Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
O31 Mahmut Aksit
Загружено:
opzz_opzzИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
O31 Mahmut Aksit
Загружено:
opzz_opzzАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
18th International Energy & Environment Fair and
Conference
SESSION 31: Domestic Design & Production in Energy
Wind Turbine Design Approaches
Assoc. Prof. Mahmut F. Akit
27.4.2012
Faculty Member at Sabanc University
Manager of MILRES (National Wind Turbine Development Project)
1
Wind Turbines - History
Early Uses of Wind Power
Persian windmill for grain
processing (500 900 A.D.)
Dutch tower mills for
grain processing and
water pumping (1300
1900 A.D.)
Brush postmill for electric
power generation. 17 m,
12 kW (1888)
Mechanical water
pumping for livestock
(1850 Present A.D.)
Wind Turbines - Power
c
Power = A
2
Energy = Power Time
Wind Turbines - Power
Larger Turbines More MW
How Large? Logistics ?
Inland vs Offshore
General Construction HAWT or VAWT?
Wind Turbine Designs
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
(HAWT)
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
(VAWT)
General Construction HAWT or VAWT?
Other VAWT Designs
H VAWT
Screen VAWT
V VAWT
Darrieus VAWT
What kind of HAWT?
Other HAWT Designs
Upwind/
Downwind ?
Wind seeking
Oscillations
CG vs Tower
moments
Number of
Blades?
What kind of HAWT?
Blades
at
of
e
a
e
Coefficient of Performance (Cp)
ncy
Tip Speed Ratio (TSR) = 2 RN/60/V
BRT wor elgnis owT
SKF Engineering Handbook Wind
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Gearbox or Direct Drive ?
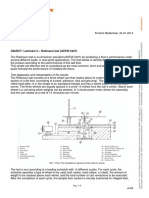
Figure 8: Direct drive wind turbine with 2-point suspension.
1.4.1.2
1-point suspension with Nautilus
Figure 9: Direct drive wind turbine with 1-point suspension.
isuoh etarapes 2 htiw noisnepsus tniop -2 :1 er ugiF
eirepxe evahtah
t srerutcafunam enibrut niaM
Efficiency
xe evisnetxe e
h asemaG dna satseV
vaRelability
.WM 3 naht rellams senibrut
Cost
M 6.3 rieht no BRS owt sesu snemeiS
.WM 5 rieht
Turbine Size?
Generator speed vs Number of Gearbox stages
Compramise
10
Gearbox or Direct Drive ?
Wind Turbine
Turbines with
gearbox
Hybrid Turbines
Gearless Turbines
(Direct Drive)
Generator speeds [rpm]
1200 1800
150 - 400
12-30
BRAC dna BRS
sBRTrain
S owTConstruction
Power
BRC dna BRTRD
2-Point
BRT wor elgnis owT
Suspension
sgnisuoh etarapes 2 htiw noisnepsus tniop -2 :1 er ugiF
cneirepxe evah Classical
taht sreruwind
tcafun
am enidesign
brut nia
M gearbox
turbine
with
pxe evisnetxe eMain
vah ashaft
semais
G supported
dna satseVwith two bearings at two ends
.W
3 naht ris
ellsupported
ams senibrseparately
ut
MGearbox
by two bushings that
WM 6.3 rieht no
BRS otorque
wt seschanges
u snemeiS
absorb
.WM 5 rieht
12
However, the trend on larger turbines is the t
weight
becomes increasingly important.
Power Train
Construction
3-Point
Suspension
2&3 Support
Bushings
GE (1.5 MW and 3.6 MW),
NEG-Micon,
Siemens-Bonus,
Nordex,
RePower
1- Main Bearing
Shorter shaft
Shrink disk coupling
Reduced torsional mass-spring
Main shaft is supported with
a bearing at front and rigidly
Figure 2: 3-point suspension.
attached to gear box ot the aft end
Gearbox and shaft are integral
1.2.1.3
1-point suspension with Nautil
Gearbox is supported separately by two bushings that absorb
The Nautilus of an integrated main bearing de
torque changes
at the same time certain components of the g
13
SKF Engineering Handbook Wind
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Power Train Construction
Figure 8: Direct drive wind turbine with 2-point suspension.
1.4.1.2
1-point suspension with Nautilus
1-Point
Suspension
1.2.1.3.1
Nautilus separate from the gearbox
Figure 9: Direct drive wind turbine with 1-point suspension.
Vestas V90-3MW
WinWind WWD3
Multibrid
Figure 3: Nautilus separate from the gearbox.
