Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Demographics
Загружено:
cbellsnlИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Demographics
Загружено:
cbellsnlАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cameroon
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 18,175 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Africa, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 2,851 (2006) undernutrition
Unmet need for family planning (%) 20 (2004)
Births (000) 649 (2006) HIV/AIDS Measles Injuries Causes of neonatal Obstructed labor Contraceptive
150 Diarrhoea 7% 4% 2% deaths Abortion 29 Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 70 (2006) Diarrhoea 2% Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) 60 (2004) Anaemia 4% 4% prevalence rate
17% Other
139 149 0%
Tetanus 3% 4% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 149 (2006) 120 Other 7% (1 or more) 82 Pregnancy
Congenital 8% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) 6 (2006)
Pneumonia Hypertensive Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 87 (2006) 22% disorders Haemorrhage 63 Birth
90 Asphyxia 25% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 34%
at birth
40 (2000) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 2, 4, 1 (2004)
25% *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 97 (2006) 60 Sepsis/Infections,
46 Infection 25% Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) 32 (2004) Exclusive
including AIDS 21 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 1,000 (2005) 30 breastfeeding
MDG Target 16%
24 (2005) Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Preterm 30% Other causes
73
0
Total maternal deaths 5,700 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 Malaria 30%
23% Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 36 (2006) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 64 (2006) 100 100 100
83 82 80
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 7 (2006) Low birthweight incidence (%) 11 (2006) 79 79 75
80 80 80
64 58 62 63
60
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses
40 40 40
At least one dose Two doses
100 100 100 95 20 20 20
100 100 100 86 86 95
81
80 80 80 0 0
1991 1998 2000 2004 2006 1991 1998 2000 2004 2006 1984 1989 1994 1999 2004 2006
60 60 60 DHS DHS MICS DHS MICS DHS DHS MICS DHS MICS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
40 40 40
24 21
20 15 16 20 7
12 20
21
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0
2004 2006 1991 1998 2004 2006 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
DHS MICS DHS DHS DHS MICS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100 100
CHILD HEALTH 77
86
80 80 80
66
59
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 50 60 48
58
51 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles 44 43
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs transmission of HIV 40
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 31 40 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib
20 20 20
100 100 30
81 0 0 0
80 80 24 22
1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
73 18
60 60 1991 1998 2000 2004 2006
Percent
Percent
Percent
DHS DHS MICS DHS MICS
40 40 12 11 10 POLICIES SYSTEMS
13 6
20 20
Coverage gap (%) 48 52 53 40 44
1 1 International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 0 Substitutes Yes Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2000 2004 2006 2004 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 83 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 1.9 1.9 1.8 2.2 2.2
Source: WHO/UNICEF MICS DHS MICS Other NS Other NS Other NS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea Yes poorest-wealthiest (%) 32 31 29 32 33
% of total government expenditure (%) 11 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics No Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 68 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age Yes
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.8 (2004)
100 100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Yes Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 80 per child (US$) 7 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
Cameroon
66
60 60 58
60 life saving interventions Yes Official Development Assistance to maternal and
53
Percent
Percent
Percent
43 44 neonatal health per live birth (US$) 4 (2005)
31 32 40 38 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
40 40 40 34 35
22 25 Convention 183 Partial National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
