Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Electronics Device PDF
Загружено:
Fariz Azhar AbdillahИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electronics Device PDF
Загружено:
Fariz Azhar AbdillahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Instructor : Dr.Eng.
Arief Udhiarto
Source : U.C. Berkeley
ELECTRONICS DEVICE
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
2
Schedule
Lectures: S.201 Th. 08:00-09.50 AM
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
3
Relation to Other Courses
Prerequisite:
Simple pn-junction, BJT and MOSFET theory;
BJT and MOSFET circuit applications.
Familiarity with the Bohr atomic model
Relation to other courses:
Electronics Circuit (ENEE600012)
Processing Technology and Laboratory
(ENEE600302)
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
4
Reading Material
Primary Text :
Semiconductor Device Fundamentals : R. F. Pierret
(Addison Wesley, 1996)
References Text:
Solid State Electronic Devices 4
th
Edition: B. G.
Stretman, S. Banerjee (Prentice Hall, 2000)
Device Electronics for Integrated Circuits 3
rd
Edition: R. Muller, T. Kamins (Wiley & Sons, 2003)
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
5
SAP
1. Course : Electronics Device
2. Course Code : ENEE610007 SKS: 2 Semester: 3
3. Instructor : Dr.Eng. Arief Udhiarto (AU)
4. Class System : Single
5. Courses Objective : the completion of this course, students are
expected to be able to understand principle of
electronic devices.
6. Grading System (%) : Homework (10), MT (35),
Seminar (15), FT (40)
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
6
Miscellany
Academic (dis)honesty
Departmental policy will be strictly followed
Collaboration (not cheating!) is encouraged
Classroom etiquette:
Arrive in class on time!
Turn off cell phones, MP3/MP4 players, etc.
No distracting conversations
Ask question as much as possible
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
7
Pre Test
1. What do you know about the following
term:
1. electron
2. hole
3. donor
4. acceptor
5. majority carrier
2. What are the differences between
conductor and semiconductor?
10 Minutes only
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
8
Course Outline
Semiconductor Fundamentals;
Metal-Semiconductor Contact
PN-Junction Diode
Bipolar Junction Transistor
MOSFET
IC Processing
(other subject)
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
9
Overview of IC Devices and
Semiconductor Fundamentals
Reading Assignment : Pierret Chap 1, Chap 2
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
10
An IC consists of interconnected electronic
components in a single piece ( chip ) of
semiconductor material
In 1958, Jack S. Kilby (Texas
Instruments) showed that it was
possible to fabricate a simple IC in
germanium.
In 1959, Robert Noyce (Fairchild
Semiconductor) demonstrated an IC
made in silicon using SiO2 as the
insulator and Al for the metallic
interconnects.
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
11
Evolution of Bipolar Junction Transistors
Point Contact BJT
1947
SiGe BJT
2000
Si Nanowire BJT
2003
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
12
From a Few, to Billions
By connecting a large number of components, each
performing simple operations, an IC that performs very
complex tasks can be built.
The degree of integration has increased at an
exponential pace over the past ~40 years.
The number of devices on a chip doubles every ~18 months, for
the same price.
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
13
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
14
IC Technology Advancement
Improvements in IC performance and cost have
been enabled by the steady miniaturization of
the transistor
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
15
Advantages of Technology Scaling
More dies per wafer, lower cost
Higher-speed devices and circuits
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
16
Today and Tomorrow
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
17
The Nanometer Size Scale
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
18
State-of-the-art Transistor Size
1m = 10-6m = 10-4 cm = 1000 nm
1 nm =10
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
19
CZ Crystal Growth
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
20
Si Bulk Wafer Specifications Bulk Wafer
Specifications
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
21
Purity of Device Grade Si
99.999999999 % (so-called eleven nines )
Maximum impurity allowed is equivalent to 1
mg of sugar dissolved in an Olympic-size
swimming pool.
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
22
Flatness deviation and particle sizes
Dimensions are equivalent to 1/1000 of a baseball
placed inside a sports dome.
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
23
Crystallographic Planes
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
24
Miller Indices
Crystallographic Notation
h: inverse x-intercept
k: inverse y-intercept
l: inverse z-intercept
(Intercept values are in multiples of the lattice constant;
h, k and l are reduced to 3 integers having the same
ratio.)
