.
A Great Circle Distance is calculated ,y )inding the interior spherical angle ,etween the two points and then multiplying that
angle ,y the radius o) the Earth. 'he interior spherical angle is calculated with the )ollowing e7uation /(nown as the :a*ersine ;ormula0.
<here
+nterior 9pherical Angle
Latitude " Latitude$
Latitude
Latitude$
Longitude " Longitude$
'his angle multiplied ,y the radius o) the Earth yields the Great Circle Distance ,etween to locations.
Excel=s trigonometric )unctions /9+8, C.9, etc0 wor( with -adians rather than Degrees, so the Latitude and Longitude *alues must ,e con*erted to -AD+A89.
'hese )unctions use the -AD+A89 )unction to carry out the con*ersion. 'his )unction is part o) the Analysis 'ool Pa(, so this add"in must ,e
loaded /'ools 1enu, then Add"+ns item0. 'his add"in is not re7uired with Excel $%%! and later.
>sing 'ime ;ormat Degress, 1inutes, and 9econds
'his section illustrates con*erting deg?min?sec *alues to degrees, minutes and seconds, and to decimal degrees
and calculating the distance ,etween two locations. Distance is also calculated )rom -adians.
chip@cpearson.com
)
Latitude Longitude
Location Deg?1in?9ec %A %%= %%B %%A %%= %%B +n these cells, enter the *alues as time, deg?min?ss
Location$ Deg?1in?9ec %%A %%= %%B %%A %%= %%B
Latitude
Deg 1in 9ec Deg
Location % % %%
Location$ % % % %%
Decimal Degrees Latitude Longitude -adians C/Degrees/4%0DP+
Location %% %.%!E322 .!E32$&
Location$ % %% % .!E32$&
Distance 5ilometers 1iles /statute0 5ilometers 1iles
.&! 6&.%&E .&! 6&.%&E
>sing Decimal Degrees
'his section illustrates con*erting ,etween decimal degrees and degrees, minutes, and seconds, and
calculating the distance ,etween two locations.
Con*ersion with array )ormula
Latitude Longitude Degrees
Location Dec Degrees $%.3 %.%%%% $%
Location$ Dec Degrees %.%%%% %.%%%% %
Distance 5ilometers 1iles /statute0
$$4%.!66 E!.$%$
+nitial And Ending Bearings
'he 9tart Bearing is the compass direction that one should set
sail to sail on a great circle. End Bearing is the compass direction
that you will ,e going when you arri*e at your destination.
8orth East
%.%%%% %.%%%%
8orth$ East$
% E3
9tart Bearing End Bearing
&% $!%
'his wor(sheet contains )ormulas )or wor(ing with Latitude and Longitude *alues in Excel. +t also illustrates )ormulas )or
A Great Circle Distance is the shortest distance ,etween two points on a sphere. All lines o) Longitude are Great Circles.
'he )unctions in this wor(sheet use the -AD+A89 )unction, which is part o) the Analysis 'ool Pa(, so the Analysis 'ool Pa( add"in must
A Great Circle Distance is calculated ,y )inding the interior spherical angle ,etween the two points and then multiplying that
angle ,y the radius o) the Earth. 'he interior spherical angle is calculated with the )ollowing e7uation /(nown as the :a*ersine ;ormula0.
'his angle multiplied ,y the radius o) the Earth yields the Great Circle Distance ,etween to locations.
Excel=s trigonometric )unctions /9+8, C.9, etc0 wor( with -adians rather than Degrees, so the Latitude and Longitude *alues must ,e con*erted to -AD+A89.
'hese )unctions use the -AD+A89 )unction to carry out the con*ersion. 'his )unction is part o) the Analysis 'ool Pa(, so this add"in must ,e
'his section illustrates con*erting deg?min?sec *alues to degrees, minutes and seconds, and to decimal degrees
and calculating the distance ,etween two locations. Distance is also calculated )rom -adians.