1.2.1.3.2
Nautilus integrated in the gearbox design
Main shaft is supported through one large bearing that supports
all axial and radial loads as well as bending moments
Compact nacelle
Reduced weight
2011 AB SKF
5 of 10
14
Other Technologies
Modular designs
High-speed many blades
Tower oscillation damping system
Realtime health monitoring
Composite or concrete towers
Segmented blades
....
15
Milres
16
THANKS !
17
Вам также может понравиться
- An Example Design of The Crossflow TurbineДокумент58 страницAn Example Design of The Crossflow TurbineBryan NanaОценок пока нет
- Tessarolo Hydro PowerДокумент108 страницTessarolo Hydro PowerJose Deniz100% (1)
- Wind EnergyДокумент20 страницWind EnergyShahanaAbdulRazakОценок пока нет
- Fish Friendly Turbines - YRC PresentationДокумент13 страницFish Friendly Turbines - YRC PresentationGaftoi Daniel AndreiОценок пока нет
- Wind Energy PDFДокумент42 страницыWind Energy PDFAnonymous oUoJ4A8xОценок пока нет
- Underwater WindmillДокумент21 страницаUnderwater Windmillbhagyashree behera100% (1)
- Hydro Power PlantДокумент41 страницаHydro Power PlantEr Mishal Gandhi100% (1)
- Its Time To Get Onboard. Maritime Reporter 2009Документ7 страницIts Time To Get Onboard. Maritime Reporter 2009joaofelipe.msОценок пока нет
- Problems of Propulsion Systems andДокумент6 страницProblems of Propulsion Systems andjoelОценок пока нет
- Electric Motor in Ship PropulsionДокумент13 страницElectric Motor in Ship PropulsionConcept of ReasoningОценок пока нет
- Development of Cassava Grating Machine - A Dual-Operational Mode From Leonardo JДокумент6 страницDevelopment of Cassava Grating Machine - A Dual-Operational Mode From Leonardo Jryxor-mrbl100% (1)
- Foot Step Power Generation System For Rural Energy Application To Run AC and DC LoadsДокумент35 страницFoot Step Power Generation System For Rural Energy Application To Run AC and DC Loadsraghunandanr199350% (2)
- Chapter - 9 Power House PlanningДокумент21 страницаChapter - 9 Power House PlanningLeul EyasuОценок пока нет
- Utilization of Wind Energy: Ever-Growing Size of Horisontal-Axis Wind TurbinesДокумент63 страницыUtilization of Wind Energy: Ever-Growing Size of Horisontal-Axis Wind TurbinesVulebg VukoicОценок пока нет
- Icse (KMW) PDFДокумент5 страницIcse (KMW) PDFtarrteaОценок пока нет
- Transmission Line ParametersДокумент141 страницаTransmission Line ParametershaiobОценок пока нет
- TidongДокумент162 страницыTidongSandeep AggarwalОценок пока нет
- DVC Andal VT ReportДокумент23 страницыDVC Andal VT Reportsatyakidutta00767% (3)
- Existing Tidal-Electric DevelopmentsДокумент24 страницыExisting Tidal-Electric DevelopmentsproteccionesОценок пока нет
- PROPULSION E-Motors 300609-014459 PDFДокумент59 страницPROPULSION E-Motors 300609-014459 PDFScott_B4U100% (1)
- High Head Small Hydro PresentationДокумент50 страницHigh Head Small Hydro PresentationfazarbadhushaОценок пока нет
- 1-11-11 YESS Technical Session 3.1 - YESS 2011 T3.1 Ingersoll US DoEДокумент15 страниц1-11-11 YESS Technical Session 3.1 - YESS 2011 T3.1 Ingersoll US DoEkazmi81Оценок пока нет
- KeywordsДокумент7 страницKeywordsHarshal PatilОценок пока нет
- A New Design of The Poded Azimuth Thruster For A DДокумент11 страницA New Design of The Poded Azimuth Thruster For A Dleo4997Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Machinery For Improvement of The Global Enviromental SystemДокумент6 страницHydraulic Machinery For Improvement of The Global Enviromental SystemFolpoОценок пока нет
- PRDCT List in WordДокумент12 страницPRDCT List in WordvelmuruganindusОценок пока нет
- Kaplan Turbines S-160 PDFДокумент8 страницKaplan Turbines S-160 PDFdrbasit93Оценок пока нет
- 3.introduction To Wind EnergyДокумент48 страниц3.introduction To Wind EnergyK Kiran VishnuОценок пока нет
- Mat Lab Simulation Procedure For DesignДокумент15 страницMat Lab Simulation Procedure For DesignAbdul wahid ButtОценок пока нет
