Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
DNA and protein synthesis
Загружено:
sepankuningИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
DNA and protein synthesis
Загружено:
sepankuningАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 6: EXPRESSION OF BIOLOGICAL INFORMATION
DNA Replication
1. Defne DNA Replication
Process of producing two identical copies from one original DNA molecule.
2. Table below is the enzmes and protein in!ol!es in the DNA replication. "omplete
the tables.
#il $nzmes % protein &unctions
a DNA Helicase
'ntwist ( unwind parental DNA strands at
replication for).
b
Sinle st!an"
#in"in p!otein
#ind to the unpaired DNA strands* )eeping
them from re+pairing.
c DNA $!ase #rea)s* swi!els and re,oins the parental DNA
ahead of the replication for)* relie!ing the
strain caused b unwinding.
d P!i%ase
-nthesize RNA primer* at ./ end of leading
strand and of each 0)aza)i fragment of lagging
strand b adding RNA nucleotides to the
template.
e DNA
pol$%e!ase
"atalze the snthesize of new DNA b
adding DNA nucleotides to a pree1isting
chain that complementar to the template
strand.
f DNA liase
2oin DNA fragment 3e.g 0)aza)i fragment4 b
formation of phosphodiester bond
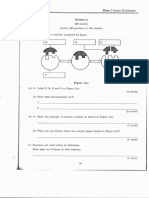
5. -teps in DNA replication 3&' Initiation( )' Elonation( *' Te!%ination 4
6. "omplete the diagram below.
.. 7h DNA replication called as semi conser!ati!e model8
Beca+se t,e "a+,te! DNA p!o"+ce" consist o- one ol" st!an" an" one
ne. st!an"
9. Describe the process of DNA Replication according to the semi conser!ati!e
theor.
Name: ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
"lass: ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
where there's a will there's a
way
,elicase
sta#ilise
/0 *0
"iscontino+s
l$
O1a2a1i
liase
DNA replication starts with the unwinding process of DNA double strands.
&irstl* the DNA ,elicase unwinds the DNA parental strands at 0rigin of replication.
$ach of the single+strand of parental DNA will acts as template strands for the new
complementar DNA strands.
The p!i%ase will then snthesize RNA primers. After the snthesis of RNA
primer* DNA pol$%e!ase III will add the free nucleotide to the growing end 35/
end4 of RNA primer to snthesise a new DNA strands that is complementar to the
bases of the template strands.
At one of the DNA template* the DNA pol$%e!ase snthesise a
complementar strands called the leading strands. The leading strands are
snthesized continuousl towards the replication for)* using onl one RNA primer.
#esides* the lagging strands elongates discontinuousl* as a series of
segments called the O1a2a1i fragments* awa from the replication for) using
se!eral RNA primers. After that* the new DNA fragment will be ,oined together b
DNA liase into a continuous DNA strands.
The RNA primer will then being replaced with DNA nucleotides b DNA
pol$%e!ase I. The new leading and lagging strands will onl elongates from ./+5/
direction and thus resulting in two identical copies of the original DNA.
PROTEIN S3NTHESIS
1. Di!ided into two steps: i4 T!ansc!iption and ii4 T!anslation
2. Transcription: A process in which genetic information in DNA is transcribed
to form %RNA
5. Translation: A process of interpreting the genetic information in the %RNA into
se<uence of a%ino aci"s'
TRANSCRIPTION
a. -teps in transcription process. 3=atch the description with the correct
stages4
-tages Description
>nitiation RNA polmerase binds to Promoter* and then
unwind DNA strands.
RNA polmerase initiates mRNA snthesis b
adding RNA nucleotides that complement to the
template base 3DNA4.
$longation Transcription terminates when RNA polmerase
reaches ?stop signal/ at termination site.
Termination RNA polmerase mo!es downstream* unwinding the
DNA and elongating RNA transcript from ./ @ 5/* b
adding nucleotides to the 5/end of growing polmer.
b. Transcription process occur in the 3n+cle+s%ctoplasm4
c. >f the DNA template base se<uence is 5/ @ AAT ""A AAA TAT A"A @ ./* what is the
base se<uence on the mRNA transcript8 /0 4 CCA GGC 5C5 A5A CGC 4 *0
d. Describe the diBerences between DNA replication and transcription.
