Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Shoe Project
Загружено:
dnt563Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Shoe Project
Загружено:
dnt563Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
You can find step-by-step instructions for making electricity generating sneakers
at Angelos Instructables site. Here are the materials youll need: generic USB
powerbank, piezoelectric transducers, rectifier diodes, hookup wire, some adhesive, and
an old pair of shoes.
There are other power-generating, in-shoe concepts. For example, SolePower stores
the energy released in each of our steps as usable electrical power; the technology
works like a hand-crank flashlight. Another idea relies on a technique called reverse
electrowetting: converting the energy of metal droplets in the soles into an electrical
current.
Read more at http://www.iflscience.com/technology/teenager-invents-energygenerating-shoe-insoles#xMIL9WpTbTo3u3qh.99
Development of The Project:
The power generating soles are one of my first concept projects. I started my first
prototype last five years ago although it was a very primitive, compared to my current
design. My old prototype had two TO-3 plastic spacer sandwiched between two piezo
discs. It produces a fair amount of current, enough to charge a Nokia 3310.
5 years later, I came back with the idea of using the sandwiched piezo setup, this time
integrated to a charge collector and powerbank. So I thought, why not add 2 more pairs?
After all, more is better.
Concept Behind The Project:
Piezoelectricity was present ever since mid-18th century. Piezoelectricity is the electric
charge that accumulates in certain solid materials (such as crystals, certain ceramics in
response to applied mechanical stress. This sounds familiar! Yes they do, you can
actually find those piezo elements in your old/ outdated earphones from the 90's.
Why Not Use Dynamos?
As much as possible, I tried to avoid using dynamos. Yes dynamos produce more
electricity but it will feel like you've stuffed a rock in your shoe. Don't forget dynamos will
create a lot of noise.
Any Practical Uses?
As funny as it sounds, charging a phone with your shoe isn't really joke. Who knows
maybe someday shoe companies like Nike could use these insole generators to power
fitness chips (inside shoes) that would sync to your phone wirelessly. This way, you
don't have to charge your smart-shoes just to sync them with your phone.
Disclaimer: This is just a little science experiment. It will show you the concept of
producing electricity using piezoelectric elements. Don't assume that is close in
becoming a product.
A Question That Bothers Me A Lot:
Why not use traditional renewable energy sources? Yes I know piezoelectricty is not as
well develop as of those solar powered devices but as a curious being, I am open to
discovering potential energy sources. Yes, footwear generators may sound crazy and
ridiculous but there's more than what meets the eye! These thin insole generators have
enough power to supply low current devices.
______________________________________________________
Problem:
Coal power is the most common energy source used in the Philippines ,also in the
world. For the past decade, our country has been tapping to renewable sources of
energy although its not rendered free and its price continuously changes (Philippine
Star, January 2014). Most undeveloped areas, specially provinces, have no access to
electricity. For the people who are living in the suburbs, charging a phone or a lamp is a
big deal for them
Over the past years, my science experiments were mostly about renewable energy. I
started my first science fair experiment when I was in third-grade, it was my first
miniature model of a solar car. The receding years of my science fair entries were
mostly about wind, solar, hydro and chemical energy.
My goal is to find a new source of renewable energy, something that does not depend
on wind, water or sunlight. I did some random research and I came through tons of ecoenergy production articles. I told myself, if I'll go with another solar/ wind experiment,
there won't be enough innovation by just remaking a project from the internet. Like all
scientists, I had to think out of the box.
Questions To Ponder On:
- Does it have enough power to supply electricity for low consumption modules?
- Will it produce enough power to charge USB devices?
- Can it reach the USB standards?
- Can it power a series of LEDs?
Future Practical Applications:
- Supply on-board/ independent power for smarts shoes and clothing.
- Aid outdoorsmen/ hikers, with GPS tracking shoes,in their journey into the vast
wilderness.
- Great for areas where electricity is scarce. - Self-powering rescue chips in shoes.
