Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Parasitology Table
Загружено:
humanupgrade0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров9 страницAnopheles culex aedes biting midges sandflies, Owl Midges horse flies and breeze flies common housefly face fly lesser housefly sweat fly stablefly buffalo fly hornfly tsetse flies blue bottle flies. Thorax has 4 longitudinal stripes of which the 2 lateral are broken.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAnopheles culex aedes biting midges sandflies, Owl Midges horse flies and breeze flies common housefly face fly lesser housefly sweat fly stablefly buffalo fly hornfly tsetse flies blue bottle flies. Thorax has 4 longitudinal stripes of which the 2 lateral are broken.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров9 страницParasitology Table
Загружено:
humanupgradeAnopheles culex aedes biting midges sandflies, Owl Midges horse flies and breeze flies common housefly face fly lesser housefly sweat fly stablefly buffalo fly hornfly tsetse flies blue bottle flies. Thorax has 4 longitudinal stripes of which the 2 lateral are broken.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
SCIENTIFIC NAME COMMON NAME CHARACTERISTICS
A. maculippennis Anopheles Crepuscular - active at twilight
Nocturnal - active at night time or in the dark; Plasmodium juxtanucleare and P. gallinaceum (avian
C. pipiens Culex malaria)
A. aegypti Aedes Diurnal - active at day time; Plasmodium juxtanucleare and P. gallinaceum (avian malaria)
Culicoides robersi Biting Midges thorax humped over the head; causes allergic dermatitis in horses (Queensland itch
Simulium Blackflies, Buffalo Gnats humped back appeatance
Phlebotomus Sandflies, Owl Midges long, slender, and hairy antennae; with 16 segments; often with beaded appearance;
blood sucking; causative organism of Carrion's disease (Oroya fever) and Transmit virus of 'sandfly
Phlebotomidae sandflies fever' where a transmission is possible
Psychodiidae moth flies not blood sucking
Tabanidae horse flies and breeze flies large robust flies with powerful wings and large eyes
Musca domestica common housefly human and animal houses and buildings
Musca autumnalis face fly nostrils and eyes of cattle and horse; Thelazia rhodesii (cattle eye worm)
Musca sorbens markets and houses
M. conducens animal houses
Fannia canicularis lesser housefly
Fannia scalaris little housefly cause "urogenital myiasis"; smaller than Musca; larvae with feathered protuberances; arista is bare
Muscina stabulans cause "intestinal myiasis"; larger and more robust than the housefly; common in stables
Morrelia hortorum sweat fly adults attracted to sweat and mucus
thorax has 4 longitudinal stripes of which the 2 lateral are broken; Serve as i.h. of equine stomach
Stomoxys calcitrans stablefly worm (Habronema spp)
Hematobia exigua buffalo fly thorax with 2 dark stripes
H. irritans hornfly thorax with 2 dark stripes; transmits mechanically surra, anthrax, hemorrhiagic septicemia
larger than the houseflies, narrow-bodied, yellowish to dark brown; common in Africa; serve as i.h. of
Trypanosoma brucei, T. congolense, and T, vivax which cause "Nagana" in animals and T. gambiense
Glossina morsitans tsetse flies and T. rhodesiense which cause "sleeping sickness" in man
Calliphora sp Blue Bottle Flies Accidental myiasis; Semi-obligate
Calliphora vomitoria Blue Bottle Flies Stout with metallic blue color; maggots of these 3 genera produce 'blowfly strike' in sheep
Lucilia sp. Green Bottle Flies Accidental myiasis; Semi-obligate
affects sheep in Australia; Stout flies with metallic coppery green; maggots of these 3 genera produce
Lucilia cuprina / Caesar Green Bottle Flies 'blowfly strike' in sheep
affects sheep in the US; Stout flies with metallic coppery green; maggots of these 3 genera produce
L. sericata Green Bottle Flies 'blowfly strike' in sheep
Sarcophaga sp. Fleshflies Accidental myiasis; Semi-obligate
Sarcophaga hemorrhoidalis Fleshflies light or dark grey in color; thorax with 3 longitudinal stripes; abdomen with dark checkered markings
S. fusicauda Fleshflies light or dark grey in color; thorax with 3 longitudinal stripes; abdomen with dark checkered markings
Wohlfartia magnifica deposit larva in cutaneous lesions or sores, nasal, and aural cavities, eyes and vagina
Wohlfartia vigil deposit larvae on intact skin
Musca sp Houseflies sp Accidental myiasis
Callitroga sp Screw worm flies Specific or obligate myiasis
Callitroga hominivorax primary screw worm fly bluish green color with 3 longitudinal stripes on thorax
C. macellaria secondary screw worm fly bluish green color with 3 longitudinal stripes on thorax
Chrysomyia sp. Screw worm flies Specific or obligate myiasis
Chryzomyia bezziania bluish green fly most important myiasis fly in the Philippines particularly in Negros and Panay islands
Gasterophilus sp Bot flies Specific or obligate myiasis
Hypoderma sp Warble flies Specific or obligate myiasis
