Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Present Simple
Загружено:
Ionuţ Dumitru0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров2 страницыxcvcxv
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документxcvcxv
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров2 страницыPresent Simple
Загружено:
Ionuţ Dumitruxcvcxv
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Present Simple
Subject + Verb (present form)
Quick examples
John lives in New York.
We play football every day.
You are really kind.
The meeting starts at 3 PM.
The Present Simple is the most basic tense in the
English language. It is an interesting tense because it can
be used to express the future. Generally, though, we use
it to describe the present activities or to talk about
routines or habits.
Use
1. Facts, generalizations and universal truths
2. Habits and routines
3. Permanent situations
4. Events that are certain to happen
5. Arrangements that we can't change (e.g.
timetables, official meetings)
6. State verbs (e.g. be, have, suppose, know)
7. Narrations, instructions or commentaries
Note
Apart from the above uses, this tense is also used in:
Zero Conditional ("If it doesn't rains, I go play
football.")
First Conditional ("We won't get our pocket
money, if we don't pass this exam.")
In sentences after when, before, till, after, as
soon as ("Before you leave, please take the
keys.")
Use 1: Facts, Generalizations and Univeral Truths
We use the Present Simple to talk about universal truths
(for example, laws of nature) or things we believe are, or
are not, true. It's also used to generalize about something
or somebody.
Water boils at 100 degrees Celcius. Universal
Truth
It is a big house. Fact
The Earth goes around the Sun. Universal Truth,
Fact
Dogs are better than cats. Generalization
Berlin is the capital city of Germany. Fact
The Elephant doesn't fly. Fact
London is the capital city of France. Fact
(Remember: the sentence does not have to be
true)
Use 2: Habits and Routines
We also use this tense to describe actions that happen
frequently. For example: habits, routines, tendencies.
We leave for work at 7:30 AM every morning.
Routine
My husband watches the TV in the evening.
Habit, Routine
Susan often meets with her friends after school.
Habit, Routine
They usually play football on Sunday. Habit,
Routine
Mark rarely visits his sick grandmother.
Tendency
Pinocchio usually tells lies. Tendency
Adverbs of Frequency
The Present Simple is often used with the frequency
adverbs:
always
frequently/often
usually
seldom/rarely
nowadays
never
every week/year
sometimes/occasionally
from time to time
every now and then
A few examples how to use them in sentences:
I always go to church on Sundays.
I never eat anything after 10 PM.
Use 3: Pernament Situations
Use the Present Simple to talk about situations in life
that last a relatively long time.
I live in Boston
He works as a fireman.
Margaret drives a Volkswagen.
Jerry doesn't teach maths at highschool.
Use 4: Events Certain to Happen
Use the Present Simple when an event is certain to
happen in the future.
My grandmother turns 100 this July.
Winter starts on December 21.
Use 5: State Verbs
You should use the Present Simple with state verbs.
I like swimming.
We know this man.
Note
Some of the verbs used in the simple form can also
appear in the continuous form. This is typically when
they have an active meaning or emphasize change.
I'm thinking of moving to San Francisco.
I'm loving your new hairdo!
Use 6: Future Arrangements
Use the Present Simple to talk about events that we can't
change (for example, an official meeting or a train
departure).
The meeting starts at 4 PM.
The train leaves at the noon.
When does the plane take off?
Jerry doesn't teach maths at high school.
Use 7: Narrations, Instructions or commentaries
The Present Simple is also used in narrations (e.g. to tell
a story or a joke), instructions (e.g. cooking) or
commentaries (especially sport commentaries).
"A man goes to visit a friend and is amazed to
find him playing chess with his dog. He watches
the game in astonishment for a while [...]"
Form
Forming a sentence in the Present Simple is easy. To
form a declarative sentence, all you need is the subject of
the sentence (e.g. I, you, he, a dog) and the verb (e.g. be,
talk, swim). Questions and negative sentences are only a
little more difficult, because they require an auxiliary
verb.
Declarative Sentences
Subject + Verb (present form)
e.g. he, she, a dog, etc. e.g. go, make, have, etc.
Sharks have sharp teeth (Use 1)
Examples
A dog is an animal.
I learn English twice a week.
I have two eggs.
The course starts in April.
The man enters the room and looks at the clock.
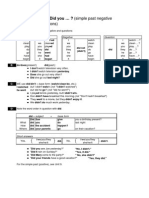
Questions
Questions require the auxiliary verb "to do" or, in the
third person singular, "does".
Do or
Does
+
Subject
+
Verb (present
form)
e.g. he, she, a dog,
etc.
e.g. go, make, have, etc.
Compare these examples:
Person A: Does she like going to the mountains?
Person B: Yes, she does.
Person A: Does John have a dog?
Person B: No, he doesn't.
When asking a question, the verb does not conjugate:
Does she have a dog?
Does she has a dog?
For the verb "to be", we do not use an auxiliary:
Is he tall?
Does he be tall?
Examples
Is he a lawyer?
