Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Basic Amines
Загружено:
Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2y0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
52 просмотров10 страницz
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
ODP, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документz
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате ODP, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
52 просмотров10 страницBasic Amines
Загружено:
Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2yz
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате ODP, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 10
Basic strength of Amines
Amines are basic in nature.
Due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom which is available
for donation.
Aliphatic amines (alkyl amines) are more basic than ammonia.
Alkyl groups are electron releasing groups (+ I effect) which increase
electron density on nitrogen atom in alkyl amines. Increase in electron density
on nitrogen atom increases its basic strength. So alkyl amines are more basic
than ammonia
the expression for Kb and pkb of amines
the relation between pkb and basic strength
pk increases basic strength decreases.
b
is the relation between kb and basic strength
Kb increases basic strength also increases.
Aromatic amines (aryl amines) are less basic then ammonia.
In aromatic amines, nitrogen has a lone pair of elections which is
involved in resonance (+ R effect) and hence it is not free for
donation. Hence it is less basic than ammonia.
the order of basic strength of primary, secondary and
tertiary amines in gas phase
Tertiary > secondary > primary
In gas phase only inductive effect decides basic strength. In
tertiary amine there are three electron releasing groups, so
tertiary is most basic then secondary and primary.
the factors that affect basic strength of amines aqueous
solution?
1.Inductive effect of alkyl group
2.Solvation effect (hydrogen bonding)
3.Steric hindrance
For small CH3 group, 20 >10 >30 >NH3 [S > P > T]
Reason: For CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to Hbonding. The stability of cation due to solvation effect >
inductive effect, hence 10 amine is more basic than 30
amine.
For big C2H5 group, 20 >30 >10 >NH3 [S > T > P]
Reason: For C2H5 group, there is steric hindrance to Hbonding. The stability of cation due to inductive effect >
solvation effect, hence 30 amine is more basic than 10
amine.
EDG (CH3, -OCH3), increases the basic strength
[increases the e- density on N].
EWG (NO2, halogen), decreases the basic strength
[decreases the e- density
Aliphatic amine > Benzyl amine >NH3 >Aromatic
amine
In gas phase, 30 >20 >10 amine > NH3
For small CH3 group, 20 >10 >30 >NH3 [S > P > T]
For big C2H5 group, 20 >30 >10 >NH3 [S > T > P]
EDG (CH3, -OCH3), increases the basic strength
EWG (NO2, halogen), decreases the basic strength
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their basic strength:
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, NH3
(C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3> C6H5NH2
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
(i) C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3, C6H5CH2NH2and (C2H5)2NH
C6H5NH2 < NH3< C6H5CH2NH2< C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
(ii) C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2
C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2< (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
(iii) In increasing order of basic strength:
(a) Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine [CH3, B.S ; NO2 B.S]
p-nitroaniline < Aniline < p-toluidine
(b) C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5CH2NH2.
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5CH2NH2
(iv) Decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase: C 2H5NH2,
(C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, NH3 (C2H5)3N > (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3
(v) In increasing order of boiling point: C2H5OH, (CH3)2NH, C2H5NH2
(CH3)2NH < C2H5NH2 < C2H5OH
(vi) In increasing order of solubility in water: C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH,
C2H5NH2.
C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2
the effect of electron releasing group on basic strength of
amines
Electron releasing group (eg: CH3 , OCH3) increases basic
strength by increasing electron density on nitrogen atom.