Research:
The project is be accomplished by using piezoelectric materials. Piezoelectricity, also
called the piezoelectric effect, is the ability of certain materials to generate an alternating
current voltage when actuated.Certain ceramics, Rochelle salts, and various other solids
exhibit this effect. For example, (Pb[ZrxTi1x]O3 where,0x1), also called PZT, will
generate measurable electricity when their structure is deformed by about 0.1% of the
original dimension(International AAAI Conference on Social Media and Weblogs, 2012).
In this project, the generated electricity on a specific time will be recorded and determine
if it would be enough to completely charge a Li-ion battery or a high capacity capacitor.
The project is be accomplished by using piezoelectric materials. Piezoelectricity, also
called the piezoelectric effect, is the ability of certain materials to generate an alternating
current voltage when actuated.Certain ceramics, Rochelle salts, and various other solids
exhibit this effect. For example, (Pb[ZrxTi1x]O3 where,0x1), also called PZT, will
generate measurable electricity when their structure is deformed by about 0.1% of the
original dimension(International AAAI Conference on Social Media and Weblogs, 2012).
In this project, the generated electricity on a specific time will be recorded and determine
if it would be enough to completely charge a Li-ion battery or a high capacity capacitor.
The piezoelectric effect, by which a material generates an electric potential in response
to a temperature change, was studied by Carl Linnaeus and Franz Aepinus in the mid18th century. Drawing on this knowledge, both Ren Just Hay and Antoine Csar
Becquerel posited a relationship between mechanical stress and electric charge;
however, experiments by both proved inconclusive. The first demonstration of the direct
piezoelectric effect was in 1880 by the brothers Pierre Curie and Jacques Curie. They
combined their knowledge of pyroelectricity with their understanding of the underlying
crystal structures that gave rise to pyroelectricity to predict crystal behavior, and
demonstrated the effect using crystals of tourmaline, quartz,topaz, cane sugar, and
Rochelle salt (sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate). Quartz and Rochelle salt
exhibited the most piezoelectricity.
A piezoelectric disk generates a voltage when deformed (change in shape is greatly
exaggerated) The Curies, however, did not predict the converse piezoelectric effect. The
converse effect was mathematically deduced from fundamental thermodynamic
principles by Gabriel Lippmann in 1881. The Curies immediately confirmed the
existence of the converse effect, and went on to obtain quantitative proof of the
complete reversibility of electro-elasto-mechanical deformations in piezoelectric crystals.
For the next few decades, piezoelectricity remained something of a laboratory curiosity.
More work was done to explore and define the crystal structures that exhibited
piezoelectricity. This culminated in 1910 with the publication of Woldemar Voigt's
Lehrbuch der Kristallphysik (Textbook on Crystal Physics), which described the 20
natural crystal classes capable of piezoelectricity, and rigorously defined the
piezoelectric constants using tensor analysis.
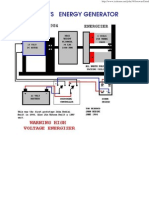
Method/ Testing And Redesign:
Please refer to section #3 to section #14
Results:
An Arduino development board was used to establish a simple oscillocope setup. It was
plugged to the computer, the built-in TTL was used to establish serial communication
between the Arduino and PC. A sketch was uploaded, using the Arduino IDE, to monitor
the Analog pin where the insole generator was connected. A separate program, called
"processing 2.0", was used to monitor the ripple given off by the converted ACDC
output of the generator.
Conclusion/ Report:
The current results showed that the product has potential to charge lithium batteries.
Though there are room for improvements, it showed positive signs for it to be further
developed. Based from the results, the insole generator has enough power to supply
voltage for low powered circuits such as MCUs (Micro Controller Units - ex. ATtiny) and
TTL Bluetooth transmitters. I can now say that the product is ready for production and is
highly usable for smart clothing/ shoes. Charging USB devices won't suffice just yet, the
charging time just isn't ideal.
FURTHER PLANS:
If a whole insole was to be made with a thin flexible sheet of metal and glazed with
double-sided piezoelectric elements then it would probably produce enough power to
charge a phone. A standardized opensource 3D printed design will certainly introduce a
new energy-production concept to the DIY community. When everyone has access to an
opensource project great ideas flourish!