- Kaplan Propeller Turbines&GeneratorsДокумент16 страницKaplan Propeller Turbines&GeneratorsErwinОценок пока нет
- Hydropower Engineering: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringДокумент24 страницыHydropower Engineering: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Electrical and Computer Engineeringtilahun kochitoОценок пока нет
- RETHydro08 1Документ70 страницRETHydro08 1Dilnesa EjiguОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Teknologi: An Innovative Vertical Axis Current Turbine Design For Low Current SpeedДокумент6 страницJurnal Teknologi: An Innovative Vertical Axis Current Turbine Design For Low Current SpeedDuzzysОценок пока нет
- Assignment - Mini HydroДокумент3 страницыAssignment - Mini HydroGayan Indunil JayasundaraОценок пока нет
- Wind Energy TechnologyДокумент15 страницWind Energy Technologytntntn86Оценок пока нет
- Background: Design of A Surge Tank Throttle For Tonstad Hydropower PlantДокумент1 страницаBackground: Design of A Surge Tank Throttle For Tonstad Hydropower PlantAgrawalAnuragОценок пока нет
- Selection of Power From Shore For An Offshore Oil and Gas DevelopmentДокумент29 страницSelection of Power From Shore For An Offshore Oil and Gas DevelopmentKURNIAWANОценок пока нет
- 2001 DE Propulsion TheoryДокумент33 страницы2001 DE Propulsion TheoryFrancis TanОценок пока нет
- Assignment - Mini HydroДокумент3 страницыAssignment - Mini HydroGayan Indunil JayasundaraОценок пока нет
- Wind Turbine Gearboxes - 2015Документ73 страницыWind Turbine Gearboxes - 2015diegodisouza100% (1)
- Investigation of The Performance of A Cross-Flow Turbine: Int. J. Energy Res., 22, 953 - 964 (1998)Документ12 страницInvestigation of The Performance of A Cross-Flow Turbine: Int. J. Energy Res., 22, 953 - 964 (1998)DavidОценок пока нет
- A Novel Design of Composite Water Turbine Using CFDДокумент6 страницA Novel Design of Composite Water Turbine Using CFDNung NingОценок пока нет
- Summer TrainingДокумент41 страницаSummer Trainingapi-382513988% (8)
- How To Plan A Mini Hydro Power ProjectДокумент15 страницHow To Plan A Mini Hydro Power Projectmario5681100% (1)
- 2015 - History and State of The Art in Commercial Electric Ship Propulsion, Integrated Power Systems, and Future TrendsДокумент14 страниц2015 - History and State of The Art in Commercial Electric Ship Propulsion, Integrated Power Systems, and Future TrendsJosé Francisco Gallardo OjedaОценок пока нет
- Tidal Energy and It's Prospects (Final - 4M - BD)Документ55 страницTidal Energy and It's Prospects (Final - 4M - BD)Masudur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Tidal PowerДокумент16 страницTidal PowermanjuОценок пока нет
- Wind TurbineДокумент61 страницаWind TurbineSafayet Ahmed SakibОценок пока нет
- Enrolamentos CSДокумент31 страницаEnrolamentos CSKidjonОценок пока нет
- DPR Pahumara SHPДокумент147 страницDPR Pahumara SHPdzikrieОценок пока нет
- Study and Analysis of Hydraulic Turbine in Aden City Main Pipiing NetworkДокумент19 страницStudy and Analysis of Hydraulic Turbine in Aden City Main Pipiing NetworkFares NasserОценок пока нет
- In Guidance Of:-Submitted By:-: Krishna Institute of Technology, KanpurДокумент20 страницIn Guidance Of:-Submitted By:-: Krishna Institute of Technology, KanpurPriyanka SinghОценок пока нет
- A Report OnДокумент12 страницA Report Onsyfullahnel0% (1)
- Hydro PowerДокумент44 страницыHydro Powerhabte gebreial shrashrОценок пока нет
- Farm Machinery - Tractors - A Collection of Articles on the Operation, Mechanics and Maintenance of TractorsОт EverandFarm Machinery - Tractors - A Collection of Articles on the Operation, Mechanics and Maintenance of TractorsОценок пока нет
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationОт EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- New Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringОт EverandNew Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics in The Automotive Design Process PDFДокумент2 страницыErgonomics in The Automotive Design Process PDFThomas0% (1)
