Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Max Plank
Загружено:
Micika0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров1 страницаjhjh
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документjhjh
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров1 страницаMax Plank
Загружено:
Micikajhjh
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Max Planck was born in Kiel, Germany, on April 23, 1858,.
His father was Professor of Constitutional Law in the
University of Kiel, and later in Gttingen.
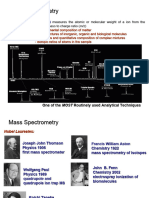
Max Plank,was a German theoretical physicist who originated quantum theory, which won him the Nobel Prize in
Physics in 1918
Max Planck's quantum theory revolutionized human understanding of atomic and subatomic processes, just as
Albert Einsteins theory of relativity revolutionized the understanding of space and time.
In 1894 Planck turned his attention to the problem of black-body radiation.
He had been commissioned by electric companies to create maximum light from lightbulbs with minimum energy.
Planck's earliest work was on the subject of thermodynamics, an interest he acquired from his studies under
Kirchhoff, whom he greatly admired, and very considerably from reading R. Clausius' publications. He published
papers on entropy, on thermoelectric ity and on the theory of dilute solutions.
At the same time also the problems of radiation processes engaged his attention and he showed that these were to be
considered as electromagnetic in nature. From these studies he was led to the problem of the distribution of energy
in the spectrum of full radiation. Experimental observations on the wavelength distribution of the energy emitted by
a black body as a function of temperature were at variance with the predictions of classical physics. Planck was able
to deduce the relationship between the ener gy and the frequency of radiation. In a paper published in 1900, he
announced his derivation of the relationship: this was based on the revolutionary idea that the energy emitted by a
resonator could only take on discrete values or quanta. The energy for a resonator of frequency v is hv where h is a
universal constant, now called Planck's constant.
This was not only Planck's most important work but also marked a turning point in the history of physics. The
importance of the discovery, with its far-reaching effect on classical physics, was not appreciated at first. However
the evidence for its validi ty gradually became overwhelming as its application accounted for many discrepancies
between observed phenomena and classical theory. Among these applications and developments may be mentioned
Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Planck's work on the quantum theory, as it came to be known, was published in the Annalen der Physik. His work is
summarized in two books Thermodynamik (Thermodynamics) (1897) and Theorie der Wrmestrahlung (Theory of
heat radiat ion) (1906).
Planck faced a troubled and tragic period in his life during the period of the Nazi government in Germany, when he
felt it his duty to remain in his country but was openly opposed to some of the Government's policies, particularly as
regards the persecuti on of the Jews. In the last weeks of the war he suffered great hardship after his home was
destroyed by bombing.He was revered by his colleagues not only for the importance of his discoveries but for his
great personal qualities. He was also a gifted pianist and is said to have at one time considered music as a
career.Planck was twice married. Upon his appointment, in 1885, to Associate Professor in his native town Kiel he
married a friend of his childhood, Marie Merck, who died in 1909. He remarried her cousin Marga von Hsslin.
Three of his children died young, leaving him with two sons.He suffered a personal tragedy when one of them was
executed for his part in an unsuccessful attempt to assassinate Hitler in 1944.He died at Gttingen on October 4,
1947.
Вам также может понравиться
- Max PlanckДокумент1 страницаMax Planckmr personalОценок пока нет
- Max Planck's Contributions to Quantum TheoryДокумент10 страницMax Planck's Contributions to Quantum TheorybilalОценок пока нет
- Max PlanckДокумент3 страницыMax PlancksarayooОценок пока нет
- Early Life: Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, (Born April 23, 1858Документ4 страницыEarly Life: Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, (Born April 23, 1858Jessabelle RamosОценок пока нет
- Max Planck's Revolutionary Contributions to Quantum TheoryДокумент2 страницыMax Planck's Revolutionary Contributions to Quantum TheoryVishal DhekaleОценок пока нет
- Lecture1 - 04 November 2022Документ17 страницLecture1 - 04 November 2022nprashantshekharОценок пока нет
- Max Planck The Father of Quantum TheoryДокумент5 страницMax Planck The Father of Quantum Theorysarath6725100% (1)
- Quantum PhysicsДокумент9 страницQuantum PhysicsLak DavisОценок пока нет
