Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Automobile Engineering (EG704ME) : Course Outlines
Загружено:
Dipendra SenИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Automobile Engineering (EG704ME) : Course Outlines
Загружено:
Dipendra SenАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
(EG704ME)
Lecture: 3
Tutorial: 1
Practical: 1.5
Year: IV
Part: A
COURSE OUTLINES
1.
INTRODUCTION
1.1
History of development
1.2
Classification of motor vehicles
1.3
Components of an automobile
2.
CLUTCH
2.1
Purpose and function
2.2
Types, main parts
2.3
Common troubles and its diagnosis
3.
GEAR BOX
3.1
Introduction
3.2
Purpose and function
3.3
Types: slidingmesh, constantmesh, synchromesh and epicyclic
gearboxes; gear shifting
3.4
Automatic gearbox
3.5
Overdrive
3.6
Common trouble and its diagnosis
4.
UNIVERSAL JOINT AND PROPELLER SHAFT
4.1
Introduction, types of universal joints
4.2
Common trouble and its diagnosis
5.
REAR AXLE
5.1
Function and types
5.2
Main parts
5.3
Differential
5.4
Fourwheel drive
5.5
Common trouble and its diagnosis
6.
WHEEL AND TYRES
3
6.1
Types of wheels, wheel dimensions
6.2
Types of tyre, properties
6.3
Tyre designations, factors affecting tyre life, tyre pressure and its effect
6.4
Changing of tyre, tyre rotation
7.
CHASSIS
7.1
Purpose, construction of a chassis
7.2
Layout and types
7.3
Defects in frames
7.4
Frameless construction
8.
SUSPENSION SYSTEM
8.1
Introduction and objective
8.2
Types, main parts
8.3
Trouble shooting
9.
BRAKES
9.1
Introduction and objective
9.2
Importance of stopping distance, braking distance
9.3
Main parts
9.4
Types: mechanical, hydraulic, power-assisted brakes
9.5
Brake adjusting
9.6
Brake shoe and lining materials
9.7
Antilock braking system
10.
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS SYSTEM
10.1 Lighting and wiring system
10.2 Battery, starter motor, generator
10.3 Electrical and electronics instrument
10.4 Accessories
10.5 Common trouble and its diagnosis
11.
STEERING SYSTEM
11.1 Need for the system and parts
11.2 Types of steering linkage and boxes
11.3 Power steering
11.4 Common trouble
11.5 Wheel alignment
12.
MOTOR VEHICLE DYNAMICS
12.1 Forces acting on a motor vehicles
12.2 Transmission efficiency
12.3 Determination of fuel consumption
13.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Driver and passenger safety
14.
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
4
14.1 Introduction to major pollutant formation
14.2 Methods of pollutant reduction
14.3 Introduction to measuring instrument such as smoke and gas analyser
14.4 Permitted emission levels in Nepal
14.5 Noise pollution
15.
VEHICLE RULES AND ACTS
2
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Motor vehicle act, registration of motor vehicle, driving license,
control of traffic, insurance against risk, claims for compensation
16.
WORKSHOP LAYOUT AND VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
4
16.1 Garage and workshop layout
16.2 Calculation of workshop post, no. of workers and area of sections of
the workshop
16.3 Measuring instruments, tool and workshop equipment
16.4 Vehicle maintenance and repair: types and purposes
PRACTICALS
1.
CLUTCH AND GEARBOX
Types, main parts, dismantling, identification and assembling of components
of clutch and gearbox; checking the conditions of clutch plate, pressure plate,
release bearing, gears.
2.
PROPELLER SHAFT, FINAL DRIVE AND DIFFERENTIAL
Main parts, dismantling, identification and assembling of main parts of
differential; checking the conditions of propeller shaft, universal joints, final
drive and differential.
3.
BRAKES
Types, main parts, dismantling, identification and assembling of brake
components; checking the conditions of master cylinder, brake drum/discs,
brake linings, pipe lines, brake oil reservoir
4.
SUSPENSION AND AXLES
Types, main parts; checking their conditions
5.
WHEEL, TYRES AND STEERING
Types, main parts; checking the conditions of tyres and tubes, wheel and
steering gearbox, steering wheels
6.