Glossary/ Terms That You Will Encounter:
Piezo Electricity - is the ability of certain materials to generate an AC
(alternating current) voltage when subjected to mechanical stress or vibration, or
to vibrate when subjected to an AC voltage, or both. The most common
piezoelectric material is quartz. Certain ceramics, Rochelle salts, and various
other solids also exhibit this effect.
Actuated - cause a machine to operate/ work/ generate.
Piezo - shorthand for piezoelectric
AC Current - the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. Piezo
elements produce these currents.
DC Current - the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. Batteries
produce these currents
Bridge Diode - usually is composed of four rectifier diodes that filter AC currents
and turn them into DC currents.
Piezo Disc/ Element/ Transducer - they are all the same, it refers to the
discrete component that produces current when actuated. They are also known
as ceramic transducers and are usually found in outdated pairs of earpiece.
Parts/ Materials:
- Cheap/ Generic USB Powerbank
- Piezoelectric Transducers (6x)
- 1N4007 Rectifier Diodes (4x)
- Hookup Wire (at least 12")
- Old Pair Of Shoes
- Contact Adhesive
Tools & Equipment:
- Digital Multimeter
- Multitool (w/ pliers)
- Rotary Tool
______________________________________________________
Optional:
- 100nF Mylar Capacitor (for testing)
- Hoop & Loop Fastener (Velcro)
- LED Indicators (for testing)
- Superglue (for fixing wires)
- Smartphone Sport Strap
- 5v Switching Regulator (w/ supercap)
Alternatives: (since not all can afford them)
- PowerBank > Old phone batteries + Recycled 5v Inverter
- Peizo Transducers > A pair of old & outdated earpiece
- Rotary tool > Hot Nail (for melting plastic)
- Multitool > A pair of pliers will do
Вам также может понравиться
- The Overunity and FreeEnergy CatalogДокумент72 страницыThe Overunity and FreeEnergy Catalogiaraaipicat70% (10)
- Bedini Free Energy GeneratorДокумент7 страницBedini Free Energy GeneratorUông TháiОценок пока нет
- Doosan DX225LCA Electric Circuit 110705Документ1 страницаDoosan DX225LCA Electric Circuit 110705Eduardo Ariel Bernal97% (30)
- Where Is The Free EnergyДокумент5 страницWhere Is The Free EnergyAnonymous CabWGmQw0% (1)
- Solar Botanic Trees Using NanoleavesДокумент5 страницSolar Botanic Trees Using NanoleavesiaetsdiaetsdОценок пока нет
- Tesla Free Energy CollectorДокумент7 страницTesla Free Energy CollectorJelle VanherckОценок пока нет
- Extraordinary TechnologyДокумент97 страницExtraordinary TechnologyodiosilloОценок пока нет
- Bedini Free Energy GeneratorДокумент7 страницBedini Free Energy GeneratorRizwan Khan Marwat0% (1)
- Capacitors That Recharge ThemselvesДокумент10 страницCapacitors That Recharge Themselvesdakkid100% (1)
- Free Energy Devices Zero PДокумент8 страницFree Energy Devices Zero PibeskosОценок пока нет
- Benefits of Solar EnergyДокумент22 страницыBenefits of Solar EnergyVinith GopalakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Dieless Wire DrawingДокумент8 страницDieless Wire DrawingRohit GothwalОценок пока нет
- Vehicular Emissions TrinidadДокумент4 страницыVehicular Emissions Trinidadstephen_debique9455Оценок пока нет
- Vinegar BatteryДокумент28 страницVinegar Batteryjennichiii75% (28)
- WP310LДокумент109 страницWP310Ljohn smithОценок пока нет
- Electronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-2Документ6 страницElectronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-2chetana100% (1)
