Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ceragon IP10 G F Management Guide
Загружено:
Atanda Babatunde Mutiu0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
973 просмотров99 страницCeragon IP10 G F Management Guide
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCeragon IP10 G F Management Guide
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
973 просмотров99 страницCeragon IP10 G F Management Guide
Загружено:
Atanda Babatunde MutiuCeragon IP10 G F Management Guide
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 99
FibeAir
IP-10
G-Series
Version 6.6
Web Based
Management
User Guide
Part ID: BM-0136-0
Doc ID: DOC-00018688 Rev a.12
May 2010
Notice
This document contains information that is proprietary to Ceragon Networks Ltd.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, modified, or distributed without prior written
authorization of Ceragon Networks Ltd.
This document is provided as is, without warranty of any kind.
Registered TradeMarks
Ceragon Networks
is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd.
FibeAir
is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd.
CeraView
is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd.
Other names mentioned in this publication are owned by their respective holders.
TradeMarks
CeraMap
TM
, PolyView
TM
, EncryptAir
TM
,
ConfigAir
TM
, CeraMon
TM
, EtherAir
TM
, and MicroWave
Fiber
TM
, are trademarks of Ceragon Networks Ltd.
Other names mentioned in this publication are owned by their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Ceragon Networks Ltd. shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damage in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this
document or equipment supplied with it.
Information to User
Any changes or modifications of equipment not expressly approved by the manufacturer
could void the users authority to operate the equipment and the warranty for such equipment.
Copyright 2010 by Ceragon Networks Ltd. All rights reserved.
Cor por at e Headquar t er s:
Ceragon Networks Ltd.
24 Raoul Wallenberg St.
Tel Aviv 69719, Israel
Tel: 972-3-645-5733
Fax: 972-3-645-5499
Email: info@ceragon.com
www.ceragon.com
Eur opean Headquar t er s:
Ceragon Networks (UK) Ltd.
4 Oak Tree Park, Burnt Meadow Road
North Moons Moat, Redditch,
Worcestershire B98 9NZ, UK
Tel: 44-(0)-1527-591900
Fax: 44-(0)-1527-591903
Email: infoeuro@ceragon.com
Nor t h Amer i c an Headquar t er s:
Ceragon Networks Inc.
10 Forest Avenue,
Paramus, NJ 07652, USA
Tel: 1-201-845-6955
Toll Free: 1-877-FIBEAIR
Fax: 1-201-845-5665
Email: infous@ceragon.com
APAC Headquar t er s:
Ceragon Networks APAC
(S'pore) Pte Ltd
100 Beach Road
#27-01/03 Shaw Towers
Singapore 189702
Tel.: 65 65724170
Fax: 65 65724199
Contents
General .......................................................................................................... 1
Getting Started .............................................................................................. 1
Menus ............................................................................................................ 2
Faults ...................................................................................................................... 2
PM & Counters ....................................................................................................... 6
Configuration ........................................................................................................ 19
Service OAM ......................................................................................................... 72
Diagnostics & Maintenance ................................................................................ 83
Security ................................................................................................................. 94
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 1
General
This guide explains how to work with the FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management.
IP-10 management is used to perform configuration operations and obtain statistical and performance
information related to the system.
Note: For full functionality and feature availability, upgrade the IDU to the latest released software version.
You can obtain the latest software version and release notes at Ceragons FTP site. For access to the site,
contact support@ceragon.com.
Getting Started
To start the management application:
1. Start your web browser.
2. In the URL address field at the top, type http://yourIP, and press Enter, whereby yourIP is the IP
address of your FibeAir unit.
3. In the Login page that appears, enter your user name and password, and click Login.
The main management page appears:
Configuration and other operations are performed by clicking the menus on the left side of the page.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 2
Menus
The following sections explain the menus that you can select from the list on the left side of the main
management web page.
Faults
Current Alarms
Select the Current Alarms item to view a list of alarms that are active in the system.
Each line on the page displays a different alarm.
Click an alarm in the list to view probable cause and corrective action information.
The date and time the alarm was triggered appear in the Date & Time column.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 3
The color in the Severity column indicates the severity of the alarm, as follows:
The source of the alarm appears in the Module column.
A description of the alarm appears in the Description column.
To send the alarm list to the printer, select File, Print.
To update the list, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 4
Event Log
The event log is a list of historical alarm information.
The Event Log displays the last 200 alarms that occurred. If the number of alarms exceeds 200, the first
alarms will be removed.
The window displays the following information:
Date & Time - The date and time the alarm was triggered.
Severity - The severity of the alarm, as follows:
Module - The module that generated the alarm.
State - The alarm status (Raised, Cleared).
Description - A description of the alarm.
To scroll through additional alarms, click the page number in the Page field.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 5
To clear the alarm list, click Clear.
To update the list, click Refresh.
To print the alarm list, select File, Print.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 6
PM & Counters
RMON (Remote Monitoring)
The RMON counters display values relating to the bridge performance. The counters are designed to
support:
RFC 2819, RMON MIB
RFC 2665, Ethernet-like MIB
RFC 2233, MIB II
RFC 1493, Bridge MIB
The statistic counters are divided into ingress statistics and egress statistics.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 7
To reset a counter, click Clear at the top of the column.
To reset all counters, click Clear All.
To update the list, click Refresh.
To print the list, select File, Print.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 8
Radio
Radio Signal Level (RSL)
The RSL Performance Report page displays received signal level values measured over the past 24 hours, in
15 min intervals, or the past month, daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval.
In the Thresholds Configuration area at the bottom of the value table, specify the value you want
for the thresholds. The range of values appears at the end of the threshold line.
Min RSL values are the minimum received level measured during the interval.
Max RSL values are the maximum received level measured during the interval.
RSL Exceed #1 displays the number of seconds the RSL threshold #1value was exceeded during the current
interval.
RSL Exceed #2 displays the number of seconds the RSL threshold #2 value was exceeded during the current
interval.
Min TSL values are the minimum transmitted level measured during the interval.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 9
Max TSL values are the maximum transmitted level measured during the interval.
TSL Exceed displays the number of seconds the TSL threshold value was exceeded during the current
interval.
The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in
the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that
occurred at that time.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the list, click Refresh.
To print the list, select File, Print.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 10
Radio Aggregate
The Radio Aggregate Performance Report page displays tributary values measured over the last 24 hours, in
15 min intervals, or the past month, daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval.
ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred.
SES is the number of severely errored seconds.
BBE is the number of background block errors.
UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds
(15 minutes).
The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in
the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that
occurred at that time.
To clear the list, click Clear.
To update the list, click Refresh.
To print the list, select File, Print.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 11
Tributaries (E1/T1)
The Tributaries Performance Report page displays values measured for the E1/T1 interfaces.
You can configure if the displayed performance covers the last 24 hours, in 15 min intervals, or covers a
month, with daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval.
ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred.
SES is the number of severely errored seconds.
BBE is the number of background block errors.
UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds
(15 minutes).
The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in
the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that
occurred at that time.
To clear the list, click Clear.
To update the list, click Refresh.
To print the list, select File, Print.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 12
STM-1/OC-3
The Tributaries Performance Report page displays values measured for the STM-1/OC-3 interface.
Select PM & Counters, STM1, STM1 #1 (for an E1 board) or OC-3 #1 (for a T1 board).
For Report Interval, you can select either every 15 minutes, or Daily for the list to include values for the
entire day.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 13
MRMC Performance
The MRMC Performance Report page displays 15-minute or daily values of Multi-Rate Multi-Constellation
performance.
Min Profile is the minimum radio profile during the last interval.
Max Profile is the maximum radio profile during the last interval.
Min BitRate (Mbps) is the minimum total radio throughput (Mbps), delivered during the last interval.
Max BitRate (Mbps) is the maximum total radio throughput (Mbps), delivered during the last interval.
Min Number of TDM interfaces is the minimum number of TDM channels (E1/T1) delivered over the
radio during the last interval.
Max Number of TDM interfaces is the maximum number of TDM channels (E1/T1) delivered over the
radio during the last interval.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 14
MSE Performance
The MSE Performance Report page displays the modems Minimum Square Error performance statistics.
The values are for every 15 minutes or daily.
Min MSE is the minimum MSE in dB, measured during the last interval.
Max MSE is the maximum MSE in dB, measured during the last interval.
MSE Exceed is the number of seconds the MSE exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the
table) during the last interval.
MSE Threshold (dB) is the value that will be compared with the current MSE value, to calculate if the limit
was exceeded.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 15
Frame Error Rate
The Frame Error Rate Performance Report page displays statistics of the Ethernet frame error rate (%)
measured on the radio Ethernet port.
Frame Error Rate (%) is the number of received error frames measured by the radio Ethernet port, relative
to all frames received by the radio Ethernet port.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 16
Throughput
The Throughput Performance Report page displays radio Ethernet throughput statistics (excluding TDM
traffic), measured on the radio port.