BATTERY, STARTING MOTOR, CHARGING SYSTEM
Battery: main parts, proper handling of electrolyte, use of battery charging and
testing equipment, charging of new/used battery, servicing of battery.
Starting motor: main parts, dismantling, identification of parts and assembling
of starting motor, testing of starting motor on test bench and on car.
Charging system: types of generator and working principle, dismantling,
identification of parts and assembling of generators, working principle of
regulator and cutouts.
7.
LIGHTING AND WIRING
Wiring layouts, identification of components, fault finding, replacing the
damaged components.
8.
EMISSION TESTING
Introduction to emission testing equipment, measurement of CO and smoke.
References:
1. Automobile Engineering, vol. 1 and 2 Kripal Singh
2. Automotive Mechanics Joseph Heitner
3. Automotive Mechanics Willium Crouse
4. Skill testing standards on motor vehicle Nepal skill testing authority, CTEVT
Вам также может понравиться
- Spicer AXSM 0030Документ43 страницыSpicer AXSM 0030slipsittinОценок пока нет
- Motor Vehicle Technician - MVTNДокумент6 страницMotor Vehicle Technician - MVTNSk Akram HossainОценок пока нет
- Aut 3Документ3 страницыAut 3Uwizeyimana Emmanuel DAОценок пока нет
- Course Title: Automobile Servicing & Maintenance Course Code: 6052 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 75 Credits: 6Документ5 страницCourse Title: Automobile Servicing & Maintenance Course Code: 6052 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 75 Credits: 6VaisakVenugopalОценок пока нет
- Course Title: Automobile Chassis Course Code: 6051 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 75 Credits: 5Документ4 страницыCourse Title: Automobile Chassis Course Code: 6051 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 75 Credits: 5VaisakVenugopalОценок пока нет
- Automobile EngineeringДокумент13 страницAutomobile EngineeringDineshNewalkarОценок пока нет
- Orals CochinДокумент70 страницOrals CochinJayeshJayarajanОценок пока нет
- B.M.U. A-25: Maintenance ManualДокумент92 страницыB.M.U. A-25: Maintenance ManualDUyОценок пока нет
- Automobile Transmissiion SystemsДокумент4 страницыAutomobile Transmissiion SystemsNeha JoshiОценок пока нет
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент5 страницElements of Mechanical EngineeringnavitgmОценок пока нет
- Vehicle Uppraisal Inspection ChecklistДокумент3 страницыVehicle Uppraisal Inspection ChecklistBirhan AbebawОценок пока нет
- Btme 505 Automobile EngineeringДокумент2 страницыBtme 505 Automobile EngineeringSumit SinghОценок пока нет
- Government of The People's Republic of Bangladesh Sample Oral Question Bank Marine Engineering Officer Class 5 (Coastal Vessel)Документ9 страницGovernment of The People's Republic of Bangladesh Sample Oral Question Bank Marine Engineering Officer Class 5 (Coastal Vessel)Parvin AkterОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - Driver Cum Auto MechanicДокумент13 страницSyllabus - Driver Cum Auto MechanicMichael Alba100% (1)
- Lab Manual of Farm Power & Engine System (Agri-Ii/I and Internal Combustion Engines (Mech-Iii/Ii)Документ350 страницLab Manual of Farm Power & Engine System (Agri-Ii/I and Internal Combustion Engines (Mech-Iii/Ii)MB SIXTEENОценок пока нет
- Automobile EngineeringДокумент4 страницыAutomobile EngineeringRita KalaniОценок пока нет
- Piston Engine (Autopesaved)Документ4 страницыPiston Engine (Autopesaved)Mohan ChetriОценок пока нет
- Mitsubishi L2E en L3 WorkshopДокумент155 страницMitsubishi L2E en L3 WorkshopAndreas EdlingerОценок пока нет
