Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ttii'jh1 3 ,",,,S: U) ' Oo Is
Загружено:
EndyMpeNkОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ttii'jh1 3 ,",,,S: U) ' Oo Is
Загружено:
EndyMpeNkАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
VII
e second term
is
Cx and Cr) of the two RFs K(u, u) and B(u,o) were chosen so that thc
randorn drifr D(u, u. w) accounted for a fixed part of the total variability of
ttii'Jh1;3;*,",,,s
drift.
tt E{R}=
5ll
STMULATION OF DEPOSITS
41, 42, ,\3 fix the rorm or rhe cuhic l@)=
A3wr+A2w2+,\1w, i.e., the general form of the drift.
0. The
irnd rcsidual, are
issurDcd that the
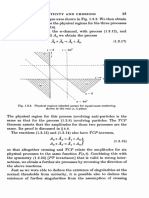
Simulation of rhe residuals The three-dimcqsional regionalization of the
RF residual R(u, u, w) is anisotropic with a more rapid variability in the
vertical dircction. The model chosen to represent this RF is the nested sum
d so a Caussian
r/+rproduceda
R(u, u, w)= Qo(u, u, w)+ Qr{u, u, w)+ Q2(4,
rrofile of gradcs
(\/lt
.'il
nugget eflect characterizing
less than the smallest
with
ranges
measurement errors and structures
dimensioo considered, which in this case is 0'5 m'
or is a stationary RF characterizing an isotropic structure with a small
range, in thiscase a sPherical model with a range dr =3 m'
Qr(", r) is a stationary RF characterizing a horizontal structure with a
larger range (a2 = 30 m) corresponding, for example' to lenses in a sedi*.Int".y deposit. The model can be rcfined by imposing a gcometric
tlepcndenl RF's
'c thrcc
positive
anisotropyon o:, c[. section III.B.4, Figs Ill.l0 and Ill.l l(b). to represent
a pseudo-elliptical form of these lenses.
The three RF's Oo' Qr' Qz arc independent. and their exprectations are
take n as zero, to e nsure rhat the expcctation of the grade is equal to that of
the RF drift:
:odulated by thc
(u, u)defines tire
](a) and (b). Thc
raximum, cf. Fig.
(F's K(u, u)
and
E{R}=o+EIZI=ElDl.
-iograms without
I sills Cx and Cs.
zontal plane *'ill
vhile pits furthcr
Thus, on any given verticat grade profile. the residuals are correlated
only if they are less than 3 m apart. On any given horizontal plane. the
residuats are correlated only if they are less than 30 m apart. The horizontal correlationof thegrades Z= D +R fordistancesfrom 30mto l00m is
due only to thc correlation of the drifts'
rd variances (sills
7
(*e)
Grode ('/.)
i
I
l
I
(ol
r.g=l;(b) (
Resulrs The vertical profiles of the mean grades of the (ll mx ll otx
0.5 m) slices of three blocks (full-line curves) and the grades of their
respectire central pits (broken-line curves) are shown on Fig. VIl.l4. The
firsi t*o blocks (u'=72, u = 6) and (u = 83, u = 6) are contiguous and have
=vpry similar mcan grade profiles, while the profiles of the gradgl of their
central pits arc notaUty dillerent. The third block (rr = 424, u = -50), which
is more than 300 m away from the first two, has a complctcly dillerent
mean gradc prolile.
Af rle selcction and mining
=1,
(VII'32)
oo is an isotropic three-dimensional
vcrishrncnt, irnd.
llsit, as show'n ttn
this drift
i.
u)'
i
I
I
i
{
t
-1.
stages, only the profiles
of, for instance, the
ccntral pits are known in practice. If the central pit profile is uscd unwarily
\1
ilt
lNlN(; (iF-()SI A[ls'T'lcs
inllucnce estimahlock grirdcs pr()tilc (polygonal
rn pl:rcc ()f rhc.nknown
will bc biirscd' cf '
'""tu"t
ri(ilt ). lllcn rhc re sulrrng csttmitlcsrr[
()'01'l' lppliccl
"toue"tblc
'llttrs
lr ctrt-tlll gra<lc :" =
lll( (:r\(' \lll(l\ t)f tcctrt'rn Vl z\'-1
oti ['tg Vll' l'l rvottltl rcsult ttt
l,, llrt rr rllr.rl Irl I)r(rltl('"1 lllc
totttl lrlotL
'e
gtirtlc tlI o 0'l(l')"'
r'l -'lll rrilll il lll(''lll lL'c()\ctetl
,t lr'rrrrt tttl lltttLtl(\\
tlf kriging
()
0J'7o'-lltc;rrnl
ll Ine itll qrciltcr than
w'lrcte as no hlou|' slrcu has
to tlrc profilc of thc
protilc as clt'sc lrs possiblc
rs ttt provitlc rtn esttmalccl
rrte ittt pltncl gr;rdcs.