DNA Replication T!ansc!iption
i4 >n!ol!e coping the .,ole DNA
molecule
i4 >n!ol!e coping speci6c regions of
DNA
ii4 Bot, DNA strands acts as a template ii4 0nl one DNA strand acts as
template
iii4 Produces t.o molecules of double
stranded DNA
iii4 Produces a sinle stranded mRNA
molecule
i!4 >n!ol!es DNA polmerase i!4 >n!ol!es RNA polmerase
!4 0ccurs during interphase onl !4 0ccurs throughout the life of the cell
e. >f the base se<uence on the RNA transcript is ./ @ AA" ''" AAA A'' "AA @ 5/*
what is the base se<uence on the non sense strand on the DNA8 *07CCG AAG CCT
TAA GCC 7/0
TRANSLATION
1. Translation process occur in the 3nucleus%c$toplas%4
2. 7hat are the stages in translation process8 3i. Initiation* ii. Elonation*
iii.Te!%ination4
5. Defne "0D0N : T!iplet #ases on %RNA st!an"
6. Defne ANT>"0D0N : T!iplet #ases on tRNA
.. &igure below is one of the ma,or component in!ol!e during translation process.
Cabel the bo1es.
. Diagram below is part of the process during translation. Answer the <uestions from
a+g.
&unction of D: Attac,%ent site -o!
a%ino aci"s
#ond E : H$"!oen #on"
F : Antico"on P site
A site
Pepti"e
#on"
P: G55
8: CCC
a. Cabel A* #* ".
b. >dentif the base se<uence on P and G.
c. Name strand E. what is the function of the strand E8
%RNA' Act as a te%plate -o! p!otein s$nt,esis9 s$nt,esis o- pol$pepti"e'
d. >dentif the stages in!ol!e in the process abo!e. 3 Initiation : Elonation4
e. 7hat is the -TART "0D0N and -T0P "0D0N- reads during the translation
process.
Sta!t co"on: A5G( Stop co"on: 5AA( 5AG( 5GA
f. >f the base se<uences on the DNA strand is TA" "TT AAA AAA TAT A"A "A" TAA
"TT "AA TAA AT" "AT A"A ATA. How man amino acids can be produced during the
translation process8 &&
g. 7hat is polribosome8 -tate the importance of polribosome.
Se;e!al !i#oso%e on t,e sa%e %RNA st!an" to p!o"+ce i"entical pol$pepti"e in a
la!e a%o+nt in a s,o!t ti%e'
LAC OPERON
1. &igure below is the process in!ol!e in regulation of Lac Operon. Answer the
<uestions.
a. Cabel R* -* T* '
b. 7hat will happen if T is absent8 Put the following list in order.
* RNA polmerase cannot bind to Promoter
6 0peron not acti!e.
< No transcription of structural genes
& LacI produce Repressor.
) Repressor binds to 0perator.
/ no enzme produced
c. 7hat will happen if T is present8 Put the following list in order.
< RNA polmerase binds to Promoter.
* Repressor cannot bind to 0perator.
=R: Lac >( S: Lac 3( T: Allolactose( 5: Rep!esso! p!otein?
6 0peron is acti!e 30N4.
/ transcription of genes occur* enzmes produced*
& CacI produce Repressor.
) Allolactose bind to Repressor* repressor change its shape
d. mRNA produced after Process R. $nzmes =* N* 0 produces after process G.
>dentif the processes.
Process R: T!ansc!iption * Process G: T!anslation
e. "omplete the tables below.
=: @7 alactosi"ase hdrolzes lactose to l+cose ( alactose
N: @7 alactosi"e
pe!%ease
Allow upta)e of lactose and increase pe!%ea#ilit$ of
membrane to lactose.