- Max Planck: Cipriani MatteoДокумент7 страницMax Planck: Cipriani MatteoJacopo FrignaniОценок пока нет
- Max Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistДокумент16 страницMax Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistAtilrep Sailep TocilОценок пока нет
- Max PlanckДокумент5 страницMax Planckkashif salmanОценок пока нет
- Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel MunichДокумент3 страницыMax Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel Municharghya_bi108Оценок пока нет
- Max Planck - A Conservative Revolutionary: Manuel Cardona and Werner MarxДокумент23 страницыMax Planck - A Conservative Revolutionary: Manuel Cardona and Werner MarxG. AlfredОценок пока нет
- Phy Theory Assignment 01Документ7 страницPhy Theory Assignment 01Ohi AhamedОценок пока нет
- Planck, The Quantum, and The Historians: Key WordsДокумент46 страницPlanck, The Quantum, and The Historians: Key WordsLuciano A.Оценок пока нет
- Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel MunichДокумент2 страницыMax Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel Municharghya_bi108Оценок пока нет
- Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: (1858 - 1947) : Letters To Progress in PhysicsДокумент4 страницыMax Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: (1858 - 1947) : Letters To Progress in PhysicsCarlos Arias JiménezОценок пока нет
- Darrigol (2008)Документ21 страницаDarrigol (2008)Luciano A.Оценок пока нет
- Max Planck: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент7 страницMax Planck: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterОценок пока нет
- PlanckДокумент5 страницPlanckLak DavisОценок пока нет
- Untitled DocumentДокумент3 страницыUntitled DocumentkaiboyceОценок пока нет
- Esercizi IngleseДокумент3 страницыEsercizi IngleseNunzia NapolitanoОценок пока нет
- Einstein and Heisenberg: The Controversy Over Quantum PhysicsОт EverandEinstein and Heisenberg: The Controversy Over Quantum PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Max PlanckДокумент15 страницMax PlanckPriyanka100% (1)
- Thirty Years that Shook Physics: The Story of Quantum TheoryОт EverandThirty Years that Shook Physics: The Story of Quantum TheoryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- Derivation of Planck's Radiation Law - Part 3Документ8 страницDerivation of Planck's Radiation Law - Part 3Kyle VerrisОценок пока нет
- Early Quantum Theory Genesis in The Intertheoretic ContextДокумент25 страницEarly Quantum Theory Genesis in The Intertheoretic ContextРинат НугаевОценок пока нет
- Thermal Radiation Formula of PlanckДокумент29 страницThermal Radiation Formula of PlanckPle NaibrudaОценок пока нет
- Max Planck ThesisДокумент8 страницMax Planck ThesisMary Calkins100% (2)
- Reading Text Kel 6-DikonversiДокумент1 страницаReading Text Kel 6-DikonversiVanny LeeОценок пока нет
- Max Planck and The Genesis of The Energy Quanta inДокумент6 страницMax Planck and The Genesis of The Energy Quanta inCatalin MeiuОценок пока нет
- Johannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionДокумент9 страницJohannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionRohit KumarОценок пока нет
- Dehmelt HansДокумент15 страницDehmelt Hanspaolospadera72Оценок пока нет
- 1009 5761018 Minnie MaxplanckДокумент8 страниц1009 5761018 Minnie Maxplanckapi-320112581Оценок пока нет
- Worlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFДокумент15 страницWorlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFFadewОценок пока нет
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinДокумент4 страницыMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoОценок пока нет
- Ujpa 18490190Документ14 страницUjpa 18490190LeonОценок пока нет
- Albert Einstein His Annus Mirabilis 1905Документ19 страницAlbert Einstein His Annus Mirabilis 1905lp456Оценок пока нет
- Albert Einstein BiographyДокумент2 страницыAlbert Einstein BiographyVavasd AsvasvdОценок пока нет
- ( T y Ə ɅDD̥ƏSNN̩ Bd̥ʁɑ ) : Tycho Brahe (Документ6 страниц( T y Ə ɅDD̥ƏSNN̩ Bd̥ʁɑ ) : Tycho Brahe (Romanuvel ShankarОценок пока нет
- History of Quantum PhysicsДокумент1 страницаHistory of Quantum Physicsalokesh1982Оценок пока нет
- Planck's Thermal Radiation Formula Centenary AnalysisДокумент24 страницыPlanck's Thermal Radiation Formula Centenary AnalysisoddcrocsОценок пока нет
- Photon MilestonesДокумент16 страницPhoton Milestones7anoochОценок пока нет
- Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel MunichДокумент1 страницаMax Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS: Theology Professors Göttingen Law Kiel Municharghya_bi108Оценок пока нет
- Albert EinsteinДокумент2 страницыAlbert EinsteinGlenn RomanoОценок пока нет
- Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: TimelineДокумент2 страницыMax Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: TimelineVivekananthan GanasonОценок пока нет
- CPD Micro ProjectДокумент15 страницCPD Micro ProjectshubhamОценок пока нет