Peak Throughput (bps) is the maximum throughput measured during the last interval.
Average Throughput (bps) is the average throughput measured during the last interval.
Throughput Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the throughput exceeded the threshold (configured
in the field below the table) during the last interval.
Throughput Threshold (Mbps) is the throughput value that will be compared with the current value, to
calculate if the limit was exceeded.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 17
Capacity
The Capacity Performance Report page displays statistics of the Ethernet capacity (including Ethernet data
and overhead bytes) measured on the radio port.
Peak Capacity (bps) is the maximum capacity measured during the last interval.
Average Capacity (bps) is the average capacity measured during the last interval.
Capacity Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the throughput exceeded the threshold (configured in
the field below the table) during the last interval.
Capacity Threshold (bps) is the capacity value that will be compared with the current value, to calculate if
the limit was exceeded.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 18
Utilization
The Utilization Performance Report page displays statistics of Ethernet utilization (%) measured on the radio
port.
Ethernet utilization is a measurement of actual Ethernet throughput, relative to the potential Ethernet
throughput of the radio (excluding TDM channels). Ethernet utilization during the last interval is displayed
as one of five bins:
1. 0-20%
2. 20-40%
3. 40-60%
4. 60-80%
5. 80-100%
Peak Utilization (%) is the maximum utilization measured during the last interval.
Average Utilization (%) is the average utilization measured during the last interval.
Utilization Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the value exceeded the threshold (configured in the
field below the table) during the last interval.
Utilization threshold (%) is utilization threshold value, which must be configured in the bin resolution
listed above.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 19
Configuration
General
Unit Parameters
This page allows you to view and define information for the IP-10 system.
(Optional) In the System name field, enter a name for the node. By convention, this is the nodes fully
qualified domain name.
In the Slot label field, enter a name for the link. By convention, this is the name and slot label of the unit
across the radio link.
In the IP address field, enter the correct IP address of the unit.
The read-only System Description field provides information about the FibeAir system.
(Optional) In the Contact person field, enter the name of the person to be contacted when a problem with
the system occurs.
(Optional) In the System location field, enter the actual physical location of the node or agent.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 20
The System up time field is read-only and shows how long the system has been operating continuously.
The read-only Voltage input field displays the current input voltage.
In the Measurement system field, select the type of measurement you want the system to use.
In the Date & Time Configuration field, click the calendar to set the date, and click the time area to set the
time. Offset from GMT is the Hours and Minutes offset of the time of day from GMT (Greenwich Mean
Time).
In the Daylight Saving Time area, you can configure the following options:
Start Date - the date when daylight saving time will automatically be activated.
End Date - the date when daylight saving time will automatically be terminated.
Offset (in hours) - the required offeset time, in hours, when daylight saving time is activated.
The read-only IDU/RFU temperature fields display the current temperatures of the IDU and RFU.
The read-only IDU serial/part number fields display the serial and part numbers of the IDU.
The read-only RFU serial/part number fields display the serial and part numbers of the RFU.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 21
Versions
The Versions page summarizes all installed and running versions of the IDU and RFU
IDU Versions
Running Version is the version that is currently running on the IDU.
Installed Version are IDU software files that were successfully installed.
Upgrade Package are IDU software files that were successfully downloaded to the IDU, and are ready to be
installed when IDU upgrade is executed.
Downgrade Package are IDU software files that were successfully downloaded to the IDU, and are ready to
be installed when IDU downgrade is executed.
RFU Installed Versions
These are RFU software packages currently installed in the IDU, as part of the overall software package.
RFU Running Versions
These are software versions that are currently running on the RFU
RFU Upgrade & Downgrade Versions
These are RFU software packages successfully downloaded to the IDU, and ready to be installed when RFU
Software Download is executed.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 22
External Alarms
The External Alarms page enables you to set up the external alarm system.
Alarm Input Configuration (up to 5 independent inputs)
Admin sets the Alarm Input to Active (Enable) or Inactive (Disable).
Text is free text for the alarm description. When an alarm input is raised, this text will appear as the alarm
description text.
Severity is used to configure the alarm's severity. When an alarm input is raised, the severity will be added
to it.
Alarm Output Configuration (single output)
Admin sets the alarm input to active (enable) or inactive (disable), disregarding current raised alarms. This
operation can be used to test the output alarm.
Group is used to configure the group of alarms that will trigger an Alarm Output:
Communication - alarms related to traffic: radio, Ethernet line, TDM line
Quality of Service
Processing - alarms related to software: configuration, resets, corrupted files
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 23
Equipment - alarms related to hardware, fan, RFU mute, power supply, inventory.
Environmental - alarms relating to temperature.
All groups - all of the groups above.
Test mode - manual switch.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 24
Management
The Management page enables you to define local and remote IP addresses and parameters.
In the Local IP Configuration area, enter the IP address of the local unit, its subnet mask, and the default
gateway.
In the Remote IP Configuration area, enter the IP address of the remote unit and its subnet mask.
Click Open Remote to open the remote unit's management page.
In the Management Ports area, for Number of ports, specify the number of ports that will be used for
management data.
For Type, select the management mode of operation - Inband or Out of band.
For Management VLAN ID, specify the VLAN ID that will be used to manage the unit, when the In-band
management type is used.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 25
In-band Management refers to a method in which the network management software sends management
packets through the same network it is managing. This differs from out-of-band management in which the
network management software uses a different network (overlay network) to communicate with the managed
elements.
For Capacity, select the bandwidth that will be allocated to the port(s).
For Auto negotiation, select On to activate the feature, or Off to disable it.
For Rate, select the bit rate you want for the port.
For Duplex, select Half or Full.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 26
Trap Managers
This page is used to configure traps sent from a Network Element to the NMS system.
Each line in the Trap Managers list displays the setup for a manager defined in the system.
To change the setup for a manager, click the plus box at the beginning of the line.
In the Traps admin field, select Enable to activate trap administration.
For Trap manager, specify the IP address to which traps will be sent.
For Manager name, specify the manager's name.
For Trap port, enter the number of the port through which traps will be sent.
For Community, specify the community name for trap forwarding.
For Heartbeat period (minutes) specify the period of the heartbeat trap.
For Trap CLLI, you can enter free text that will be sent with the trap.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 27
For Trap status change filter, select On if you want a trap to be sent to the manager you defined only when
the most-severe alarm of the unit changes. For example, if the most severe status in the system is warning,
and a new warning alarm is raised, no trap will be sent (if you selected On for this option). On the other
hand, if the new alarm has the severity major, a trap will be sent to the manager you defined.
For Filter by severity, select the severity level(s) to determine which types of alarms will be forwarded.
To select/deselect all levels, choose Select All.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 28
Licensing
This page allows you to view and set IP-10 licensing information.
In the Current License area, the following options are available:
License type - Shows the current license type.
License code - The code you enter to allow usage of specific system features.
In the License Features area, the following options are available:
ACM license - Indicates whether or not the ACM feature is available.
Switch application license - Displays the type of switch application.
Capacity -Displays the maximum capacity available for the radio.
In the Demo License area, the following options are available:
Demo admin - Use this option to activate the demo license.
Demo timer - Displays the elapsed time of the demo license.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 29
NTP
This page allows you to view and set IP-10 Network Timing Protocol information.
For Admin, select Enable to activate the NTP client, or Disable to deactivate it.
For Server IP, enter the IP address of the NTP server.
Status shows the current condition of the NTP client, which can be Up or Down.
Sync Server shows the IP address of the NTP server with which the system is currently synchronized.
The values that can appear include:
IP of the remote NTP server
Local, if locked to the local elements real-time clock.
NA, if not synchronized with any clock (valid only when Admin is set to Disable).
Poll Interval is the the interval used by the NTP client to maintain synchronization with the current NTP
server.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 30
IP Table
This page allows you to configure the characteristics of the peer port, which the local port of the element is
connected to.
Each IDU port has its own IP table, allowing the configuration of the characteristics of the peer port to which
it is connected.
For Peer MAC address, enter the MAC address of the peer port.
For Peer IP address, enter the IP address of the peer port.
For Peer Slot ID, enter the slot ID of the element (IDU) the peer port is located in.
For Peer port Number, enter the peer port number.
For Peer Description, you can add a general description of the peer port.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 31
SNMP
This page allows you to configure SNMP parameters.
In the SNMP Version field, select V1 for SNMP V1, or V3 for SNMP V3.
In the SNMP V3 User Settings area, you can configure the following:
Security Mode - determines the SNMPv3 security mode, which can be:
Authentication (default)
Authentication Privacy
No security
Authentication Algorithm - valid only when security mode is not set to No security. The value can be MD5
or SHA.
User name - the SNMPv3 user name.
Password - if a security mode other than No security was selected, you will be prompted for a password,
which has to be at least eight characters.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 32
All ODU
This page allows you to activate support for the All ODU enclosure.