0: @7 alactosi"e
t!ansacet$lase
An enzme that transfers an acetl group from acet$l
CoA to @7 alactosi"es'
Вам также может понравиться
- Jawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)Документ45 страницJawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)azamsensei94% (32)
- SKEMA - SOALAN ALA FORMAT PSPM I Set 1 SK015 2020Документ7 страницSKEMA - SOALAN ALA FORMAT PSPM I Set 1 SK015 2020MOHAMAD ARMAN AZMEОценок пока нет
- Lab Report Bio Experiment 3 - Reproductive, Endocrine & Respiratory System (Group 4)Документ15 страницLab Report Bio Experiment 3 - Reproductive, Endocrine & Respiratory System (Group 4)FARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMОценок пока нет
- Collection PYQ SM025 LatestДокумент100 страницCollection PYQ SM025 LatestZizan WSОценок пока нет
- Skema Trial SPM Bio 2016 SBPДокумент22 страницыSkema Trial SPM Bio 2016 SBPSammy Easter Faurillo100% (1)
- Tutorial 8Документ5 страницTutorial 8Aina AqilahОценок пока нет
- Bio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Документ11 страницBio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Ismaliza IshakОценок пока нет
- Phy150 Laboratory Report Experiment 3Документ11 страницPhy150 Laboratory Report Experiment 3Nurul Adira FaziraОценок пока нет
- Reading TaskДокумент17 страницReading TaskLonelylifeОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsДокумент8 страницExperiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKОценок пока нет
- (P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanДокумент2 страницы(P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanKar Ru100% (3)
- Enzyme Homework ExplainedДокумент3 страницыEnzyme Homework ExplainedAZIANA YUSUFОценок пока нет
- Experiment Physics Form 5 5.3 Emf and RДокумент13 страницExperiment Physics Form 5 5.3 Emf and RCheah Soon Tike0% (1)
- SPM TRIAL EXAMINATION 2013 MARA JUNIOR SCIENCE COLLEGE CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKING SCHEMEДокумент18 страницSPM TRIAL EXAMINATION 2013 MARA JUNIOR SCIENCE COLLEGE CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKING SCHEMEJaaizah JaafarОценок пока нет
- Kertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2011Документ12 страницKertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2011Muhamad FarisОценок пока нет
- t4 Amali Peka Bab 3 IsotonikДокумент12 страницt4 Amali Peka Bab 3 IsotonikAnita HashimОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент65 страницCell Structure and FunctionIsmaliza IshakОценок пока нет
- Biology SPM 2004 Paper 3Документ6 страницBiology SPM 2004 Paper 3Sean0% (3)
- Paper 3 Physics PendulumДокумент2 страницыPaper 3 Physics Pendulumnik mohamad solehinОценок пока нет
- Bab 07 - ElektrikДокумент39 страницBab 07 - ElektrikAl Nazuris100% (2)
- 2 Heat of PrecipitationДокумент22 страницы2 Heat of PrecipitationSyawal AnizamОценок пока нет
- Test Biology Form 4 Chapter 123Документ4 страницыTest Biology Form 4 Chapter 123stanleyleeОценок пока нет
- Sk015 - Jawapan Tutor EditДокумент22 страницыSk015 - Jawapan Tutor EditAriff IskandarОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 8 f4 KSSMДокумент19 страницCHAPTER 8 f4 KSSMEtty Saad0% (1)
- Rajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulДокумент6 страницRajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulTai ZikingОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Folio Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemicals For ConsumersДокумент28 страницChemistry Folio Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemicals For ConsumersMyramel Klaris85% (72)
- SPM 2005 Past Year Paper AnswersДокумент13 страницSPM 2005 Past Year Paper AnswersStanley Lee50% (8)
- Sample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Документ10 страницSample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Adsham100% (3)
- Panduan Penulisan Laporan AmaliДокумент2 страницыPanduan Penulisan Laporan AmalirickysuОценок пока нет
