Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mathematics 1
Загружено:
Anonymous JnvCyu85Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mathematics 1
Загружено:
Anonymous JnvCyu85Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
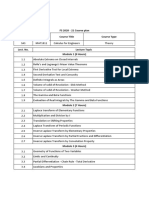
NPTEL Syllabus
Mathematics I - Web course
COURSE OUTLINE
Basic calulus of one and several variables.
COURSE DETAIL
Modules
MODULE 1.
Lectures
NPTEL
Numbers, functions, and sequences
1.1 Real numbers
1.2 Functions
1.3 Need to consider sequences
2.1 Convergent sequences
2.2 Bounded sequences
3.1 Monotone sequences
3.2 Limit theorems
3.3 Some extensions of the limit concept
MODULE 2.
Prof. Inder K Rana
Department of
Mathematics
IIT Bombay
theorem
Maxima, minima and curve sketching
10.1 Sufficient conditions for increasing/decreasing
10.2 Sufficient conditions for local extremum
11.1 Absolute maximum/minimum
11.2 Convex /concave functions
12.1 Asymptotes
12.2 Curve sketching
MODULE 5.
Pre-requisites:
Higher secondary
Coordinators:
Differentiation
7.1 Differentiation
8.1 Chain rule
8.2 Successive differentiation
9.1 Rolles theorem and mean value
MODULE 4.
Basic courses(Sem 1 and 2)
Limit and continuity
4.1 Limit of a function at a point
5.1 Extending the limit concept
5.2 Continuity of functions
6.1 Discontinuities of a function
6.2 Properties of continuous functions
MODULE 3.
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
Approximations
13.1 Linear approximations
13.2 Error estimate for linear approximations
14.1 Taylors theorem
14.2 Quadratic approximations
15.1 Newtons method for locating zeros of a function
15.2 Picards method
MODULE 6.
Integration
16.1 Integral from upper and lower sums
16.2 Integral as a limit of Riemann sums
17.1 Fundamental theorem of calculus
17.2 Applications of fundamental theorem of calculus
18.1 Approximating integral: Trapezoidal rule
18.2 Approximating integrals: Simpsons rule
MODULE 7.
Logarithmic and exponential functions
19.1 Definition of the natural logarithmic function
19.2 Exponential function with natural base
20.1 General exponential function and the power function
20.2 LHopitals rules
21.1 Relative growth rates of functions
21.2 Area bounded by two curves
MODULE 8.
Applications of Integration
22.1 Arc length of a plane curve
22.2 Arc length of a curve in parametric form
23.1 Area of a surface of revolution
23.2 Volume of a solid by slicing
24.1 Volumes of solids by the washer method
24.2 Volume of a solid of revolution by shell method
MODULE 9.
Series of numbers and functions
25.1 Series of numbers
25.2 Simple tests of convergence
26.1 More tests of convergence
26.2 Absolute and conditional convergence
27.1 Power Series
27.2 Taylor series and Maclaurin series
MODULE 10.
Limit and continuity of scalar fields
28.1 Spaces R2 and R3 272
28.2 Scalar fields, level curves and contour lines
29.1 Limit of a scalar field
29.2 Limit theorems
30.1 Continuity of scalar fields
30.2 Properties of continuous scalar fields
MODULE 11.
Differentiation of scalar fields
31.1 Partial derivatives
31.2 Differentiability
32.1 Chain rules
33.1 Implicit differentiation
33.2 Directional derivative
MODULE 12.
Gradient, tangent plane and linearization
34.1 Gradient of a scalar field
35.1 Tangent plane and normal to a surface
35.2 Higher order partial derivatives
36.1 Mean value theorem and linearization
MODULE 13.
Maxima and minima for scalar fields
37.1 Maxima and minima
37.2 Saddle points
38.1 Second derivative test for maxima/minima
39.1 Absolute maxima/minima
39.2 Constrained maxima/minima
MODULE 14.
Multiple Integration
40.1 Double integrals over rectangular domains
40.2 Integral on general domains
41.1 Triple integrals
41.2 Applications of multiple integrals
42.1 Change of variables
42.2 Polar, cylindrical and spherical coordinates
MODULE 15.
Vector fields
43.1 Vector fields and their properties
44.1 Gradient, divergence and curl
45.1 Curves in space 406
45.2 Velocity vector, tangent vector
MODULE 16. Line integrals and Greens theorem
46.1 Line integrals
46.2 Application of line integrals
47.1 Fundamental Theorems of Calculus for line integrals.
47.2 Conservative vector fields
48.1 Greens theorem
48.2 Applications of Greens theorem
MODULE 17.