Phormia sp Black Bottle Flies
Phormia regina Black Bottle Flies Black with metallic blue-green sheen; maggots of these 3 genera produce 'blowfly strike' in sheep
Occurs in tropical Africa; light brown in color; Eggs laid on sleeping places of man and other animals
Cordylobia anthropophaga tumbu fly or skin maggot fly with perspiration odor
The same size as the housefly but light yellow in color; Common during the dry season in Laguna,
Booponus intonsus foot maggot fly Quezon, Leyte, and Mindanao
Gasterophilus intestinalis horse bot flies Tongue mucosa to Cardiac portion of stomach
Gasterophilus nasalis horse bot flies Mucosa between molar teeth to Pylorum and duodenum
G. hemorrhoidalis horse bot flies Tongue mucosa to Stomach and rectum
G. pecorum horse bot flies Cheek mucosa to Stomach and rectum
G. inermis horse bot flies Cheek mucosa to Pharynx, esophagus, and stomach
sheep nasal fly / nasal bots /
Oestrus ovis sheep Nose fly/ head maggot fly causes “false gid”
Hypoderma warble flies/ ox bot flies/ heel flies
Hypoderma bovis northern cattle grub affects cattle; most important species; “Gadding”
H. lineatum common cattle grub affects cattle; Butcher Jelly
H. ageratum sheep and goats (India); Butcher Jelly
H. crossi sheep and goats; Butcher Jelly
deer (Europe); light yellow color as honey bees; mouthparts are redumentary and do not feed; Butcher
H. diana Jelly
larvae satges are obligatory parasites of the nasal sinuses and larynx of horses; - cause
Rhinoestrus purpurensis gadfly opthalmomyiasis of man
Cuterebra emasculator rodent bot fly occurs under the skin of rodents, rabbits, dogs, cats and man
Dermatobia hominis human bot fly / tropical warble fly cause “Uva” swellings in the various body parts which may suppurate and cause severe pain
Hippobosca equina horse lousefly / horse ked attacks horse and cattle world wide
H. rufipes forest flies attacks cattle and hoses in Africa
H. maculala forest flies attacks cattle and horse in tropics and subtropics; with yellow spots or bands
Pseudolynchia
maura/cauariensis pigeon lousefly or pigeon fly serve as i.h of haemoproteus columbae “pigeon malaria”
both sexes are winged but when the female found a host, the wings breaks off and resemble
Lepopthena cervi deer ked Melophagus ovinus
wingless with strong legs and stout claws; with brown hairy body; predisposes the sheep to “blowfly
Melophagus ovinus sheep ked strike”
attacks mammals and poultry; adult has a pair of ventral thoracic stink glands while the nymph has
dorsal abdominal stink gland responsible for the characteristic bedbug odor; may produce influenza-like
symptoms; transmits Pasteurella spp (plague), leprosy virus, Leishmania donovani (kala-azar),
Cimex lectularius common bedbug Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas dss), Rickettsia sp (relapsing fever), and Leptospirosis
attacks mammals and birds; adult has a pair of ventral thoracic stink glands while the nymph has dorsal
abdominal stink gland responsible for the characteristic bedbug odor; may produce influenza-like
symptoms; transmits Pasteurella spp (plague), leprosy virus, Leishmania donovani (kala-azar),
C. hemiptereus oriental bedbug Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas dss), Rickettsia sp (relapsing fever), and Leptospirosis
attacks poultry in US and Mexico; adult has a pair of ventral thoracic stink glands while the nymph has
dorsal abdominal stink gland responsible for the characteristic bedbug odor; may produce influenza-like
symptoms; transmits Pasteurella spp (plague), leprosy virus, Leishmania donovani (kala-azar),
Haematosiphon inordorus Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas dss), Rickettsia sp (relapsing fever), and Leptospirosis
Triatoma rubrofaciata Kissing Bugs serve as i.h and transmitter of Trypanosoma cruzi “chagas disease” in man
Panstrongylus sp Kissing Bugs serve as i.h and transmitter of Trypanosoma cruzi “chagas disease” in man
Rhodnius sp. Kissing Bugs serve as i.h and transmitter of Trypanosoma cruzi “chagas disease” in man
Reduvius sp. Kissing Bugs serve as i.h and transmitter of Trypanosoma cruzi “chagas disease” in man
Blatella germanica german roach / croton bug small, light brown in color with 2 longhitudinal black stripes prothorax and wings
Blatta orientalis oriental cockroach large, dark brown; wings vestigial in female and not reaching tip of abdomen in male
1.5 inched, chestnut brown; pronotal markings less defined and the last segment of cercus twice as
Periplaneta americana American roach long as it is wide
Periplaneta fuliginose smokey brown in color; pronotum solid dark brown to black
Periplaneta australasiae Australian roach resembles P. Americana but pronotum has yellow borders
Supella superlectilium tropical cockroach 2 brown cross band on tegmina
Staphilinidae rove beetles larvae and adult feeds on dung, decaying animal matter etc
Silphidae burying beetles feeds on dead animals and decomposing flesh