Select Enable for All ODU support, or Disable if your system is not configured as All ODU.
If you select Enable, the All ODU enclosure interface is activated, and the enclosure controller can then be
powered to monitor fan failure alarms.
When the enclosure is enabled, External Alarm Input #1 becomes an output, which together with 3.3V is
used to drive the enclosures electronic board.
External Alarm Input #2 is set with a specific text & severity, and is used to monitor any enclosure fan
failure, and to raise an alarm for it (polarity change was required to adapt it to the enclosure behavior).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 33
Ethernet Switch
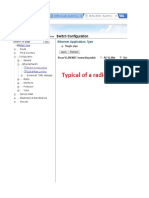
Switch Configuration
FibeAir IP-10 supports Single Pipe and Managed Switch configurations.
Single Pipe is the default method, and does not require a license. The Managed Switch method requires a
license.
Single (Smart) Pipe is the default method, which allows only a single GBE interface for traffic (optical
GBE-SFP or Electrical GBE, 10/100/1000 mbps). Traffic originating from any GBE interface will be
sent directly to the radio and vice versa. This method allows QoS configuration. Other FE (10/100 mbps)
interfaces are "functional" interfaces (WSC, Protection, Management).
Managed Switch is a 802.1Q VLAN-aware bridge, allowing L2 switching based on VLANs. Each
traffic port can be configured as an "access" port or a "trunk" port, as follows:
Type VLANs
Allowed Ingress
Frames
Allowed Egress
Frames
Access
Specific VLAN should
be associated with the
access port
Only untagged frames
(or frames tagged with
VID=0 ("Priority
Tagged")
Untagged frames
Trunk
A range of VLANs or all
VLANs should be
associated with the
trunk port
Only tagged frames Tagged frames
The Managed Switch method allows QoS configuration, and all Ethernet ports are allowed for traffic.
Metro Switch is a 802.1ad Provider Bridge, allowing Q-in-Q switching capabilities. Each traffic port
can be assigned as a "Customer Network" port or a "Provider Network" port. The port attributes are
listed in the following table:
Type VLANs
Allowed Ingress
Frames
Allowed Egress
Frames
Customer
Network
Specific S-VLAN
should be associated
with the customer
network port
Untagged frames or
tagged (C-tag) frames
Untagged frames of
tagged (C-tag) frames
Provider
Network
A range of S-VLANs or
all S-VLANs should be
associated with the
provider network port
Only S-tagged frames,
(in accordance with the
configured "provider
ether-type", which is
0x88a8 by default)
S-tagged frames,
carrying the configured
provider ether-type,
(0x88a8 by default)
Note that S-Tag Ether type can be configured to one of the following values: 0x88a8 (default), 0x8100,
0x9100, or 0x9200.
In theSwitch Configuration page, you can choose the Ethernet switching method.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 34
Choose the method you want, as follows:
Single pipe - Ethernet switching is disabled, whereby only a single Ethernet interface is used for traffic and
the unit operates as a point-to-point microwave Ethernet radio.
Metro switch - To enable Ethernet Q-in-Q provider switch.
LAG Load Balancing can be configured as Simple XOR or HASH.
Simple XOR performs XOR on the last three bits of the Packet Source MAC address (SA) and the
Destination MAC address (DA), and according to the result, selects the link to be used in the LAG.
The HASH mechanism distributes flows across multiple egress ports in a LAG. It uses a proprietary
scrambling function, and uses the last three bits (LSBs) of the DA, SA. This means that two flows with the
same three LSB bits, but different MSB bits, will still go to the same port. Thus, the HASH will simply
distribute more evenly.
In the Unit allowed VIDs area, you can define VLANs for the managed switch, as follows:
In the Operation field, select the operation you want to perform for the VLANs:
Set - to add the VLANs to the database.
Remove - to remove the VLANs from the database.
Change name - to change the VLAN name you specified previously.
Disable - to suspend usage of the VLAN you specified.
Enable - to activate the VLAN you specified.
In the Start/End VID fields, enter the VLAN start and end IDs.
In the Name field, specify a unique name for the VLAN.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 35
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
STP Protocol
This page allows you to configure STP parameters.
This option is available only when the system operates in the Managed Switch mode.
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) ensures a loop-free topology for any bridged LAN. Spanning tree allows a
network design to include spare (redundant) links for automatic backup paths, needed for cases in which an
active link fails. The backup paths can be included with no danger of bridge loops, or the need for manual
enabling/disabling of the backup links. Bridge loops must be avoided since they result in network "flooding".
Note that only Ring RSTP optimized to a ring topology network is supported.
Select either Enable to activate the STP protocol, or Disable to deactivate it.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 36
Ring RSTP
This page allows you to configure RSTP parameters and view status information.
RSTP algorithms are designed to create loop-free topologies in any network design, which makes it sub-
optimal to ring topologies.
In the Ring RSTP Status area, the following information is provided:
Bridge ID - The ID of the bridge in the current monitored IDU.
Root ID - The ID of the root bridge.
Root Path Cost - The cost of the path from the current monitored IDU to the root bridge.
Bridge Role - The role of the bridge, which can be Root or Designated.
In the Ring RSTP Configuration area, you can configure the following:
Priority - The priority of the bridge, which is part of the bridge ID.
In the Ethernet Ports that Support Ring RSTP table, each interface in the IDU can be configured with the
following RSTP parameters:
Priority
Path Cost.
Edge port. This port is not part of the ring itself, and is used as a service access port. Non-edge ports are
those that construct the ring.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 37
QoS & Rate Limiting
The QoS feature allows you to configure classification and scheduling to ensure packets are forwarded and
discarded according to their priority. QoS can be configured for all switch methods (Single Pipe, Managed
Switch, and Metro Switch).
The QoS flow is as follows:
Egress Port #y Ingress Port #x
Calssifier
(4 Queues)
5 Policers
(Ingress
Rate
Limiting)
Queue
Controller
Shaper
(Egress rate
limiting)
Marker Scheduler
The QoS & Rate Limiting page lets you configure Quality of Service parameters for each Ethernet port.
Ingress Classifier
A frame ingressed to a port will be classified according to the following criteria:
1. First Criteria: MAC DA (Destination Address) overwrite. A frame ingressed to a port, carrying a
MAC DA that appears in the Static MAC table (see details below), will be classified, its VLAN Pbits
will be overwritten (assuming the frame egress is tagged) according to the following options:
Disable - No MAC DA classification or VLAN Pbits will be overwritten (no marking).
Queue Decision - There will only be classification to queue. No marking.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 38
VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Only VLAN Pbits will be overwritten (marked). Classification according to a
lower criteria.
Queue Decision & VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Both classification and VLAN Pbits overwrite.
2. Second Criteria: VLAN ID overwrite. If the first criteria is not fulfilled (whether it is disabled, or the
ingress frame does not carry a MAC DA that appears in the Static MAC table), classification and/or
marking (VLAN Pbits overwrite, assuming the frame egress is tagged) will be decided according to the
VLAN ID to Queue table (see below), in accordance with the following options:
Disable - No VLAN ID classification or VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking).
Queue Decision - Only classification to queue. No marking.
VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Only VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking). Classification will be according to
lower criteria.
Queue Decision & VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Both classification and VLAN Pbits overwrite.
3. Third Criteria: If both the first and second criteria are not fulfilled (whether they are both disabled, or the
ingress frame does not carry a MAC DA or VLAN ID that appears in the tables), it will be classified
according to the following configuration:
VLAN Pbits - Classification according to VLAN Pbits. Queue is assigned according to the VLAN Pbits
to Queue table (see below).
IP TOS - Classification according to IP TOS (IP precedence, or IP diffserv). Queue is assigned
according to IP Pbits to Queue table (see below).
VLAN Pbits over IP TOS - Classification according to VLAN Pbits, if the ingress frame carries a
VLAN and has an IP header.
IP TOS over VLAN Pbits - classification according to IP TOS, if the ingress frame carries a VLAN and
has an IP header.
Port (Default) - If any of the above criteria is not fulfilled, the default classification will be assigned to
the ingress frame.
4. Default Classification - The default queue decision.
Classifier Tables (in the Advanced field)
The following tables are available for configuration:
VLAN-Pbits to Queue - Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to
the frames Pbits (CoS), assuming the frame is tagged. The number of table entries is eight (all CoS
legal values).
IP-Pbits to Queue - Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to the
frames IP priority bits (IP-Precedence or Diffserv), assuming the frame is an IP packet. The number of
table entries is:
IP Precedence configuration: 8 entries.
DiffServ configuration: 64 entries.
VLAN-ID to Queue - Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to the
frames VLAN-ID. The number of table entries depends on the number of VLANs that have a "Queue
allocation" definition. By default, VLANs do not have a pre-determined "Queue allocation".