+n these cells, enter the *alues as time, deg?min?ss
Longitude
1in 9ec
% %
% %
C/Degrees/4%0DP+
'his section illustrates con*erting ,etween decimal degrees and degrees, minutes, and seconds, and
Con*ersion with array )ormula
1inutes 9econds
2% E%
% %
Вам также может понравиться
- (G) Altitude-Intercept Method 1Документ39 страниц(G) Altitude-Intercept Method 1Bernard MamoraОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics PresentationДокумент158 страницFluid Mechanics PresentationJlee LepuruОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Heat ConvectionДокумент41 страницаChapter 3 Heat ConvectionFarooq AhmadОценок пока нет
- Unidad #2 Centroids and Centre of GravityДокумент37 страницUnidad #2 Centroids and Centre of GravityAnna E A. Camaño100% (2)
- Solar Power Economics IndiaДокумент8 страницSolar Power Economics IndiaSMОценок пока нет
- Mercator ProjectionДокумент19 страницMercator ProjectionNyan Min Htet100% (1)
- 2021 02 11 Hydrogen Economy Shi2Документ29 страниц2021 02 11 Hydrogen Economy Shi2Ram KrishОценок пока нет
- Air TemperatureДокумент38 страницAir TemperatureConcepcion Jasmin Jodloman100% (1)
- Map ProjectionДокумент36 страницMap ProjectionBeherawy WondimagegnehuОценок пока нет
- Coordinate System and Map ProjectionsДокумент27 страницCoordinate System and Map ProjectionsAmbachew AlitahОценок пока нет
- Map Projections: Types of DistortionДокумент6 страницMap Projections: Types of DistortionraghurmiОценок пока нет
- Hour Angle (Time Diagram)Документ9 страницHour Angle (Time Diagram)Mico Yogore100% (1)
- Solar RadiationДокумент30 страницSolar RadiationHiren Kumar0% (1)
- GOOD DAY! Welcome To Week 2 Topics:: Your Instrucor: Meteorologist Engr - Danilo M.MadiamДокумент70 страницGOOD DAY! Welcome To Week 2 Topics:: Your Instrucor: Meteorologist Engr - Danilo M.MadiamAlexander NazarenoОценок пока нет
- 3.0 Notice To MarinersДокумент19 страниц3.0 Notice To MarinersShailendra Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Echo Sounder: Submitted By: Marino BSMTДокумент11 страницEcho Sounder: Submitted By: Marino BSMTJhonny MarinoОценок пока нет
- On GyroДокумент41 страницаOn GyroShyam Pandey100% (1)
- Mechanical Operations FiltrationДокумент17 страницMechanical Operations FiltrationTsega IsraelОценок пока нет
- Elec - Nav L11 Satellite Nav-GPSДокумент144 страницыElec - Nav L11 Satellite Nav-GPSEreN100% (1)
- GPS (Global Positioning System) & DGPS (Differential Global Positioning System)Документ103 страницыGPS (Global Positioning System) & DGPS (Differential Global Positioning System)NoCopyrightTunesОценок пока нет
- Unit I Condction PDFДокумент81 страницаUnit I Condction PDFRishabh AhujaОценок пока нет
- GyroscopeДокумент27 страницGyroscopeLisa Goodwin100% (1)
- Principles of GPS 4-13-04Документ54 страницыPrinciples of GPS 4-13-04GenОценок пока нет
- Polaris Fun 1 MainДокумент20 страницPolaris Fun 1 MainJayesh Solaskar100% (1)
- Types of CompassДокумент2 страницыTypes of Compassyeng botzОценок пока нет
- Chart Projection & Its Types: Using GoresДокумент4 страницыChart Projection & Its Types: Using GoresalihassantoorОценок пока нет
- Chart Projections PDFДокумент2 страницыChart Projections PDFSanjay WaghmodeОценок пока нет
- Function: Navigation at The Operational Level Competence: Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine PositionДокумент4 страницыFunction: Navigation at The Operational Level Competence: Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine PositionAbu Nawshad100% (3)
- CapacitanceДокумент6 страницCapacitancesenakevinОценок пока нет
- Solar Power Green Savings CalculatorДокумент1 страницаSolar Power Green Savings CalculatorJasdeep Singh BhogalОценок пока нет