Does Mike go swimming every Sunday?
Does she live in London?
Do you turn 40 in April?
Negative Sentences
Subject + Don't or Doesn't + Verb (present form)
Вам также может понравиться
- Present Simple: Continuous Form. This Is Typically When They Have An ActiveДокумент1 страницаPresent Simple: Continuous Form. This Is Typically When They Have An ActiveIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Reported Speech Indirect Requests Reported and Indirect QuestionsДокумент1 страницаReported Speech Indirect Requests Reported and Indirect QuestionsmariolafernandezcarОценок пока нет
- InterjectionДокумент2 страницыInterjectionTooba Anis100% (1)
- Past Simple - All FormsДокумент1 страницаPast Simple - All FormsrenataОценок пока нет
- Letter U Long Vowel WorksheetДокумент1 страницаLetter U Long Vowel WorksheetRodica Lucica PopОценок пока нет
- Name: Yuni Maulidia: Parallelism: Exercise 1Документ3 страницыName: Yuni Maulidia: Parallelism: Exercise 1Yuni Maulidia0% (1)
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент2 страницыActive and Passive Voicesirthana697547Оценок пока нет
- Inversion (Question? (Verb + Subject) / Negative Adverbial / Conditionals / Tag Questions)Документ9 страницInversion (Question? (Verb + Subject) / Negative Adverbial / Conditionals / Tag Questions)Cecilia LunaОценок пока нет
- Simple Past 0 English Grammar Rules Explanations PDFДокумент3 страницыSimple Past 0 English Grammar Rules Explanations PDFhasanalbanahakimОценок пока нет
- Direct & Reported Speech: Grammar Practice WorksheetsДокумент13 страницDirect & Reported Speech: Grammar Practice WorksheetsKenny YuОценок пока нет
- Days (2) Every Month (3) Last Year.: Adverbs of Time What Is An Adverb of Time?Документ4 страницыDays (2) Every Month (3) Last Year.: Adverbs of Time What Is An Adverb of Time?Jennefer HernandezОценок пока нет
- 2.1. Noun Possessive CaseДокумент10 страниц2.1. Noun Possessive CaseAna DerilОценок пока нет
- Past Simple - Irregular VerbsДокумент4 страницыPast Simple - Irregular Verbsjohana faustinoОценок пока нет
- WH QuestionsДокумент2 страницыWH QuestionsAngelica Lobo Moraga100% (1)
- The Present of Be: Statements,: Negatives andДокумент19 страницThe Present of Be: Statements,: Negatives andSirikan SriwisanОценок пока нет
- Grammar Exercises With Indirect SpeechДокумент13 страницGrammar Exercises With Indirect SpeechancutzsaОценок пока нет
- Second ConditionalДокумент25 страницSecond ConditionalJosé Henrique Tobias PereiraОценок пока нет
- Talking About The FutureДокумент6 страницTalking About The FutureGrecu Oana MariaОценок пока нет
- Past Simple Negative FormsДокумент2 страницыPast Simple Negative FormsYulia LogunovaОценок пока нет
- Singular and Plural NounsДокумент11 страницSingular and Plural NounsMarta TrenadoОценок пока нет
- Simple Past or Past PerfectДокумент1 страницаSimple Past or Past PerfectSalah OualiОценок пока нет
- If Clause Type 3Документ20 страницIf Clause Type 3fajar sukmanaОценок пока нет
- Reported SpeechДокумент17 страницReported SpeechalwiОценок пока нет
- 'Will & Going To' - English Quiz & Worksheet PDFДокумент2 страницы'Will & Going To' - English Quiz & Worksheet PDFjorge figueroa NarvaezОценок пока нет
- Modals of ObligationДокумент34 страницыModals of ObligationMarie Ellaine Concepcion GabayОценок пока нет
- Possessive Adjective WorksheetДокумент4 страницыPossessive Adjective WorksheetGoldianaОценок пока нет
- Active-Passive QuizДокумент2 страницыActive-Passive QuizJane Bagas LumilisОценок пока нет
- Adjective Verb Clause Adverb: Everywhere, Nowhere, and Upstairs Are A FewДокумент2 страницыAdjective Verb Clause Adverb: Everywhere, Nowhere, and Upstairs Are A FewGermaeGonzalesОценок пока нет
- Gs Past Simple Regular - Exercises 1Документ2 страницыGs Past Simple Regular - Exercises 1AnaAleksic0% (3)
- By Before (+time) : RememberДокумент8 страницBy Before (+time) : RememberfranosullivanОценок пока нет
- Zero and First ConditionalsДокумент3 страницыZero and First Conditionalsddzako9140Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet-Modal Verbs-Might-2014Документ5 страницWorksheet-Modal Verbs-Might-2014MaximilianoJesus0% (1)
- Conjunction NotesДокумент14 страницConjunction NotesBryan LeeОценок пока нет
- Basic Sentence Patterns in EnglishДокумент16 страницBasic Sentence Patterns in EnglishAnneza HusseinОценок пока нет
- Worksheet-Tenses Revision (4 Basic Tenses)Документ5 страницWorksheet-Tenses Revision (4 Basic Tenses)Army Sijaya100% (1)
- Bài Tập Câu Điều KiệnДокумент4 страницыBài Tập Câu Điều KiệnHương100% (1)
- Read Sonia's Calendar. Choose The Right AnswerДокумент2 страницыRead Sonia's Calendar. Choose The Right AnswerValentina Garrido0% (1)