VLAN Pbits Priority Remap - Single table per port. Allows you to remap VLAN-priority bit values 0-
7, to any other preferable value in the range of 0-7. The number of table entries is eight (all CoS legal
values).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 39
Remapping a table can be used to scale down some port priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 3:0), while
at same time scaling up some port priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 7:4), or to ensure that specific
priorities are reserved for specific purposes, by initially remapping all frames away from reserved
priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 4:0, protecting priorities 7:5).
Scheduler - Determines how frames will be output from the queues.
Note that the fourth queue is the Highest Priority Queue, and the first queue is the Lowest Priority
Queue.
The following scheduling schemes are supported:
Strict for all queues.
Strict for fourth queue, and HRR (Hierarchical Round Robin) for third, second, and first queues.
Strict for fourth and third queues, and HRR for second and first queues.
HRR for all queues.
In the HRR scheduling scheme, a weight is assigned to each queue, so that frames egress from the
queues according to their assigned weight, to avoid "starvation" of lower priority queues. In addition,
frames will egress in a "mixed" manner, to avoid "bursts" of frames from the same queue.
Each queue weight can be configured, and the weight will be used by the scheduler when the specific
queue is part of the HRR scheduling scheme.
The queue weight is a value between 1 and 32, and is configured via the Queue Weights table. The
default queue weights are 8,4,2,1.
Shaper - Determines the scheduler rate (egress rate limit). Select ON or OFF. The default is OFF.
Shaper Rate - The following rate steps are available:
For 64 Kbps <=Rate <=960 Kbps, in steps of 64 Kbps.
For 1000 Kbps <=Rate <=100,000 Kbps, in steps of 1000 Kbps.
For 100,000 Kbps <Rate <=1,000,000 Kbps, in steps of 10,000 Kbps.
Policer - Port Ingress Rate Limit. Up to five policers per port can be configured, as follows:
The system supports a color blind leaky bucket scheme.
Each policer has the following parameters:
CIR - Committed Information Rate. Rate limiting resolution:
For 64 Kbps <=CIR <=960 Kbps, in steps of 64 Kbps
For 1000 Kbps <=CIR <=100,000 Kbps, in steps of 1000 Kbps
For 100,000 Kbps <CIR <=1,000,000 Kbps, in steps of 10,000 Kbps
CBS - Committed Burst Size. CBS is CIR-dependent, and should be configured in bytes:
For 64 Kbps <=CIR <=960 Kbps, 0 <CBS <=273,404 bytes.
For 1000 Kbps <=CIR <=100,000 Kbps, 0 <CBS <=132,585 bytes.
For 100,000 Kbps <CIR <=1,000,000 Kbps, 0 <CBS <=4,192,668 bytes.
Data Type - Rate can be limited based on the following data types:
None (no limiting), Unknown unicast, Unknown multicast, Broadcast, Multicast, Unicast,
Management, ARP, TCP-Data, TCP-Control, UDP, Non- UDP, Non-TCP-UDP, Queue1,
Queue2, Queue3, Queue4.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 40
Limit Exceed Action:
- Discard frame.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
Policer List
Click Policer List in the Advanced options area at the bottom of the QoS & Rate Limiting page.
This page enables you to add policy rules to a policer.
Operation - add or delete the policer.
Policer Name - assign a general purpose name for the policer. Note that the name cannot include spaces
(you can use underscores instead).
It is possible to configure up to five policy rules per policer.
When a policer definition is completed, it can be associated with any port, by attaching its name to the port.
This will enforce all policy rules of the policer on the port.
If a policer is attached to a port, you can use the detach command to remove the policer (and all its policy
rules) from the port.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 41
Static MAC
Click Static MAC in the Advanced options area at the bottom of the QoS & Rate Limiting page.
This table is used to load static MAC addresses to the forwarding table of the switch.
The static MACs are never flushed.
VLAN ID is the ID of the frame. Each frame is attached with a VLAN ID. Frames are learned and filed in
the static MAC table under their VLAN ID.
Static MAC is the 48-bit MAC address, in octet format (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx).
Forward to indicates which port the frame will be forwarded to.
Priority sets the classification and/or VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking), according to the QoS configurations
(see QoS & Rate Limiting page above).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 42
Radio
The Radio menu includes the Radio Parameters and Radio Thresholds items.
Radio Parameters
In this page, you can configure how the radio operates.
In the Status Parameters area, the following options are available:
RFU type - The RFU used in the system (1500HP, RFU-C, other).
Tx/Rx frequency separation - Read-only, Tx/Rx separation values.
Tx/Rx level - Read-only, current Tx/Rx level values.
MSE - Mean Square Error value, which quantifies the performance of the receiver.
Defective blocks - Amount of blocks in which errors were detected. The larger the amount, the poorer
the radio link quality.
In the Frequency Control area, the following options are available:
Tx/Rx frequency - Used to select the desired band.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 43
Set also remote unit - Used to set the remote unit with the specified local unit values.
In the Configuration Parameters area, the following options are available:
ATPC - To enable/disable the ATPC (Automatic Transmit Power Control) mechanism.
ATPC reference RSL - The RSL reference value for the ATPC mechanism.
Mute Tx - To enable/disable Tx muting.
Max Tx level - The maximum operational Tx value.
Link ID - The identification number of the link. When working with an IDU that has the Link ID feature
on one end and an IDU that does not have this feature on the other end, set the Link ID to 1.
Mac header compression - Radio transmission (compared with Fiber optics and other line base links)
has limited bandwidth and compression is required to improve available capacity utilization.
The benefit of using MAC header compression is that it can be used as a supplement to the other without
affecting traffic performance.
Ceragon proprietary MAC Header compression improves the effective throughput by up to 45%, and
does not affect user traffic.
MAC header compression is based on the following:
Dropping the Preamble +SFD +IFG saves 20 bytes
Dropping the Ethernet type saves 2 bytes
Adding a GFP header adds 4 bytes
In addition:
Frequently repeating SA & DA are learned
Learned DA & SA are not transmitted
A short pointer is used instead of the original 12 bytes
Note that effectiveness is reduced if a high number of L2 flows is used.
The capacity reached after header compression, in accordance with the Ethernet packet length, is as
follows:
Ethernet
Packet Size
Capacity after
Compression
64 45%
96 29%
128 22%
256 11%
512 5%
To reset the counters, click Clear Counters.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 44
Remote Radio
In this page, you can configure how the remote radio operates.
Remote communication - The current communication status of the remote unit.
Remote IP address - The IP address of the remote unit.
To open the remote radio configuration, click Open Remote.
Remote Rx level - The current Rx level of the remote unit.
Remote force max Tx level - Used to force the remote unit maximum transmit level.
To unmute the remote unit transmitter ouptut, click Force Unmute.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 45
Radio Thresholds
In this page, you can configure radio threshold levels.
For Radio excessive BER threshold, click the drop-down list and select the level above which an excessive
BER alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link.
For Radio signal degrade threshold, select the level above which a Signal Degrade alarm is issued for
errors detected over the radio link.
The Radio BER field is read-only and shows the value above which a BER alarm is issued for errors
detected over the radio link.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 46
MRMC Configuration
In this page, you can configure MRMC script parameters.
Configuration
MRMC Scripts displays the current selected radio script.
Occupied bandwidth (MHz) displays the actual bandwidth occupied by the radio signal. This should not be
confused with Channel Spacing, which indicates the allocated bandwidth for the RF channel.
Operational mode can be ACM Adaptive, ACM Fixed, Regular (non ACM radio script).
Max adaptive ACM profile is the maximum configured profile that will never be exceeded when ACM is
active.
Current TX
ACM adaptive profile indicates the current ACM profile used for transmission.
QAM indicates the current modulation used for transmission.
Bitrate indicates the current transmitted bit rate, in Mbps.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 47
Current RX
ACM adaptive profile indicates the current ACM profile used by the receiver.
QAM indicates the current modulation used by the receiver.
Bitrate indicates the current receiving bit rate, in Mbps.
MRMC Table
This table contains all available radio scripts.
Select the desired script and mode (ACM/Non-ACM). ACM scripts can be distinguished from regular scripts
by their ACM prefix.
When you expand the line of the selected script (by clicking the +) all available options for the selected
script will appear.
For regular scripts (non-ACM), expand the line (by clicking the +), and then click Apply.
For ACM scripts, expand the line (by clicking the +).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 48
Two options are available for ACM scripts:
ACM Fixed Mode
In this mode, the ACM engine will be disabled. To select a desired profile, expand the line (click the +),
and choose the profile. The radio will use only the profile you selected.
ACM Adaptive Mode (shown in the page below)
In this mode, the radio will be adaptive, and the ACM engine will be enabled. To select a maximum
profile, expand the line (click the +), and select the profile. The profile is the maximum that the ACM
may reach, but never exceed.