Dermestidae hide beetles feeds on dead animals, cured meat, cheese, cereals, dried flesh, blood etc
Tenebrionidae grain beetles common feeds
Tribolium castaneum grain beetles common feeds
T confusum grain beetles common feeds
Setophilus oryzae rice weevil
S. zeamais corn weevil
Meloidae Blister beetles
Macrodactylus subspinosus beetles are poisonous to chickes, duckling and turkeys
Lytta vesicatoria Spanish fly beetle beetles cause blister formation
Sessinia collaris skin blister/ coconut beetles
Sessinia decolor skin blister beetle
Oxicopis vittala blister beetles
Epicauta pestifera blister beetles
Zonabris nubica blister beetles
affects chickens in southeastern US; head is angular; no ctenidia; may attack other animals; may
Echidnophaga gallinacea stick tight flea cause module formation and ulcers in the comb and wattles and around the eyes of chickens
affects man primarily but may also attack pigs, rats, skunks, etc; thorax reduced; frons sharply angled
Tunga penetrans sand flea or jigger or angular; cause ulceration and subsequent bacterial infection in the feet
affects man and other mammals; genal and pronotal ctenidia absent; mesopleural rod absent; smoothly
Pulex irritans human fleas rounded frons
occurs in brown rats but readily bites man; common in brown and black rats; frons smoothly rounded;
mesopleural rod present; genal and pronotal ctenidia absent; Bubonic plague (P. pestis) and Typhus
Xenopsylla cheopis oriental rat flea (R. typhi)
oral and pronotal ctenidia present; frons pointed; 1st oral/genal ctenidia about as long as the 2nd; head
Ctenocephalis felis et felis cat flea is elongated; most common species in dogs and cats
less common than Ct. felis; occurs in both dogs and cats; 1st spine about half as long as the 2nd; head
Ctenocephalides canis dog flea is rounded
Ceratophyllus fasciatus northern rat flea present in the Philippines; occurs in rodents; oral ctenidia present
Ceratophyllus gallinae chickens
Ceratophyllus niger chickens
Leptopsylla cuniculli rabbit flea transmits myxomatosis of rabbits
Leptopsylla segins mouse flea presence of vertical genal ctenidia
Anoplura sucking lice slow-moving but have a powerful leg; thigmotactic; phototactic; with 3 nymphal stages
Hematopinus tuberculatus short-nosed louse carabao and buffaloes in Asia and Pacific
H. quadripertusus short-nosed louse cattle and buffalo in temperate and trophic regions
H. eurysternus short-nosed louse cattle (absent in the Philippines)
H. buffalo short-nosed louse buffaloes in South Africa
H. suis short-nosed louse swine; largest anopluran found in domestic animals; African swine fever virus and swine pox virus
H. asini short-nosed louse horses
Linognathus vituli long-nosed cattle louse cattle; present in the Philippines
L. africanus sucking louse of sheep and goats goats and sheep
L. stenopsis goats
L. pedalis foot louse of sheep sheep
L. ovillus body/blue/face louse of sheep sheep
L. setosus canine sucking louse dogs
Solenopotes capillatus tubercled lice reported from imported cattle
Pediculus humanus capitis human head louse
P.h. corporis human body louse
Pediculus eurygaster macaque
P. obtusus monkeys, baboons
Phthirus pubis crab louse or pubic louse occurs in the pubic region; may also occur in the armpit, eyelashes, eye brows, beard, mustache
Polyplax serrata mouse Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
Polyplax spinulosa mouse rat Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
Hoplopleura acanthopus mice Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
H. captiosa mouse Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
H. pacifica rats Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
Haemodipsus ventricosus rabbit Paratergal plates project apically from the body; Tergal and sternal plates usually distinct
Antarctophthirus microchir sea lions Body densely clothed with thick setae sometimes modified into scales
Mallophaga biting lice
Damalinia bovis/Trichodectes
scalaris cattle absent in the Phils; present in the US
D. equi horses
D. ovis sheep
D. limbata goats
Trichodectes canis dog reported in the Philippines but not common; intermediate host of Dipylidium caninum
Heterodoxus spiniger dogs most common biting louse of dogs in the Philippines; intermediate host of Dipylidium caninum
Heterodoxus longitarsus kangaroos, wallabies
Felicola subrostratus cats common in the Philippines especially stray cats
Gyropus ovalis guinea pig and other rodents present in the Philippines
Gliricola porceli guinea pig and other rodents
Trimenopon hispidum guinea pig
Menopon gallinae shaft louse biting lice of chicken; transmits ornithosis
Menacanthus stramineus body louse biting lice of chicken; is the injurious of the poultry lice; carry equine encephalitis virus
M. pallidulus small body louse biting lice of chicken
M. cornutus body louse biting lice of chicken
Lipeurus caponis slender wing louse biting lice of chicken