- Dana Ajuste Difer.Документ66 страницDana Ajuste Difer.Alejo Giraldo Vélez100% (1)
- 6th Sem Auto. Engg. SyllabusДокумент22 страницы6th Sem Auto. Engg. Syllabusrudey18Оценок пока нет
- Drilling Assistant: Further Details PROGRAMME No. 11/2019 (Item No.24)Документ3 страницыDrilling Assistant: Further Details PROGRAMME No. 11/2019 (Item No.24)Skill WorldОценок пока нет
- Vento PHR4i REPAIR MANUAL PDFДокумент88 страницVento PHR4i REPAIR MANUAL PDFErick HinojosaОценок пока нет
- Pgo PMX Sport ServicemanualДокумент116 страницPgo PMX Sport ServicemanualMoppie HofstedeОценок пока нет
- MITSUBISHI L2 L3 Diesel Engine Service Manual 08-2004Документ156 страницMITSUBISHI L2 L3 Diesel Engine Service Manual 08-2004jf100% (2)
- 5 1Документ13 страниц5 1gabrieltinОценок пока нет
- August QuestionsДокумент8 страницAugust Questionsbaba maachoОценок пока нет
- Course Title: Vehicle Testing Lab Course Code: 6058 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 90 Credits: 3Документ2 страницыCourse Title: Vehicle Testing Lab Course Code: 6058 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 90 Credits: 3VaisakVenugopalОценок пока нет
- SauggДокумент34 страницыSauggGanesh PandeyОценок пока нет
- 2005 Sportsman 6x6 - SMДокумент289 страниц2005 Sportsman 6x6 - SMRicardin Baltazar100% (1)
- Function 4b BHAUMIKДокумент3 страницыFunction 4b BHAUMIKhdhdОценок пока нет
- XV 250Документ291 страницаXV 250Muñoz Roaddog Ariel100% (2)
- Vmoto Monaco HandbookДокумент40 страницVmoto Monaco HandbookHamish CleghornОценок пока нет
- Automobile Engineering: Course Code:13ME1142 L TPC 4 0 0 3Документ3 страницыAutomobile Engineering: Course Code:13ME1142 L TPC 4 0 0 3NiranjanBandaОценок пока нет
- Automobile EngineeringДокумент4 страницыAutomobile EngineeringAshley_Rulzzzzzzz0% (2)
- Automobile Systems - 9057Документ5 страницAutomobile Systems - 9057Khushbu JoshiОценок пока нет
- Course File AEДокумент13 страницCourse File AESp PatelОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Diesel Engine Manual Gi1ek1Документ136 страниц3.3 Diesel Engine Manual Gi1ek1Ljupco RistovskiОценок пока нет
- A180 Service ManualДокумент213 страницA180 Service ManualramiroОценок пока нет
- LW900KN Service ManualДокумент553 страницыLW900KN Service ManualEder Salinas100% (1)
- 2005 Polaris Sportsman 400 500 Service Manual NoPWДокумент312 страниц2005 Polaris Sportsman 400 500 Service Manual NoPWMike Haden100% (2)
- 6.0L Power Stroke Tech Manual (2004 Update)Документ80 страниц6.0L Power Stroke Tech Manual (2004 Update)dustyboner96% (48)
- TM 9-1709 Chassis and Body For Scout Cars M3A1 1942Документ263 страницыTM 9-1709 Chassis and Body For Scout Cars M3A1 1942RobertLockieОценок пока нет
- Mooney M20 100 Hour Annual 2007Документ2 страницыMooney M20 100 Hour Annual 2007flyokie100% (1)
- 1 Ca4250p25k15t1e5a80Документ17 страниц1 Ca4250p25k15t1e5a80Jorge IsraelОценок пока нет
- Operating Manual RVM by JAWA-ADVENTURE-ENGДокумент40 страницOperating Manual RVM by JAWA-ADVENTURE-ENGFatih NakОценок пока нет
- Yamaha YZF R6 2006-07 Manual de Taller ENG PDFДокумент437 страницYamaha YZF R6 2006-07 Manual de Taller ENG PDFJaime Blazquez100% (1)
- Annual Vehicle ChecklistДокумент2 страницыAnnual Vehicle ChecklistabdouОценок пока нет
- MG ZR R65 Uprated Manual Gearbox Overhaul ManualДокумент37 страницMG ZR R65 Uprated Manual Gearbox Overhaul ManualAras Serdaroğlu0% (1)
- 1-CA3250P25K15L3T1E5A80-DW014H-Entire Vehicle and InstructionsДокумент16 страниц1-CA3250P25K15L3T1E5A80-DW014H-Entire Vehicle and InstructionsJesus gomez corvalanОценок пока нет
- Stella-4T Service Station Manual PDFДокумент178 страницStella-4T Service Station Manual PDFVroum Vroumvroum100% (1)
