Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics I Problems PDF
Загружено:
bosschellenИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics I Problems PDF
Загружено:
bosschellenАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Discussion Questions
BRIDGING PROBLEM
127
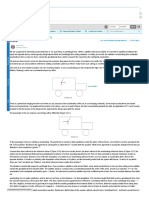
Links in a Chain
A student suspends a chain consisting of three links, each of mass
m 0.250 kg, from a light rope. She pulls upward on the rope, so
that the rope applies an upward force of 9.00 N to the chain. (a) Draw
a free-body diagram for the entire chain, considered as a body, and
one for each of the three links. (b) Use the diagrams of part (a) and
Newtons laws to nd (i) the acceleration of the chain, (ii) the force
exerted by the top link on the middle link, and (iii) the force exerted
by the middle link on the bottom link. Treat the rope as massless.
4. Use your lists to decide how many unknowns there are in this
problem. Which of these are target variables?
EXECUTE
5. Write a Newtons second law equation for each of the four
objects, and write a Newtons third law equation for each
actionreaction pair. You should have at least as many equations as there are unknowns (see step 4). Do you?
6. Solve the equations for the target variables.
SOLUTION GUIDE
See MasteringPhysics study area for a Video Tutor solution.
IDENTIFY and SET UP
1. There are four objects of interest in this problem: the chain as a
whole and the three individual links. For each of these four
objects, make a list of the external forces that act on it. Besides
the force of gravity, your list should include only forces exerted
by other objects that touch the object in question.
2. Some of the forces in your lists form actionreaction pairs (one
pair is the force of the top link on the middle link and the force
of the middle link on the top link). Identify all such pairs.
3. Use your lists to help you draw a free-body diagram for each of
the four objects. Choose the coordinate axes.
Problems
EVALUATE
7. You can check your results by substituting them back into the
equations from step 6. This is especially important to do if you
ended up with more equations in step 5 than you used in step 6.
8. Rank the force of the rope on the chain, the force of the top link
on the middle link, and the force of the middle link on the bottom link in order from smallest to largest magnitude. Does this
ranking make sense? Explain.
9. Repeat the problem for the case where the upward force that
the rope exerts on the chain is only 7.35 N. Is the ranking in
step 8 the same? Does this make sense?
For instructor-assigned homework, go to www.masteringphysics.com
. , .. , ... : Problems of increasing difculty. CP: Cumulative problems incorporating material from earlier chapters. CALC: Problems
requiring calculus. BIO: Biosciences problems.
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
Q4.1 Can a body be in equilibrium when only one force acts on it?
Explain.
Q4.2 A ball thrown straight up has zero velocity at its highest
point. Is the ball in equilibrium at this point? Why or why not?
Q4.3 A helium balloon hovers in midair, neither ascending nor
descending. Is it in equilibrium? What forces act on it?
Q4.4 When you y in an airplane at night in smooth air, there is no
sensation of motion, even though the plane may be moving at
800 km>h 1500 mi>h2. Why is this?
Q4.5 If the two ends of a rope in equilibrium are pulled with forces
of equal magnitude and opposite direction, why is the total tension
in the rope not zero?
Q4.6 You tie a brick to the end of a rope and whirl the brick around
you in a horizontal circle. Describe the path of the brick after you
suddenly let go of the rope.
Q4.7 When a car stops suddenly, the passengers tend to move forward relative to their seats. Why? When a car makes a sharp turn,
the passengers tend to slide to one side of the car. Why?
Q4.8 Some people say that the force of inertia (or force of
momentum) throws the passengers forward when a car brakes
sharply. What is wrong with this explanation?
Q4.9 A passenger in a moving bus with no windows notices that a
ball that has been at rest in the aisle suddenly starts to move toward
the rear of the bus. Think of two different possible explanations,
and devise a way to decide which is correct.
Q4.10 Suppose you chose the fundamental SI units to be force,
length, and time instead of mass, length, and time. What would be
the units of mass in terms of those fundamental units?
Q4.11 Some of the ancient Greeks thought that the natural state
of an object was to be at rest, so objects would seek their natural
state by coming to rest if left alone. Explain why this incorrect
view can actually seem quite plausible in the everyday world.
Q4.12 Why is the earth only approximately an inertial reference
frame?
Q4.13 Does Newtons second law hold true for an observer in a
van as it speeds up, slows down, or rounds a corner? Explain.