Surface integrals and divergence theorem
49.1 Surfaces and parameterizations
49.2 Area of a surface
50.1 Surface integrals
50.2 Applications of surface integrals
51.1 Divergence theorem
51.2 Applications of divergence theorem
MODULE 18.
Stokes theorem and applications
52.1 Orienting the boundary of an orientable surface
52.2 Stokes theorem
53.1 Verification of Stokes theorem
53.2 Extending Stokes theorem to general domains
54.1 Applications of Stokes theorem
References:
Calclus by Thomas and Finney, Nineth Edition, Adison Weseley
A joint venture by IISc and IITs, funded by MHRD, Govt of India
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
Вам также может понравиться
- Academic Year 2021/2022: MATH 2041: APPLIED MATHEMATICS II (Pre Engineering Students)Документ2 страницыAcademic Year 2021/2022: MATH 2041: APPLIED MATHEMATICS II (Pre Engineering Students)Abiy Alemu100% (1)
- Multivariable Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential EquationsОт EverandMultivariable Calculus, Linear Algebra, and Differential EquationsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (6)
- Math 2041: Applied Mathematics Ii: Academic Year 2023/2024Документ2 страницыMath 2041: Applied Mathematics Ii: Academic Year 2023/2024FishОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Ordinary Differential EquationsДокумент3 страницыChapter 1: Ordinary Differential EquationsColorgold BirlieОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Mathematical Methods for Environmental Engineers and ScientistsОт EverandIntroduction to Mathematical Methods for Environmental Engineers and ScientistsОценок пока нет
- Model Curriculum Diploma Electrical Engineering 310812.PDF-Copy ExportДокумент24 страницыModel Curriculum Diploma Electrical Engineering 310812.PDF-Copy ExportnavneetОценок пока нет
- Math 2A Suggested Syllabus (Based On 29 Lectures) : TextДокумент1 страницаMath 2A Suggested Syllabus (Based On 29 Lectures) : TextIihya UlumnОценок пока нет
- Network Theory Syllabus 2Документ12 страницNetwork Theory Syllabus 2anuОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: - Euclidean Three SpaceДокумент2 страницыChapter One: - Euclidean Three SpaceoscartttОценок пока нет
- Electronics and Communication EngineeringДокумент154 страницыElectronics and Communication EngineeringVinitha SankerОценок пока нет
- Sample 8118Документ11 страницSample 8118Aarav MahajanОценок пока нет
- Silibus QQM 1023 S10910Документ3 страницыSilibus QQM 1023 S10910kshufeiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics for Electronic Technology: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesОт EverandMathematics for Electronic Technology: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesОценок пока нет
- Strang DataДокумент2 страницыStrang DataJustA DummyОценок пока нет
- Difcal TopicsДокумент1 страницаDifcal Topicsjutr ruyluОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Jan09 MAT183Документ2 страницыSyllabus Jan09 MAT183Mike ZakwanОценок пока нет
- Calculus II 2 1 1 2Документ3 страницыCalculus II 2 1 1 2Amante ChalaОценок пока нет
- Solid State Devices Syllabus - Ktunotes - inДокумент7 страницSolid State Devices Syllabus - Ktunotes - inNISHIYA VIJAYANОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент3 страницыSyllabusDevang SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mathematics for Engineering, Technology and Computing Science: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionОт EverandMathematics for Engineering, Technology and Computing Science: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionОценок пока нет
- CALCULUS: Single Variable: SYLLABUS: Each Lecture Approximately 12-16 MinutesДокумент2 страницыCALCULUS: Single Variable: SYLLABUS: Each Lecture Approximately 12-16 MinutesAnnie FreebiesОценок пока нет
- Lec # Topics Key Dates I. Vectors and MatricesДокумент2 страницыLec # Topics Key Dates I. Vectors and MatricesliznОценок пока нет
- 2nd Year Course OutlineДокумент19 страниц2nd Year Course OutlineMiliyon TilahunОценок пока нет
- Bridge Course MATHS - I FinalДокумент457 страницBridge Course MATHS - I FinalSarvan KumarОценок пока нет
- SMK Puteri, Seremban. Item Specification Table Additional Mathematics Paper 1Документ2 страницыSMK Puteri, Seremban. Item Specification Table Additional Mathematics Paper 1ziehan995610Оценок пока нет
- (Umran S. Inan, Robert A. Marshall) Numerical Elec PDFДокумент406 страниц(Umran S. Inan, Robert A. Marshall) Numerical Elec PDFRodrigo PaivaОценок пока нет
- Numerical Electromagnetics The FDTD MethodДокумент406 страницNumerical Electromagnetics The FDTD MethodMarcelle LemosОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra and Multivariable CalculusДокумент3 страницыLinear Algebra and Multivariable Calculusj73774352Оценок пока нет
