Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Food Chain and Energy Flow
Загружено:
StephenTumulakАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Food Chain and Energy Flow
Загружено:
StephenTumulakАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Food Chain and Energy Flow
Food Chain
A food chain is the sequence of who eats whom in a biological
community (an ecosystem) to obtain nutrition.
A food chain starts with the primary energy source, usually the
sun or boiling-hot deep sea vent.
The next link in the chain is an organism that makes its own
food in the primary energy source an example is the
photosynthetic plants that make their own food from the
sunlight (using a process called photosynthesis) and
chemosynthetic bacteria that make their food energy from the
chemicals in hydrothermal vents, using the process called
chemosynthesis.
Next come organisms that eat the autotrophs: these
organisms are called herbivores or primary consumers.
The next link in the chain is the animals that eat the herbivores
these are called secondary consumers. In turn, these
animals are eaten by larger predators which we call tertiary
consumers.
The tertiary consumers are eaten by quaternary consumers.
Each food chain ends with a top predator and animal with no
natural enemies (like an alligator, hawk, or polar bear).
The arrows in a food chain show how flow of the energy, from
the sun or hydrothermal vent to a predator. As the energy
flows from organism to organism, energy is lost in each step. A
network of many food chains is called a food web.
EXAMPLES OF FOOD CHAIN
Sun to Grass to Grasshopper to Frog to Snake to Hawk
Corn to chicken to Snake to Man to Decomposer
Phytoplankton to crustacean/shrimp to Fish to Dolphin to Killer
whale
Types of food chain
Grazing food chain- Primary producers are the living green
plants which are grazed on by grazing animas. It is found in
aquatic and grassland ecosystem. The grazing food chain
begins with the photosynthetic fixation of light, carbon dioxide,
and water by plants (primary producers) that produce sugar
and other organic molecules. Once produced, these
compounds can be used to create the various types of plant
tissues.
E.g. of aquatic ecosystem:
PhytoplanktonZooplankton Fish Hawk
E.g. grassland ecosystem
Grass Rabbit Fox Wolf Tiger
Grass Grasshopper Frog Snake Hawk
Characteristics of Grazing Food Chain
These are directly dependent upon dollar radiations as the
primary source of energy and the producers (green plants)
synthesize their plant biomass by the process of
photosynthesis. Producers form the first trophic level.
Herbivores or primary consumers eat upon the producers and
form the second trophic level.
Herbivores are in turn eaten by different categories of
carnivores forming the higher trophic levels.
Grazing food chains are longer food chains and they always
end at decomposer level.
Detrital food chain- this type of food chain starts from dead
organic matter and so it is less dependent on solar energy.
The dead organic matter is broken down into simple nutrients
by microorganisms like fungi and bacteria. This type of food
chain is found in forest ecosystem.
Dead organic matter Detritivores predator
Ex. Dead plant to Mushroom to Chicken
The food relationship among different organism is an
ecosystem.
Characteristics of Detritus Food chain
Primary source of energy is dead organic matter called
detritus which are fallen leaves, plant parts or dead animal
bodies.
The food chains are the living components of biosphere
These are the vehicles of transfer of energy from one level to
another.
Primary consumers are detritivores including protozoans,
bacteria, fungi, etc. which feed upon the detritus saprophytic
ally.
Detritivores are in turn eaten by secondary consumers such as
insect6 larvae, nematodes, etc.
Detritus food chains are generally shorter than grazing food
chains
In nature, detritus food chains are indispensable as the dead
organic matter of grazing food chain is acted upon by the
detritivores to recycle the inorganic elements into the
ecosystem.
Parasitic food Chain-In this type of food chain either the
producer or the consumer is parasitized and therefore the food
passes to the smaller organism. The energy transfer through
this kind of food chain is significant.
Producer Herbivores Parasite Hyperparasites
Tree Fruit eating birds Lice and bugs Bacteria and fungi
Significance of Food chain
The studies of food chains help in understanding some of the
important aspects of the ecosystem in particular and
environment in general.
Through the food chains, transfer of materials and nutrients
also takes place.
The movement of some toxic substances in the ecosystem
sprayed to kill to the pests and insects, and also other
organisms can be studied.
They help in maintaining the ecological balance.