- The Night of the Physicists: Operation Epsilon: Heisenberg, Hahn, Weizsäcker and the German BombОт EverandThe Night of the Physicists: Operation Epsilon: Heisenberg, Hahn, Weizsäcker and the German BombОценок пока нет
- 30 2 CarsonДокумент14 страниц30 2 Carsonrussell_mahmoodОценок пока нет
- Chm222 Leboltzman BioДокумент18 страницChm222 Leboltzman Biopraku04Оценок пока нет
- Albert Einstein: Ell Astronomers Menu Edwin HubbleДокумент5 страницAlbert Einstein: Ell Astronomers Menu Edwin HubbleBharat RanaОценок пока нет
- Turning Points in Physics: A Series of Lectures Given at Oxford University in Trinity Term 1958От EverandTurning Points in Physics: A Series of Lectures Given at Oxford University in Trinity Term 1958Оценок пока нет
- AlbertДокумент1 страницаAlbertMahamudul HassanОценок пока нет
- Albert Einstein BiographyДокумент12 страницAlbert Einstein BiographyAnkush ThapaОценок пока нет
- Modelling and Optimising an Ethylene PlantДокумент115 страницModelling and Optimising an Ethylene PlantFred Faber100% (1)
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Solutions ManualДокумент8 страницMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Solutions ManualmarisorbornewwssОценок пока нет
- Part - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : ElectrochemistryДокумент51 страницаPart - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : ElectrochemistryGOURISH AGRAWALОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 3 Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент45 страницForm 4 Biology Chapter 3 Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneMarcus LeeОценок пока нет
- Andono Kusuma Jati Sampel (Dengan Pemisahan Azeotrop) Prarancangan Pabrik Etilendiamin Dari Bahan Baku Monoetanolamin Dan Amonia Dengan Proses Amonolisis Katalitik Kapasitas 55.000 TonДокумент118 страницAndono Kusuma Jati Sampel (Dengan Pemisahan Azeotrop) Prarancangan Pabrik Etilendiamin Dari Bahan Baku Monoetanolamin Dan Amonia Dengan Proses Amonolisis Katalitik Kapasitas 55.000 Tonandono kusuma jatiОценок пока нет
- He - Ne LASERДокумент20 страницHe - Ne LASERPardeep BhambhuОценок пока нет
- Motorola MSDS 2023 MotorolaДокумент2 страницыMotorola MSDS 2023 MotorolaRizki HerdiawanОценок пока нет
- Water Potential LabreportДокумент3 страницыWater Potential LabreportmichyyyyyОценок пока нет
- 421 821 Chapter 11 20Документ51 страница421 821 Chapter 11 20shaikriyaz4965Оценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips - Pressure Loss of Orifice Plates According To Iso 5167 1Документ3 страницыDokumen - Tips - Pressure Loss of Orifice Plates According To Iso 5167 1Tomi GánnОценок пока нет
- Concise Physics Solutions for MachinesДокумент18 страницConcise Physics Solutions for MachinesBharati GulajkarОценок пока нет
- Principles and Applications Of: PyrometallurgyДокумент19 страницPrinciples and Applications Of: PyrometallurgyChamel Jamora RuperezОценок пока нет
- Smart Materials BookДокумент304 страницыSmart Materials BookemonetoОценок пока нет
- Preschool Science Curriculum Essentials DocumentДокумент18 страницPreschool Science Curriculum Essentials DocumentMuhammad AsadОценок пока нет
- Manual Motor Etron GT Electric - Drive - Motor - 0EGДокумент334 страницыManual Motor Etron GT Electric - Drive - Motor - 0EGRoberto Garcia GodoyОценок пока нет
- Eee 1102Документ26 страницEee 1102Rayhanul Islam LamunОценок пока нет
- 25 Words SilicaДокумент5 страниц25 Words SilicaJahRed FronterasОценок пока нет
- Entrance Exam - 2020: Test No. 2Документ24 страницыEntrance Exam - 2020: Test No. 2Shaestah Fatima100% (2)
- Carbons Support HydroprocessingДокумент3 страницыCarbons Support HydroprocessingsyaОценок пока нет
- Engg Thermodynamics PDFДокумент44 страницыEngg Thermodynamics PDFBrandon FunaОценок пока нет
- Influence of Test Time On The Mechanical Behaviour of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene "ABS"Документ4 страницыInfluence of Test Time On The Mechanical Behaviour of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene "ABS"International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- HumiK Bio WSG FunctionsДокумент5 страницHumiK Bio WSG FunctionsEvelyn Fierro PinoОценок пока нет
- Programmand AbstrctsДокумент272 страницыProgrammand Abstrctsvitis12Оценок пока нет
- Aieee-2010 Model Paper/SAMPLE PAPER BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSESДокумент7 страницAieee-2010 Model Paper/SAMPLE PAPER BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSESANURAG TYAGIОценок пока нет
- PhysicscaДокумент19 страницPhysicscabishal2632Оценок пока нет
- Vibration Analysis and Control Exam QuestionsДокумент4 страницыVibration Analysis and Control Exam QuestionsAshokОценок пока нет
- Physical Properties of Matter LessonДокумент6 страницPhysical Properties of Matter LessonKylene MontalbaОценок пока нет
- Polimeri Uropa StyreneДокумент8 страницPolimeri Uropa StyreneSubrata BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Cie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Документ2 страницыCie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Chris KapendaОценок пока нет