Oxylipeurus dentalus neck louse biting lice of chicken
Goniodes dissimilis brown louse biting lice of chicken
Goniodes gigas large body louse biting lice of chicken
Goniocotes gallinae fluff louse biting lice of chicken
Cuclotogaster heterographus head louse absent in the Philippines; biting lice of chicken
Menacanthus stramineus turkey biting lice of turkey
Menopon gallinae turkey biting lice of turkey
Chelopistes/ Goniodes
meleagridis turkey biting lice of turkey
Oxylipeurus polytrapezius turkey biting lice of turkey
Menopon giganteum pigeon biting lice of pigeon
Columbicola columbae pigeon most common biting lice of pigeon
Campanulotes bidentalus pigeon biting lice of pigeon
Colphocephalum turbinatum pigeon biting lice of pigeon
Trinoton anseris duck and geese biting lice of duck and geese
Menopon gallinae duck and geese biting lice of duck and geese
Anaticola crassicornis duck and geese biting lice of duck and geese
Anaticola anseris duck and geese biting lice of duck and geese
Holomenopon leucoxanthum duck and geese causes “wet feather” in ducks; biting lice of duck and geese
Menopon gallinae quail biting lice of quail
Goniocotes spp. quail biting lice of quail
Argasidae Soft tick
Argas persicus fowl tick found in domestic poultry in the tropics but not in the Philippines
found in pigeons; bears “buttons” and “plates”; a. Borrelia anserine (fowl spirochetosis) and
A. reflexus Aegyptienella pullorum (Avian piroplasmosis/ Aegyptienellosis)
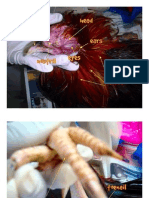
integument bears spine-like processes; animal exudes waxy or oily material from the ears that the
Otobius megnini spinose ear tick animal tends to shake the head and scratch the ears
attacks man, domestic and wild animals including birds in Africa; reservoir host for African Swine fever
virus and African relapsing fever (Borrelia recurrentis); a vector of Coxiella burnetti (O. fever), A.
Ornithodorus moubata pullorum and B. anserine
O. savignyi affects domestic animals and man in Africa and India
affects domestic animals and man in US; transmits O. fever, Anaplasmosis, Theileriosis and cause tick
O. turicata paralysis in sheep
some species may have a series of “marginal grooves” or a row of posterior notch called “festoons"; 2.
Ixodidae hard tick genital opening is in the ventral midline; anus is posterior
Principal species associated with “tick paralysis” in cattle; Three-host tick; Transmits babesiosis cattle,
anaplasmosis, louping ill, rickettsial tick borne fever of sheep and tick pyemia of lambs caused by
Ixodes ricinus castor bean tick Staphylococcus aureus
Ixodes canisuga British dog tick
Ixodes rubicundus paralysis tick of Southern Africa
Ixodes holocyclus paralysis tick of Australia
Ixodes scapularis black-legged tick attacks livestock, dogs and cats
North American cattle tick / Texas
Boophilus annulatus fever cattle tick One-host tick; Transmits Babesia bigemina (Texas fever or bovine piroplasmosis)
Boophilus decoloratus blue tick One-host tick; Transmits Babesia bigemina, Anaplasma marginate and Borrelia theileri of ruminants
Most common cattle tick in the Philippines; One-host tick; Transmits Babesia bigemina, B. bovis,
Boophilus microplus tropical cattle tick Anaplasma marginale, Coxiella burnetti and Borrelia theileri
Three-host tick; Transmits theileriosis (Theileria parva and T. mutans), Hepatozoon canis, Babesia
Rhipicephalus appendiculatus brown ear tick bigemina and Rickettsia canori (tick bite fever)
Two-host tick; Transmits Theileria mutans and T. parva (Eastcoast fever), Babesia bigemina, Babesia
R. evertsi red-legged tick equi, and Hepatozoon canis
R. bursa Transmit Babesia ovis, B. equi, Theileria ovis, Anaplasma marginale, Coxiella burnetti
Common in the Philippines; Primarily affects dogs; Three-host tick; Transmits Babesia canis, B. equi,
B. caballi, Ehrlichia canis, Hepatozoon canis, Rickettsia canis, Pasteurella tularensis and Coxiella
R. sanguineus brown dog tick / kennel tick burnetti; cause tick paralysis
Dermacentor reticulates
D. variabilis American dog tick
D. nitens tropical horse tick
D. albipictus winter tick
D. occidentalis moose tick
Three-host tick; Ornate; Causes tick paralysis; Transmits Rickettsia rickettsii (D. andersoni is the
D. andersoni/venustus rocky mountain wood tick primary vector), Anaplasma marginale, Babesia canis, Coxiella burnetti, Leptospira Pomona
Haemaphysalis leachi leachi yellow dog tick Transmits Babesia canis, Rickettsia conori, and Coxiella burnetti
H. leporis-palustris Transmit Q fever, tularemia and Rickettsia rickettsii
Hyalomma truncatum Causes “sweating sickness” in cattle
Amblyomma hebraeum bont tick
A. variegatum tropical bont tick
Characterized by the presence of white spot on the scutum of female; Three-host tick; Transmits
A. americanum lone star tick Rickettsia ruminantium (heartwater disease), Q fever. Tularemia and RMSF
Aponomma Occurs almost exclusively in reptiles (phytons, snakes, lizards, etc.)
