Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
English Presentation - Corrected.
Загружено:
callaunpoco19Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
English Presentation - Corrected.
Загружено:
callaunpoco19Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
English presentation:
48.
Hi, my name is Monica and I am going to talk about the fundamental characteristics of
power MOSFETs which are: maximum drain-source voltage, maximum drain current,
drain-source on state resistance, drain-source breakdown voltage and gate threshold
voltage, and switching process.
The maximum drain-source voltage corresponds to the breakdown voltage of the
junction forming the substrate and the drain. It is measured with the shorted gate to
source.
The maximum drain-source voltage is represented as Vdd or Vbrdss. This value is used
to classify the power MOSFET transistors. An example of classification is shown in this
slide, which is classified into low, medium and high voltage. Low voltage goes from 15 V
to 80V, medium voltage from 100 V to 400 V and high voltage from 500 to 1200 V.
49.
Another characteristic is the maximum drain current. The manufacturer supplies two
values (at least); these two values are the maximum continuous drain current, Id and
the maximum pulsed drian current, Idm.
This table shows the different parameters mentioned so far and the conditions that have
to accomplish to reach a certain maximum or minimum.
Between a (operating junction) temperature of 25 C and 175C (degrees
Celsius) the drain-source voltage reaches a maximum voltage of 100 volts.
Between a (operating junction) temperature of 25 C and 175C (degrees
Celsius) and a gate-source resistance of 20 KOhmios, the drain-gate voltage
reaches a maximum voltage of 100 volts.
In the same conditions of the previous parameter (drain-gate voltage), the gatesource voltage reaches a maximum voltage of 20 volts and a minimum of 20
volts.
With a mounting base temperature of 25C and gate-source voltage of 10 volts,
the continuous drain current reaches a maximum intensity of 23 Amps.
With a mounting base temperature of 100C and gate-source voltage of 10
volts, the pulsed drain current reaches a maximum intensity of 16 Amps and
the same parameter with a mounting base temperature of 25C it reaches a
maximum intensity of 92 Amps.
With a mounting base temperature of 25C, the total power dissipation reaches
a maximum of 100 watts and operating junction and storage temperature
reaches a minimum of -55C and a maximum of 175C.
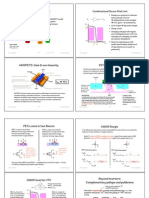
In this graph shows that the maximum continuous drain current ID depends on the
mounting base temperature. With the temperature increases the intensity decreases.
50.
The third characteristic is drain-source on state resistance. It is one of the most
important parameters in a MOSFET. The device is better when decreases drain-source
on state resistance. It is represented by the letters RDS (on). For a particular device, it
increases with the temperature. For a particular device, it decreases with the gate
voltage. This decrease is limited.
The graph on the left shows that increasing junction temperature also increases
normalized on-state resistance. In the graph on the right is shown that with typical onstate resistance of 25 C the drain-source on resistance depends on the drain current
for different values of gain-source voltage.
51.
The following tables compare different devices with similar Id values, RDS (on) increases
with the value of VDSS.
52.
In recent times values for RDS (on) have been improved in devices of VDSS relatively
high (600-1000 V).