- Catalog 12 Section 2 TabДокумент40 страницCatalog 12 Section 2 TabAnonymous oPInocXОценок пока нет
- HandBook FE Devices 02Документ422 страницыHandBook FE Devices 02smcmoОценок пока нет
- How Batteries WorkДокумент8 страницHow Batteries WorkJagdeep S.0% (1)
- Testing & Commissioning of Chilled Water PumpsДокумент3 страницыTesting & Commissioning of Chilled Water Pumpsamg00733% (3)
- ELSD IQ OQ ProtocolДокумент7 страницELSD IQ OQ ProtocolRajan RamaswamiОценок пока нет
- Solar Panel Improvement: 1950–2016: For Solar, by Solar, to SolarОт EverandSolar Panel Improvement: 1950–2016: For Solar, by Solar, to SolarОценок пока нет
- Tesla CapstoneДокумент29 страницTesla CapstoneRaven ZeijikuОценок пока нет
- Solar Water HeaterДокумент10 страницSolar Water HeaterTijani MellalОценок пока нет
- Lightning Rabbit - An Application of Sound EnergyДокумент6 страницLightning Rabbit - An Application of Sound EnergyMuntarin RahmanОценок пока нет
- Vinegar BatteryДокумент28 страницVinegar Batterykmata092006Оценок пока нет
- FYP Generation Electricity Piezoelectric CrystalДокумент29 страницFYP Generation Electricity Piezoelectric CrystalHamzah Reza0% (1)
- BU-001: Sharing Battery Knowledge: EngineersДокумент17 страницBU-001: Sharing Battery Knowledge: EngineersMoo VeОценок пока нет
- 2022-Coins As Makeshift Battery (Research Proposal)Документ16 страниц2022-Coins As Makeshift Battery (Research Proposal)Titan DantdmОценок пока нет
- Power Shoe:piezoelectric Wireless Power Transfer Using Mobile Charging TechniqueДокумент13 страницPower Shoe:piezoelectric Wireless Power Transfer Using Mobile Charging TechniqueNarendra PallaОценок пока нет
- Research Paper Photovoltaic CellДокумент4 страницыResearch Paper Photovoltaic Cellfvg6kcwy100% (3)
- S.I.P Group 2Документ27 страницS.I.P Group 2jennichiii0% (1)
- Use of Piezoelectrics (Human Powered Energy) : QuestionsДокумент5 страницUse of Piezoelectrics (Human Powered Energy) : QuestionsShiella Barroga LorenzoОценок пока нет
- Steptricity: A Physics Project Report: Harnessing Energy, Step by Step..Документ20 страницSteptricity: A Physics Project Report: Harnessing Energy, Step by Step..Ria MirchandaniОценок пока нет
- Research Paper On Solar PanelДокумент8 страницResearch Paper On Solar Panelegzxpwsp100% (3)
- Wonders of The FutureДокумент2 страницыWonders of The FutureBraulio IrrutiaОценок пока нет
- Exploravision Rolling ThunderДокумент11 страницExploravision Rolling Thunderapi-288179228Оценок пока нет
- Photovoltaic Cell Research PapersДокумент6 страницPhotovoltaic Cell Research Papersphqfgyvkg100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Strategies ExamplesДокумент5 страницReading Comprehension Strategies ExamplesLucaDildaОценок пока нет
- International Journals Call For Paper HTTP://WWW - Iiste.org/journalsДокумент7 страницInternational Journals Call For Paper HTTP://WWW - Iiste.org/journalsAlexander DeckerОценок пока нет
- Research Paper On Solar CellsДокумент7 страницResearch Paper On Solar Cellsc9jg5wx4100% (1)
- Nuclear Batteries ReportДокумент50 страницNuclear Batteries Reportgauravpgi4550% (2)
- Non-Conventional Energy Source Harnessing Energy From Busy City TrafficДокумент5 страницNon-Conventional Energy Source Harnessing Energy From Busy City TrafficEjaz KОценок пока нет
- Writing A Research Paper On Static ElectricityДокумент6 страницWriting A Research Paper On Static Electricityxmniibvkg100% (1)
