Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Psychiatry High Yield Notes
Загружено:
gregry2Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Psychiatry High Yield Notes
Загружено:
gregry2Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Psychiatry: high-yield facts + uworld
Study online at quizlet.com/_egcze
1.
"A&Ox4" meaning?: Alert and oriented to time, place, person,
8.
23 yo male brought to ER with 2-day hx of fever,
and situation.
2.
headaches, and confusion. He slips into a coma and
dies several days after admission. Autopsy reveals
intense, bilateral hemorrhagic necrosis of the inferior
and medial temporal lobes. Etiology?: HSV-1 encephalitis:
TEMPORAL LOBE involvement is characteristic!
Gross brain examination reveals edema and hemorrhagic
necrosis. Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (Cowdry type A)
are present in glial cells and neurons. Multinucleated giant cells
may also be found.
Know the first vs. second-gen H1 receptor blockers: Firstgen H1 blockers (have antimuscarinic, antiserotonergic, and
alpha-blocking side effects):
Hydroxyzine
Promethazine
Chlorpheniramine
Diphenhydramine
Dimenhydrinate
9.
43 yo female presents with bilateral paresthesias in
Antimuscarinic = blurry vision, dry mouth, urinary retenion
Antiserotonergic = appetite stimulation
Alpha-blocking = postural dizziness
Second-gen H1 blockers:
Fexofenadine
Loratadine
Desloratadine
Cetirizine
3.
10.
11.
12.
6.
13.
7.
14.
Benzos or haloperidol can be used to treat overdose of
which 2 drug categories?: 1) Cocaine/amphetamines
2) PCP
4 drugs that can help prevent relapse in recovering
15.
Besides schizophrenia, what disorder can be treated
16.
Best treatment for atypical depression?: MAOIs, SSRIs
17.
Binge eating disorder vs. Compulsive eating disorder:
with antipsychotics?: Tourette's (haloperidol; risperidone
(preferred over TCAs)
4 indications of diazepam (long-acting benzo)?: 1)
Anxiolytic
2) Sedative-hypnotic
3) Anticonvulsant
4) Muscle relaxant
Axonal conduction:
Space constant (aka length constant)
Time constant: Space (length) constant = a measure of how far
along an axon an electrical impulse can propagate; this value is
increased by myelination
Time constant = time it takes for a change in membrane potential
to achieve 63% of the new value; myelination decreases
membrane capacitance and thus reduces the time constant
(allowing for fasting axonal confuction speed)
3 adverse effect disorders that are very similar:
alcoholics?: 1) Disulfiram (Antabuse)
2) Naltrexone
3) Topiramate
4) Acamprosate
Autism vs. Aspergers: Autism = usu below-normal
intelligence
Aspergers = usu normal intelligence "little professors"
2 most common causes of delirium: 1) Drugs (esp those with
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Serotonin syndrome
Malignant hyperthermia
Atypical antipsychotics:
MOA?
AE?: MOA: varied effects on serotonin, dopamine, alpha, H1
AE: clozapine and agranulocytosis; ziprasidone and prolonged
QT; quetiapine/olanzapine/clozapine and weight gain (incr risk
for diabetes)
anticholinergic side effects, remember "mad as a hatter")
2) UTIs
5.
43 yo male complains of double vision when walking
down stairs. He's healthy. Has T2DM well controlled
with glyburide. What is causing his complaints?: NOT
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
TROCHLEAR NERVE (a common cause of vertical diplopia,
which is most noticeable when the affected eye looks toward the
nose, as when reading the newspaper or walking down stairs)
*What NT changes do you see with the following
diseases?
1) Anxiety disorders =
2) Depression =
3) Mania =
4) Alzheimer's =
5) Huntington's =
6) Schizophrenia =
7) Parkinson's = *: 1) Anxiety disorders = high NE; low GABA
and serotonin
2) Depression = low serotonin; NE; dopamine
3) Mania = high serotonin; NE; dopamine
4) Alzheimer's = low ACh
5) Huntington's = low ACh and GABA; high dopamine
6) Schizophrenia = high dopamine
7) Parkinson's = high ACh; low dopamine
4.
thumbs, middle, and index fingers. She undergoes
hemodialysis for chronic renal failure due to
uncontrolled HTN. Her condition is most likely assoc
with __:: Nerve compression within an anatomic compartment
(carpal tunnel syndrome causing median nerve compression)
Binge eating disorder is a maladaptive coping mechanism.