the effect of electron withdrawing group on basic strength
of amines
Electron withdrawing group (eg: N02) decreases basic strength
by decreasing electron density on nitrogen atom.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Class Xi Chemistry Value Based QuestionsДокумент12 страницClass Xi Chemistry Value Based QuestionsAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2y100% (3)
- Chem Set IIIxxДокумент10 страницChem Set IIIxxAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- (Class 3) 28 May 2015 Thursday: M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Junior Section QUIZ CLUB ACTIVITY, 2015-2016Документ2 страницы(Class 3) 28 May 2015 Thursday: M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Junior Section QUIZ CLUB ACTIVITY, 2015-2016Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Section 1 - Revision of Atomic Structure: Mass Number 23Документ2 страницыSection 1 - Revision of Atomic Structure: Mass Number 23Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry Ans PDFДокумент1 страницаIGCSE Chemistry Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry Ans PDFAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- 3 ArenesДокумент7 страниц3 ArenesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Electro Chemistry: To calculate Λº for a weak and strong electrolyte from the λ of individual ionsДокумент7 страницElectro Chemistry: To calculate Λº for a weak and strong electrolyte from the λ of individual ionsAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- CH 1 Solid State SsnotesДокумент29 страницCH 1 Solid State SsnotesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Chemistry The D and F Block ElementsДокумент29 страницChemistry The D and F Block ElementsAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chemical Kinetics PDFДокумент20 страницChemistry Chemical Kinetics PDFAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Solid State PPTДокумент72 страницыSolid State PPTAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesДокумент34 страницыChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructurefДокумент1 страницаAtomic StructurefAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Assignment2 of HMT ME 6003-1Документ2 страницыAssignment2 of HMT ME 6003-1Faraz KhanОценок пока нет
- Trans Fat ReadingДокумент4 страницыTrans Fat ReadingrachelОценок пока нет
- Rodenstock Apo Sironar SДокумент3 страницыRodenstock Apo Sironar SPawan KumarОценок пока нет
- Naming Inorganic CompoundsДокумент29 страницNaming Inorganic CompoundsLove TakaОценок пока нет
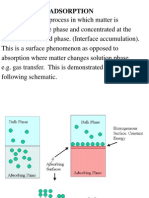
- 8 AdsorptionДокумент85 страниц8 AdsorptionRush WahabОценок пока нет
- TDs - Masterseal MCI 2120Документ2 страницыTDs - Masterseal MCI 2120Venkata RaoОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsДокумент2 страницыMechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsmehtabpathanОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Pipe Reinforcement ASME B31 3Документ5 страницCalculation of Pipe Reinforcement ASME B31 3Umar Aslam0% (1)
- Sabkha Trafficability, JubailДокумент163 страницыSabkha Trafficability, JubailAdly Al-SaafinОценок пока нет
- History of Photo Volatic CellДокумент12 страницHistory of Photo Volatic CellKarthick ThiyaguОценок пока нет
- 10 1016@j Jclepro 2019 03 260Документ10 страниц10 1016@j Jclepro 2019 03 260Rose BleueОценок пока нет
- MSDS - Coratex 030700Документ7 страницMSDS - Coratex 030700shafaykhan78603Оценок пока нет
- Removal of Methyl Orange Dye From Textile Effluent Using Adsorption On Chitosan Hydrogel BeadsДокумент8 страницRemoval of Methyl Orange Dye From Textile Effluent Using Adsorption On Chitosan Hydrogel BeadsESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionОценок пока нет
- GE Healthcare: Instructions For Sephadex MediaДокумент2 страницыGE Healthcare: Instructions For Sephadex Mediaponbohacop0% (1)
- 06 05 16 Heko Bucket ElevatorДокумент36 страниц06 05 16 Heko Bucket ElevatorLeoncio Alexander Maza InfantesОценок пока нет
- Biology QuestionaireДокумент2 страницыBiology Questionairelyll ann100% (1)
- Sudhir Memorial Institute Chemistry Quantity of CaesinДокумент16 страницSudhir Memorial Institute Chemistry Quantity of CaesinKi NgОценок пока нет
- Gilsonite - Modified Gilsonite - Fluid Loss ControlДокумент3 страницыGilsonite - Modified Gilsonite - Fluid Loss ControlManargudi mannarОценок пока нет
- Dna Extraction Using Chelex ResinДокумент7 страницDna Extraction Using Chelex Resinu77Оценок пока нет
- Optimization of Shell Thickness of Sub-Baric Fryer For Manufacture of Fried Food Products Using Finite Element Analysis (FEA)Документ10 страницOptimization of Shell Thickness of Sub-Baric Fryer For Manufacture of Fried Food Products Using Finite Element Analysis (FEA)journalОценок пока нет
- G171.1207962-1 - Standard Test Scratch HardnessДокумент7 страницG171.1207962-1 - Standard Test Scratch HardnessVictor Manuel Florez FrancoОценок пока нет
- Raychem Heat Shrink Terminations HVTДокумент18 страницRaychem Heat Shrink Terminations HVTgerardoОценок пока нет
- Program Design: Construct and Algorithms Using Problems Solving Tools - Sample ExercisesДокумент57 страницProgram Design: Construct and Algorithms Using Problems Solving Tools - Sample ExercisesJuan PorceleinОценок пока нет
- Sol-Gel Synthesis and Structure of Cordieritetialite Glass-CeramicsДокумент6 страницSol-Gel Synthesis and Structure of Cordieritetialite Glass-CeramicsahadsajjadiОценок пока нет
- Aluminium Cookware To MinimizeДокумент7 страницAluminium Cookware To MinimizeKeep CalmОценок пока нет
- Geo MarkДокумент51 страницаGeo MarkmustafaОценок пока нет
- ACG Glass Installation - Setting Block, Edge CoverДокумент29 страницACG Glass Installation - Setting Block, Edge CoverDave LiОценок пока нет
- PolyolsДокумент12 страницPolyolsA MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Aipmt 1999Документ16 страницAipmt 1999sumit kumarОценок пока нет
- En - 0122 8706 Ccta 20 01 00149Документ10 страницEn - 0122 8706 Ccta 20 01 00149mrcariОценок пока нет