Rhipicentor nuttali Present in large animals
Margaropus winthemi argentine tick Attacks horses and cattle; One-host tick
M. reidi Affects giraffe in Sudan; With beady-legged tick
Dermanyssus gallinae red mite of poultry transmits Borrelia anserine (spirochetosis), St. Louis encephalitis and eastern and western encephalitis
Ornithonyssus sylviarum northern fowl mite transmits fowl pox, St. Louis encephalitis, and eastern and western encephalomyelitis
O. bursa tropical fowl mite common in the Philippines; known as “hanip”
transmits Yersinia pestis (Bubonic plague), Rickettsia typhi (murine typhus) and Coxiella burnetii (Q
O. bacoti tropical rat mite fever)
Allodermanyssus sanguineus house mouse mite vector of rickettsial pox in man caused by Rickettsia acari
Echinolaelaps echidninius spiny rat mite definitive host of Hepatozoon muris in rats
Railletia auris found in the external ear canal of cattle in America and Europe
R. Rhopkinski found in the ears of antelopes
found in the nasal passages and nasal sinuses of dogs in US, Hawaii and Australia; causes reddining
Pneumonyssus caninum of the nasal mucosa, sneezing, head-shaking and rubbing of the nose
P. simicola found in the bronchi of rhesus monkey
cause irritation, inflammation and pruritus; dermatitis results from secondary bacterial infection due to
Thrombicula autumnalis scratching
vector of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi which causes Mite or Scrub typhus or River Valley fever of man in
Thrombicula akamushi Japan and New Delhi (“akamushi” means larval mite in Japan and “tsutsugamushi” means river valley)
T. sarcina leg itch occurs in sheep in Queensland; attaches on skin of pastern, coronet and heel of sheep
T. alfreddugesi affects mammals birds and reptiles, and man in the US
Neochongastia americana produce skin lesions which reduce the value of dressed fowl
Demodex canis dog worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. ovis sheep worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. caprae goat worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. equi horse worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. bovis cattle worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. phylloides pig worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. folliculorum man worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. bubalis carabao worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. cunuculi rabbits worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. musculi rats worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
D. gambiae guinea pig worm-like, cigar-shaped, elongate with stumpy legs; 2nd larval form (protonymph) which is a hexapod
Psorergates Australian itch
P. ovis sheep
P. bos cattle moves about rapidly that is why they are called “walking dandruff
Syringophilus bipectinatus quills of fowl feather
S. columbae quills of pigeon feather
quills of pheasant and peacock
S. uncinata feather
Cheyletiella parasitivorax rabbit fur mite
C. yasguri dog
C. blakei cat causes mild dermatitis
causes intense pruritus in man and domestic animals who acquire the infestation by access to infected
Pediculoides ventricosus grain itch mite grains and straw
Myobia musculi causes loss of hair and dermatitis in laboratory animals
Sarcoptes scabiei variabilis globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas; Thickened,
canis dog wrinkled skin covered with crusts
S.s. var. felis cat globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas
globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas; Generalized
S.s. var. suis pig focal erythema
globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas; Emanciation and
S.s. var. equi horse cachexia
S.s. var. ovis sheep globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas
globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas; Pruritus and bald
S.s. var. bovis cattle patches on head and neck with marked thickening of the skin
S.s. var. cuniculi rabbit globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas
S.s. var. caprae goat globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas
S.s. var. bubalis buffalo globose or round body and striae of skin are interrupted by scales and spinose areas
Notoedres cati ears, head and back of the neck of cat
N. cati var. cuniculi ear of rabbit
N. muris rats Causes ear mange
Mites burrow deep into the skin alongside the shafts of the feathers and cause an itching, inflammatory
Cnemidocoptes gallinae depluming itch mite of fowl condition
Inflammation with exudate that hardens on the surface and displaces the scales; this is accompanied
C. mutans scaly leg mite by keratinization which renders the scales “powdery” in appearance
C. pilae scaly leg mite Occurs in caged birds like parakeets and lovebirds; Beaks become deformed, scaly, and crusty