Compulsive eating disorder is a type of OCD.
18.
Childhood disintegrative disorder: Most common age of
31.
onset is 3-4 yo, after at least 2 yrs of normal development.
More common in boys.
Significant loss of expressive/receptive language skills, social
skills, adaptive behavioral, bowel/bladder control, play, motor
skills.
19.
2) Severe depression, headache, fatigue,
insomnia/hypersomnia, hunger
4) Belligerence, impulsiveness, nystagmus, homicidal
ideations, psychosis =
5) Headache, anxiety/depression, weight gain =
6) Euphoria, social withdrawal, impaired judgment,
hallucinations =
7) Rebound anxiety, tremors, seizures, life-threatening
=: 2) Severe depression, headache, fatigue,
insomnia/hypersomnia, hunger =
cocaine/amphetamine withdrawal
4) Belligerence, impulsiveness, nystagmus, homicidal ideations,
psychosis = PCP overdose
5) Headache, anxiety/depression, weight gain =
nicotine/caffeine withdrawal
6) Euphoria, social withdrawal, impaired judgment,
hallucinations = LSD intoxication
7) Rebound anxiety, tremors, seizures, life-threatening
= alcohol/benzo/barbiturate withdrawal
Classical presentation of homocystinuria? What enzyme
is deficient?: Thromboembolic episodes involving both large
and small vessels, esp those of the brain. Other clinical
manifestations resemble those of Marfan syndrome: lens
subluxation, elongated limbs, arachnodactyly, scholiosis.
Deficiency in cystathione synthetase
20.
Concentrations of which 3 NTs are increased by
MAOis?: NE
Dopamine
Serotonin
21.
Corneal reflex is mediated by which CN?: CN V
22.
Define dissociative amnesia: Inability to recall personal
information subsequent to severe trauma/stress
23.
32.
Define folie a deux: Development of delusional disorder in a
Delirium vs. Dementia: Delirium has altered consciousness
("waxing and waning"), and acute onset and ABNORMAL EEG.
Dementia does not, and has gradual onset and normal EEG.
25.
Difference between postpartum blues and postpartum
depression: Blues last <2 weeks
(also, postpartum depression = major depressive disorder)
26.
Displacement =: Process whereby bothersome ideas and
33.
Dissociation =
Extreme forms can result in _?: Temporary, drastic change
in personality, memory, consciousness, or motor behavior to
avoid emotional stress
Extreme forms can result in multiple personality disorder
28.
Drug of choice for treatment of generalized anxiety
34.
disorder?: Buspirone (stimulates 5-HT1A receptors)-treatment of GAD is its ONLY indication
Drug that can treat bulimia?: SSRI (note this can't be used
30.
Drugs for treatment of Tourette's syndrome?: 1)
for anorexia)
Haloperidol (neuroleptic; old)
2) Fluphenazine, Pimozide, Tetrabenazine (dopamine
antagonists; current DOC)
Dx of schizophrenia: (according to DSM): >6 mo of:
2 of the following sx:
1) Delusions
2) Hallucinations
3) Disorganized speech (loose associations)
4) Disorganized/catatonic behavior
5) Negative sx (flat affect, social withdrawal, lack of motivation,
lack of speech or thought, thought blocking)
Clean drug!
29.
Dx criteria for manic episode:: 3+ of the following over 1+
week (or hospitalization):
DIGFAST
1) Distractibility
2) Irresponsibility (hedonistic)
3) Grandiosity
4) Flight of ideas
5) Agitation; increase in goal-directed Activity
6) Sleep decreased
7) Talkative / pressured speech
feelings are transferred to a neutral person/object (Mom yells at
child because husband yelled at her).
27.
Dx criteria for major depressive disorder:: Depressed
mood + 5 of the following, over 2+ weeks: SIGECAPS
1) Sleep disturbance
2) Interests loss
3) Guilt
4) Energy loss
5) Concentration loss
6) Appetite change
7) Psychomotor retardation or agitation
8) Suicidal ideation
person in a close relationship with someone who has delusional
disorder. (aka shared psychotic disorder)
24.