20 20 20 13 services (% of recommended minimum) 29 (2000)
Specific notification of maternal deaths No
0 0 0
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
2004
DHS
2006
MICS
2000
MICS
2004
DHS
2006
MICS
1991
DHS
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
2004
DHS
2006
MICS
Countdown to 2015
2008 Report
Вам также может понравиться
- Special Education ResourcesДокумент13 страницSpecial Education Resourcesapi-248001857Оценок пока нет
- What Should - Abstract ConceptsДокумент20 страницWhat Should - Abstract Conceptsampicca100% (1)
- Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer ZTДокумент36 страницGenetic Testing For Breast Cancer ZTJose Luis Morales BautistaОценок пока нет
- User'S Guide User'S Guide: Diane Bricker Joann (JJ) JohnsonДокумент32 страницыUser'S Guide User'S Guide: Diane Bricker Joann (JJ) JohnsonPamGarcíaОценок пока нет
- Arc GeneralДокумент7 страницArc GeneralMistor Dupois WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Infant 1.1Документ127 страницModule 1 Infant 1.1Tadeous Laurent100% (2)
- Ramona Mercer, Marternal Role AttainmentДокумент27 страницRamona Mercer, Marternal Role AttainmentTamara sapotaОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Ben inДокумент1 страницаBen incbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Guinea BissauДокумент1 страницаGuinea BissaucbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- An Go LaДокумент1 страницаAn Go LacbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Burkina FasoДокумент1 страницаBurkina FasocbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Ye MenДокумент1 страницаYe MencbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Liberia: Country ProfileДокумент4 страницыLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Оценок пока нет
- Country Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child SurvivalДокумент4 страницыCountry Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survivalpaperpin27Оценок пока нет
- Nutrition IDN PDFДокумент2 страницыNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaОценок пока нет
- Nutrition LCAДокумент2 страницыNutrition LCAShernia EliboxОценок пока нет
- Maternal CZEДокумент4 страницыMaternal CZEYajie LuoОценок пока нет
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Документ35 страницReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationОценок пока нет
- Nutrition PHL PDFДокумент2 страницыNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoОценок пока нет
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalДокумент5 страницThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariОценок пока нет
- Par To GraphДокумент15 страницPar To GraphcarОценок пока нет
- Pakistan 2015Документ2 страницыPakistan 2015shujahkianiОценок пока нет
- 1malnutrition As Health ProblemДокумент37 страниц1malnutrition As Health ProblemIntan Sahara BachsinОценок пока нет
- Cervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020Документ2 страницыCervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020nour abdallaОценок пока нет
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Документ63 страницыKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiОценок пока нет
- CAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008Документ1 страницаCAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008raissa leeОценок пока нет
- Jamaica: Country ProfileДокумент4 страницыJamaica: Country ProfileZineil BlackwoodОценок пока нет
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Документ2 страницыMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiОценок пока нет
- Globo Can Ecuador 2020Документ2 страницыGlobo Can Ecuador 2020Park Triple S Kim HyungОценок пока нет
- HMIS Analysis 2013 14: - Andhra Pradesh - GunturДокумент21 страницаHMIS Analysis 2013 14: - Andhra Pradesh - GunturshaikmanojОценок пока нет
- 1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanДокумент56 страниц1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanmaryamОценок пока нет
- Mal2009 Indonesia 0024Документ3 страницыMal2009 Indonesia 0024Tristiani YogastutiОценок пока нет
- Annotated-Powerpoint Presentation - RevisedinfographicДокумент1 страницаAnnotated-Powerpoint Presentation - Revisedinfographicapi-710355795Оценок пока нет
- 20 Breast Fact SheetДокумент2 страницы20 Breast Fact Sheetyuliaindahp18Оценок пока нет
- STD Clinical CliniciansДокумент69 страницSTD Clinical Cliniciansayush231195Оценок пока нет
- FrequencyДокумент7 страницFrequencysawsanОценок пока нет