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
25
Crystallographic Planes and Si
Wafers
Silicon wafers are usually cut along the (100)
plane with a flat or notch to orient the wafer
during IC fabrication
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
26
Bulk Si Wafer to IC Chip
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
27
Bohr Model
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
28
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
29
Silicon Atom
1s, 2s, 2p orbitals filled by 10
electrons
3s, 3p orbitals filled by 4
electrons
4 nearest neighbors
unit cell length = 5.43
5 10
22
atoms/cm3
diamond cubic structure
The Si Atom The Si Crystal
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
30
Conduction Band and Valence Band
Electron
Potential
Energy
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
31
The Simplified Energy Band
Diagram
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
32
Semiconductors, Insulators, and
Conductors
Totally filled band and totally empty bands do not allow
current flow. (just as there is no motion of liquid in a
totally filled or totally empty bottle
Metal conduction band is half-filled
Semiconductors have lower Egs than insulators and
can be doped
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
33
Compound Semiconductors
Zincblende Structure
III-V compound semiconductors : GaAs, GaP, GaN, etc.
important for optoelectronics and high speed ICs
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
34
Density of States
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
35
Density of States at Conduction Band:
The Greek Theater Analogy
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
36
Concept of a hole
An unoccupied electronic state in
the valence band is called a hole
Treat as positively charge mobile particle in the semiconductors
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
37
Bond Model of Electrons and Holes
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
38
Electrons and Holes
Вам также может понравиться
- Automotive Microelectronics 2001Документ93 страницыAutomotive Microelectronics 2001sayapopai100% (16)
- Contact Details of Indian CompaniesДокумент52 страницыContact Details of Indian CompaniesMadhavi Kurra0% (1)
- Basic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesОт EverandBasic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Semiconductor Circuits: Theory, Design and ExperimentОт EverandSemiconductor Circuits: Theory, Design and ExperimentРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Advances in High Voltage EngineeringДокумент669 страницAdvances in High Voltage EngineeringShashidhar Kasthala91% (11)
- Week7Advanced Materials Electronic MaterialsДокумент16 страницWeek7Advanced Materials Electronic Materialsmarlon corpuzОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6-Introduction To NanoelectronicsДокумент83 страницыChapter 6-Introduction To NanoelectronicsshobiiiscОценок пока нет
- VVVF 4+manual (English)Документ16 страницVVVF 4+manual (English)Felix Romero67% (3)
- Semiconductor Device: Lecturers: DR - Eng. Arief Udhiarto, S.T.,M.T Source: U.C. Berkeley, Trinity College Dublin, EtcДокумент18 страницSemiconductor Device: Lecturers: DR - Eng. Arief Udhiarto, S.T.,M.T Source: U.C. Berkeley, Trinity College Dublin, EtcMess YeahОценок пока нет
- ECEG-4281-MDC-Lec 02 Semiconductor Materials PropertyДокумент33 страницыECEG-4281-MDC-Lec 02 Semiconductor Materials PropertyerenaОценок пока нет
- Electronic Science 1Документ41 страницаElectronic Science 1Vinit KhaiwalОценок пока нет
- Unit 1diode FinalДокумент139 страницUnit 1diode FinalKISHAN SHUKLAОценок пока нет
- ED - Mid Lecture-1 - 2Документ30 страницED - Mid Lecture-1 - 2Pritam ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- PG - M.Sc. - Physics - 345 14 - Lab - Advance Electronic Physics - 4758Документ80 страницPG - M.Sc. - Physics - 345 14 - Lab - Advance Electronic Physics - 4758HARSH RAJPAL 511Оценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Doping Techniques Surface EngineeringДокумент21 страницаSemiconductor Doping Techniques Surface EngineeringRatandeep PandeyОценок пока нет
- Lte TechnologyДокумент22 страницыLte TechnologySneha BadanikaiОценок пока нет
- Department of Electrical EngineeringДокумент20 страницDepartment of Electrical EngineeringgadaОценок пока нет