Drugs of abuse:
35.
Dysthymia vs. Hypomania vs. Cyclothymia: All are milder
versions of things, i.e.
Dysthymia = mild depression for 2+ YEARS
Hypomania = mild manic episode not severe enough to
necessitate hospitalization
Cyclothymia = mild bipolar consisting of rapidly fluctuating
dysthymia and hypomania for 2+ YEARS
36.
Evolution of EPS side effects:: 4 hr = acute dystonia (tx: give
drugs with anticholinergic side effects)
4 days = akisthesia (restlessness)
4 wk = bradykinesia (Parkinsonism)
4 mo = tardive dyskinesia: irreversible
37.
47.
(describing murder in graphic detail with no emotional
response)
48.
assume the "sick role" (unlike malingering, their goals are not
external incentives).
38.
49.
50.
Fixation =: Partially remaining at a more childish level of
40.
Heme synthesis pathway defects:
List some SNRIs and their uses.: 1) Venlafaxine
2) Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
3) Nefazodone (no sexual side effects)
4) Milnicipran
Progresses to antisocial personality disorder (>18 yo)
39.
List drugs that can be used for bipolar disorder: 1)
Lithium
2) Seizure drugs (valproic acid; carbamazepine)
3) Atypical antipsychotics
Features of conduct disorder? What can this progress
to?: Cruelty to animals; violation of the basic rights of others
List 3 atypical antidepressants:: 1) Buproprion = increases
NE and dopamine (mech. unknown); good for cotherapy with
SSRIs; lowers seizure threshold
2) Mirtazapine = alpha2-antagonist; increases release of NE and
serotonin; has antihistamine side effects (sedation; incr appetite;
dry mouth)
3) Trazodone = inhibits serotonin reuptake; mostly used for
insomnia; may cause priapism
Factitious disorder =: Consciously creates sx in order to
Ex: nurse has episodes of hypoglycemia. Blood analysis reveals
no elevation in C protein. Dx? (C protein would be elevated if the
insulin was high due to endogenous production; this is a case of
factitious disorder in which the nurse has been injecting herself
with insulin)
Isolation (of affect) =: Separation of feelings from events
development (Z Chen)
ALA synthase =
ALA dehydratase =
Uroporphyinogen I synthase (aka porphobilinogen
deaminase) =
Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase =
Ferrochelatase =: ALA synthase = X-linked sideroblastic
anemia
ALA dehydratase = lead poisoning
Uroporphyinogen I synthase (aka porphobilinogen deaminase)
= acute intermittent porphyria (urine will darken upon exposure
to light; acute abdomen; acute psychosis)
Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase = porphyria cutanea tarda
(most common)
Ferrochelatase = lead poisoning
41.
How long after a pt's last drink for delirium tremens to
Used for depression; venlafaxine also for GAD and panic
disorders. Duloxetine also for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
(greater effect on NE)
51.
2) Humor
3) Sublimation
4) Suppression
52.
53.
Also fetal cardiac defects (Ebstein's anomaly; malformation of
the great vessels)
54.
month
43.
44.
45.
55.
56.
If you have to use a TCA in an elderly pt, which one, and
why?: Nortriptyline (secondary TCA; better than the tertiary
TCAs like amitriptyline) bc less anticholinergic effects
Name the famous SSRIs: 1) Sertraline (Zoloft)
2) Fluoxetine (Prozac)
3) Paroxetine (Paxil)
4) Citalopram
5) Fluvoxamine
Identification =: Modeling behavior after someone who is
more powerful (not necessarily more admired)
46.