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Experimenter: The Impoverished RadioДокумент52 страницыExperimenter: The Impoverished Radiobenra1100% (1)
- Ad8626arz 1706439Документ20 страницAd8626arz 1706439callaunpoco19Оценок пока нет
- OP07Документ16 страницOP07enzo_60Оценок пока нет
- OP07Документ16 страницOP07enzo_60Оценок пока нет
- PSMN069-100YS: 1. Product ProfileДокумент15 страницPSMN069-100YS: 1. Product Profilecallaunpoco19Оценок пока нет
- Mitigation Strategies For ECG Design ChallengesДокумент6 страницMitigation Strategies For ECG Design Challengescallaunpoco19Оценок пока нет
- EC1401 VLSI - Question Bank (N.shanmuga Sundaram)Документ35 страницEC1401 VLSI - Question Bank (N.shanmuga Sundaram)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram50% (2)
- Oxide Electronics and Functional Properties. FPДокумент253 страницыOxide Electronics and Functional Properties. FPPetrОценок пока нет
- EE6503 Power Electronics NotesДокумент234 страницыEE6503 Power Electronics Notessyed ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Durg: CertificateДокумент18 страницKendriya Vidyalaya Durg: Certificates praneetОценок пока нет
- AlGaN/GaN HEMTsДокумент44 страницыAlGaN/GaN HEMTsGagandeep Singh KalerОценок пока нет
- Cci 4202 Electronics Course Outline September Decemeber 2022Документ6 страницCci 4202 Electronics Course Outline September Decemeber 2022Blueprint MihОценок пока нет
- Electrical Power Steering Design Guide TEXASДокумент18 страницElectrical Power Steering Design Guide TEXASacmilan4eva1899100% (1)
- The Depletion Type MOSFETДокумент4 страницыThe Depletion Type MOSFETsarvajee216Оценок пока нет
- An - 5494 Mga-635p8Документ8 страницAn - 5494 Mga-635p8biastee7690Оценок пока нет
- Rca-Ctc185 (ET)Документ50 страницRca-Ctc185 (ET)Luis QuiñonesОценок пока нет
- Chap04 (12 21 06) PDFДокумент66 страницChap04 (12 21 06) PDFHassan FarssiОценок пока нет
- GaN Power Device Tutorial Part2 GaN DrivingДокумент63 страницыGaN Power Device Tutorial Part2 GaN DrivingdjyОценок пока нет
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент16 страницEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017Оценок пока нет
- A1707 N - MosДокумент9 страницA1707 N - MosAnonymous Im6zx7xiyОценок пока нет
- 5300地阻表使用说明Документ20 страниц5300地阻表使用说明leo_j9Оценок пока нет
- Physics of The Ignition System PDFДокумент10 страницPhysics of The Ignition System PDFmeetbalakumar100% (1)
- Project PresentationДокумент17 страницProject PresentationBhushan JoshiОценок пока нет
- Freescale Semiconductor: Application NoteДокумент28 страницFreescale Semiconductor: Application NotehecormarОценок пока нет
- NGD8201N, NGD8201AN Ignition IGBT: 20 A, 400 V, N Channel DPAKДокумент8 страницNGD8201N, NGD8201AN Ignition IGBT: 20 A, 400 V, N Channel DPAKKevine KhaledОценок пока нет
- SPICE Simulation Analysis Using Net Listing and Default/Commercial ModelsДокумент91 страницаSPICE Simulation Analysis Using Net Listing and Default/Commercial ModelsSiva YellampalliОценок пока нет
- Electrician: Syllabus of Semester System For The Trade ofДокумент27 страницElectrician: Syllabus of Semester System For The Trade ofTusharОценок пока нет
- Datasheet - HK R2a20112 1756Документ1 страницаDatasheet - HK R2a20112 1756joe ramОценок пока нет
- IGBT HandbookДокумент130 страницIGBT HandbookmrchlОценок пока нет
- IRIS A6359 InternationalRectifierДокумент7 страницIRIS A6359 InternationalRectifierosito6197Оценок пока нет
- 100 Top Electronic Devices and Circuits Questions and Answers PDF Electronic Devices and Circuits QuestionsДокумент15 страниц100 Top Electronic Devices and Circuits Questions and Answers PDF Electronic Devices and Circuits QuestionsAnandPrakashSinhaОценок пока нет
- MTP3055Документ9 страницMTP3055lisandroantonОценок пока нет
- PMMD Model Questions Semiconductor PhysicsДокумент4 страницыPMMD Model Questions Semiconductor PhysicslavishОценок пока нет
- An 84 FДокумент160 страницAn 84 FАлександр АндриановОценок пока нет
- CMOS Technology: Combinational Device Wish ListДокумент6 страницCMOS Technology: Combinational Device Wish Listkunalsekhri123Оценок пока нет