Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AP Physics B CH 5 8 9 PPT Review
Загружено:
harshanauocОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AP Physics B CH 5 8 9 PPT Review
Загружено:
harshanauocАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
2
Periodic Motion
Repetitive, cyclical motion that occurs along the
same path in a fixed period of time
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) path = circle
1 cycle = 1 revolution
# of revolutions
frequency =
1 second (or minute)
f
# of seconds
period =
1 complete revolution
T
Inverse relationship between T, f
1 1
T f
f T
!
3
Frequency Period Relationship
T = 2 s
f = ?
f = 2 revs/sec
1 s
0 s
T = ?
4
5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion: motion in a circle of
constant radius at constant speed
Instantaneous velocity is always tangent to
circle.
5
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
Object revolving around a center point in a
circular path at a constant speed v
2 r
v
T
circle circumference
Speed r circular path radius
period
T
! !
Can an object moving at constant speed
be accelerating?
Velocity is constantly changing due to its
change in direction as it moves around the
circle
Change in velocity means the object is
accelerating
5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
Looking at the change in velocity in the limit that
the time interval becomes infinitesimally small,
we see that
(5-1)
5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
This acceleration is called the centripetal, or
radial, acceleration, and it points towards the
center of the circle.
Centripetal Force
Net force directed radially towards center of
circle
Causes the centripetal acceleration
Responsible for changing the direction of the
velocity vector so object moves in circular
path
2
c c
v
F ma m
r
7 ! !
You must be able to identify the applied force that
provides the centripetal force causing UCM
11
Tension in string creates centripetal force
UCM Vertical Circles
Centripetal force provided by a
net force of 2 applied forces
Two different cases
vertical loop-the-loop track
normal force and weight
ball on a string
Tension and weight
Vertical circle ball on a string
Top:
r
v
m mg T
2
!
Bottom:
r
v
m mg T
2
!
r
Approach for solving any UCM problem:
Set net force = mv
2
/r
+
v
v
F
c
stays constant
at all points.
Tension changes
due to inclusion
of weight force
14
Critical velocity at top of a vertical circle
Minimum velocity necessary to keep
object in circular path
Occurs when the normal force (or
tension in string) = 0
2
2
N
mv
mg
r
mv
mg
r
v rg
!
!
!
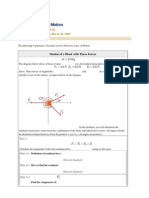
When a car goes around a curve, there must be
a net force towards the center of the circle of
which the curve is an arc. If the road is flat, that
force is supplied by friction.
There are no centrifugal forces pushing person against door
16
Determine maximum speed
car can have to round a
horizontal circular turn and not
skid out of circle
Max speed derivation
max
2
2
,
s c
s N
s
s
f F
mv
F
r
mv
mg
r
u rg v
Q
Q
!
!
!
!
speed is independent
of cars mass
18
Predict direction of object upon leaving UCM circle
Chapter 8
Rotational Motion
8-4 Torque
To make an object start rotating, a force is needed;
the position and direction of the force matter as well.
The perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation
to the line along which the force acts is called the
lever arm.
8-4 Torque
A longer lever
arm is very
helpful in
rotating objects.
8-4 Torque
Here, the lever arm for F
A
is the distance from the
knob to the hinge; the lever arm for F
D
is zero;
and the lever arm for F
C
is as shown.