Most common location of an intracranial
schwannoma?: Cerebllopontine angle (between the cerebellum
and lateral pons)
Hypnopompic vs. Hypnogogic hallucinations:
Hypnopompic occurs upon awakening
Hypnogogic occurs while going to sleep
Mirtazapine: MOA; indications: MOA: alpha2-selective
blocker
Indications: depression
Hx of sexual abuse is associated with what disorder?:
Dissociative identity disorder (formerly known as multiple
personality disorder)
Lithium side effects:: MNOP:
Movement (tremor)
Nephrogenic DI (blocks ADH--thus can be used to treat SIADH)
HypOthyroidism
Tx: benzos
How long do sx have to last for a diagnosis of PTSD?: >1
List the personality disorders by cluster:
A
B
C: Mnemonic: "Weird, Wild, Worried"
Cluster A = Paranoid, Schizoid, Schizotypal
Cluster B = Antisocial, Borderline, Histrionic, Narcissistic
Cluster C = Avoidant, Obsessive-compulsive, Dependent
set in? Treatment?: 2-5 days: life-threatening ANS
hyperactivity (tachycardia, tremors, anxiety, seizures) -->
psychotic sx --> confusion
42.
List the 4 mature ego defenses:: 1) Altruism
57.
Neurofibromas are derived from what cell type / what
embryonal layer?: Schwann cells, which are derived from the
neural crest.
58.
Non-schizophrenia psychotic disorders (3):: 1) Brief
69.
psychotic disorder (<1 mo)
2) Schizophreniform disorder (between 1 and 6 mo)
3) Schizoaffective disorder (psychotic sx + an episode of a mood
disorder--depressive, manic, or mixed): note a stable mood must
have been present for at least 2 weeks (or else you would consider
it a primary mood disorder with psychotic sx)
59.
production and motivation are both UNCONSCIOUS
drives
1) Somatization disorder
2) Conversion disorder
3) Hypochondriasis
4) Body dysmorphic disorder
5) Pain disorder: 1) Somatization disorder = laundry list of
complaints
2) Conversion disorder = V for Voltage (think nerves);
unexplained sensory/motor loss following acute stressor; pt is
unconcerned (la belle indifference)
3) Hypochondriasis
4) Body dysmorphic disorder
5) Pain disorder
Normal bereavement: pts are allowed to meet full
criteria for MDD for up to ____ (period of time)?: 2
months
60.
Opioid effects:
Intoxication
Overdose
Withdrawal: Post-op constipation and/or resp depression =
opioid intoxication
70.
Splitting =: Belief only in the extremes (i.e. people are either all
71.
SSRI withdrawal sx:
good or all times); cannot tolerate ambiguity.
Pinpoint pupils, n/v, seizures = opioid overdose
Anxiety, sweating, dilated pupils, piloerection, fever, rhinorrhea,
nausea, diarrhea = opioid withdrawal
61.
62.
How to avoid?: Dizziness, nausea, fatigue, muscle aches,
anxiety, irritability
Avoid by using a fluoxetine taper (long half life)
Oppositional defiant disorder?: Enduring pattern of hostile,
defiant behavior towards authorities
72.
Projection =: Unacceptable internal impulse is attributed to an
external source (ex: man who wants another woman thinks his
wife is cheating on him)
64.
A pt who needs an MRI says he can't go through with it
because of claustrophobia. What can you do to help?:
Give him 2 benzos
65.
A pt with ST elevation inferior MI is treated with the
appropriate therapy, including a medication for her
bradycardia. After initial treatment, her BP is 120/70
and pulse is 76/min. However, she now complains of
severe right-sided eye pain. Why?: Inferior MIs are due to
blockage of the RCA, which supplies the SA and AV nodes. Thus
sx include bradycardia. To treat this bradycardia, atropine is
given (blocks vagal input at SA and AV nodes in order to increase
HR). However, its antimuscarinic effects can precipitate an
attack of acute closed-angle glaucoma in individuals of high risk
(esp Asians) bc atropine causes mydriasis, resulting in
narrowing of the anterior chamber angle and fiminished outflow
of aqueous humor.
66.
67.
Regression =: Turning back the maturational clock and going
back to earlier modes of dealing with the world
68.
73.
Sleep patterns of depressed pts:: Decr slow-wave sleep (i.e.
stages 3-4)
Decr REM latency; Incr total REM
Early morning awakening
Suffixes for TCAs:: -triptamine
-pramine
74.
Sx of serotonin syndrome?
Mainstays of treatment?: Muscle rigidity
Hyperthermia
CV collapse
Tx: cooling and benzos (then cyproheptadine--5HT2 receptor
antagonist--if needed)
75.