- Koleksi Soalan Chapter 2, Biology Form 4.Документ6 страницKoleksi Soalan Chapter 2, Biology Form 4.SyahirahMohdAriffОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4-Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChemistry Form 4-Chapter 1Imanina Batrisyia75% (8)
- Biology Assignment SB015 Semester 2Документ3 страницыBiology Assignment SB015 Semester 2Hey YouОценок пока нет
- STA108 - Tutorial 2 (With Answers)Документ4 страницыSTA108 - Tutorial 2 (With Answers)sofiya fatiniОценок пока нет
- SPM Biology Nutrition Notes Cover Carbs, Proteins, FatsДокумент12 страницSPM Biology Nutrition Notes Cover Carbs, Proteins, FatsArthur IsaacОценок пока нет
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k2Документ24 страницыSPM 4551 2005 Biology k2pss smk selandarОценок пока нет
- PAPER 3 (Set2) PDFДокумент13 страницPAPER 3 (Set2) PDFjess2025Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Документ55 страницChapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Aisyah Zahra Zairul Adli100% (3)
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Документ21 страницаMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarОценок пока нет
- Biology SPM 2004 Paper 2Документ12 страницBiology SPM 2004 Paper 2Sean100% (3)
- Chapter 16 OH LaNunДокумент7 страницChapter 16 OH LaNunshehdilanun100% (1)
- Biology FolioДокумент27 страницBiology FolioNeru Singh100% (1)
- NaphthaleneДокумент1 страницаNaphthaleneNovah Guruloo75% (4)
- Free Fall Physics LabДокумент3 страницыFree Fall Physics LabNISHANTHINI A/P KUMAR Moe100% (1)
- SPM Probability TableДокумент1 страницаSPM Probability TableMard Zarul86% (7)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3Документ14 страницTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3NgauHWОценок пока нет
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Документ8 страницBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Amalina Kasmunee100% (1)
- Exercise For in EquilibriumДокумент7 страницExercise For in EquilibriumPauling ChiaОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6Документ50 страницBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6wenwen160499Оценок пока нет
- Latihan Bab 3Документ12 страницLatihan Bab 3Hasnah GhaniОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Tutorial AnswersДокумент18 страницElectrochemistry Tutorial AnswersHaikal AminОценок пока нет
- Question Score A Chapter 1Документ14 страницQuestion Score A Chapter 1Dee -AdilaОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS KBAT CompilatioДокумент6 страницPHYSICS KBAT CompilatiojirongОценок пока нет
- CH 7Документ17 страницCH 7c00ltimesОценок пока нет
- B M B 400Документ32 страницыB M B 400syamaladevinОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент12 страницLab ReportJISAS CLIMAXОценок пока нет
- Replication 2 PostДокумент51 страницаReplication 2 PostAndy TranОценок пока нет
- Biochem Mynote IIIДокумент3 страницыBiochem Mynote IIIAnonymous t5TDwdОценок пока нет
- Replication and DNA Repair RecitДокумент10 страницReplication and DNA Repair RecithoythereОценок пока нет
- SDFGHJKДокумент28 страницSDFGHJKstephsymОценок пока нет
- Transcription: Gene Expression and Protein SynthesisДокумент21 страницаTranscription: Gene Expression and Protein SynthesisAli Akand AsifОценок пока нет
- Datasheet qrn-1610sДокумент3 страницыDatasheet qrn-1610ssepankuningОценок пока нет
- Suruhanjaya Tenaga - Guidelines For Wiring ResidentialДокумент55 страницSuruhanjaya Tenaga - Guidelines For Wiring Residentialkingcloud7100% (24)
- Schedule of Rates For Civil Engineering Works in Sarawak 2018 PDFДокумент32 страницыSchedule of Rates For Civil Engineering Works in Sarawak 2018 PDFcollinОценок пока нет
- Ewaste FS4Документ2 страницыEwaste FS4sepankuningОценок пока нет
- GATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenДокумент31 страницаGATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenSatish BojjawarОценок пока нет