When configuring ACM script with Aadaptive Mode, you can determine whether or not the RFU power
will be adaptive as well.
In the Adaptive Power admin field, enable or disable the capability to adapt the power.
In the Reference class field, configure the system reference class, which can be "Class-2/4/5B/6A"
for ETSI, or FCC for FCC.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 49
ACM can operate in one of two scenarios:
a. Increase capacity (increase throughput)
b. Increase availability
The first scenario is for customers with links of several E1s in a low class, and now want to use ACM to add
Ethernet traffic with lower availability.
The second scenario is for customers who plan the link for a specific availability and capacity, but want
lower capacity even in higher fades.
In the first scenario, the user will plan the link according to low class channel, and when the condition
allows, the link will increase the modulation. This increase of modulation may require lowering the output
power to decrease the non-linearity of the transmitter for the higher constellations.
Adaptive power options can be enabled or disabled. If disabled, the maximum tx power in lower
constellations is limited by the highest modulation. If enabled, the maximum tx power in lower
constellations is limited by the reference class configured, as listed in the following table.
Reference Class
Configuration
Reference QAM
Class2 4
Class 4 16
Class 5B 64
Class 6A 256
FCC 4
If the adaptive feature is used, a few critical dBs can be gained in the lower constellations.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 50
Interfaces
Ethernet Ports
In this page, you can configure Ethernet port parameters.
In the Managed Switch, Metro Switch, or Single Pipe Ethernet Ports area, you can configure the
following:
In the Port admin field, select Enable if you want to activate the port.
In the Type field, the option depends on the Ethernet application, which may be
Single Pipe is not a valid field.
Managed Switch - option can be Acess or Trunk.
Metro Switch - option can be Customer Network or Provider Network.
For Default VLAN ID (not used in the single pipe switch application), enter the VLAN ID number.
For Flow Control (used only in the single pipe switch application), select On or Off to activate or deactivate
the traffic control mechanism.
Rate is read-only and displays the Ethernet rate.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 51
Actual Rate is read-only and displays the rate the port is actually converged to.
For Auto Negotiation, select On if you want the system to control the flow of data.
For Duplex, select full or half duplex.
Actual Duplex is read-only and displays the duplex type the port is actually converged to.
Operational Status is read-only and indicates whether or not the port is operating.
Automatic state propagation - This feature enables propagation of radio failures back to the line, to
improve the recovery performance of resiliency protocols (such as xSTP). You can enable or disable this
feature.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 52
Click Create Lag port to define a LAG port group.
Link aggregation allows the user to group several ports into a single logical channel bound to a single MAC
address. Traffic sent to the ports in such a group is distributed through a load balancing function. The group
is called a LAG.
There can be up to three LAG groups per IDU. Only traffic ports (including a radio port) can belong to a
LAG group. The following groups of ports can be in the same LAG (ports from different groups cannot be in
the same LAG):
Ports 1-2 and 8 (GBE ports and radio)
Ports 3-7 (FE only ports)
To add or remove ports in the LAG group, select the desired port in the window. Ports selected for the LAG
group are highlighted; and ports selected for deletion are cleared in the window.
The system will not allow selection of ports with different configurations (such ports will not be
highlighted).
Ports removed from a LAG will remain with their existing parameters, but will be initially disabled to
prevent loops.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 53
Deselecting all ports will clear the entire LAG port.
A LAG port can be configured as LAG #1, #2, #3, since there can be up to three LAG ports in the system.
When a LAG is created by adding a first port to it, the LAG will automatically inherit all characteristics of
the ports, except for the xSTP role (edge, non-edge), and the path cost. The LAG will initially receive default
values for those parameters.
In the Configuration page, the lag ports are listed as shown in the following example:
In the Advanced line, you can click Allowed VIDs to assign VIDs to the LAG.
LAG Group Notes:
For GBE LAG groups, both interfaces must be of the same type (electrical/optical).
A radio port can be in a LAG with either electrical or optical line ports.
All ports in a LAG group must be of the same data rate (10, 100, or 1000 Mbps).
A GBE LAG group may include the radio port.
The configurations must be identical in all ports before adding them to the LAG logical port.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 54
In the Fault Criteria area of the Ethernet Ports page, the following options allow you to determine
which faults should be propagated back to the line:
Local LOF - When Automatic State Propagation is enabled, an LOF (Radio Loss of Frame) fault
will always be propagated.
Link ID Mismatch - When Automatic State Propagation is enabled, a Radio Link ID mismatch
fault will always be propagated.
Ethernet shutdown Rx profile threshold - When ACM adaptive mode is active, you can
determine an Rx profile that will be considered a fault when the radio performance degrades
below that profile.
Local Excessive BER - When an Excessive BER alarm is raised locally, it will be propagated as
a fault.
Local LOC - When a Loss of Carrier alarm (only for optical GBE interface) is raised, it will be
propagated as a fault.
Remote Fault - If any of the events described above occurs at the remote (remote fault), it will be
propagated locally as a fault.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 55
E1/T1 Ports
In this page, you can configure E1/T1 port parameters.
In the All Ports area at the top of the page, the parameters you can configure include the following:
Line code - Click the drop-down list and select the line coding you want for the port.
Excessive BER threshold - Click the drop-down list and select the level above which an excessive BER
alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link.
SD threshold - Click the drop-down list and select the level above which a Signal Degrade alarm is
issued for errors detected over the link.
Click the plus sign at the beginning of an E1/T1 line to configure parameters for that specific port.
The parameters include:
Port admin - To activate or deactivate the port.
Cable length - Select the length of the cable used to connect to the interface.
Priority -Specify the priority of the interface to determine when it will be dropped, if the radio capacity
decreases.
Current BER (read only) - Measured BER on the interface.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 56
AIS Detection - This column appears if AIS Detection Admin is enabled. This column shows if AIS is
detected in incoming traffic at any E1 line interface.
To activate all the ports in the list, click Enable All.
To deactivate all the ports in the list, click Disable All.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
E1/T1 T-Card
The T-Card is not a stand-alone entity within the IP-10 IDU. When inserted in the system, the new interfaces
become integral interfaces of the IP-10.
As an example, if you insert a 16 x E1 T-Card in the IDU, no special menu will appear for it. Instead, E1s
#17-32 will be added to the existing 1-16.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 57
STM-1/OC-3 (T-Card)
IP-10 with STM-1/OC-3 T-Card
To configure the STM-1/OC-3 T-Card interface, do the following:
1. Click in the area of the STM-1/OC-3 interface, or, from the menus on the left side of the window, select
Configuration, Interfaces, STM1 Ports (for an E1 board) or OC-3 Ports (for a T1 board).
The following window appears:
2. Fill in the fields as follows:
Admin - Select Enable to activate the interface, or Disable to deactivate it.
Mute Tx - Used to force mute or unmute the T-Card interface. If muted, the radio will still receive
signals, but will not transmit any.
Clock Source - the clock source used, which can be Internal clock, Loop, or STM-1 VC.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 58
The clock source and the clock source status may be different when the configuration does not match
the current clock source in use, due to the signal failures listed below.
If you choose Internal Clock (the default option), the quality will be SMC/SEC (ITU-T G.813).
If you choose Loop (CDR mode), the signal clock source will be taken in accordance with the
following table:
# LOF from Framer
LOS from
Optics
Mode of Operation Clock Source
1 LOF LOS Free run/holdover Local clock
2 LOF NO LOS Free run/holdover Local clock
3 NO LOF LOS N/A Local clock
4 NO LOF NO LOS Lock mode (loop timing) CDR
If you choose STM-1 VC, the signal will be synchronized to the signal clock derived from a TDM
trail. The clock will be taken from the first VC-12 configured in the STM-1 port.
There is no web support for this, but there is a way to change the VC source through the CLI using
the following commands:
cd interfaces/sdh/stm1/
get sync-vc (shows the VC that the system will use as the clock and sync)
Set sync-vc XX (XX =VC number)
AIS VC Signalling Admin - when enabled, if a signal failure at the trail outgoing from the STM-1
interface occurs, the system will signal AIS at the VC level (AIS-V) in the V5 byte of the overhead.
Line Tx Protection Mode - If you choose Normal, the system will behave regularly when configuring
the system to 1+1 with the STM-1 card. The redundant STM-1 will not transmit signals unless the
primary IDU performs a switch due to a failure. Choose Uni-direction MSP when the system is
configured for 1+1 with STM-1 cards. Both cards will transmit, and the decision of which will actually
function, will be decided by other equipment connected to it.
Received Trace Identifier - Read-only field. The received trace identifier, used to verify ongoing
connection to the transmitter.
Transmit Trace Identifier - The trace identifier used to verify ongoing connection to the receiver.
Expected Trace Identifier - The trace identifier that will be used to verify ongoing connection to the
remote side of the link.
Trace Identifier String Length - Can be between 1 and 15 characters.