- Polaris Predator 50 - Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 2008 9921487Документ178 страницPolaris Predator 50 - Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 2008 9921487vincent_devine777dОценок пока нет
- Manual Motor Luv - 4ZD1 PDFДокумент112 страницManual Motor Luv - 4ZD1 PDFmiguel_alb18100% (1)
- Fun 4b and 6 Recent QuestionsДокумент18 страницFun 4b and 6 Recent Questionsonly indianОценок пока нет
- Practical Boat Mechanics: Commonsense Ways to Prevent, Diagnose, and Repair Engines and Mechanical ProblemsОт EverandPractical Boat Mechanics: Commonsense Ways to Prevent, Diagnose, and Repair Engines and Mechanical ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Performance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallОт EverandPerformance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- A330Документ79 страницA330Dipendra Sen100% (1)
- Nepalese Civil Airworthiness Requirements: List of Effective Pages Issue 2 JANUARY 2009Документ10 страницNepalese Civil Airworthiness Requirements: List of Effective Pages Issue 2 JANUARY 2009Dipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Nepalee Civil Airworthiness RequirementsДокумент1 страницаNepalee Civil Airworthiness RequirementsDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Notice To Crews and Engineers: Deferred Defects & Out of Phase Maintenance Must Be Reviewed During Transit & Daily ChecksДокумент2 страницыNotice To Crews and Engineers: Deferred Defects & Out of Phase Maintenance Must Be Reviewed During Transit & Daily ChecksDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Aeroplane Aerodynamics: LevelДокумент7 страницAeroplane Aerodynamics: LevelDipendra Sen0% (1)
- The Unsteady Aerodynamics Ofslender Wings and Aircraft Undergoing Large Amplitude ManeuversДокумент66 страницThe Unsteady Aerodynamics Ofslender Wings and Aircraft Undergoing Large Amplitude ManeuversDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Table of ContentsДокумент27 страницTable of ContentsDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Data Used: 1 AMM 2 EMM 3 SRM 4 CMM 5 WDM 6 IPCДокумент2 страницыMaintenance Data Used: 1 AMM 2 EMM 3 SRM 4 CMM 5 WDM 6 IPCDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- List of Routine Tasks-3 Monthly, 6 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionДокумент4 страницыList of Routine Tasks-3 Monthly, 6 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Osce Room Midwifery-IДокумент9 страницOsce Room Midwifery-IDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- List of Routine Tasks-3,6 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionДокумент4 страницыList of Routine Tasks-3,6 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Maternal DistressДокумент8 страницMaternal DistressDipendra Sen80% (5)
- Parts Required For 9N-ABTДокумент2 страницыParts Required For 9N-ABTDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- List of Routine Task-SB: Maintenance Planning DivisionДокумент4 страницыList of Routine Task-SB: Maintenance Planning DivisionDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Service Bulletins Dhc-600Документ4 страницыService Bulletins Dhc-600Dipendra SenОценок пока нет
- Check Order 2 Set 3 or 6 Monthly Inspection Schedule List of Routine Tasks Applicable SbsДокумент1 страницаCheck Order 2 Set 3 or 6 Monthly Inspection Schedule List of Routine Tasks Applicable SbsDipendra SenОценок пока нет
- List of Routine Tasks-3 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionДокумент4 страницыList of Routine Tasks-3 Monthly and SBS: Maintenance Planning DivisionDipendra SenОценок пока нет