- Eee132 Sii 2012 2013 Obe 20130207Документ2 страницыEee132 Sii 2012 2013 Obe 20130207abuakifОценок пока нет
- ED - Mid Lecture-1Документ30 страницED - Mid Lecture-1IMdad HaqueОценок пока нет
- Types of Semiconductor, Its Uses and ApplicationДокумент3 страницыTypes of Semiconductor, Its Uses and ApplicationIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- CH 1Документ60 страницCH 1avishek aviОценок пока нет
- EE3013 Slides WH Wk1Документ19 страницEE3013 Slides WH Wk1Sean TanОценок пока нет
- ED - Mid Lecture-1Документ30 страницED - Mid Lecture-1ahmedtanvir11387Оценок пока нет
- Characterization of Colloidal Particles Using Electrical Impe 2015 ProcediaДокумент7 страницCharacterization of Colloidal Particles Using Electrical Impe 2015 ProcediaTân HoàngОценок пока нет
- LICДокумент152 страницыLICdean.academicОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Solution ManualДокумент39 страницElectromagnetic Solution ManualMohammad AsimОценок пока нет
- Lecture16 19 MOSFETsДокумент30 страницLecture16 19 MOSFETsAnandRajОценок пока нет
- Assignment ECEG-4261 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits (MDC)Документ7 страницAssignment ECEG-4261 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits (MDC)erenaОценок пока нет
- AAIT Microelectronics Lecture on Devices and Circuits TrendsДокумент38 страницAAIT Microelectronics Lecture on Devices and Circuits TrendserenaОценок пока нет
- Microelectronics Part1Документ39 страницMicroelectronics Part1Abraham JemberuОценок пока нет
- Physical ElectronicsДокумент15 страницPhysical ElectronicsBryar HusenОценок пока нет
- Ece ModuleДокумент303 страницыEce ModuleDominic VeleñaОценок пока нет
- Et PBLДокумент17 страницEt PBLSoumen PathakОценок пока нет
- Physics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniДокумент17 страницPhysics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniKrunalKapadiya1Оценок пока нет
- Semiconductor-EDC Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFДокумент16 страницSemiconductor-EDC Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFSameer Mansuri100% (1)
- A Cell Equalization Technique.Документ16 страницA Cell Equalization Technique.Em OnОценок пока нет
- Dr. Nasim Zafar's Electronics 1 Course OutlineДокумент43 страницыDr. Nasim Zafar's Electronics 1 Course OutlineAhmerz Chillz WinterzОценок пока нет
- 22PH102 - Unit - 3 - Semiconducting MaterialsДокумент77 страниц22PH102 - Unit - 3 - Semiconducting MaterialsvkabdmwycОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Full For Service Design With Lecture PlanДокумент27 страницLab Manual Full For Service Design With Lecture PlanNazmus SakibОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Diodes: Dr. Md. Rifat HazariДокумент54 страницыSemiconductor Diodes: Dr. Md. Rifat HazariShahriar MahirОценок пока нет
- Title and PrefaceДокумент4 страницыTitle and PrefaceZeyad AymanОценок пока нет
- Molecular Electronics AbstractДокумент26 страницMolecular Electronics AbstractMurali Krishna Chaitanya RajuОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Документ49 страницBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalОценок пока нет
- Fund. Of. Electronics-ch01-Course OutlineДокумент30 страницFund. Of. Electronics-ch01-Course OutlineHaneen AlSuradiОценок пока нет
- Tesla coil project report on wireless power transferДокумент16 страницTesla coil project report on wireless power transferSumit JhaОценок пока нет
- Electronics1 06 Feb 2012Документ13 страницElectronics1 06 Feb 2012samiОценок пока нет
- PHYS 308 SyllabusДокумент2 страницыPHYS 308 Syllabusهبوب الريحОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1566119918304683 MainДокумент17 страниц1 s2.0 S1566119918304683 Mainkamru5555l.malОценок пока нет
- JEC Home Page List of Assigned PapersДокумент1 страницаJEC Home Page List of Assigned PaperspatelsspОценок пока нет
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Electronic Engineering Department Course Outline Ee-380 Integrated Electronic (3+1)Документ2 страницыSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Electronic Engineering Department Course Outline Ee-380 Integrated Electronic (3+1)wasifazimОценок пока нет
- SSM College of Engineering and Technology: MoletronicsДокумент24 страницыSSM College of Engineering and Technology: MoletronicsQaifat Siddique100% (1)
- IOT Based Temperature and Mask Scan Entry for Covid Prevention Seminar ReportДокумент13 страницIOT Based Temperature and Mask Scan Entry for Covid Prevention Seminar ReportPavanОценок пока нет