Sx of TCA overdose?
Treatment for cardiotoxicity?: Tri C's:
1) Cardiotoxicity (treat with NaHCO3)
2) Convulsions
3) Coma
+ Respiratory depression and Hyperpyrexia
Reaction formation =: Emphasizing the opposite (ex: person
with libidinous thoughts enters a monastery)
SSRIs can be used in the treatment of.... (basically
everything; list 7): 1) Depression
2) Panic disorder
3) Social phobia
4) OCD
5) PTSD
6) Generalized anxiety disorder
7) Bulimia
Presentation of bulimia?: Parotitis, enamel erosion,
hypochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, dorsal hand
calluses from induced vomiting (Russell's sign)
63.
Somatoform disorders: remember that illness
76.
Temporarily inhibiting thinking but continuing to build
more tension = ?
Avoiding interpersonal intimacy to resolve conflict and
obtain gratification = ?: Temporarily inhibiting thinking but
continuing to build more tension = blocking (seen in
schizophrenics)
Avoiding interpersonal intimacy to resolve conflict and obtain
gratification = schizoid fantasy
77.
Ticking timebomb of global cerebral ischemia::
87.
What is important to remember when treating an
alcoholic with IV fluids?: ALWAYS GIVE THIAMINE
BEFORE GLUCOSE
Why? Think about it. 2 of the enzymes that thiamine acts as a
cofactor for directly feed into glucose utilization for energy
production (pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate).
The third enzyme, transketolase, functions in the HMP shunt to
convert pentoses to G3P (a glycolytic intermediate).
Thus pts with thiamine deficiency have severe under-utilization
of glucose due to these non-functioning enzymes. If you give
more glucose, this would worsen the Wernicke-Korsakoff
symptoms. ALWAYS GIVE THIAMINE FIRST!
5-10 seconds: syncope
>1 minute: cessation of neuronal activity
4-5 min: permanent tissue damage
78.
Tx for ADHD? What is the MOA?: CNS stimulants:
methylphenidate, amphetamines
MOA: increase catecholamine (esp NE and dopamine) vesicle
release at synaptic cleft
88.
pregnant?: Pseudocyesis
89.
Typical antipsychotics: AE: 1) EPS (high potency)
2) Anticholinergic (dry mouth, constipation; delirium in elderly)
3) Histamine (sedation)
4) Endocrine (dopamine block --> hyperprolactinemia)
80.
81.
83.
92.
93.
94.
95.
Blocks NMDA receptor activation
Which defense mechanism underlies all other defense
mechanisms?: Repression (involuntary withholding of a
thought or idea from conscious awareness)
infant due to long-term deprivation of affection
What is another name for PCP: PHENCYCLIDINE
Which antidepressant...:
1) Lowers seizure threshold
2) Works well with SSRIs and increases REM sleep
3) Stimulates appetite (weight gain)
4) Can be used for bedwetting in kids
5) AE: priapism: 1) Lowers seizure threshold = bupropion
2) Works well with SSRIs and increases REM sleep = trazodone
3) Stimulates appetite (weight gain) = mirtazepine
4) Can be used for bedwetting in kids = imipramine
5) AE: priapism = trazodone
Note co-dosing of MAOis and beta-agonists can also trigger this
reaction.
86.
Which 3 enzymes is thiamine a cofactor for?: 1) Pyruvate
dehydrogenase (glycolysis into TCA)
2) Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (TCA cycle)
2) Transketolase (HMP pathway: converts pentose --> G3P)
What happens if you ingest tyramine while on MAOis?:
What is anaclitic depression?: Withdrawn, unresponsive
What kind of amnesia is caued by thiamine deficiency?:
Korsakoff's amnesia is anterograde (no new memories); assoc
with mammillary body destruction. Seen in alcoholics. Also
accompanied by confabulation.
Hypertensive cheese crisis = risk for hemorrhagic stroke; cardiac
arrhythmias
85.
What is unique about the atypical antipsychotics?: Have
been shown to improve both positive and negative sx of
schizophrenia
Clozapine, Olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone
What are the components of the CAGE questionnaire?:
Used to assess alcoholism:
Cut back
Annoyed
Guilt
Eye opener
84.
91.