Do not burrow into the skin and are parasitic in its surface layers causing the formation of a thick,
Psoroptes scab mites heavy scab rather than a thickened skin
P. ovis sheep,most common host
P. equi horse
P. natalensis cattle, buffalo, carabao
P. cuniculi ears of rabbit, goat, sheep, horse
Chorioptes bovis leg of cattle
C. equi fetlock of horse
C. ovis pastern of sheep
C. caprae leg of goat
C. cuniculi Foot Mange / Itchy Leg ear of rabbit
Otodectes cynotis Ear mite of wild and domestic carnivores causing “otodectic mange”, parasitic otitis” or “otoacariasis”
Megninia cubitalis feather and skin of chicken and turkeys; common in the Philippines
M. velata feathers of ducks
M. columbae Pigeon
Megninia sp turkey
Pterolichus obtusus Feather and skin of chickens; Very common in the Philippines; Causes feather pulling
Tongue shape; convex dorsally and flat ventrally; Signs include sneezing, coughing, dyspnea, snoring,
Linguatula serrata tongue worm ribbing its nose with forefeet, often blood stained nasal discharge and restlessness
Adults in the nasal cavity, trachea, and lungs of snakes, crocodiles, lizards and other reptiles; Body has
Porocephalus moniliformis a beaded appearance
Ergasilus sp Found in gills of freshwater fishes
Salmincola sp Found in gills and fins of salmonids
Achteres spp Gills of freshwater fish
Anchor parasites of freshwater fishes; the head (cephalic horn) is buried in host’s tissue; Destroy
scales and cause ulcer at the site of penetration leading to attack of other infections (viral, bacterial,
Lernaea sp Anchor Worm fungal)
Argulus sp Fish Lice Cause erratic swimming “flashing” and poor growth
Cyclops intermediate host of dog pseudophyllidean tapeworm
Diaptomus intermediate host of dog pseudophyllidean tapeworm
Parasitology species
Don M. Velasquez
DVM – 3b
Вам также может понравиться
- Gangbusters - GBE2 Man's Best FriendДокумент11 страницGangbusters - GBE2 Man's Best FriendSeng Heng Pte Ltd100% (1)
- Mycology Lab Procedures Summer 2012Документ23 страницыMycology Lab Procedures Summer 2012leoОценок пока нет
- We'Re Going On A Bear HuntДокумент5 страницWe'Re Going On A Bear HuntMaria BОценок пока нет
- New Scientist-3255 2019Документ61 страницаNew Scientist-3255 2019SIXTO GUTIERREZ75% (4)
- Gram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Документ45 страницGram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Charmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- RTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningДокумент50 страницRTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningElías Tamez100% (1)
- Wildlife Fact File - Birds - 11-20Документ20 страницWildlife Fact File - Birds - 11-20ClearMind84Оценок пока нет
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasДокумент8 страниц2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnОценок пока нет
- TrematodesДокумент9 страницTrematodesLewis P. SanchezОценок пока нет
- Parasitology (Laboratory) - Trichuris TrichiuraДокумент4 страницыParasitology (Laboratory) - Trichuris TrichiuraJunno Turiano100% (1)
- Intestinal Nematodes (Unholy Trinity)Документ6 страницIntestinal Nematodes (Unholy Trinity)DAN JR. M. BAUSAОценок пока нет
- ParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFДокумент6 страницParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDJ RelojОценок пока нет
- Parasitology - Lec - FinalДокумент69 страницParasitology - Lec - FinalJannah Monaliza BambaОценок пока нет
- Summary Table - TrematodesДокумент4 страницыSummary Table - TrematodesNeil Joshua SuyatОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To CytogeneticsДокумент6 страницMolecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To Cytogeneticselijah montefalcoОценок пока нет
- NematodesДокумент10 страницNematodesNicolette Go100% (1)
- Characteristics: Description: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius Vermicularis Capillaria PhilippinensisДокумент8 страницCharacteristics: Description: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius Vermicularis Capillaria PhilippinensisAlcera JemОценок пока нет
- Malarial ParasitesДокумент27 страницMalarial ParasitesHANNAH SHALOM FERNANDEZОценок пока нет
- Morphologic Differences Cestodes (Tapeworms) Trematodes (Flukes) Nematodes (Roundworms)Документ15 страницMorphologic Differences Cestodes (Tapeworms) Trematodes (Flukes) Nematodes (Roundworms)Noelle Grace Ulep BaromanОценок пока нет
- Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisОт EverandPathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisMukesh SamantОценок пока нет
- Equus PDFДокумент8 страницEquus PDFcfeauxОценок пока нет
- Poultry Health ManagementДокумент12 страницPoultry Health Managementhumanupgrade100% (1)
- NematodesДокумент4 страницыNematodesPrincess Shaina CanapeОценок пока нет
- Parasitology SummaryДокумент10 страницParasitology SummaryLeahОценок пока нет