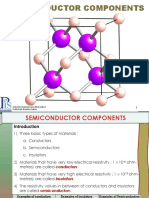
- Semiconductor ComponentsДокумент44 страницыSemiconductor ComponentsKhairul NaimОценок пока нет
- Syllabus EceДокумент85 страницSyllabus EceHemanthОценок пока нет
- EE2 Semiconductor Devices: Switching of Bipolar DevicesДокумент63 страницыEE2 Semiconductor Devices: Switching of Bipolar DevicesAnita GloriaОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices 3: Course InformationДокумент4 страницыElectronic Devices 3: Course InformationmjhtjuyОценок пока нет
- EE-112 Solid State Electronics PDFДокумент3 страницыEE-112 Solid State Electronics PDFMohammed Ahmad Osama0% (1)
- Fundamental of Electronics: Dr. Andi AdriansyahДокумент24 страницыFundamental of Electronics: Dr. Andi AdriansyahhidyatamaОценок пока нет
- The Importance of Semiconductors in ElectronicsДокумент17 страницThe Importance of Semiconductors in ElectronicsTerrigbade TaiwoОценок пока нет
- BEL-Introduction To MaterialsДокумент32 страницыBEL-Introduction To MaterialsUddipta MahatoОценок пока нет
- Vlsi LabДокумент17 страницVlsi LabbitseceОценок пока нет
- TeaM4 ProjectДокумент40 страницTeaM4 Projectsai venkatОценок пока нет
- Seminar Report on Transparent ElectronicsДокумент28 страницSeminar Report on Transparent ElectronicsBhardwajsahalОценок пока нет
- Ijrsp 19 (5&6) 306-308Документ3 страницыIjrsp 19 (5&6) 306-308Harshal VaidyaОценок пока нет
- MPC5748GRMДокумент4 039 страницMPC5748GRMTaoufik BelkebirОценок пока нет
- DS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat GuideДокумент16 страницDS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat GuideAnassFouadОценок пока нет
- Fire Alarm DetectorДокумент4 страницыFire Alarm DetectorNEERAJ0% (1)
- A New Multilevel Inverter Topology With Reduce Switch CountДокумент11 страницA New Multilevel Inverter Topology With Reduce Switch CountRodovarОценок пока нет
- SMART MATERIALS MERITSДокумент6 страницSMART MATERIALS MERITSRahul Darshan Srt100% (2)
- Harman Kardon Avr8000Документ242 страницыHarman Kardon Avr8000videosonОценок пока нет
- LM350 Adjustable Voltage RegulatorДокумент33 страницыLM350 Adjustable Voltage RegulatorferdinandОценок пока нет
- Manual Pce Ut603.pdfsfДокумент14 страницManual Pce Ut603.pdfsfAnees Ahmed KzОценок пока нет
- Half Wave Rectifier With Mathematical AnalysisДокумент13 страницHalf Wave Rectifier With Mathematical AnalysisKJMWebsite.xyz100% (9)
- Grundfosliterature 6375Документ109 страницGrundfosliterature 6375javivivivОценок пока нет
- Cadence Tutorial PDFДокумент61 страницаCadence Tutorial PDFJinesh Kb100% (1)
- DC Choppers ExplainedДокумент56 страницDC Choppers Explainedsaikarthick023Оценок пока нет
- Dielectrics Lecture Notes PDFДокумент33 страницыDielectrics Lecture Notes PDFGokul Subramanyan100% (1)
- Safety Circuit: Status: August 19, 1999Документ12 страницSafety Circuit: Status: August 19, 1999raymon janszenОценок пока нет
- APM2054N: Pin Description FeaturesДокумент12 страницAPM2054N: Pin Description FeaturespotatoОценок пока нет
- Superheterodyne ReceiverДокумент10 страницSuperheterodyne ReceiverAndhika Kumara DjaffriОценок пока нет
- STD, STB y Stp5,8nm60Документ18 страницSTD, STB y Stp5,8nm60Alfredo Valencia RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Sad Raf Shari 2016Документ9 страницSad Raf Shari 2016mhmedОценок пока нет
- ch03 PDFДокумент9 страницch03 PDFFaisal MumtazОценок пока нет
- 2021 A High-Efficiency Self-Synchronous RF-DC Rectifier With A Fixed Broadband Phase OffsetДокумент4 страницы2021 A High-Efficiency Self-Synchronous RF-DC Rectifier With A Fixed Broadband Phase OffsetAzrinYunusОценок пока нет
- Operating Principles For Inductive Proximity Sensors: ProductsДокумент6 страницOperating Principles For Inductive Proximity Sensors: Productsaravindan476Оценок пока нет
- E&M Question BankДокумент18 страницE&M Question BankEzhilya VenkatОценок пока нет
- Features General Description: 3A, Ultra Low Dropout (0.23V Typical) Linear RegulatorДокумент17 страницFeatures General Description: 3A, Ultra Low Dropout (0.23V Typical) Linear RegulatorLangllyОценок пока нет
- MLX90640 Datasheet MelexisДокумент12 страницMLX90640 Datasheet MelexisBartОценок пока нет
- FR9984Документ13 страницFR9984Giovanni Carrillo VillegasОценок пока нет
- GATE Transducers BookДокумент12 страницGATE Transducers BookFaniAli100% (1)