What are the 3 key elements of a DNR?: 1) No intubation or
mechanical ventilation
2) No defibrillation or IV drugs to acutely treat a terminal rhythm
3) No chest compressions
What is the triad seen in Wernicke's encephalopathy
(thiamine deficiency)?: 1) Confusion
2) Ophthalmoplegia
3) Ataxia
Typical vs. Atypical neuroleptics (antipsychotics)::
Typical = block dopamine D2 receptors (incr cAMP)
Atypical = block dopamine and 5-HT
82.
90.
Typical antipsychotics: high vs. low potency: High
potency = Trifluoperazine, Fluphenazine, Haloperidol (high rate
of EPS)
Low potency = Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine (high rate of
anticholinergic side effects)
What is the "on-off" phenomenon of Parkinson's dz?:
After a period of time of L-dopa therapy, there may be periods of
time when L-dopa efficacy is lost; this may last several hours and
occur sporadically throughout the day, resulting in hypokinesia
and rigidity. This is unpredictable and dose-independent. (Drug
holidays are not helpful in preventing this phenomenon).
Atomoxetine = NE reuptake inhibitor
79.
What is it called when you falsely believe you're
96.
Which immature ego defense?
Closet homosexual hates all homosexuals because of the
way they "make him feel": Projection
97.
Which NT is involved in the development of morphine tolerance?: Glutamate: binds/activates NMDA receptors --> incr
phosphorylation of opioid receptors and incr NO levels leading to morphine tolerance
NMDA receptor antagonists like ketamine can block the actions of glutamate and potentially block morphine tolerance from developing.
(Dextromethorphan is another drug that may be able to do this)
98.
Which personality disorder is assoc. with splitting?: Borderline
99.
Which property of methadone makes it a good substitute for heroin in detoxification of addicts?: Long half-life.
Other properties of methadone: extended, mild withdrawal syndrome (due to concentration in tissues and gradual release); good oral
bioavailability; potent mu receptor agonist with strong analgesic effects; can cause resp depression (just like most other opioids)
100.
You prescribe diazepam to a patient in order to decrease muscle spasticity. You should caution him to avoid which
drug?: Chlorpheniramine (and other first-generation H1 blockers: they have CNS penetration and block both central and peripheral H1
receptors, resulting in sedation)
This would potentiate the sedating effects of benzos, and be dangerous.
Вам также может понравиться
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSunel100% (35)
- Study Psych DrugsДокумент14 страницStudy Psych Drugsapi-369732698% (47)
- Notes For PMHNP CertificationДокумент23 страницыNotes For PMHNP CertificationKristine Frost92% (13)
- Psychiatric History and ExaminationДокумент14 страницPsychiatric History and ExaminationPaolo Bonifacio100% (14)
- BEHS Disorders ChartДокумент7 страницBEHS Disorders ChartAndrew PatelОценок пока нет
- Psych Shelf StuffДокумент16 страницPsych Shelf Stuffbostickdrew16100% (7)
- Psych Meds Review MaterialДокумент2 страницыPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (7)
- Antidepressant ChartДокумент7 страницAntidepressant Chartinher1tance100% (4)
- Assessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDДокумент85 страницAssessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDAlbghdadi CristianОценок пока нет
- Psych Case FilesДокумент21 страницаPsych Case Filesshina100% (1)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- PsychiatryДокумент52 страницыPsychiatryEma100% (13)
- Study Guide PMHNP Must Know Exam Topics Cheat Sheet: by ViaДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide PMHNP Must Know Exam Topics Cheat Sheet: by ViaDodo Eggo100% (4)
- BoardReviewClass PsychiatryДокумент28 страницBoardReviewClass PsychiatryyepherenowОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry PharmacologyДокумент2 страницыPsychiatry PharmacologyMegatFitriAziz100% (4)
- Psychiatry History Taking and Physical ExaminationДокумент16 страницPsychiatry History Taking and Physical ExaminationEma100% (17)
