Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care Plans
Загружено:
deincediannaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care Plans
Загружено:
deincediannaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care Plans
Definition
Bronchial asthma is a disease caused by increased responsiveness of the tracheobronchial tree to various
stimuli. The result is paroxysmal constriction of the bronchial airways. Bronchial asthma is the more
correct name for the common form of asthma.
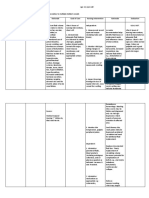
Nursing diagnosis : Ineffective airway clearance RT bronchoconstriction, increased mucus production,
and respiratory infection AEB wheezing, dyspnea, and cough
Interventions Rationale
1. Adequately hydrate the pt.
2. Teach and encourage the use of diaphragmatic
breathing and coughing exercises.
3. Instruct pt to avoid bronchial irritants such as
cigarette smoke, aerosols, extremes of
temperature, and fumes.
4. Teach early signs of infection that are to be
reported to the clinician immediately.
Increases sputum production
Change in color of sputum
Increased thickness of sputum
Increased SOB, tightness of chest, or
fatigue
Increased coughing
Fever or chills
5. If indicated, perform postural drainage with
percussion and vibration in the morning and at
night as prescribed.
6. Assist in administering nebulizer, as indicated.
7. Administer ATX as prescribed.
1. Systemic hydration keeps secretion
moist and easier to expectorate.
2. These techniques help to improve
ventilation and mobilize secretions
without causing breathlessness and
fatigue.
3. Bronchial irritants cause
bronchoconstriction and increased
mucus production, which then
interfere with airway clearance.
4. Minor respiratory infections that are
of no consequence to the person with
normal lungs can produce fatal
disturbances in the lungs of an
asthmatic person. Early recognition is
crucial.
5. Uses gravity to help raise secretions
so they can be more easily
expectorated.
6. This ensures adequate delivery of
medications to the airways.
7. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat
the infection.
Nursing diagnosis : Ineffective breathing pattern r/t presence of secretions AEB productive cough and
dyspnea
Interventions Rationale
1. Establish rapport.
2. assess pt.s condition
3. VS monitor and record
4. Auscultate breath sounds and assess airway
pattern
5. Elevate head of the bed and change
position of the pt. every 2 hours.
6. Encourage deep breathing and coughing
exercises.
7. Demonstrate diaphragmatic and pursed-lip
1. To gain pt.s trust.
2. To obtain baseline data
3. Serve to track important changes
4. to check for the presence of adventitious
breath sounds
5. To minimize difficulty in breathing
6. To maximize effort for expectoration.
7. To decrease air trapping and for efficient
breathing.
8. Encourage increase in fluid intake
9. Encourage opportunities for rest and limit
physical activities.
10. Reinforce low salt, low fat diet as ordered.
breathing.
8. To prevent fatigue.
9. To prevent situations that will aggravate
the condition
10. To mobilize secretions.
http://nurseslabs.com/bronchial-asthma-nursing-care-plans/
Name : Deince Dianna
Class : 2C
NIM : 3013041030
Вам также может понравиться
- Barry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFДокумент1 813 страницBarry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFhalamadrid77100% (2)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент2 страницыAsthma Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Breathing PatternjamieboyRN88% (65)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To SinusitisДокумент3 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance Related To SinusitisBarbara Detaro71% (7)
- Paces Guide 2012 From Online NotesДокумент228 страницPaces Guide 2012 From Online NotesThistell ThistleОценок пока нет
- Long Term:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingДокумент7 страницLong Term:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingAbie Jean BalbontinОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент10 страницNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmДокумент2 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataОценок пока нет
- Occupational Industrial and Environmental Toxicology, 2nd EditionДокумент3 страницыOccupational Industrial and Environmental Toxicology, 2nd EditionTalha AfzalОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaДокумент8 страницNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis For AsthmaДокумент6 страницNursing Diagnosis For AsthmaTINAIDA33% (3)
- NCP BaiaeДокумент7 страницNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Planapi-309251523Оценок пока нет
- NCP Copd4Документ15 страницNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeRryje Salleva100% (1)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент8 страниц1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorОценок пока нет
- NCP HemothoraxДокумент3 страницыNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Документ1 страницаChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalОценок пока нет
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент22 страницыNursing Care PlanjamОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPДокумент1 страницаImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary-Tuberculosis - NCPДокумент5 страницPulmonary-Tuberculosis - NCPMae Therese B. MAGNOОценок пока нет
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaОценок пока нет
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCPДокумент7 страницNCPMarius Clifford BilledoОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaОценок пока нет
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationДокумент6 страницImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaДокумент9 страницLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisДокумент2 страницыNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniОценок пока нет