- Research Papers On Solar Cell EfficiencyДокумент8 страницResearch Papers On Solar Cell Efficiencyefjem40q100% (3)
- d4 Foot Step Power Generation Using Piezoelectric MaterialДокумент29 страницd4 Foot Step Power Generation Using Piezoelectric Materialvarshakulkarni100% (1)
- Harnessing Light Energy Possibilities and ChallengesДокумент5 страницHarnessing Light Energy Possibilities and ChallengesNeel ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Report Infrared Solar CellДокумент22 страницыReport Infrared Solar Cellabhishek5singh5surajОценок пока нет
- Wireless Electricity Is Here (Seriously)Документ7 страницWireless Electricity Is Here (Seriously)rickyamarОценок пока нет
- Solar Cell DissertationДокумент7 страницSolar Cell DissertationBuyCollegePaperOnlineBillings100% (1)
- Inquiry Into Physics 8th Edition Ostdiek Solutions ManualДокумент38 страницInquiry Into Physics 8th Edition Ostdiek Solutions Manualmathewsandersa13j100% (11)
- Inquiry Into Physics 8Th Edition Ostdiek Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент37 страницInquiry Into Physics 8Th Edition Ostdiek Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgregorythurv0e100% (10)
- Investigación InteresanteДокумент15 страницInvestigación InteresanteEduardo CamachoОценок пока нет
- Electricity From Solar, Wind, and HydroДокумент13 страницElectricity From Solar, Wind, and HydroThesalonika PasaribuОценок пока нет
- Solar EnergyДокумент10 страницSolar Energysagelemuelds2Оценок пока нет
- Paper Battery 10153 PV8YjqIДокумент17 страницPaper Battery 10153 PV8YjqIMuteeb BandayОценок пока нет
- Fyp Nanotchnology GeneratorДокумент6 страницFyp Nanotchnology GeneratorMohdZishanKhokherОценок пока нет
- Exploring Nanotechnology and The Future of Renewable EnergyДокумент10 страницExploring Nanotechnology and The Future of Renewable Energycatarina bastosОценок пока нет
- An Electromagnetic Crane: Supported Projects For Grades 4-6 (Elementary Projects)Документ5 страницAn Electromagnetic Crane: Supported Projects For Grades 4-6 (Elementary Projects)Edna Barra-Bandiola100% (1)
- Design and Construction of An Electrical Energy Generator Using Sound EnergyДокумент30 страницDesign and Construction of An Electrical Energy Generator Using Sound EnergyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Solutionary Log 8 Pre-Recorded Interview RevisedДокумент2 страницыSolutionary Log 8 Pre-Recorded Interview Revisedapi-658241754Оценок пока нет
- Ece Solar Mobile Charger ReportДокумент19 страницEce Solar Mobile Charger ReportTinku BudhwarОценок пока нет
- Research Paper On Solar PanelsДокумент8 страницResearch Paper On Solar Panelsxfykuuund100% (1)
- SCRIPTДокумент2 страницыSCRIPTcelestineОценок пока нет
- Ece Solar Mobile Charger ReportДокумент19 страницEce Solar Mobile Charger Reportfolagtech50% (2)
- Project Title - Piezoelectric Tiles ReportДокумент7 страницProject Title - Piezoelectric Tiles ReportAditya SinghОценок пока нет
- Whole Research Chapter 1Документ13 страницWhole Research Chapter 1Estoesta, Alejandra ElizeОценок пока нет
- Lectric Vehicles: T-611-NYTI-21652 New TechnologyДокумент22 страницыLectric Vehicles: T-611-NYTI-21652 New TechnologyDeepak ChaurasiaОценок пока нет
- Nano Tech PaperДокумент8 страницNano Tech Paperapi-341656796Оценок пока нет
- UN12Документ17 страницUN12dnt563Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5 SolutionsДокумент5 страницTutorial 5 Solutionsdnt563Оценок пока нет