- ECDIS Mandatory ECDIS Marine Equipment For Merchant Marine FURUNOДокумент11 страницECDIS Mandatory ECDIS Marine Equipment For Merchant Marine FURUNOIhwan AsrulОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Parallel and Plane Sailing: StructureДокумент13 страницUnit 2 Parallel and Plane Sailing: StructureJohn Carlo Magculang100% (1)
- 9.1 - Gas-Liquid and Gas-Liquid-Solid ReactionsДокумент100 страниц9.1 - Gas-Liquid and Gas-Liquid-Solid ReactionsHendriyana StОценок пока нет
- Unit-3 Mass Transfer Operation1Документ41 страницаUnit-3 Mass Transfer Operation1chinna erannaОценок пока нет
- Sheet: Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS)Документ2 страницыSheet: Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS)victorbarrabaja81Оценок пока нет
- Shams Ma'An Solar PV Power Plant Project (50MW) : 14 July 2014 Rev - 0Документ13 страницShams Ma'An Solar PV Power Plant Project (50MW) : 14 July 2014 Rev - 0MohamedОценок пока нет
- A Presentation On: Accounting For Merchandising OperationДокумент26 страницA Presentation On: Accounting For Merchandising OperationKayesCjОценок пока нет
- 1.cre IntroДокумент33 страницы1.cre IntroArunPThomasОценок пока нет
- Fertilizermanualunidoandifdc 150114054041 Conversion Gate02Документ626 страницFertilizermanualunidoandifdc 150114054041 Conversion Gate02usmanalihaashmiОценок пока нет
- RADAR PlottingДокумент9 страницRADAR PlottingRichard Jr. HogarОценок пока нет
- Vapour Power Cycle 1Документ132 страницыVapour Power Cycle 1Bhabatosh SenapatiОценок пока нет
- Solar Radiation Calculation: Dr. Mohamad KharsehДокумент49 страницSolar Radiation Calculation: Dr. Mohamad KharsehShwe Zaw AungОценок пока нет
- Charts and DistancesДокумент5 страницCharts and DistancesKryle Dusaban100% (2)
- Renewable Power Generation Costs PDFДокумент12 страницRenewable Power Generation Costs PDFSergiu UngureanuОценок пока нет
- Estimation of UncertaintiesДокумент7 страницEstimation of UncertaintiesNeelMishraОценок пока нет
- Weather InstumentsДокумент23 страницыWeather InstumentsTakchandra JaikeshanОценок пока нет
- Production of OlefinsДокумент39 страницProduction of OlefinsshubhamОценок пока нет
- Fire Fighting EnglishДокумент38 страницFire Fighting Englishyousry_aly8127Оценок пока нет
- Dynamics Solns Ch05Документ191 страницаDynamics Solns Ch05jbeaubrun93100% (2)
- Calculation of Day Length and NumericalДокумент10 страницCalculation of Day Length and NumericalRushi patel SavaliyaОценок пока нет
- Lecture3 Electromagnetics 1Документ46 страницLecture3 Electromagnetics 1Esteban Dalas LeonОценок пока нет
- 32 Weather InsturmentsДокумент26 страниц32 Weather InsturmentsDaniel EnglandОценок пока нет
- Conversion of Units of Temperature PDFДокумент7 страницConversion of Units of Temperature PDFrizal123Оценок пока нет
- Explain Local Nomenclature of TRSДокумент50 страницExplain Local Nomenclature of TRSLizette CruzОценок пока нет
- Map Projection Group 5Документ21 страницаMap Projection Group 5Pearl LoskiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 - Chartwork Exercises (Plotting) : Learning OutcomesДокумент5 страницLesson 2 - Chartwork Exercises (Plotting) : Learning OutcomesMico Santos100% (2)
- Phy 4215 Lecture NoteДокумент15 страницPhy 4215 Lecture NoteMohammed Abdulhamid BabiОценок пока нет
- Naval Architecture Open Day PresentationДокумент33 страницыNaval Architecture Open Day PresentationAkash KОценок пока нет
- Anu Glar Measurements SP 11Документ5 страницAnu Glar Measurements SP 11Akatew Haile Mebrahtu100% (1)
- Appendix A-ShapeДокумент10 страницAppendix A-ShapeAhmadMoaazОценок пока нет