- Angel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisДокумент2 страницыAngel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisSalvaje CaballeroОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans All PresentationsДокумент23 страницыNursing Care Plans All PresentationsKaren Joyce Costales Magtanong100% (3)
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionДокумент3 страницыNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Anaphylactic Shockwith A Primary NursingДокумент11 страницNursing Care Plan For Anaphylactic Shockwith A Primary NursingKenn Harl CieloОценок пока нет
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Документ9 страницRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatОценок пока нет
- Bronchial Asthma NCPДокумент6 страницBronchial Asthma NCPRacelle DelesОценок пока нет
- Aminogen Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case StudyДокумент5 страницPneumonia Case StudycrisolandОценок пока нет
- NCA2 PosttestsДокумент20 страницNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange Care PlanДокумент5 страницImpaired Gas Exchange Care Planjakifer50% (2)
- NCP CopdДокумент4 страницыNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Документ6 страницNURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Princess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Care Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic FeverДокумент16 страницCare Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic Feverapi-256360167Оценок пока нет
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationgreyciee은Оценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент4 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoОценок пока нет
- Asthma Care PlanДокумент3 страницыAsthma Care PlanSam ParkОценок пока нет
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaДокумент2 страницыName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNOОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisДокумент19 страницNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiДокумент9 страницChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchangelouie roderos100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- Careplan 5 MedsurgДокумент8 страницCareplan 5 Medsurgapi-509642710Оценок пока нет
- NCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingДокумент3 страницыNCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingCedie BarcaОценок пока нет
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanДокумент6 страницIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент2 страницыIneffective Breathing PatternjuanmarcostaglishОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneОценок пока нет
- NCP #2Документ4 страницыNCP #2Nutz TolentinoОценок пока нет
- AssesmentДокумент9 страницAssesmentmizrypОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент9 страницNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Copd CaseДокумент36 страницCopd Casejho_Оценок пока нет
- Orthodontic Pearls PDFДокумент2 страницыOrthodontic Pearls PDFortho123Оценок пока нет
- Right-Sided Heart Failure: College of NursingДокумент30 страницRight-Sided Heart Failure: College of NursingMatelyn OargaОценок пока нет
- (PDF) Impact of Orthodontic Treatment On Periodontal Tissues A Narrative Review of Multidisciplinary LiteratureДокумент10 страниц(PDF) Impact of Orthodontic Treatment On Periodontal Tissues A Narrative Review of Multidisciplinary LiteratureMirnaLizОценок пока нет
- HIRA ToolДокумент26 страницHIRA Toolsreekala2007Оценок пока нет
- Module 4 Mia Solihati 19.124Документ7 страницModule 4 Mia Solihati 19.124Mia SolihatiОценок пока нет
- Template MRДокумент27 страницTemplate MRdipo buyerОценок пока нет
- New ACR EULAR Guidelines For Systemic Sclerosis ClassificationДокумент8 страницNew ACR EULAR Guidelines For Systemic Sclerosis Classificationadri20121989Оценок пока нет
- Hayya Moph QLMДокумент4 страницыHayya Moph QLMrrthamadОценок пока нет
- Pre Eclampsia Blood TestДокумент2 страницыPre Eclampsia Blood TestAbhishek RampalОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Excretion (Updated)Документ23 страницыIGCSE Excretion (Updated)buhОценок пока нет
- Assisting Arterial Blood Gas: Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыAssisting Arterial Blood Gas: Lesson PlanSwapnil MahapureОценок пока нет
- Principles & Practice of First AidДокумент298 страницPrinciples & Practice of First AidJoshua100% (2)
- Care PlanДокумент2 страницыCare PlanLorina Lynne ApelacioОценок пока нет
- Non Communicable DiseasesДокумент13 страницNon Communicable Diseaseszzzsubedi100% (1)
- MRSPTU M. Sc. (Anaesthesia and Operation Theater Technology) (1-4 Sem Scheme) (1st Sem Syllabus) 2021 Batch OnwardsДокумент12 страницMRSPTU M. Sc. (Anaesthesia and Operation Theater Technology) (1-4 Sem Scheme) (1st Sem Syllabus) 2021 Batch OnwardsMamta SharmaОценок пока нет
- PBL 4 - Acyanotic Heart DiseaseДокумент27 страницPBL 4 - Acyanotic Heart DiseaseNadiah Abdul HalimОценок пока нет
- BPD Practice ToolДокумент6 страницBPD Practice ToolRogelio TorresОценок пока нет
- ImciДокумент3 страницыImciJohn Benzon0% (1)
- Avian Product Dosage Instructions Jun2017Документ4 страницыAvian Product Dosage Instructions Jun2017vetthamilОценок пока нет
- Hearing ImpairmentДокумент20 страницHearing ImpairmentAlexandra Villaflor HernandezОценок пока нет
- Sas 20Документ4 страницыSas 20Sistine Rose LabajoОценок пока нет
- 4HB0 01 Que 20180110 PDFДокумент28 страниц4HB0 01 Que 20180110 PDFCrustОценок пока нет
- Acyclovir - Iarc Monographs 76-6Документ25 страницAcyclovir - Iarc Monographs 76-6NitinPrachiJainОценок пока нет
- Muscular DystrophyДокумент64 страницыMuscular DystrophysridharОценок пока нет
- New Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis FinalДокумент26 страницNew Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis FinalSuman DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Lugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Документ1 страницаLugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Mary's CatzОценок пока нет
- The Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionДокумент40 страницThe Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionRadoslav FedeevОценок пока нет