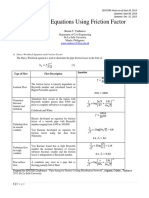
- Notes 2. On Headloss - in Piping SystemsДокумент12 страницNotes 2. On Headloss - in Piping SystemsAngel Lisette LaoОценок пока нет
- Belt ConveyorДокумент8 страницBelt ConveyorneoОценок пока нет
- Science and Empricism in Pile Foundation Design (Randolph 2003)Документ34 страницыScience and Empricism in Pile Foundation Design (Randolph 2003)Abdul Mozid ShikderОценок пока нет
- Fixed Speed CatalogueДокумент26 страницFixed Speed CatalogueSarfaraz Hoda100% (1)
- Air Repair Obdii ReviewДокумент36 страницAir Repair Obdii Reviewroberto caiado100% (1)
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana Cost Estimate For Road ConstructionДокумент3 страницыPradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana Cost Estimate For Road ConstructionLucky TraderОценок пока нет
- Is 1448PT 32Документ23 страницыIs 1448PT 32RAKESH SRIVASTAVAОценок пока нет
- DIN 17100 ST 37-2 SteelДокумент2 страницыDIN 17100 ST 37-2 SteelSiddiqui Abdul KhaliqОценок пока нет
- Astm A105, A105mДокумент5 страницAstm A105, A105mMike Dukas0% (1)
- Uk Oti 66 1.7.06Документ44 страницыUk Oti 66 1.7.06Nassar Al-shabiОценок пока нет
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) : Date: 2017/04/09Документ1 страницаWelding Procedure Specification (WPS) : Date: 2017/04/09akalОценок пока нет
- Feb IssueДокумент40 страницFeb Issuesppram100% (1)
- Thermo Electron 15Документ2 страницыThermo Electron 15AlexОценок пока нет
- MSDS Dan LainnyaДокумент5 страницMSDS Dan Lainnyachristian de vano vienijghansОценок пока нет
- ATLAS OF ISOTHERMAL TRANSFORMATION AND COOLING TRANSFORMATION DIAGRAMS - CompressedДокумент430 страницATLAS OF ISOTHERMAL TRANSFORMATION AND COOLING TRANSFORMATION DIAGRAMS - CompressedYENIFER PLATA LOPEZОценок пока нет
- Introduccion Al Polietileno Industrial PDFДокумент29 страницIntroduccion Al Polietileno Industrial PDFFabrizzio Valer89% (9)
- PBL MTCP LabДокумент7 страницPBL MTCP LabAdarsh SinghОценок пока нет
- Two Years' Operational Experience and Further Development of Full-Scale Co-Firing of StrawДокумент7 страницTwo Years' Operational Experience and Further Development of Full-Scale Co-Firing of StrawvatttenfallОценок пока нет
- Metal Nanoparticles For Catalysis Advances and ApplicationsДокумент284 страницыMetal Nanoparticles For Catalysis Advances and ApplicationsMoreno MarcatiОценок пока нет
- Development in Sizing Machine: By: Tanveer Malik, P.K.Roy & H.K.SinghДокумент24 страницыDevelopment in Sizing Machine: By: Tanveer Malik, P.K.Roy & H.K.SinghAnonymous Pt7NHkat9Оценок пока нет
- Metal Forming OverviewДокумент120 страницMetal Forming OverviewSang Ka KalaОценок пока нет
- Yanmar Engine L48N L100N User ManualДокумент104 страницыYanmar Engine L48N L100N User ManualDavid Alfonso Caraballo100% (5)
- Hl500pin ManualДокумент1 страницаHl500pin ManualMarious NavОценок пока нет
- Fence Gate CatalogДокумент3 страницыFence Gate CatalogtempfencingОценок пока нет
- Bucky PaperДокумент22 страницыBucky PaperShreyashkumar ZingadeОценок пока нет
- MRT Medical Devices PDFДокумент64 страницыMRT Medical Devices PDFtecxv100% (1)
- Extraction and Uses of Metals 3 MS PDFДокумент7 страницExtraction and Uses of Metals 3 MS PDFAngus AnizОценок пока нет
- Protek Etl: Technical Data SheetДокумент1 страницаProtek Etl: Technical Data SheetArnel G. PetalioОценок пока нет
- AS LAB Man IДокумент84 страницыAS LAB Man IVadivel AeroОценок пока нет
- Delphi Mt88 Engine Control ModuleДокумент2 страницыDelphi Mt88 Engine Control ModuleAngelJoseОценок пока нет