- Longitude Points Using Haversine Formula in JavaScriptДокумент18 страницLongitude Points Using Haversine Formula in JavaScriptezolezziОценок пока нет
- Coordinate and Distance Calculate FormulaДокумент6 страницCoordinate and Distance Calculate Formulaanh00Оценок пока нет
- 061 - General Navigation - AnswersДокумент76 страниц061 - General Navigation - AnswersEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (1)
- Great Circle Distance - Distance CalculationДокумент3 страницыGreat Circle Distance - Distance CalculationTuấnMinh100% (1)
- Mercator's Projection: A Comparative Analysis of Rhumb Lines and Great CirclesДокумент36 страницMercator's Projection: A Comparative Analysis of Rhumb Lines and Great CirclesGeani MihaiОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 - Great Circle and Composite SailingДокумент56 страницUnit 6 - Great Circle and Composite SailingUtpal Kant100% (1)
- Electronics 12 01759Документ19 страницElectronics 12 01759ghita.mouhassineОценок пока нет
- Intro Metric FinalДокумент51 страницаIntro Metric FinalBrendo CostaОценок пока нет
- GT Aide (Global) 1.1: A Freeware For Field PlanningДокумент11 страницGT Aide (Global) 1.1: A Freeware For Field PlanningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Worksheet ICSE 9 GeographyДокумент3 страницыWorksheet ICSE 9 GeographyleenaapОценок пока нет
- Distance Calculation Algorithms - Geoscience AustraliaДокумент3 страницыDistance Calculation Algorithms - Geoscience Australiabluebird1969Оценок пока нет
- Spherical TrigonometrypdfДокумент18 страницSpherical TrigonometrypdfSandunMigaraОценок пока нет
- 12.215 Homework #1 SolutionsДокумент6 страниц12.215 Homework #1 SolutionsHeaven 156Оценок пока нет
- 061 - General Navigation - QuestionsДокумент47 страниц061 - General Navigation - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (3)
- Helping Hand - An Advance Way To Communicate With An Orphanage OrganizationДокумент3 страницыHelping Hand - An Advance Way To Communicate With An Orphanage OrganizationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Geopy Python ModuleДокумент35 страницGeopy Python ModuleRabina Twayana100% (1)
- L7 Distance Measurement Nautical MileДокумент9 страницL7 Distance Measurement Nautical MileMoamen AbdienОценок пока нет
- Aviation Formulary v1.46Документ38 страницAviation Formulary v1.46paulbowesОценок пока нет
- Mockvita QuesДокумент9 страницMockvita QuesAkhil Sunita JainОценок пока нет
- Gps Guided Autonomous RobotДокумент44 страницыGps Guided Autonomous RobotHemanth DОценок пока нет
- Distance Calculation Between 2 Points On EarthДокумент3 страницыDistance Calculation Between 2 Points On EarthGirish Madhavan Nambiar100% (2)
- CH 06 Great Circle SailingДокумент12 страницCH 06 Great Circle SailingNarendra Kumar100% (1)
- Ptolemy West Africa ReconstructedДокумент10 страницPtolemy West Africa ReconstructedLulDer100% (1)
- Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesДокумент4 страницыLatitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesTaz NazОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios de Programación 03Документ5 страницEjercicios de Programación 03Angel Huillca HuallpaОценок пока нет
- Calculate Distance Bearing - Movable Type ScriptsДокумент24 страницыCalculate Distance Bearing - Movable Type ScriptsNuru J. HauleОценок пока нет
- Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances by Chip PearsonДокумент4 страницыLatitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances by Chip PearsonSyed Subtain HussainОценок пока нет
- Maths SL IAДокумент22 страницыMaths SL IANavjosh83% (6)