- PFMEAДокумент6 страницPFMEAAcep GunawanОценок пока нет
- 21 Sumitava CVДокумент2 страницы21 Sumitava CVchatuusumitavaОценок пока нет
- Audi A6 Qu (1) - 3.0 TdiДокумент4 страницыAudi A6 Qu (1) - 3.0 TdiStanescu CatalinОценок пока нет
- Brother Sewing Machine InstructionsДокумент56 страницBrother Sewing Machine InstructionsDwaine Webb100% (1)
- Welding Electrode CatalogДокумент11 страницWelding Electrode CatalogSompon ModekamОценок пока нет
- Narrative Statement NPP-0050-QENFB Infra Structure & Utility BuildingsДокумент16 страницNarrative Statement NPP-0050-QENFB Infra Structure & Utility BuildingsLokesh KonganapalleОценок пока нет
- ABB REL5xx RIOConverterДокумент10 страницABB REL5xx RIOConverterzinab90100% (1)
- 6 TKA 155a Technical SpecificationДокумент3 страницы6 TKA 155a Technical Specificationar2925Оценок пока нет
- BE Mechanical Engineering CBCGS Syllabus 2016 OnwardsДокумент9 страницBE Mechanical Engineering CBCGS Syllabus 2016 OnwardsShubhamJangleОценок пока нет
- Master Scheduling Chapter 1Документ19 страницMaster Scheduling Chapter 1Bosco GodfreyОценок пока нет
- JJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter2 Hand ToolsДокумент12 страницJJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter2 Hand ToolsAh TiangОценок пока нет
- Forming Process ReportДокумент4 страницыForming Process ReportAqib ZamanОценок пока нет
- Paver Brochure 1 ZenbesДокумент2 страницыPaver Brochure 1 ZenbesOng Ju EeОценок пока нет
- Shell Omala BrochureДокумент2 страницыShell Omala BrochurehuseynseymenОценок пока нет
- Dep Rate 1-n Scrap Value/ori Cost 100 Residual Value 5% of Original Cost Useful Life & Depreciation Rates (WDV) As Per Companies Act 2013Документ2 страницыDep Rate 1-n Scrap Value/ori Cost 100 Residual Value 5% of Original Cost Useful Life & Depreciation Rates (WDV) As Per Companies Act 2013Mahaveer DhelariyaОценок пока нет
- Pihak Berkuasa Penerbangan Awam Malaysia (Civil Aviation Authority of Malaysia) Application For Unmanned Aircraft System (Uas) / DroneДокумент11 страницPihak Berkuasa Penerbangan Awam Malaysia (Civil Aviation Authority of Malaysia) Application For Unmanned Aircraft System (Uas) / DroneMuhammad Fahmi MahmudОценок пока нет
- Terex All Terrain Cranes Spec Df99efДокумент16 страницTerex All Terrain Cranes Spec Df99efPaizinho Imms GomezОценок пока нет
- CV Ravi ShenkerДокумент6 страницCV Ravi ShenkerRavi ShenkerОценок пока нет
- Metallurgical Factors Influencing The Machinability of Inconel 718 - SchirraДокумент12 страницMetallurgical Factors Influencing The Machinability of Inconel 718 - SchirraAntonioОценок пока нет
- MB20-200 LMSP-DP STD en Glovebox Manual - MBraunДокумент182 страницыMB20-200 LMSP-DP STD en Glovebox Manual - MBraunbariumbitmapОценок пока нет
- System Manager 7.4 User GuideДокумент158 страницSystem Manager 7.4 User GuidemasterboloОценок пока нет
- High Powered Committee Final Report On Traffic Management For MumbaiДокумент51 страницаHigh Powered Committee Final Report On Traffic Management For MumbaiRishi AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Resource Planning & ProductivityДокумент19 страницResource Planning & ProductivityVinit Kant Majumdar67% (3)
- Night Hawk StandДокумент2 060 страницNight Hawk StandRavi Tej GОценок пока нет
- Demystifying The Usage of Sub-Items in is-OIL TSWДокумент21 страницаDemystifying The Usage of Sub-Items in is-OIL TSWmagforuОценок пока нет
- ASTM C627 Robinson TestДокумент4 страницыASTM C627 Robinson TestSiu Hei LauОценок пока нет
- Logistics Integration For Customer Satisfaction Distribution Cost Control and Customer ServiceДокумент50 страницLogistics Integration For Customer Satisfaction Distribution Cost Control and Customer ServiceKanika GoyalОценок пока нет
- JobSparx - June 18th IssueДокумент36 страницJobSparx - June 18th IssueJobSparxОценок пока нет