- High Yield PsychiatryДокумент44 страницыHigh Yield PsychiatryAntony Awad100% (2)
- Psychiatry MnemonicsДокумент4 страницыPsychiatry MnemonicsHiruni Tharuka100% (2)
- CHT Psyc AntidepressantДокумент3 страницыCHT Psyc AntidepressantRicardo Lugon ArantesОценок пока нет
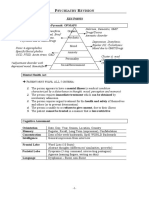
- K P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionДокумент36 страницK P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionArama CristiОценок пока нет
- Psych-CLEAR: Psychopathology Made Clear and EasyДокумент31 страницаPsych-CLEAR: Psychopathology Made Clear and EasynurulОценок пока нет
- PMHNP Ancc ReviewДокумент4 страницыPMHNP Ancc ReviewEllie Mehr75% (4)
- Psych Med ChartsДокумент5 страницPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (5)
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsДокумент7 страницPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- HighYieldPsychiatry PDFДокумент43 страницыHighYieldPsychiatry PDFYay100% (4)
- Psychiatry Shelf Spreadsheet P.montenigro M3Документ5 страницPsychiatry Shelf Spreadsheet P.montenigro M3JamesHowson100% (1)
- Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionОт EverandMedication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionОценок пока нет
- 72 PerinatalPsychiatry PDFДокумент11 страниц72 PerinatalPsychiatry PDFCetVital100% (1)
- Psychiatry Study Guide For ShelfДокумент42 страницыPsychiatry Study Guide For Shelfappolinia64% (14)
- Lecture Notes On PsychiatryДокумент38 страницLecture Notes On PsychiatryMing Wang50% (6)
- PsychiatryДокумент95 страницPsychiatryJarwoto RoestanajieОценок пока нет
- High Yield PsychiatryДокумент43 страницыHigh Yield Psychiatryconfusedmage91% (11)
- "Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry PharamacologyДокумент9 страниц"Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry Pharamacologytycobb63100% (4)
- Psychological TestsДокумент5 страницPsychological TestsNat de CastroОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry - Shelf ReviewДокумент101 страницаPsychiatry - Shelf Reviewluck2liv100% (4)
- CESD-R - Center For Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale Revised Online Depression Assessment CESD-R ExplanationДокумент2 страницыCESD-R - Center For Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale Revised Online Depression Assessment CESD-R ExplanationMi RoОценок пока нет
- Psych Drugs Info SheetДокумент4 страницыPsych Drugs Info SheetPauline ChanОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry Shelf ReviewДокумент11 страницPsychiatry Shelf ReviewAhmad Syahmi YZ75% (4)
- 10 Cognitive DisordersДокумент16 страниц10 Cognitive DisordersFarrah MaeОценок пока нет
- USMLE Mnemonics PsychДокумент4 страницыUSMLE Mnemonics Psychzhzizhzi100% (3)
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsДокумент4 страницыDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (1)
- Psychiatry Made EasyДокумент14 страницPsychiatry Made EasyTinesh Rajah83% (6)
- Notes PsychiatryДокумент36 страницNotes Psychiatryvinodksahu0% (1)
- Antidepressant Comparison ChartДокумент3 страницыAntidepressant Comparison Chartiggyputtty100% (29)
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionДокумент2 страницыHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- Clerkship - Psychiatric History and MseДокумент24 страницыClerkship - Psychiatric History and MsefahmiОценок пока нет
- 1.02 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination PDFДокумент4 страницы1.02 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination PDFEp-ep Jeffrey Sibayan Ramos100% (1)
- High Yield Psychiatry: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday RamahiДокумент43 страницыHigh Yield Psychiatry: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday Ramahigreg100% (1)
- PsychopharmacologyДокумент64 страницыPsychopharmacologyGaurav Tandon100% (2)
- Notes On Psychiatry: TypesДокумент17 страницNotes On Psychiatry: TypesMAY100% (1)