- MycologyДокумент55 страницMycologyAlpana Laisom100% (2)
- 3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Документ14 страниц3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Micah Daniel TapiaОценок пока нет
- s4 l3 Nematodes IIДокумент14 страницs4 l3 Nematodes II2013SecB100% (1)
- Nematodes: 2. Enterobius VermicularisДокумент2 страницыNematodes: 2. Enterobius VermicularisCia QuebecОценок пока нет
- TrematodesДокумент30 страницTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteОценок пока нет
- Medical Mycology Study Questions PDFДокумент4 страницыMedical Mycology Study Questions PDFPauline JoramОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyДокумент27 страницIntroduction To Medical Parasitologyamrokhalidyousif77Оценок пока нет
- Parasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTДокумент39 страницParasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTShane Ann RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Tissue and Blood NematodesДокумент53 страницыTissue and Blood NematodesVincent ManganaanОценок пока нет
- Ustrasana - Camel Pose - Yoga International PDFДокумент8 страницUstrasana - Camel Pose - Yoga International PDFToreØrnОценок пока нет
- Cestode SДокумент79 страницCestode SVincent Manganaan67% (3)
- Squamous Cell Onion Cell Simple Squamous - LungsДокумент4 страницыSquamous Cell Onion Cell Simple Squamous - LungshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Squamous Cell Onion Cell Simple Squamous - LungsДокумент4 страницыSquamous Cell Onion Cell Simple Squamous - LungshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Animal FlashcardsДокумент31 страницаAnimal FlashcardsMary Grace PacianoОценок пока нет
- Review Parasitology Exam (Permanent Stain Images)Документ12 страницReview Parasitology Exam (Permanent Stain Images)Tony DawaОценок пока нет
- TREMATODESДокумент31 страницаTREMATODESKen Mark ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Proceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964От EverandProceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964Augusto CorradettiОценок пока нет
- Intestinal Nematodes Maricelle ManlutacДокумент64 страницыIntestinal Nematodes Maricelle ManlutacGlanela ManalotoОценок пока нет
- ParaДокумент1 страницаParaEriq BaldovinoОценок пока нет
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesДокумент3 страницыTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizОценок пока нет
- Tables - CestodesДокумент8 страницTables - CestodesSid Loverholic50% (4)
- Nematode NotesДокумент2 страницыNematode Notesapi-247084136100% (1)
- The Intestinal NematodesДокумент9 страницThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyОценок пока нет
- Parasitology Table ProtozoaДокумент10 страницParasitology Table ProtozoaMae Rose Charlene MendozaОценок пока нет
- Fasciolopsis Buski: F Hepatica F. BuskiДокумент4 страницыFasciolopsis Buski: F Hepatica F. BuskiGela ReyesОценок пока нет
- CestodesДокумент10 страницCestodessarguss14100% (1)
- Trematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsДокумент3 страницыTrematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsGlenn PerezОценок пока нет
- ParasitologyДокумент3 страницыParasitologyKCSotelo_xxviiОценок пока нет
- Parasitology: An IntroductionДокумент8 страницParasitology: An IntroductionRuthenie RedobleОценок пока нет
- Para-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Документ20 страницPara-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Aysha AishaОценок пока нет
- Helminth 3Документ2 страницыHelminth 3Farlogy100% (6)
- Entamoeba SPPДокумент21 страницаEntamoeba SPPragnabulletinОценок пока нет
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroДокумент74 страницыFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013Оценок пока нет
- PROTOZOAN Part 2Документ1 страницаPROTOZOAN Part 2Meccar Moniem H. ElinoОценок пока нет
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYДокумент68 страницRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféОценок пока нет
- Cestode NotesДокумент26 страницCestode NotesJOSEPH NDERITUОценок пока нет
- PROTOZOAN Part 1Документ1 страницаPROTOZOAN Part 1Meccar Moniem H. Elino100% (1)
- TrematodesДокумент5 страницTrematodesdhaineyОценок пока нет
- Parasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TДокумент21 страницаParasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TJen CAОценок пока нет
- Nematodes NotesДокумент9 страницNematodes NotesAlbert AlegreОценок пока нет
- 3rd Year Medicine Parasitology LabДокумент98 страниц3rd Year Medicine Parasitology LabHassan.shehri100% (3)
- 2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesДокумент13 страниц2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesTricia LlorinОценок пока нет