- My NounДокумент24 страницыMy NounReski0% (1)
- Countable Uncountable NounsДокумент23 страницыCountable Uncountable NounsEmmanuel PaulinoОценок пока нет
- Writing An Informal Letter PDFДокумент1 страницаWriting An Informal Letter PDFvero_poluxОценок пока нет
- Tenses of Verbs HandoutДокумент5 страницTenses of Verbs HandoutCheryl AquinoОценок пока нет
- Not Only But Also: InversionДокумент6 страницNot Only But Also: InversionSlobodan Kanza KanovicОценок пока нет
- Identifying Linking Verbs: Name: DateДокумент3 страницыIdentifying Linking Verbs: Name: DateEmon MijasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11-Expressing Future Time, Part 2Документ26 страницChapter 11-Expressing Future Time, Part 2noravintelerОценок пока нет
- Sports - Comprehension ReadingДокумент3 страницыSports - Comprehension ReadingNoe Tapia33% (3)
- Simple Past QuestionДокумент2 страницыSimple Past QuestionAlexandre RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Sentence Types NotesДокумент14 страницSentence Types NotesMicheal ChienОценок пока нет
- Verb TensesДокумент5 страницVerb Tensesangel caoОценок пока нет
- Common Proper Nouns WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCommon Proper Nouns WorksheetGretcel CelisОценок пока нет
- Conditional and WishДокумент2 страницыConditional and Wishfatima ikenОценок пока нет
- English B2: Reading ComprehensionДокумент9 страницEnglish B2: Reading ComprehensionThaliaОценок пока нет
- Grammer A1 A2Документ21 страницаGrammer A1 A2احمد سامي قطاونهОценок пока нет
- Burlington English Intermediate: Superlative AdjectivesДокумент2 страницыBurlington English Intermediate: Superlative AdjectivesandreeaОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive QuizДокумент2 страницыActive and Passive QuizJane Daming AlcazarenОценок пока нет
- Handout Second ConditionalДокумент2 страницыHandout Second ConditionalFatima C. DiazОценок пока нет
- Indirect Speech 2Документ17 страницIndirect Speech 2rajesh dua100% (1)
- Present Tense - Reading MaterialДокумент14 страницPresent Tense - Reading MaterialMs Chikoti Sai Vaishnavi IPEОценок пока нет
- Present TensesPresent SimpleДокумент16 страницPresent TensesPresent SimpleHarsha SusarlaОценок пока нет
- Simple Present TenseДокумент8 страницSimple Present TenseKhoerul Anwar100% (1)
- Tenses English GrammarДокумент50 страницTenses English GrammarAbhishek TiwariОценок пока нет
- 1 (02) Belarus SkuratovichДокумент5 страниц1 (02) Belarus SkuratovichIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Lm41830281992199aaa03 MTLДокумент2 страницыLm41830281992199aaa03 MTLIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- StatiaДокумент3 страницыStatiaIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Fig 5Документ1 страницаFig 5Ştefania MarinОценок пока нет
- How To Win Every Argument PDFДокумент196 страницHow To Win Every Argument PDFRice RS100% (7)
- Present Simple: Quick ExamplesДокумент2 страницыPresent Simple: Quick ExamplesIonuţ Dumitru100% (1)
- Present Continuous: Quick Examples: Use 4: Future (Personal) Arrangements and PlansДокумент1 страницаPresent Continuous: Quick Examples: Use 4: Future (Personal) Arrangements and PlansIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Continuous: Quick Examples: Use 4: Future (Personal) Arrangements and PlansДокумент1 страницаPresent Continuous: Quick Examples: Use 4: Future (Personal) Arrangements and PlansIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect ConДокумент1 страницаPresent Perfect ConIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Stative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearДокумент1 страницаStative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect: Quick Examples Use 2: Effect On The Present MomentДокумент1 страницаPresent Perfect: Quick Examples Use 2: Effect On The Present MomentIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Stative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearДокумент1 страницаStative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Stative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearДокумент1 страницаStative (State) Verbs: I Have Seen It Yesterday. We Have Gone To Paris Last YearIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect: Quick Examples Use 2: Effect On The Present MomentДокумент1 страницаPresent Perfect: Quick Examples Use 2: Effect On The Present MomentIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect ConДокумент1 страницаPresent Perfect ConIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect ConДокумент1 страницаPresent Perfect ConIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет
- PSTДокумент1 страницаPSTIonuţ DumitruОценок пока нет