- Psychiatry VIVA Preparation DocumentДокумент24 страницыPsychiatry VIVA Preparation DocumentPhiNguyen83% (6)
- Psychiatry: Mental State ExaminationДокумент3 страницыPsychiatry: Mental State ExaminationSok-Moi Chok100% (3)
- Prescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsОт EverandPrescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- 1st Periodical Exam in Personal Development For ALS ANSWER KEY FOR SHARINGДокумент8 страниц1st Periodical Exam in Personal Development For ALS ANSWER KEY FOR SHARINGMadelaine VillavicencioОценок пока нет
- DSM 5 Mood DisorderДокумент9 страницDSM 5 Mood DisorderErlin IrawatiОценок пока нет
- Oneiromancy Lesson 5 - Lucid DreamingДокумент4 страницыOneiromancy Lesson 5 - Lucid DreamingHanka PanОценок пока нет
- Marijuana Facts For TeensДокумент23 страницыMarijuana Facts For Teensneeraj_prajapati_16Оценок пока нет
- Psychiatry Practice Boosters, Second Edition: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workОт EverandPsychiatry Practice Boosters, Second Edition: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workОценок пока нет
- Concept of Pain in AyurvedaДокумент31 страницаConcept of Pain in Ayurvedagunjanlata aryaОценок пока нет
- Bauer, M., & Gitlin, M. (2016) - The Essential Guide To Lithium Treatment. Doi10.1007978-3-319-31214-9 PDFДокумент167 страницBauer, M., & Gitlin, M. (2016) - The Essential Guide To Lithium Treatment. Doi10.1007978-3-319-31214-9 PDFdanilomarandolaОценок пока нет
- The Buying BrainДокумент2 страницыThe Buying BrainHussain Aftab Changi50% (2)
- BFB For Psycmatric Disorders PDFДокумент28 страницBFB For Psycmatric Disorders PDFratusemut13Оценок пока нет
- (Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersДокумент3 страницы(Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersGus AbellaОценок пока нет
- Voluntary and Involuntary ActionДокумент23 страницыVoluntary and Involuntary Actionridwan91% (11)
- Contributions of Media To The Learning ProcessДокумент3 страницыContributions of Media To The Learning ProcessEzekiel D. Rodriguez100% (7)
- Memory Dysfunction.9Документ14 страницMemory Dysfunction.9Luis Antonio Cespedes HernandezОценок пока нет
- Sample Consent FormДокумент2 страницыSample Consent FormFabio CalefatoОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios DBT (TDC)Документ4 страницыEjercicios DBT (TDC)vanessa_lm_Оценок пока нет
- PSY 101 Fall - 2017 Nasif Bin Saif Sangita Baidya SwarnaДокумент21 страницаPSY 101 Fall - 2017 Nasif Bin Saif Sangita Baidya SwarnaS KhanОценок пока нет
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching FormativeДокумент13 страницFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching FormativeLeah Mae BulosanОценок пока нет
- 感覺&知覺IIДокумент72 страницы感覺&知覺IIPeter ChangОценок пока нет
- Islam 2014 Social Identity Theory Chapter Only EcpДокумент4 страницыIslam 2014 Social Identity Theory Chapter Only EcpsharkassОценок пока нет
- GlupostДокумент5 страницGlupostamra ibreljicОценок пока нет
- Pupil Dilation During Visual Target DetectionДокумент14 страницPupil Dilation During Visual Target DetectionShane G MoonОценок пока нет
- Andrade (2010) Psychology As NotesДокумент10 страницAndrade (2010) Psychology As NotesishaniagheraОценок пока нет
- Clinical Report 2Документ7 страницClinical Report 2suhail iqbal sipraОценок пока нет
- CJR Baru Kel 1-1Документ4 страницыCJR Baru Kel 1-1desertfox27Оценок пока нет
- Business PsychologyДокумент2 страницыBusiness Psychologyabdulrehman4088495Оценок пока нет
- Planning and Designing A Teaching PortfolioДокумент6 страницPlanning and Designing A Teaching PortfolioIvy Marie MaratasОценок пока нет
- Mental RetardationДокумент38 страницMental RetardationMeggan CabaluОценок пока нет
- Applied Linguistics MДокумент4 страницыApplied Linguistics MMuhammad MazharОценок пока нет
- Neuro-Linguistic Programming: We Live Five Lives at Any Given MovementДокумент13 страницNeuro-Linguistic Programming: We Live Five Lives at Any Given MovementVivek GhodvindeОценок пока нет
- Concept Paper TheoriesДокумент12 страницConcept Paper TheoriesKeven Ong OpaminОценок пока нет