Excessive BER Threshold - The value can be 1e-3, 1e-4, or 1e-5.
Signal Degrade Threshold - The value can be 1e-6, 1e-7, 1e-8, or 1e-9.
AIS Status on VC12 - If AIS Detection Admin is enabled, this section will appear in the page. The table
shows if AIS is detected in incoming traffic at any VC-12, from the STM-1 interface.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 59
Wayside Channel
In this page, you can configure wayside channel parameters.
The parameters you can configure include:
Wayside admin - select Enable if you want to activate the channel.
Capacity - select Narrow or Wide for the wayside channel capacity.
Auto negotiation - select On if you want the system to control the data flow between the wayside
channel and other ports activated in the system.
Duplex - select full or half duplex.
Rate - select the data rate for the port.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 60
User Channel
In this page, you can configure user channel parameters.
Admin - To enable or disable the user channel.
Type - Two user channel types are available:
Asynchronous RS-232
Asynchronous V.11
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 61
EOW
This page displays the EOW channel status.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 62
AIS
This page is used to enable/disable AIS Line Detection.
If enabled, a signal failure is generated at the corresponding trail, which will cause the far end not to receive
a signal (including trail ID indications). The trail status will show signal failure. In addition, an indication
is sent to the relevant interface.
Note that this is not a system alarm, since the problem originates elsewhere in the network.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 63
Protection
1+1 Protection
In this page, you can configure IP-10 1+1 protection parameters.
Protection Configuration
Protection admin - Used to enable or disable 1+1 protection.
Protection mode - Shows if the unit is Active or Standby.
Mate Parameters
Mate IP address - the IP address of the mate unit.
Mate MAC address - the MAC address of the mate unit.
Open Mate - a link for opening the remote mate unit.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 64
Protection Switch Criteria
External alarm #1 admin (enable/disable) - initiate a switchover when external alarm #1 is raised.
Radio excessive BER admin (enable/disable) - initiate a switchover when a radio excessive BER
alarm is raised. This option is valid only when the MRMC script is regular or ACM running in Fixed
mode.
Protection Commands
Protection Lockout - freeze the current protection state.
Protection force switch - force a protection switchover and then freeze the protection state.
Manual Switch - issue a switchover, which will take affect when no other protection related alarms
are raised.
Copy to mate - copy all configurations to the mate unit (configuration synchronization between
local and mate).
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 65
Trails
TDM Trails
This page is used to configure the FibeAir
IP-10 Cross Connect (XC) system for operation.
FibeAir IP-10 Cross Connect system serves as a node in a microwave radio network.
The system is designed to comply with requirements of a node in a network that aggregates several sites
(downlinks) into a radio pipe (uplink). It can also be deployed in a mesh network configuration.
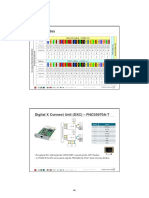
The system consists of up to six IDUs placed together in a single chassis, for TDM traffic cross connect.
Up to Six IP-10 IDUs Installed in a Nodal Enclosure
Once the IDUs are linked through the common backplane (as shown in the photo above), the XC system is
constructed by building trails.
To configure the trails for Cross-Connect operation:
1. Start the IP-10 Web Management application.
The following web page is an example of the IP-10 IDUs that appear in a nodal configuration.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 66
Note: Trail building is only done via the Main IDU (Slot 1 at the bottom). However, you can select any other
IDU to set other configuration parameters for all the othe IDUs in the shelf.
2. On the left side of the main window, select Configuration, Trails, TDM Trails.
Initially, the page that appears is empty.
3. Click Add, to create a new trail.
The Add New Trail window appears.
4. To select the E1/T1 ports for the trail, in the Add New Trail window, click the E1/T1 interface in any
IDU, and select the E1/T1, as shown in the example below.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 67
For STM-1/OC-3 trails, the window appears as follows:
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 68
To select the VC number you want to assign to the trail, click the RF interface in any IDU, as shown in
the example page above.
5. Continue the trail configuration using the following options in the Add New Trail window:
Protected - Select Yes if you want a secondary trail to cover for the main trail if it fails.
If you chose Yes for Protected, a second interface will appear in the Add New Trail window, as follows:
Trail ID - Enter the ID of the trail. This ID is used to ensure that the flow of data over the link matches
the trail designations.
Trail Description - Enter a textual description of the trail for further identification purposes.
ACM Priority - Adaptive Coding & Modulation employs the highest possible modulation during
changing environmental conditions, which may be from QPSK to 256 QAM. If you select High for
priority, the system will ensure that this trail is used to pass traffic when throughput for other trails is less
efficient.
Active/Reserved - Set the trail to Active, to enable its operation. If you want to define the trail, but keep
it inactive for the time being, select Reserved.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 69
Important Notes
For the trail to function properly, it must be configured accordingly on both sides of the link.
If a unit (IDU) is disconnected from the nodal enclosure and ceases to function as part of the shelf
configuration, the removal will be acknowledged as an alarm.
The IDU can then function as a stand-alone unit, using a "default" E1/T1 configuration.
You can configure E1/T1 ports in the E1/T1 Ports page:
However, note that you do not enable the ports in this page.
The ports are enabled only in accordance with the trails that you configure, as described in this guide.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 70
Connected Ports
The following is an example of connected trail ports and their system status.
Example of Trail List for the E1/T1 Interface
Example of Trail List for the STM-1/OC-3 Interface
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 71
Cross Connection at the KLM Level
Cross connection at the KLM level operates the same way as that for E1s.
When a trail is defined, you can choose one of the interfaces to be an STM-1 VC-12.
Note that in the CLI (Command Line Interface), this is done by setting the interface type to STM1 instead of
Line.
For example, for a trail between VC#1 in the radio and VC-12 #1 in the STM-1 interface of slot number one,
you would use the following command:
add- t r ai l i d1 desc1 hi gh oper at i onal unpr ot ect ed 1 st m1 1 1 r adi o 1
As with other interface types, the number after the interface type represents the interface number.
For STM-1, this means which VC-12 to use. The KLM slot to be used corresponds to the VC number
chosen, as specified in the ITU-T G.707 clause 7.3 standard.
The following table summarizes:
Thus, for example, interface number 35 corresponds to TS#35 in the above table, which is KLM address 252
(TU-3#2, TU-2#5, TU-12#2).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 72
Service OAM
MAID List
MAID (Maintenance Association Identifier) is an identifier for a Maintenance Association, unique over the
domain that CFM is to protect against the accidental concatenation of service instances. The MAID has two
parts: the Maintenance Domain Name and the Short MA Name.
MAID List Columns
# is the domain number (internal number of the displayed function).
Status is the status of the current domain, which can be one of the following:
No Meps - only MAID configured, no MEPs. This state is used for empty domains, before defining
MEPs, or for a domain that contains only MIPs.
Monitoring - CFM (CCM) - proactive monitoring is running, no error found.
Failure - connectivity error in at least one MEP.
Domain name is the maintenance domain name.
Level is the maintenance domain level.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 73
Association name is the maintenance domain association name.
VLAN ID is the identification #of the VLAN
Send CCM shows the CCM status:
Disable - no continuity (CCM) frames are sent from the local MEP to remote MEPs.
Enable - continuity (CCM) frames are sent from the local MEP to remote MEPs.
CCM interval is the (periodic) time interval during which CCM messages are sent. Valid values include
1Sec, 10Sec, 1Min, and 10Min.
Note: Click the +in each MAID entry for more options.
MAID List Operations
Click Add to add a new MAID.
In the Add Maid window, for Domain name specify the maintenance domain name.
Level is the maintenance domain level.
Association name is the maintenance domain association name.
VLAN ID is the MAID VLAN ID.
To delete a MAID, mark the checkbox at the end of its line, and click Delete selected.
Click Refresh to refresh the page.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 74
MAID List MEPs
Local MEP
Add - add new local MEP.
Level- Specify the MAID domain level.
VLAN ID - Specify the MAID VLAN.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 75
Ethernet port - Select the port number on which the local MEP is located.
Local MEP ID - The ID of the MAID local MEP.
Direction - The local MEP direction.
Priority - The Pbit priority that the CCM message carries.
Delete selected - delete the selected local MEP.
Local MEP Columns:
MEP ID - the local MEP ID.
Direction - MEP direction (up or down).
Ethernet port - the Ethernet port the MEP is located on.
MAC address - Ethernet protection MAC address.
Priority - the Pbit priority that the CCM message carries.
LDI - Local Defect Indication. If the value Yes, a +in the right corner of the table describes the
reasons for this bug.
Connected - Local MEP connection status.
CCM Configuration
Send CCM - Select Disable if you don't want continuity messages (CCM) sent over the specific MAID.
Select Enable if you want continuity messages (CCM) sent over the MAID.
CCM Interval - Set the MAID time interval, which can be 1 second, 10 seconds, 1 Minute, or 10 Minutes.