Gr
(72 6)
O OOr
means
o(
cross-semi-
Non-condit
Only the n
prcsentcd
proSrams
oOc ( /ol
(81 5)
004 0 00,
mctho<J. Kr
values, and
{ion restore
t424
o03
ooa
50)
o04
ool
IIl.C.4) {or
problcm ol
simulating
with given
following t
I
I
(i) Thc
simr
ti(
I
I
I
I
a',
\l
I
I
I
rl
\2
As
var
!t
'.1
,:l
(ii)
Ac
an
v\
Itl
sP,
Frc. \'ll.ll.
qrades and central pit gradcs
Sirnulatcd prtrtrlcs of bltxk
Pr
oI
co
co
Vll.B.2. Programming simulations
Bastc steps irt a conditional sitnulotion
thc rrlr>cle I its'-lI lusr b1 cstablished
Ilefttrc bcginnrng any simulation'
II lhc-vilriablc Z is to bc slmulfltc(lis
through a structural clatit:rnrtlYsr\
irnalysis
= qzt (Z)' then thc struclural
through its Gaussian t"t^tt"t"'"
is tlrc
srmulatron
lirst step of thc actual
made on the variable U"lle
bands
simularion using rhc rurning
non-conditionrt. -nor-otty drstribured
be
(iii)
n
CC
bi
fc
Вам также может понравиться
- LL LL LL X20:: Px0'5 Vil.L2Документ2 страницыLL LL LL X20:: Px0'5 Vil.L2EndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- C2 (R) May 2014 MSДокумент7 страницC2 (R) May 2014 MSfarahgraceОценок пока нет
- Vii.I I Of: The ThatДокумент2 страницыVii.I I Of: The ThatEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- PR (U) of Of: VII Methd. Z ofДокумент2 страницыPR (U) of Of: VII Methd. Z ofEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Solving Equations, Integrals & Geometry Problems With Step-by-Step SolutionsДокумент18 страницSolving Equations, Integrals & Geometry Problems With Step-by-Step SolutionsreemarifkhanОценок пока нет
- Transition Curves WordДокумент12 страницTransition Curves WordDushan SenarathneОценок пока нет
- ilnl/ ( : .LLRRL Llcxitlrlitl'Oi /ltli Rcillity. TheДокумент2 страницыilnl/ ( : .LLRRL Llcxitlrlitl'Oi /ltli Rcillity. TheEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Img 20140511 0007Документ1 страницаImg 20140511 0007Az MYОценок пока нет
- DAO 2011 Solved Paper 2 Mensuration With KEYДокумент18 страницDAO 2011 Solved Paper 2 Mensuration With KEYbhunkri92% (12)
- Circle - 1Документ4 страницыCircle - 1rask2k1Оценок пока нет
- Qsthge: Special Pitysical ChemistryДокумент15 страницQsthge: Special Pitysical ChemistryChamith HerathОценок пока нет
- R " Lo-Dr Itr R'.: of T (RLDRДокумент2 страницыR " Lo-Dr Itr R'.: of T (RLDREndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Analytic Continuation and Particle CrossingДокумент2 страницыAnalytic Continuation and Particle CrossingFishboneОценок пока нет
- Paper 2Документ18 страницPaper 214570001Оценок пока нет
- Geophysical Prospecting Finite-Difference Evaluation of Apparent Resistivity CurvesДокумент21 страницаGeophysical Prospecting Finite-Difference Evaluation of Apparent Resistivity CurvesKousik SasmalОценок пока нет
- Raffles Junior College Jc1 Promotion Examination 2008Документ10 страницRaffles Junior College Jc1 Promotion Examination 2008Mathathlete100% (1)
- SaS Topic3 Slides 1 8Документ8 страницSaS Topic3 Slides 1 8Dinko BešlagićОценок пока нет
- Schroder SolutionДокумент11 страницSchroder SolutionHee Seok KimОценок пока нет
- Antonio J.C. Varandas and Jonathan Tennyson - On The Isotropic and Leading Anisotropic Terms of The H-H2 Potential Energy SurfaceДокумент7 страницAntonio J.C. Varandas and Jonathan Tennyson - On The Isotropic and Leading Anisotropic Terms of The H-H2 Potential Energy SurfaceMaxnamewОценок пока нет
- Problem 6.20 JacksonДокумент2 страницыProblem 6.20 Jacksondacastror2Оценок пока нет
- Heteroclinic Cycles in The Three-Dimensional Postbifurcation Motion of O (2) - Symmetric Fluid Conveying TubesДокумент9 страницHeteroclinic Cycles in The Three-Dimensional Postbifurcation Motion of O (2) - Symmetric Fluid Conveying TubesAdrian Calin MurzaОценок пока нет
- You Can't Get Through Szekeres Wormholes or Regularity, Topology and Causality in Quasi-Spherical Szekeres ModelsДокумент47 страницYou Can't Get Through Szekeres Wormholes or Regularity, Topology and Causality in Quasi-Spherical Szekeres ModelsKunma050Оценок пока нет
- M.Sc. Mathematics Entrance Exam 2012Документ12 страницM.Sc. Mathematics Entrance Exam 2012sumitruОценок пока нет