- STM ScheduleДокумент1 страницаSTM Schedulednt563Оценок пока нет
- Supervisor Evaluation Form: B 0 2 1 5 1 0 2 5 8 B E N GДокумент7 страницSupervisor Evaluation Form: B 0 2 1 5 1 0 2 5 8 B E N Gdnt563Оценок пока нет
- Ieee 2016Документ2 страницыIeee 2016dnt563Оценок пока нет
- FKEKK Thesis Template Version February 2018Документ48 страницFKEKK Thesis Template Version February 2018dnt563Оценок пока нет
- Industrial Training Final Report FormatДокумент7 страницIndustrial Training Final Report Formatdnt563Оценок пока нет
- Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: DianaДокумент1 страницаDiana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Diana: Nizam: Dianadnt563Оценок пока нет
- ApplicationsДокумент10 страницApplicationsdnt563Оценок пока нет
- SingleДокумент4 страницыSinglednt563Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ10 страницChapter 3dnt563Оценок пока нет
- ConclusionДокумент1 страницаConclusiondnt563Оценок пока нет
- Diagnosis TechДокумент35 страницDiagnosis Techdnt563Оценок пока нет
- Tudung Bawal ColorДокумент1 страницаTudung Bawal Colordnt563Оценок пока нет
- Muahahahahahahah PhuiiiiДокумент1 страницаMuahahahahahahah Phuiiiidnt563Оценок пока нет
- LPДокумент1 страницаLPdnt563Оценок пока нет
- WM SongsДокумент1 страницаWM Songsdnt563Оценок пока нет
- Diagnosis TechДокумент35 страницDiagnosis Techdnt563Оценок пока нет
- B20ME067 SeminarДокумент14 страницB20ME067 SeminarSanjay 69ffОценок пока нет
- Report WISHДокумент51 страницаReport WISHNss Aissms Coe PuneОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент8 страницSyllabusSameer SolankiОценок пока нет
- Exp 05Документ11 страницExp 05Zharlene SasotОценок пока нет
- Flow Master V7 Release NotesДокумент6 страницFlow Master V7 Release NotesGabriel ValdiviaОценок пока нет
- Detroit S60 SpecsДокумент2 страницыDetroit S60 Specsgrgramm50% (2)
- Blowdown Strainer DesignДокумент2 страницыBlowdown Strainer DesignElias EliasОценок пока нет
- DR - Swapna BhowmikДокумент21 страницаDR - Swapna BhowmikAnil Anil ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Fuel Less GRNTRДокумент4 страницыFuel Less GRNTRKamran ImtiyazОценок пока нет
- LC X71 Service Manual FullДокумент122 страницыLC X71 Service Manual FullMaurilio CaetanoОценок пока нет
- 2012 SpiraxialДокумент1 страница2012 SpiraxialNistha ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Helios Uk ElsДокумент22 страницыHelios Uk ElssanitermОценок пока нет
- Shell Turbo Oil T32: Performance, Features & BenefitsДокумент2 страницыShell Turbo Oil T32: Performance, Features & BenefitsElias GabrielОценок пока нет
- Discussion Tray DryerДокумент3 страницыDiscussion Tray DryerNoor Fatihah100% (1)
- M16 PPT Piston Engine 1Документ42 страницыM16 PPT Piston Engine 1Thoriq RoziОценок пока нет
- Biefeld-Brown Effect and Space CurvatureДокумент6 страницBiefeld-Brown Effect and Space CurvaturejayandbobОценок пока нет
- 3RH29111FA22 Datasheet enДокумент6 страниц3RH29111FA22 Datasheet enFlavioОценок пока нет
- Datasheet For On/Off Valve (Xv-001) Datasheet For On/Off Valve (Xv-001)Документ2 страницыDatasheet For On/Off Valve (Xv-001) Datasheet For On/Off Valve (Xv-001)usama666Оценок пока нет
- T-23 BOQ (Katol)Документ40 страницT-23 BOQ (Katol)rajesh kumarОценок пока нет
- Laser FF - V30T: Product Data SheetДокумент2 страницыLaser FF - V30T: Product Data Sheetgmoc19Оценок пока нет
- Paper Insulated Distribution CablesДокумент10 страницPaper Insulated Distribution Cablesdeepak2628Оценок пока нет