Remote MEP
Add - add new remote MEP.
Domain name - Maintenance domain name (appears automatically to prevent errors).
Vlan ID - MAID VLAN (appears automatically to prevent errors).
Remote MEP ID - the ID of the remote MEP.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 76
Remote MEP Columns:
MEP ID - the remote MEP ID.
Actual MAC address - the MAC address of the remote MEP, which the local MEP recognizes.
Configured MAC address - used when you decide to specify a selected MAC address for the remote
MEP.
Status - the local MEP connection status.
Cross Check - indicates if the current remote MEP was cross checked (pre-configured) or learned from
incoming CCMs.
RDI - Remote Defect Indication.
Ping - run ping (loopback) from the local MEP to a specific remote MEP ID by clicking the ping icon.
The upper part of the window provides a short summary of the MAID and the remote MEP
being pinged.
The lower part shows the ping success rate percentage (LBM packet transmission over the
received LBR packets).
Checkbox - used to delete the selection or issue a linktrace (ETH-LT) command from the local MEP to
the current remote MEP.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 77
Linktrace
Mark a remote MEP checkbox (only one) and click Linktrace, to trace the link.
The upper part of the window provides a short summary of the MAID and the Remote MEP being traced.
In the Linktrace Hops table:
Reply TTL shows the hop number.
Mac Address shows the hop (MEP/MIP) MAC address.
Relay Action shows the hop LTM releay action.
Note: You can click Ping to ping a particular hop.
Automatic Link-trace results appear at the bottom of the page. The table is refreshed automatically every
fixed period of time (configurable, set to 15 min by default), displaying the last updated date and time.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 78
MEP & MIP List
This page shows in which Ethernet port the user defined an MEP or MIP.
Table Columns:
Ethernet port shows the Ethernet port number.
MAC address shows the Ethernet port MAC address.
Connector type shows the Ethernet port connector type.
Function shows the Ethernet port function.
MEP or MIP defined is marked with a check when you define an MEP or MIP on this port.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 79
Additional MEP/MIP Configuration
Click the +beside a line for additional MEP/MIP configuration on the current port.
Add MEP
Click the Add button to add new local MEPs on the port.
Ethernet port is the port you will be adding (appears automatically to prevent errors).
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 80
Local MEP ID is the ID of the local MEP (appears automatically to prevent errors).
For Level, select the MAID level.
VLAN ID is the MAID VLAN (appears automatically to prevent errors).
For Direction, select the MEP direction (up or down).
For Priority, select the Pbit priority that the CCM message carries.
Add MIP
Click the Add button to add MIPs from specific levels.
Ethernet port appears automatically to prevent errors.
For Level, select the MIP level.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 81
Advanced
Under Service OAM in menu list on the left side of the window, click Advanced for additional MEP/MIP
operations.
Manual Ping
Click the Manual Ping item to send a ping to the remote MEP/MIP.
MAC address is the target MEP/MIP MAC address.
Level is the MAID level.
VLAN ID is the ID of the VLAN.
Priority is the Pbit priority bit for the outgoing ETH-LBM packets.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 82
Manual Linktrace
Click the Manual Linktrace item to send a linktrace command to the remote MEP/MIP.
MAC address is the target MEP/MIP MAC address.
Level is the MAID level.
VLAN ID is the ID of the VLAN.
Priority is the Pbit priority bit for the outgoing ETH-LTM packets.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 83
Diagnostics & Maintenance
Radio Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for a radio loopback test.
The parameters you can configure include:
Timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run.
IF loopback - select On if you want to perform an IF test.
RFU RF loopback - select On if you want to perform an RFU RF test.
To apply any change you made and start the test, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 84
Line Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for a PDH loopback test.
The parameters you can configure include:
Timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run.
# loopback - for each line interface, select On if you want to perform a loopback test, Off if you don't
want to perform a test for that line, or Loopback towards radio to test the radio data flow.
To apply any change you made and start the test, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 85
SDH Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for an SDH loopback test.
Timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run (in minutes).
Line Loopback - select Enabled if you want to perform a loopback test, or Disabled if you don't want to
perform a test for that line.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 86
Configuration Management
In this page, you can perform system configuration operations.
Uploading
Uploading a configuration involves the following steps:
1. Create archive - This command creates a default archive in the target (IDU). The IDU configuration will
first be copied to this location.
2. Upload Archive - Uploading the IDU configuration to the host PC.
In theUpload Status & Commands area:
Config creation status - indicates whether or not the configuration file was created successfully.
Config upload status - indicates whether or not the configuration file was uploaded successfully from
target to host.
Configuration:
Click Create Archive to create the requested archive file on the target.
Click Upload Archive to upload the archive file on the host.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 87
Unit Information:
Click Create Archive to create the requested archive file on the target.
Click Upload Archive to to upload the archive file on the host.
Downloading
This option allows you to download uploaded files from a host (such as a PC) to the target (IDU).
Downloading a configuration involves three steps:
1. Download archive - This command copies the configuration file from the host to the target.
2. Install archive - This command installs the configuration file, which will be operational only after a
hardware reset.
3. HW reset - When the system is up and running, the new downloaded configuration will be valid.
In theDownload Configuration Status & Commands area:
Config download status - indicates indicates whether or not the configuration file was downloaded
successfully from host to target.
Config install status - indicates whether or not the configuration file was installed successfully on the
target.
Click Download Archive to download the archive file from the host to the target.
Click Install Archive to install the requested archive file on the target.
In theConfiguration Management Parameters area:
Host IP - IP of the host where the archive is to be stored.
Host path - path in the host (FTP directory) where the archive is to be stored. For the default FTP
path use set // for Windows, or set / for Linux.
User name - the user name for the FTP session.
User password - password for the FTP session. If you use the default user name (anonymous), use the
host login for the password.
In the Set to Default Configuration area:
Click Activate to set the unit to the default configuration.
To apply changes you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 88
Software Management
In this page, you can perform system software operations.
In the Software Management Status & Commands area:
Status download - last software download status.
Status install - last software installation status.
New Version:
Click Download to download newer packages from the remote server (without installation).
Click Upgrade to upgrade all installed or requested packages.
Click Rollback to undo the recent IDU application upgrade operation (one step back).
CAUTION!
Packages are still upgraded after a rollback is applied to the IDU!
Note:
Rollback does not reverse a "downgrade" operation. To do so, use the "upgrade" command instead.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 89
Old Version:
Click Download to download a package file for downgrade.
Click Downgrade to install all downloaded files (for downgrade). The downgraded version will be
activated only after a cold reset.
In the Remote Server Parameters area:
Remote SW update server URL - remote software update server URL, where the software updates
reside.
Remote server login - login for the remote server.
In the Proxy Server Parameters area:
Proxy URL - URL of the proxy.
Proxy user name - user name passed to the proxy.
To apply changes you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 90
RFU Download
In this page, you can perform RFU software download.
To perform the download, click Software Download.
RFU software download status - shows the current state of RFU software download.
RFU software download progress - shows the download progress.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 91
IDU-RFU Interface Monitoring
In this page, you can monitor the IDU-RFU traffic.
RFU receiver errors - monitors IDU-RFU interface errors detected by the RFU.
IDU receiver errors - monitors IDU-RFU interface errors detected by the IDU
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 92
Resets
In this page, you can perform a reset operation.
Cold System Reset - Click Reset to reset the IDC.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 93
File List
This page displays all application related files on the disk.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 94
Security
Security Configuration
In this page, you can configure IP-10 security.
Upload public key status - The current status of the uploading process.
Upload public key (button) - Click to upload the public key of the element.
Download security status - The current status of the digital certificate download process.
Download certificate (button) - Click to download the Target certificate (WEB server digital
certificate) or Target ca certificate (WEB CA digital certificate) to the element.
Download Certificate Parameters
Security file name - Name of the digital certificate file.
Security file type - The digital certificate type. The options include "Target certificate" for WEB
server digital certificate, or "Target ca certificate" for WEB CA digital certificate.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 95
Security file format - The format of the downloaded digital certificate. Options include Pem or
Der.
WEB CA certificate - Select Enable if the downloaded file is WEB CA digital certificate or
Disable if the file is "WEB server digital certificate".
Security Parameters
WEB Protocol - Determines whether the Web protocol is HTTP or HTTPS (Secured HTTP).
Telnet protocol admin - Allows you to enable or disable the telnet protocol.
Automatic logout period - The amount of minutes the system will wait for web activity before
closing the management session.
FTP parameters Link - Use this link to configure FTP parameters.
To apply any change you made, click Apply.
To update the information, click Refresh.
FibeAir
IP-10 Web Based Management Guide 96
Users & Groups
This page displays the users and groups defined in the system.
Click Add User to create a new user to the element.
In the Add a user ewindow, enter the following information:
User privilege - Can be one of the following:
Viewer - This user cannot configure parameters, but only view them.