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupДокумент14 страниц1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaОценок пока нет
- Parasitology ProtozoansДокумент13 страницParasitology ProtozoansMay LacdaoОценок пока нет
- Entamoeba ColiДокумент14 страницEntamoeba ColiHanisha Erica100% (1)
- Parasite Trematodes PDFДокумент2 страницыParasite Trematodes PDFGougle MuteОценок пока нет
- Saver MinutesДокумент3 страницыSaver MinuteshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 2 QuestionsДокумент9 страницAnatomy 2 QuestionshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Feline Heart WormsДокумент27 страницFeline Heart WormshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Micro TechniqueДокумент2 страницыMicro Techniquehumanupgrade100% (1)
- Veterinary Helminthology MidtermsДокумент4 страницыVeterinary Helminthology Midtermshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Estrous CycleДокумент3 страницыEstrous CyclehumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Sample No. Shell Length Shell Width Shell WeightДокумент2 страницыSample No. Shell Length Shell Width Shell WeighthumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Scientific Name Common NameДокумент18 страницScientific Name Common NamehumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Animal NutritionДокумент3 страницыAnimal NutritionhumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Scientific Name Transmission Hosts Characteristics/ Causes / Area of InfectionДокумент23 страницыScientific Name Transmission Hosts Characteristics/ Causes / Area of Infectionhumanupgrade100% (1)
- Scientific Name Transmission Hosts Characteristics/ Causes / Area of InfectionДокумент8 страницScientific Name Transmission Hosts Characteristics/ Causes / Area of Infectionhumanupgrade100% (2)
- Famous NematologistsДокумент3 страницыFamous NematologistshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- External Anatomy of Domesticated AnimalsДокумент2 страницыExternal Anatomy of Domesticated AnimalshumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Chicken External and Internal AnatomyДокумент22 страницыChicken External and Internal Anatomyhumanupgrade100% (2)
- ProtzoologyДокумент37 страницProtzoologyhumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Fish Anatomy For Fish BreedingДокумент2 страницыFish Anatomy For Fish BreedinghumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Annotated Reading LogДокумент13 страницAnnotated Reading LoggaureliОценок пока нет
- Australian Animals ScreenДокумент31 страницаAustralian Animals ScreenLTookerОценок пока нет
- Med-RM - Zoo - SP-4 - Ch-17 - Strategies For Enhancement in Food ProductionДокумент22 страницыMed-RM - Zoo - SP-4 - Ch-17 - Strategies For Enhancement in Food Productionkrish masterjeeОценок пока нет
- Ket Exam 1 ReadingДокумент10 страницKet Exam 1 ReadingFranciscaBalasSuarezОценок пока нет
- Jareds BoyДокумент31 страницаJareds BoyAnaОценок пока нет
- SITHCCC014 Prepare Meat DishesДокумент50 страницSITHCCC014 Prepare Meat Dishesrajgill1808Оценок пока нет
- Leo GoatДокумент5 страницLeo GoatIndre IndraniОценок пока нет
- Belotero Product CatalogueДокумент36 страницBelotero Product CatalogueNiculae Bogdan DimitrieОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент12 страницGrammarMuhamad Zaini MasryОценок пока нет
- Prohibited & Restricted Item For IndonesiaДокумент13 страницProhibited & Restricted Item For IndonesiaAhmad AmirudinОценок пока нет
- Brigada Pagbasa StoriesДокумент11 страницBrigada Pagbasa Storiesnica pidlaoanОценок пока нет
- Akin To PityДокумент356 страницAkin To PityPaul StewartОценок пока нет
- The Thickety by J.A. White ExcerptДокумент79 страницThe Thickety by J.A. White ExcerptHarperCollins Childrens BooksОценок пока нет
- The Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayДокумент8 страницThe Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayCleber Dos SantosОценок пока нет
- Bobcat Classification and EvolutionДокумент3 страницыBobcat Classification and EvolutionagnaОценок пока нет
- ITC HS Export Policy 2018 PDFДокумент392 страницыITC HS Export Policy 2018 PDFSachin AhujaОценок пока нет
- Aspartame and Neuordegenerative DiseasesДокумент102 страницыAspartame and Neuordegenerative Diseasesedi_wsОценок пока нет
- Radiological Features of BronchiectasisДокумент24 страницыRadiological Features of BronchiectasisOxana TurcuОценок пока нет
- Anaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationДокумент6 страницAnaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationAchmad NugrohoОценок пока нет
- B IngДокумент7 страницB Ingsumire shiny dartokОценок пока нет
- Mandala Effects by Maryanne JohnsonДокумент38 страницMandala Effects by Maryanne JohnsonKaren MersonОценок пока нет
- Bird Imagery in Portrait of The Artist As A Young ManДокумент2 страницыBird Imagery in Portrait of The Artist As A Young ManProfadeengleza8Оценок пока нет