- Biology - Canizales - 1(A) Lab: Albinism QuizДокумент1 страницаBiology - Canizales - 1(A) Lab: Albinism QuizArijan SchiffererОценок пока нет
- CENTRAL DOGMAДокумент14 страницCENTRAL DOGMASecond BooksОценок пока нет
- DNA: Structure & FunctionДокумент3 страницыDNA: Structure & Function孙美美Ezra Paola TaysonОценок пока нет
- Histology Uestions From LecturioДокумент80 страницHistology Uestions From LecturioChinyere OkoraforОценок пока нет
- A New Tool For CRISPR-Cas13a-Based Cancer Gene TherapyДокумент14 страницA New Tool For CRISPR-Cas13a-Based Cancer Gene TherapySharon TribhuvanОценок пока нет
- Import Routes and Nuclear Functions of Argonaute and Other Small RNA - Silencing ProteinsДокумент12 страницImport Routes and Nuclear Functions of Argonaute and Other Small RNA - Silencing ProteinsMariaAndreaLaraSalasОценок пока нет
- Lac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsДокумент15 страницLac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsDiandra AnnisaОценок пока нет
- Molecular Pathology of Lung Diseases - D. Zander, Et Al., (Springer, 2008) WW PDFДокумент691 страницаMolecular Pathology of Lung Diseases - D. Zander, Et Al., (Springer, 2008) WW PDFMoldovan TiberiuОценок пока нет
- Post Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyДокумент4 страницыPost Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyRyan CuisonОценок пока нет
- Essential Cell BiologyДокумент95 страницEssential Cell BiologyMahmoud Abdelrahman60% (5)
- (Medical Masterclass, Module 1) Background To Medicine 1-Royal College of Physicians (2008)Документ262 страницы(Medical Masterclass, Module 1) Background To Medicine 1-Royal College of Physicians (2008)centauro1119100% (2)
- Mol Bio SyllabusДокумент2 страницыMol Bio SyllabusGandhiraj VОценок пока нет
- Paper I Unit Ii:-Gene Expression Rna Polymerase DefinitionДокумент53 страницыPaper I Unit Ii:-Gene Expression Rna Polymerase DefinitionRithwik ZОценок пока нет
- B. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewДокумент8 страницB. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewNagalla Umalatha100% (1)
- 12th Bio Botany EM Important Questions English Medium PDF DownloadДокумент7 страниц12th Bio Botany EM Important Questions English Medium PDF DownloadPrase 1815Оценок пока нет
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsДокумент49 страницBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsAshwinashishashwathy Kumar100% (1)
- BIOTECH Syllabus PDFДокумент29 страницBIOTECH Syllabus PDFsurajss8585Оценок пока нет
- B21a7e87 1Документ136 страницB21a7e87 1Bogdan ZorilaОценок пока нет
- Review COVID-19 NEJMДокумент13 страницReview COVID-19 NEJMElielОценок пока нет
- CH Test BДокумент4 страницыCH Test BTahfeel -- GamingОценок пока нет
- OpenStax Biology PDFДокумент1 519 страницOpenStax Biology PDFAlejandro Nápoles50% (2)
- Naga City Science High School Junior High School Department Fourth Quarterly Examination in BiotechnologyДокумент4 страницыNaga City Science High School Junior High School Department Fourth Quarterly Examination in BiotechnologyRodge BuereОценок пока нет
- Bio MoleculesДокумент35 страницBio MoleculeskailashОценок пока нет
- Q3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisДокумент13 страницQ3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisJazther Keishan RectoОценок пока нет
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyДокумент45 страницThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyEirla Kneriz Trinidad67% (3)
- Aqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSДокумент19 страницAqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSestee.onyeОценок пока нет
- SDM Lab ReportДокумент3 страницыSDM Lab Reportapi-462451258Оценок пока нет
- DNAresonancedraft Max Rempel 2018Документ23 страницыDNAresonancedraft Max Rempel 2018Fabrice BresilОценок пока нет
- Treatment of Leprosy-Hansens Disease in The Early 21st CenturyДокумент21 страницаTreatment of Leprosy-Hansens Disease in The Early 21st CenturyDinka RoselyОценок пока нет