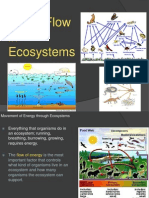
ENERGY FLOW
In Ecology, energy flow, also called calorific flow, refers to the
flow of energy through a food chain. In an ecosystem,
ecologists seek to quantify the relative importance of different
components of species and feeding relationships. It also refers
to the spontaneous transformation of energy flowing in a
complex ecosystem through food chain or a food web in which
the sun is the primary source.
Given example of the diagram showed:
SUN GRASS GRASSHOPPER BIRD MAN
DECOMPOSER
Wherein the sun is the source with 100% energy , pass to the
frays which will only have 80% of energy, eaten by the
grasshopper which will receive 60% of energy, eaten by bird
which will receive 40% energy, eaten by man with 20% energy
and by decomposers with only 10% of energy received.
*We can see that the energy is diminishing since the energy
taken by taken by consumers were already taken by
producers. The energy being used is called mechanical
energy, while the stored energy being passed in the chain is
called chemical energy.
Вам также может понравиться
- Biodiversity ECOSYSTEMДокумент23 страницыBiodiversity ECOSYSTEMpaulangelomicoОценок пока нет
- Food ChainДокумент8 страницFood ChainMJ CorpuzОценок пока нет
- Energy Flow in EcosystemsДокумент21 страницаEnergy Flow in EcosystemsMarlon MarcaidaОценок пока нет
- Our EnvironmentДокумент9 страницOur EnvironmenthafsaОценок пока нет
- FoodДокумент6 страницFoodamrit123qsОценок пока нет
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetДокумент3 страницыEcological Pyramids Worksheetapi-26236818833% (3)
- How Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksОт EverandHow Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksОценок пока нет
- Ecology 2Документ18 страницEcology 2ramloghun veerОценок пока нет
- The World of Food Chains with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОт EverandThe World of Food Chains with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОценок пока нет
- Food Chain and Food WebДокумент12 страницFood Chain and Food Websriyoga100% (2)
- By - N.G.PalitДокумент34 страницыBy - N.G.PalitDeep PatelОценок пока нет
- What Is A Food ChainДокумент2 страницыWhat Is A Food ChainLuzANgelaBAenaОценок пока нет
- The Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksОт EverandThe Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksОценок пока нет
- What Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?Документ3 страницыWhat Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?carlОценок пока нет
- AksinghДокумент18 страницAksinghzehensayan275Оценок пока нет
- Web and Chain FoodДокумент3 страницыWeb and Chain FoodLorena Ruiz BenaventeОценок пока нет
- PEE Module 2Документ3 страницыPEE Module 2Aki WasakosupОценок пока нет
- Food Chain: Food Chains & Food WebsДокумент16 страницFood Chain: Food Chains & Food WebsRose Ann VeloriaОценок пока нет
- Food ChainsДокумент1 страницаFood ChainsOlumide FamakindeОценок пока нет
- Food Chain and Food WebДокумент7 страницFood Chain and Food WebJacqueline Lim Hui ChernОценок пока нет
- EcosystemДокумент56 страницEcosystemlojeОценок пока нет
- Unit 15 NotesДокумент13 страницUnit 15 NoteschainzОценок пока нет
- FOOD CHAIN AND FOOD WEB by Jenie Gyn MasoДокумент17 страницFOOD CHAIN AND FOOD WEB by Jenie Gyn Masonoreen fuentesОценок пока нет
- S5M3L1 Energy Production16!11!2016Документ63 страницыS5M3L1 Energy Production16!11!2016Nipun GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Sum CH3Документ45 страницSum CH3علي نبيل ابو المعاليОценок пока нет
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОт EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОценок пока нет
- Food Chains and WebДокумент15 страницFood Chains and WebJimena MariejoyОценок пока нет
- Energy Flow in An Ecosystem01Документ14 страницEnergy Flow in An Ecosystem01ALIGNDALОценок пока нет