- Chebyshev and Fourier Spectral Methods: Second Revised EditionОт EverandChebyshev and Fourier Spectral Methods: Second Revised EditionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- SYLLABUSДокумент2 страницыSYLLABUStressОценок пока нет
- Calculus: Introductory Theory and Applications in Physical and Life ScienceОт EverandCalculus: Introductory Theory and Applications in Physical and Life ScienceРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Classical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIДокумент342 страницыClassical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIDavid PattyОценок пока нет
- 3rd Sem SyllabusДокумент9 страниц3rd Sem SyllabusibuОценок пока нет
- Std11 Maths EM 1 PDFДокумент271 страницаStd11 Maths EM 1 PDFTshegofatso Ntsime100% (1)
- Mathematics - Ia: Telangana State Board of Intermediate Education, HyderabadДокумент3 страницыMathematics - Ia: Telangana State Board of Intermediate Education, HyderabadUdayОценок пока нет
- Course Outline - Engineering Mathematics - IIIДокумент6 страницCourse Outline - Engineering Mathematics - IIIShivam KumarОценок пока нет
- EC SyllabusДокумент118 страницEC SyllabusSriganeshОценок пока нет
- Microwave LiaoДокумент545 страницMicrowave Liaoramuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuu100% (6)
- Mathematical Methods: A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsОт EverandMathematical Methods: A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence DesignОт EverandMagnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence DesignРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Understanding Least Squares Estimation and Geomatics Data AnalysisОт EverandUnderstanding Least Squares Estimation and Geomatics Data AnalysisОценок пока нет
- A Course of Mathematics for Engineerings and Scientists: Volume 2От EverandA Course of Mathematics for Engineerings and Scientists: Volume 2Оценок пока нет
- Introductory Calculus: With Analytic Geometry and Linear AlgebraОт EverandIntroductory Calculus: With Analytic Geometry and Linear AlgebraРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Providing Healthy Media Usage Among Children PDFДокумент9 страницProviding Healthy Media Usage Among Children PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Nature and Nuture PDFДокумент6 страницNature and Nuture PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Principles of Growth and Development PDFДокумент9 страницPrinciples of Growth and Development PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Types of Socializing Agent PDFДокумент7 страницTypes of Socializing Agent PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Marginalized Group PDFДокумент5 страницMarginalized Group PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Child Abuse PDFДокумент8 страницChild Abuse PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Studies Support Environment PDFДокумент5 страницStudies Support Environment PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- School As Socializing Agency PDFДокумент2 страницыSchool As Socializing Agency PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Important Problems of Adolescent PDFДокумент4 страницыImportant Problems of Adolescent PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Factors Influencing Gender Stereotypes PDFДокумент9 страницFactors Influencing Gender Stereotypes PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Environment Pollution PDFДокумент3 страницыFactors Affecting Environment Pollution PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Dimensions of Growth and Development PDFДокумент7 страницDimensions of Growth and Development PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Gender School Type in Child PDFДокумент4 страницыGender School Type in Child PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Gender Identity PDFДокумент5 страницGender Identity PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Impact of Media Violence PDFДокумент4 страницыImpact of Media Violence PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Growth and Development PDFДокумент9 страницCharacteristics of Growth and Development PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Marginalized Children PDFДокумент4 страницыMarginalized Children PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Dimensions of Development PDFДокумент7 страницDimensions of Development PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Impact of Mass Media PDFДокумент6 страницImpact of Mass Media PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Factors Influencing Growth and Development PDFДокумент6 страницFactors Influencing Growth and Development PDFAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 ProgramДокумент23 страницыChapter 12 ProgramAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Stoichiometry 1 QPДокумент9 страницStoichiometry 1 QPTee Xin RuiОценок пока нет