lever arm
8-4 Torque
The torque is defined
as:
(8-10a)
lever arm
Chapter 9
Static Equilibrium
25
2 conditions for equilibrium
1) 7F
y
= 0 and 7F
x
= 0
2) The net torque about any axis = 0
All objects will be in static equilibrium no motion
26
3 different types of equilibrium problems in chapter 9
1
st
type does not have any
torques to consider
Key is to resolve vectors into
x, y components correctly
27
2
nd
type is balancing a horizontal beam
beam does not have any significant mass
must calculate both forces and torques
28
3
rd
type is beam balancing again
Beam does have significant mass that is concentrated at
its center of gravity (CG) = point where all of its weight
could be concentrated
It is convenient to use one end of the beam as the axis of
rotation this causes the lever arm for that force = 0, thus
simplifying the net torque calculation.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14Документ2 страницыCambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14harshanauoc100% (1)
- 2017 p1Документ14 страниц2017 p1harshanauocОценок пока нет
- A CarДокумент6 страницA CarharshanauocОценок пока нет
- UnitДокумент8 страницUnitharshanauocОценок пока нет
- A2 FinalДокумент24 страницыA2 FinalharshanauocОценок пока нет
- EOCQ Ans 19Документ2 страницыEOCQ Ans 19harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Harshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1Документ15 страницHarshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- EOCQ Ans 15Документ1 страницаEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- EOCQ Ans 22Документ2 страницыEOCQ Ans 22harshanauocОценок пока нет
- W MCQДокумент8 страницW MCQharshanauocОценок пока нет
- A Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsДокумент2 страницыA Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 6Документ3 страницыSAQ Ans 6harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (3)
- SAQ Ans 3Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 3harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент1 страницаAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 28Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 28harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент1 страницаAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 10Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 10harshanauoc0% (1)
- SAQ Ans 24Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 24harshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 32Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 32harshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 6Документ3 страницыSAQ Ans 6harshanauocОценок пока нет
- SAQ Ans 7Документ2 страницыSAQ Ans 7harshanauocОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- FORCE AliceДокумент8 страницFORCE AliceWimas AbadiОценок пока нет
- Weekend Assignment 3Документ2 страницыWeekend Assignment 3Veenus GirdharОценок пока нет
- Laws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsДокумент8 страницLaws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsEduard Benjamin LauronОценок пока нет
- StaticsДокумент347 страницStaticsDanica Yanson100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Learner's Module on Forces and MotionДокумент30 страницGrade 8 Science Learner's Module on Forces and MotionNini Jimbuu50% (2)
- Science-8-Q1-Mod1-Force, Motion - EnergyДокумент27 страницScience-8-Q1-Mod1-Force, Motion - EnergyAngelica BuquiranОценок пока нет
- Edit GeasДокумент5 страницEdit GeasMichael Angelo Perez100% (1)
- Newton's Second LawДокумент5 страницNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Centre of GravityДокумент17 страницCentre of GravityanupamОценок пока нет
- NEWTONS-LAWS-OF-MOTION-ENRICHMENT-ACTIVITIESДокумент14 страницNEWTONS-LAWS-OF-MOTION-ENRICHMENT-ACTIVITIESTohmОценок пока нет
- 13 Rotational Dynamics v2Документ5 страниц13 Rotational Dynamics v2Hubert YuanОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam Attempt Review PDFДокумент15 страницMidterm Exam Attempt Review PDFNiño Jose A. Flores (Onin)Оценок пока нет
- Linear MachanicsДокумент36 страницLinear Machanicssaifextra88% (8)
- Lecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionДокумент55 страницLecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionRazan AlmuairfiОценок пока нет
- Newton's First Law of MotionДокумент4 страницыNewton's First Law of MotionMax SaubermanОценок пока нет
- Static Equilibrium ConditionsДокумент24 страницыStatic Equilibrium ConditionsAnita PatelОценок пока нет
- Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion: ContinuedДокумент36 страницForces and Newton's Laws of Motion: ContinuedJerica AlondraОценок пока нет
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 Q1 Week 5 - v2Документ25 страницGENERAL PHYSICS 1 Q1 Week 5 - v2Jasmen CordovaОценок пока нет
- Force Board: ENGD1005 Mechanical PrinciplesДокумент6 страницForce Board: ENGD1005 Mechanical PrinciplesLegendaryNОценок пока нет
- 8em PhyДокумент170 страниц8em Phyrameshaarya99Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Activity No.3Документ5 страницLaboratory Activity No.3NICOLE RUTH RECTOОценок пока нет
- Physics Lab Report 5Документ3 страницыPhysics Lab Report 5raphaelОценок пока нет
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in PhysicsДокумент3 страницыSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in PhysicsFerlin Paru Rapal100% (1)
- Experiment 104: Newton's Second Law of MotionДокумент7 страницExperiment 104: Newton's Second Law of MotionJaz DionisioОценок пока нет
- Skills Worksheet Coulomb's LawДокумент4 страницыSkills Worksheet Coulomb's LawFatma AhliОценок пока нет
- CH 11Документ55 страницCH 11Mega LialitaОценок пока нет
- Net Force and Acceleration Practice WorksheetДокумент2 страницыNet Force and Acceleration Practice WorksheetZyryl Zane100% (2)
- 9th Notes PhysicsДокумент18 страниц9th Notes PhysicsSardar BilalОценок пока нет
- Science 8 LMДокумент351 страницаScience 8 LMHelma Jabello AriolaОценок пока нет
- 9.2 Engaged Discussion: TorqueДокумент14 страниц9.2 Engaged Discussion: TorqueMischelle BeerbaumОценок пока нет