- 3.unit - I, Subunit-C, Producers, Consumers and Decomposers in An EcosystemДокумент2 страницы3.unit - I, Subunit-C, Producers, Consumers and Decomposers in An Ecosystemmilf hunterОценок пока нет
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetДокумент4 страницыEcological Pyramids WorksheetTrilok SawantОценок пока нет
- Brief Notes On The Meaning and Importance of Food Chain and Food WebДокумент2 страницыBrief Notes On The Meaning and Importance of Food Chain and Food WebSumitОценок пока нет
- EssayДокумент8 страницEssayShontel ArcherОценок пока нет
- Circle of Life ProjectДокумент4 страницыCircle of Life Projectapi-238444838Оценок пока нет
- Food Chain and Food WebДокумент15 страницFood Chain and Food WebDr Riaz Ahmad RajaОценок пока нет
- Relationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesДокумент18 страницRelationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesBalakrishnan MarappanОценок пока нет
- The EcosystemДокумент8 страницThe EcosystemRishabh Vasudev KapatkarОценок пока нет
- HSB - Lesson A-2Документ29 страницHSB - Lesson A-2Osmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Organisms and Their EnvironementДокумент19 страницOrganisms and Their EnvironementAlag MohammedОценок пока нет
- Unit-2 Ecosystem and Bio DiversityДокумент160 страницUnit-2 Ecosystem and Bio DiversityRaghavendra Prasad0% (1)
- What Is Food ChainДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Food ChainLovelManaloLacastesantosОценок пока нет
- FoodchainДокумент13 страницFoodchainSchahyda ArleyОценок пока нет
- EVS - Unit-1 (Notes)Документ51 страницаEVS - Unit-1 (Notes)Saksham AroraОценок пока нет
- EcosystemДокумент6 страницEcosystemLonnie AsisОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 EcosystemДокумент19 страницLecture 2 EcosystemParva PatelОценок пока нет
- Our Environment: Chapter - 15Документ10 страницOur Environment: Chapter - 15IshvaryaОценок пока нет
- EcosystemДокумент25 страницEcosystemSoumya RanjanОценок пока нет
- Energy Flow in An EcosystemДокумент12 страницEnergy Flow in An EcosystemAnita VardhanОценок пока нет
- Amazing Grace Christian School: Food WebДокумент6 страницAmazing Grace Christian School: Food WebpenshipОценок пока нет
- Energy Flow in An EcosystemДокумент3 страницыEnergy Flow in An EcosystemTristan NatsirtОценок пока нет
- Our Environment Notes 1Документ9 страницOur Environment Notes 1Kanishka ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Usable Energy Decreases With Each Link in A Food Chain or WebДокумент9 страницUsable Energy Decreases With Each Link in A Food Chain or WebPaul Jeremy MendozaОценок пока нет
- The Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartsДокумент3 страницыThe Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartskoiaitraazОценок пока нет
- EcosystemДокумент20 страницEcosystemFaraz NaqviОценок пока нет
- Unit I Chapter 2-EcosystemsДокумент49 страницUnit I Chapter 2-EcosystemsSATISHОценок пока нет
- Key Points:: Producers, or Autotrophs, Make Their Own OrganicДокумент13 страницKey Points:: Producers, or Autotrophs, Make Their Own Organicjoyce sumagaysayОценок пока нет
- Food Chains and Webs WorksheetsДокумент10 страницFood Chains and Webs Worksheetsitz tyreezyОценок пока нет
- Food Chain & WebДокумент14 страницFood Chain & WebJun Bryan AcobОценок пока нет
- Low and High BiodiversityДокумент14 страницLow and High BiodiversityPRINTDESK by DanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 10 Energy Flow in EcosystemДокумент2 страницыLecture 10 Energy Flow in EcosystemPaui Parado EranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 2 Ecosystem-1Документ18 страницChapter 1 2 Ecosystem-1nikhil110705Оценок пока нет
- Opinion For Tuvera Case 1985Документ9 страницOpinion For Tuvera Case 1985StephenTumulakОценок пока нет
- Opinion For Tuvera Case 1985Документ9 страницOpinion For Tuvera Case 1985StephenTumulakОценок пока нет