- Ch23 Solved ProblemsДокумент9 страницCh23 Solved Problemsabd altwierОценок пока нет
- Transactions American Geophysical UnionДокумент6 страницTransactions American Geophysical Unionlo5tboy5Оценок пока нет
- Understanding momentum, kinetic energy and graphsДокумент10 страницUnderstanding momentum, kinetic energy and graphskesnaОценок пока нет
- SQA Higher Maths Exam 1993Документ13 страницSQA Higher Maths Exam 1993StephenMcIОценок пока нет
- The Analytic S-Matrix 3Документ2 страницыThe Analytic S-Matrix 3FishboneОценок пока нет
- 1WCE2009 pp435-440Документ6 страниц1WCE2009 pp435-440Noureddine BounaslaОценок пока нет
- Of o (R N But: L. .I For. LoДокумент2 страницыOf o (R N But: L. .I For. LoEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Rf-Gap Model Presentation: V.A.Moiseev, INR of RAS, Moscow, Russia Moiseev@Документ3 страницыRf-Gap Model Presentation: V.A.Moiseev, INR of RAS, Moscow, Russia Moiseev@Khaoula SamaaliОценок пока нет
- B) @ (CCW) : Questions and Example Problems From Chapter 10Документ8 страницB) @ (CCW) : Questions and Example Problems From Chapter 10Shruti GiriОценок пока нет
- chp5 PDFДокумент44 страницыchp5 PDFSagar KumarОценок пока нет
- Design Criteria of High Performance Synchronous Reluctance MotorsДокумент8 страницDesign Criteria of High Performance Synchronous Reluctance MotorsYusuf YaşaОценок пока нет
- Yr7 Hy 2002 SolnsДокумент5 страницYr7 Hy 2002 SolnsDavid TangОценок пока нет
- Block 13 ExamS12Документ2 страницыBlock 13 ExamS12TJ LewisОценок пока нет
- Engineering Materials and Design: Fatigue Analysis and Gearbox DesignДокумент9 страницEngineering Materials and Design: Fatigue Analysis and Gearbox DesignOliver RubioОценок пока нет
- Sulit 954/2 Mathematics T2 2011 3 Hours 954/2Документ17 страницSulit 954/2 Mathematics T2 2011 3 Hours 954/2SKОценок пока нет
- DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF LAMINATED CROSS-PLY PANEL UNDER LOCALIZED MOMENT by Ali Be IglooДокумент6 страницDYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF LAMINATED CROSS-PLY PANEL UNDER LOCALIZED MOMENT by Ali Be Iglooantony1993Оценок пока нет
- Curved Finite Elements for Solving PDEsДокумент13 страницCurved Finite Elements for Solving PDEsFernando ZCenasОценок пока нет
- 1939 Carslaw & Jaeger - On Green's Functions in The Theory of Heat ConductionДокумент7 страниц1939 Carslaw & Jaeger - On Green's Functions in The Theory of Heat ConductionjbtrenОценок пока нет
- PHD Acrhem PDFДокумент24 страницыPHD Acrhem PDFShashi KolaОценок пока нет
- Transformasi Tegangan Dan Teori Kegagalan PDFДокумент24 страницыTransformasi Tegangan Dan Teori Kegagalan PDFdidiek noor100% (1)
- Electromagnetic field problems and solutionsДокумент27 страницElectromagnetic field problems and solutionsSAHIN InspireОценок пока нет
- Generalization of The BLT EquationДокумент21 страницаGeneralization of The BLT EquationAnonymous 0qYv7WpgОценок пока нет
- Motor Model For Torsional Analysis of Variable Speed Drives With Induction MotorДокумент11 страницMotor Model For Torsional Analysis of Variable Speed Drives With Induction MotorRadu BabauОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Modelling of Induction Motor and Performance Analysis with Bearing FaultДокумент5 страницMathematical Modelling of Induction Motor and Performance Analysis with Bearing FaultTawhid Bin TarekОценок пока нет
- Wave Scatter DiagramДокумент8 страницWave Scatter Diagramcr231181Оценок пока нет
- AmeeДокумент13 страницAmeeaishwaryayogananthamОценок пока нет
- Scantling CalculationsДокумент70 страницScantling Calculationsjrladdu100% (4)
- Statistical Thermodynamics of Rubber ElasticityДокумент8 страницStatistical Thermodynamics of Rubber Elasticitychiuchan888Оценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Semiconductor Devices - Physics and Technology (Sze, S. M) SolutionДокумент130 страницSolution Manual For Semiconductor Devices - Physics and Technology (Sze, S. M) SolutionPhạm Việt Dũng95% (42)