Operator - This user can configure all parameters in the system, except for security-related
parameters (such as adding privilege groups).
Admin - This user has all Operator privileges, as well as the ability to add new users.
Tech (technician) - Has all Admin privileges, as well as access to the Linux OS shell.
User name - The name you want the user to have.
Password - The password that will authenticate the user.
Вам также может понравиться
- UI Academic Positions in Agriculture, Arts & MoreДокумент21 страницаUI Academic Positions in Agriculture, Arts & MoreAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Evolution E1 Colour CodeДокумент1 страницаEvolution E1 Colour CodeAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Creative Writing Lesson Plans for All LevelsДокумент8 страницCreative Writing Lesson Plans for All LevelsAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- NSE Acknowledge FormДокумент1 страницаNSE Acknowledge FormAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- IP 10g ConfigДокумент36 страницIP 10g ConfigAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- List of 38 Candidates admitted into Nigerian Army UniversityДокумент12 страницList of 38 Candidates admitted into Nigerian Army UniversityAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- List of 38 Candidates admitted into Nigerian Army UniversityДокумент12 страницList of 38 Candidates admitted into Nigerian Army UniversityAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Ceragon Availability PatternДокумент3 страницыCeragon Availability PatternAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- GED Test Prep FullДокумент592 страницыGED Test Prep Fullpcalver200095% (21)
- Lesson Plan: Unit 1 Arithmatics ObjectivesДокумент5 страницLesson Plan: Unit 1 Arithmatics ObjectivesAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- 300-101 Latest Dumps - Real Exam Questions 2018Документ2 страницы300-101 Latest Dumps - Real Exam Questions 2018Atanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- COREN Assembly Invitation LetterДокумент1 страницаCOREN Assembly Invitation LetterAnene EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- SPECIAL REPORT - How National Assembly Forced Buhari To Divert N121 Billion Meant For Poor NigeriansДокумент7 страницSPECIAL REPORT - How National Assembly Forced Buhari To Divert N121 Billion Meant For Poor NigeriansAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- (Vol - Ii) Microwave Filters, Impedance-Matching Networks, and Coupling StructuresДокумент572 страницы(Vol - Ii) Microwave Filters, Impedance-Matching Networks, and Coupling Structuressuchit91Оценок пока нет
- The CORRECT Nigeria Zip Code: Have A Look at A List of All Nigeria's Post CodesДокумент3 страницыThe CORRECT Nigeria Zip Code: Have A Look at A List of All Nigeria's Post CodesAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Math Review Number SystemДокумент16 страницMath Review Number Systemapi-19803639Оценок пока нет
- LOS On All Interfaces at B4484 16102018Документ15 страницLOS On All Interfaces at B4484 16102018Atanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Scribed ViewerДокумент1 страницаScribed ViewerAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Middle School Debate TopicsДокумент7 страницMiddle School Debate TopicsAtanda Babatunde Mutiu100% (3)
- Math Review Number SystemДокумент16 страницMath Review Number Systemapi-19803639Оценок пока нет
- SPECIAL REPORT - How National Assembly Forced Buhari To Divert N121 Billion Meant For Poor NigeriansДокумент7 страницSPECIAL REPORT - How National Assembly Forced Buhari To Divert N121 Billion Meant For Poor NigeriansAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Festus KeyamoДокумент1 страницаFestus KeyamoAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Research and Development of Computer Aided - FinalДокумент12 страницResearch and Development of Computer Aided - FinalAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Sule Lamido's Comments on Buhari Reveal Ethnic Supremacism That Could Destroy NigeriaДокумент7 страницSule Lamido's Comments on Buhari Reveal Ethnic Supremacism That Could Destroy NigeriaAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- TOEFL Order Receipt ConfirmationДокумент2 страницыTOEFL Order Receipt ConfirmationAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Upgrade 9600 LH System with MPT-HL Extendable TechnologyДокумент26 страницUpgrade 9600 LH System with MPT-HL Extendable TechnologyAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- Why UK Fraud Office Isn't Prosecuting Billionaire Indimi's Oil Firm Named in Criminal ConvictionДокумент7 страницWhy UK Fraud Office Isn't Prosecuting Billionaire Indimi's Oil Firm Named in Criminal ConvictionAtanda Babatunde MutiuОценок пока нет
- 9500 MPR Long Haul - Training I&C R5.1 DraftДокумент49 страниц9500 MPR Long Haul - Training I&C R5.1 DraftAtanda Babatunde Mutiu100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test v6.2Документ10 страницDiagnostic Test v6.2Michał JanowiczОценок пока нет
- Critical Reasoning Practice Test QuestionsДокумент84 страницыCritical Reasoning Practice Test QuestionstiaraalfenzaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsДокумент3 страницыExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Automatic Railway Gate ControlДокумент6 страницAutomatic Railway Gate ControlRithesh VRОценок пока нет
- C1362Документ8 страницC1362Lucas CamposОценок пока нет
- 2021 & Beyond: Prevention Through DesignДокумент9 страниц2021 & Beyond: Prevention Through DesignAgung Ariefat LubisОценок пока нет
- SMALL, LIGHTWEIGHT AND AMAZINGLY SILENT AC MASTER POWER INVERTERSДокумент2 страницыSMALL, LIGHTWEIGHT AND AMAZINGLY SILENT AC MASTER POWER INVERTERSJimy HendrixОценок пока нет
- Em A3cfДокумент566 страницEm A3cfSimo Ben OuaradОценок пока нет
- Arango DBДокумент12 страницArango DBrchawla8Оценок пока нет
- COMSATS University Islamabad Lab Sessional IДокумент2 страницыCOMSATS University Islamabad Lab Sessional IAdnan AadiОценок пока нет
- Software Requirements Document PDFДокумент54 страницыSoftware Requirements Document PDFAshishJaiswalОценок пока нет
- Rrs 5 LOCAL ALBIOLДокумент2 страницыRrs 5 LOCAL ALBIOLYeye YtОценок пока нет
- Ella Mae C. Acla Resume 2023 PDFДокумент2 страницыElla Mae C. Acla Resume 2023 PDFMark Wilber Diano GuzonОценок пока нет
- iVIZION Quick Reference PDFДокумент16 страницiVIZION Quick Reference PDFjoseОценок пока нет
- Filcordrange en NewДокумент4 страницыFilcordrange en Newburak cikirkanОценок пока нет
- 50 Hydraulics Probs by Engr. Ben DavidДокумент43 страницы50 Hydraulics Probs by Engr. Ben DavidEly Jane DimaculanganОценок пока нет
- Smart Automated Irrigation System Seminar ReportДокумент30 страницSmart Automated Irrigation System Seminar ReportSCOC53 Parth NegiОценок пока нет
- Appendix I Boq For Supply Installation and Comm of Integrated Security System For KRДокумент4 страницыAppendix I Boq For Supply Installation and Comm of Integrated Security System For KRLes De JesusОценок пока нет
- DNV Os 101Документ80 страницDNV Os 101preceptiveinquirerОценок пока нет
- DS-2TD4136-25/50: Thermal & Optical Bi-Spectrum Network Speed DomeДокумент5 страницDS-2TD4136-25/50: Thermal & Optical Bi-Spectrum Network Speed Domeal lakwenaОценок пока нет
- Dffa b10100 02 7600.pdДокумент8 страницDffa b10100 02 7600.pdTraian SerbanОценок пока нет
- Introduction Data ManagementДокумент12 страницIntroduction Data ManagementGeofrey BasalirwaОценок пока нет
- TQMДокумент2 страницыTQMMahaveer SepatОценок пока нет
- Azure FundamentalsДокумент5 страницAzure FundamentalsRamziОценок пока нет
- Subaru Diesel - TuningДокумент28 страницSubaru Diesel - TuningEdwinОценок пока нет
- CH 5 - Engine ElectricalДокумент62 страницыCH 5 - Engine ElectricalEnrrique LaraОценок пока нет
- PCS-9705 Bcu - V1.00Документ29 страницPCS-9705 Bcu - V1.00Bharath ErОценок пока нет
- Operation Manual of REDLIFT R Series IC ForkliftДокумент153 страницыOperation Manual of REDLIFT R Series IC Forkliftroberto_robledo_6Оценок пока нет
- Pekerjaan Plumbing Ruang PompaДокумент1 страницаPekerjaan Plumbing Ruang PompaAnisa YОценок пока нет
- PMDG 737 Checklist 2.0 LightДокумент6 страницPMDG 737 Checklist 2.0 LightHenry O'sunaОценок пока нет
- Ge Oil and Gas-Rtpu-8, 9, 60 Tr-prx080Документ1 страницаGe Oil and Gas-Rtpu-8, 9, 60 Tr-prx080syed mustafa aliОценок пока нет
- Game LogДокумент29 страницGame LogMaja DenderaОценок пока нет