- Opinion For Tuvera Case 1985Документ9 страницOpinion For Tuvera Case 1985StephenTumulakОценок пока нет
- Abstract of Cebuano MusicДокумент12 страницAbstract of Cebuano MusicStephenTumulakОценок пока нет
- Geraldine M. Repolidon Nice Ann L. TeleronДокумент12 страницGeraldine M. Repolidon Nice Ann L. TeleronStephenTumulakОценок пока нет
- APA Style Format Daftar Pustaka PDFДокумент4 страницыAPA Style Format Daftar Pustaka PDFfilantropiОценок пока нет
- Tmp669e TMPДокумент302 страницыTmp669e TMPFrontiersОценок пока нет
- Good Agricultural PracticesДокумент2 страницыGood Agricultural Practicesselvi cvieОценок пока нет
- Kagera TfcaДокумент2 страницыKagera Tfcaapi-278754474Оценок пока нет
- Lam 101-11Документ240 страницLam 101-11mrcdtsОценок пока нет
- Peperone Di SeniseДокумент3 страницыPeperone Di SenisepikermiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Section 1 OutlineДокумент4 страницыChapter 4 Section 1 Outlineapi-263455059Оценок пока нет
- Epifitas Da Pedra AzulДокумент13 страницEpifitas Da Pedra AzulAndre AssisОценок пока нет
- Chicaque Natural ParkДокумент11 страницChicaque Natural ParkA'p DanielОценок пока нет
- Forest EcologyДокумент17 страницForest EcologyHamed MemarianОценок пока нет
- New Guinea New Species 2011Документ60 страницNew Guinea New Species 2011Alberto Chan100% (1)
- Project On Water ScarcityДокумент22 страницыProject On Water ScarcityGaurav100% (1)
- Ecological Concerns - Hasmukh ShahДокумент6 страницEcological Concerns - Hasmukh ShahSomnath BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- EVS (1st & 2nd Sem)Документ105 страницEVS (1st & 2nd Sem)api-372366486% (97)
- HA 108-04 Landscape Management Handbook (DMRB, 2004)Документ150 страницHA 108-04 Landscape Management Handbook (DMRB, 2004)sandycastleОценок пока нет
- Notes - Ch. 11 Biodiversity and Conservation EcologyДокумент59 страницNotes - Ch. 11 Biodiversity and Conservation Ecologymishra_suvasmita100% (1)
- Guided Notes - Bio 365 - Estuaries by Lucia Galan MartinДокумент5 страницGuided Notes - Bio 365 - Estuaries by Lucia Galan MartinLuci G.MОценок пока нет
- Tiger Fact Sheet FINALДокумент2 страницыTiger Fact Sheet FINALVijay PatilОценок пока нет
- Still About Though, Although, EventhoughДокумент2 страницыStill About Though, Although, EventhoughAndre Wahyu100% (1)
- New Australian Curriculum Senior Secondary BiologyДокумент44 страницыNew Australian Curriculum Senior Secondary Biologyapi-252350138Оценок пока нет
- Ecology ToolsДокумент11 страницEcology ToolsSupriyadiОценок пока нет
- Biopsychosocial Model in Depression Revisited: Mauro Garcia-Toro, Iratxe AguirreДокумент9 страницBiopsychosocial Model in Depression Revisited: Mauro Garcia-Toro, Iratxe AguirreayannaxemОценок пока нет
- Flagship SpeciesДокумент12 страницFlagship SpeciesGuildner AntunesОценок пока нет
- Tes Evaluasi Reading Comprehension 8Документ4 страницыTes Evaluasi Reading Comprehension 8YELLY ANDRIANI BARLIANОценок пока нет
- Marine Science Semester 1 ReviewДокумент18 страницMarine Science Semester 1 ReviewJoe Xavier ReidyОценок пока нет
- Biodiversity and Natural Selection (Miller and Spoolman)Документ58 страницBiodiversity and Natural Selection (Miller and Spoolman)John OsborneОценок пока нет
- 4.1.2 - Observable Characteristics of Healthy Outdoor Environments Work TaskДокумент9 страниц4.1.2 - Observable Characteristics of Healthy Outdoor Environments Work TaskChrisОценок пока нет
- Enviornmental Education & Disaster Management SPVC Practice Test Series P.R.S Educational Trust Module-IДокумент18 страницEnviornmental Education & Disaster Management SPVC Practice Test Series P.R.S Educational Trust Module-IAkhil SharmaОценок пока нет
- November 2015 Wolf Delisting LetterДокумент8 страницNovember 2015 Wolf Delisting LetterDetroit Free PressОценок пока нет
- PhaesantsДокумент74 страницыPhaesantsbolbocОценок пока нет