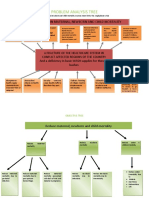
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisДокумент2 страницыPROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisEpie marcОценок пока нет
- HMIS Data Analysis - 2015 - 16 Karnataka - BangaloreДокумент27 страницHMIS Data Analysis - 2015 - 16 Karnataka - BangaloreholysaatanОценок пока нет
- Demographics: Maternal and Newborn HealthДокумент2 страницыDemographics: Maternal and Newborn Healthmichael8spree8michaeОценок пока нет
- Indicative Target TemplateДокумент11 страницIndicative Target TemplateMulugeta DagneОценок пока нет
- 496 Mongolia Fact SheetsДокумент2 страницы496 Mongolia Fact SheetsShotokan Karate MongoliaОценок пока нет
- Philippines: No Data Available No Data AvailableДокумент1 страницаPhilippines: No Data Available No Data Availablemed wardОценок пока нет
- Mort Afro Tza TanzaniaДокумент2 страницыMort Afro Tza TanzaniaJan TanzaniaОценок пока нет
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudДокумент52 страницыStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640Оценок пока нет
- 1 The High Risk MotherДокумент161 страница1 The High Risk MotherRaquel M. MendozaОценок пока нет
- 20 Breast Fact Sheet PDFДокумент2 страницы20 Breast Fact Sheet PDFRaghad Al NatshehОценок пока нет
- G Minaccia Parto PretДокумент64 страницыG Minaccia Parto PretEleonora Francesco Consalvo DonzelliОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Ye MenДокумент1 страницаYe MencbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- Guinea BissauДокумент1 страницаGuinea BissaucbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- DemographicsДокумент1 страницаDemographicscbellsnlОценок пока нет
- 2023 Qu EnfantstroublesdvptДокумент10 страниц2023 Qu EnfantstroublesdvptWil HelmОценок пока нет
- Understanding AdolescenceДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding AdolescenceJeff BuenoОценок пока нет
- Extremely Post-Term Infant With Adverse OutcomeДокумент4 страницыExtremely Post-Term Infant With Adverse OutcomeasclepiuspdfsОценок пока нет
- Mutual Guardianships Application Ststus Form PDFДокумент3 страницыMutual Guardianships Application Ststus Form PDFShibu SamuelОценок пока нет
- Theory 2: Facilitating Learning: Activity 1Документ3 страницыTheory 2: Facilitating Learning: Activity 1Andrea GalangОценок пока нет
- Infant Feeding CompetencyДокумент2 страницыInfant Feeding Competencymadimadi11Оценок пока нет
- Sample Module FormatДокумент7 страницSample Module Formatlia castroОценок пока нет
- Uterine Synechiae and Pregnancy ComplicationsДокумент5 страницUterine Synechiae and Pregnancy ComplicationsBianca CaterinalisendraОценок пока нет
- Data Pengajuan Judul KTI Mhasiswa Kampus UMMI CianjurДокумент15 страницData Pengajuan Judul KTI Mhasiswa Kampus UMMI CianjurAnnisaОценок пока нет
- Understanding Changes/development: Awareness of Adolescence Period and Friendship Formation and MaintenanceДокумент6 страницUnderstanding Changes/development: Awareness of Adolescence Period and Friendship Formation and Maintenancezinawbizu filiposОценок пока нет
- Krasniqi, Cakirpaloglu 2020Документ11 страницKrasniqi, Cakirpaloglu 2020eliora.christyОценок пока нет
- Personal Development Pointers To ReviewДокумент7 страницPersonal Development Pointers To ReviewAshleyОценок пока нет
- Soal Bahasa Inggris UTS Semester 1 Kelas 8 KTSPДокумент5 страницSoal Bahasa Inggris UTS Semester 1 Kelas 8 KTSPLaila FazaОценок пока нет
- Human Development Is ContinuityДокумент4 страницыHuman Development Is ContinuityWilson BalisacanОценок пока нет
- B. Schematic Diagram 26-38Документ13 страницB. Schematic Diagram 26-38Real TetisoraОценок пока нет
- Ifsp FinalДокумент10 страницIfsp Finalapi-294798019Оценок пока нет
- Speech Outline Template With ExampleДокумент4 страницыSpeech Outline Template With ExampleMyke Daniel PualengcoОценок пока нет
- Life of A Single MomДокумент2 страницыLife of A Single MomBSAScitiОценок пока нет
- Peer PressureДокумент1 страницаPeer PressureVEDIKA TOMARОценок пока нет
- Readings Prelim Midterm Period Week 1 6.tutorial.23Документ43 страницыReadings Prelim Midterm Period Week 1 6.tutorial.23Ricardo Batictic Jr.Оценок пока нет
- State Only - Child Care Homes and CenterДокумент254 страницыState Only - Child Care Homes and CenterSeadu UssoОценок пока нет
- 302340KWДокумент22 страницы302340KWValarmathiОценок пока нет
- Speech For Parents DraftДокумент1 страницаSpeech For Parents DraftA.I. R.Оценок пока нет
- PolpolДокумент4 страницыPolpolChristian Paul Villavert TuazonОценок пока нет