- Chapter 12 Heat Transfer Problems and SolutionsДокумент13 страницChapter 12 Heat Transfer Problems and Solutionsmsaqibraza93Оценок пока нет
- 1975 Finite Strip-Difference Calculus Technique ReddyДокумент11 страниц1975 Finite Strip-Difference Calculus Technique ReddyMilica BebinaОценок пока нет
- Computational Techniques in Civil Engineering IOE BCE Past Questions CollectionДокумент32 страницыComputational Techniques in Civil Engineering IOE BCE Past Questions CollectionFlush BinОценок пока нет
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlОт EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlОценок пока нет
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationОт EverandInfrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationОценок пока нет
- VII of If l0 N N Will: DepositsДокумент2 страницыVII of If l0 N N Will: DepositsEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Of o (R N But: L. .I For. LoДокумент2 страницыOf o (R N But: L. .I For. LoEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- VII. Simulation and Statistical Analysis of Deposit Models for Mining PlanningДокумент2 страницыVII. Simulation and Statistical Analysis of Deposit Models for Mining PlanningEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Stolen PDFДокумент5 страницStolen PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 3 PDFДокумент1 страница3 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Generating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesДокумент1 страницаGenerating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 39 40 PDFДокумент2 страницы39 40 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Img 20140704 0003 NewДокумент1 страницаImg 20140704 0003 NewEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Of o (R N But: L. .I For. LoДокумент2 страницыOf o (R N But: L. .I For. LoEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 39 40 PDFДокумент2 страницы39 40 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 5 - 6 PDFДокумент2 страницы5 - 6 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Ttii'jh1 3 ,",,,S: U) ' Oo IsДокумент2 страницыTtii'jh1 3 ,",,,S: U) ' Oo IsEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- R " Lo-Dr Itr R'.: of T (RLDRДокумент2 страницыR " Lo-Dr Itr R'.: of T (RLDREndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Generating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesДокумент1 страницаGenerating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 39 40 PDFДокумент2 страницы39 40 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 182 487 1 PB PDFДокумент18 страниц182 487 1 PB PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- VII. Simulation and Statistical Analysis of Deposit Models for Mining PlanningДокумент2 страницыVII. Simulation and Statistical Analysis of Deposit Models for Mining PlanningEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 5 - 6 PDFДокумент2 страницы5 - 6 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 27 28 PDFДокумент2 страницы27 28 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 1 PDFДокумент1 страница1 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Generating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesДокумент1 страницаGenerating Conditional Simulations of Geological ReservesEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Of For: of Tion Activity ofДокумент1 страницаOf For: of Tion Activity ofEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- ilnl/ ( : .LLRRL Llcxitlrlitl'Oi /ltli Rcillity. TheДокумент2 страницыilnl/ ( : .LLRRL Llcxitlrlitl'Oi /ltli Rcillity. TheEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- 81 PDFДокумент1 страница81 PDFEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- Flguro Aligned Plagioclase Crystals Enclosed Liquid Ol Titano Bushveld ComplexДокумент1 страницаFlguro Aligned Plagioclase Crystals Enclosed Liquid Ol Titano Bushveld ComplexEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
- LN For Of: To 5-l TheДокумент1 страницаLN For Of: To 5-l TheEndyMpeNkОценок пока нет
![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)