- Digital Video Is Sequence ofДокумент2 страницыDigital Video Is Sequence ofAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Amplifier Builders Guide - Hugo Gernsback - 1964Документ33 страницыAmplifier Builders Guide - Hugo Gernsback - 1964TheAncientOneОценок пока нет
- 11 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 10 2Документ15 страниц11 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 10 2Anonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- EC6016 SyllabusДокумент1 страницаEC6016 SyllabusAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 5 by RajatДокумент52 страницыRajkumar Biology Unit - 5 by RajatShrikant KumarОценок пока нет
- EC6001 Medical ElectronicsДокумент15 страницEC6001 Medical ElectronicsAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- 2009 TNPSC Group I Preliminary Question PaperДокумент56 страниц2009 TNPSC Group I Preliminary Question PaperKrishna KumarОценок пока нет
- Raspberry Pi IOT 2 Days Agenda - NewДокумент2 страницыRaspberry Pi IOT 2 Days Agenda - NewAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Wintergreen Interactive 2012Документ44 страницыWintergreen Interactive 2012natasha_bretonОценок пока нет
- 9709 s09 Ms 1Документ6 страниц9709 s09 Ms 1Thapa GorkhaОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 Electric PotentialДокумент4 страницыLab 4 Electric PotentialJorge Tenorio0% (1)
- G11-M4-GEN MATH (New)Документ10 страницG11-M4-GEN MATH (New)Rizah HernandezОценок пока нет
- D DX X X D DX X T D DX T: Antiderivative of A FunctionДокумент1 страницаD DX X X D DX X T D DX T: Antiderivative of A FunctionCherry Pye TerradoОценок пока нет
- 2 Linear TransformationsДокумент32 страницы2 Linear TransformationsShanОценок пока нет
- 2.7 - Gauss Divergence TheoremДокумент44 страницы2.7 - Gauss Divergence TheoremindraОценок пока нет
- Homotopy PDFДокумент9 страницHomotopy PDFPllamenowa IvoОценок пока нет
- Problem Set Surv2Документ2 страницыProblem Set Surv2Karl TristanОценок пока нет
- Points & Straight Lines - SolutionsДокумент11 страницPoints & Straight Lines - SolutionswolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Numerical LiteracyДокумент14 страницNumerical LiteracybiahОценок пока нет
- Fraction - Practice Worksheet - 3Документ3 страницыFraction - Practice Worksheet - 3Sahaj GhaiОценок пока нет
- 03-Time-Domain Analysis of LTI SystemsДокумент32 страницы03-Time-Domain Analysis of LTI Systemsmesfin snowОценок пока нет
- QB BcsДокумент10 страницQB BcsKrishna Reddy Y.VОценок пока нет
- 7 2 Division Properties of ExponentsДокумент35 страниц7 2 Division Properties of Exponentsahmdhjw24Оценок пока нет
- File Cbse Class 9 Formulas 1582195334 PDFДокумент19 страницFile Cbse Class 9 Formulas 1582195334 PDFAtiqueОценок пока нет
- Alan Bain - Stochastic CalculusДокумент89 страницAlan Bain - Stochastic CalculusSachin BamaneОценок пока нет
- Boards Subjective Assignment 1 Determinants-1Документ2 страницыBoards Subjective Assignment 1 Determinants-1fortrial197Оценок пока нет
- Sap Focus Math 1Документ2 страницыSap Focus Math 1api-268693524Оценок пока нет
- ProblemsДокумент7 страницProblemsZhugzhuang ZuryОценок пока нет
- 2014 PaperДокумент8 страниц2014 PaperTuff BubaОценок пока нет
- Vdocument - in - by Balraj Khurana Vidyarthi Tutorials h10 Raghu Nagar Pankha Roadopp c3 Janakpuriph9818084221Документ18 страницVdocument - in - by Balraj Khurana Vidyarthi Tutorials h10 Raghu Nagar Pankha Roadopp c3 Janakpuriph9818084221Naeem AhmadОценок пока нет
- FA2.3 Pythgoras' TheoremДокумент6 страницFA2.3 Pythgoras' TheoremanthonyОценок пока нет
- R1.6 Scientific Notation Review ANSWERSДокумент8 страницR1.6 Scientific Notation Review ANSWERSNavam S PakianathanОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1270963809001060 Main PDFДокумент4 страницы1 s2.0 S1270963809001060 Main PDFali_raza117Оценок пока нет
- Question Paper Code: 3098: B.A./B.Sc. (Part-III) Examination, 2018Документ4 страницыQuestion Paper Code: 3098: B.A./B.Sc. (Part-III) Examination, 2018ShivamОценок пока нет
- Discrete Control SystemsДокумент4 страницыDiscrete Control SystemsVijay PrabhuОценок пока нет
- Types of Lines and AnglesДокумент5 страницTypes of Lines and Anglesdeep72100% (1)
- Unit2 CS8792 CNS Notes PECДокумент65 страницUnit2 CS8792 CNS Notes PECdharshukiran2096Оценок пока нет
- Matched Filter - WikipediaДокумент9 страницMatched Filter - WikipediaPaidamoyo MuzvidziwaОценок пока нет