S
Q4.14 Some students refer to the quantity ma as the force of
acceleration. Is it correct to refer to this quantity as a force? If so,
what exerts this force? If not, what is a better description of this
quantity?
Q4.15 The acceleration of a falling body is measured in an elevator traveling upward at a constant speed of 9.8 m>s. What result is
obtained?
Q4.16 You can play catch with a softball in a bus moving with
constant speed on a straight road, just as though the bus were at
rest. Is this still possible when the bus is making a turn at constant
speed on a level road? Why or why not?
Вам также может понравиться
- Force and Laws of Motion - Shobhit NirwanДокумент13 страницForce and Laws of Motion - Shobhit NirwanLearn with happiness63% (8)
- NCERT Class 11 Physics Part 1Документ199 страницNCERT Class 11 Physics Part 1Extra WorkОценок пока нет
- S.S. Bhavikatti - Engineering Mechanics - Vector and Classical Approach (All India) (2020, NEW AGE INTERNATIONAL) - Libgen - LiДокумент512 страницS.S. Bhavikatti - Engineering Mechanics - Vector and Classical Approach (All India) (2020, NEW AGE INTERNATIONAL) - Libgen - LiKrishna Sen 3051100% (1)
- Cape Physics Unit 1st EditionДокумент70 страницCape Physics Unit 1st EditionJunior Dollas100% (9)
- Physics Important Questions For Inter 1st YearДокумент3 страницыPhysics Important Questions For Inter 1st Yearkakashi hatake100% (2)
- Physics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions Manual 1Документ5 страницPhysics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions Manual 1bertha100% (48)
- The Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineОт EverandThe Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Newton's Third Law of MotionДокумент8 страницNewton's Third Law of MotionLani Buenaventura100% (1)
- Grade 8Документ14 страницGrade 8Dandan Ostria100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFДокумент61 страницаEngineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFdebra.glisson665100% (46)
- Science 8 Q1 Summative TestДокумент10 страницScience 8 Q1 Summative TestJessah Chris Eve Valle100% (4)
- Science 9 Q4 WK1 2Документ33 страницыScience 9 Q4 WK1 2leo mark100% (1)
- Gened FinalДокумент88 страницGened FinalLoie LyndonОценок пока нет
- M-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHДокумент9 страницM-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHVenu GopalОценок пока нет
- Newtons Laws Webquest Answer KeysДокумент3 страницыNewtons Laws Webquest Answer KeysMarisol Tan AlbercaОценок пока нет
- Most Important Theory Questions & Derivations For Class 11 - 2024 ExamДокумент10 страницMost Important Theory Questions & Derivations For Class 11 - 2024 Examashmitaramoliya123Оценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- AP Phys1 Rotational Motion AP Style Free Response Questions 2022-02-27Документ19 страницAP Phys1 Rotational Motion AP Style Free Response Questions 2022-02-27robbossofficial2Оценок пока нет
- Class 11 Physics Term 1 Most Imp QuestionsДокумент7 страницClass 11 Physics Term 1 Most Imp QuestionsSANJAY PARMARОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Energy and Projectile MotionДокумент16 страницConservation of Energy and Projectile MotionRenz MaguilaОценок пока нет
- Physics1styr 2marksДокумент7 страницPhysics1styr 2marksRP Sir QuizzesОценок пока нет
- Slo's Based Question - Phy - XIДокумент6 страницSlo's Based Question - Phy - XISingularityОценок пока нет
- Science 8 Lesson 1 Three Laws of MotionДокумент34 страницыScience 8 Lesson 1 Three Laws of MotionMyra JuanОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1Документ11 страницPHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1labonetelabs21Оценок пока нет
- Pendulum Demonstration ActivityДокумент5 страницPendulum Demonstration ActivityNatasha AndrewsОценок пока нет
- Physics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions Manual 1Документ36 страницPhysics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions Manual 1christophermorrisybfimgadzk100% (23)
- Class 9 Exercise ConceptualДокумент6 страницClass 9 Exercise Conceptualzeeshanhameedz1996Оценок пока нет
- Physicsexp 7Документ8 страницPhysicsexp 7Shelby NewtonОценок пока нет
- Physics TestДокумент7 страницPhysics Testzeeshanhameedz1996Оценок пока нет
- 11physics Impt. Qs+derivationsДокумент11 страниц11physics Impt. Qs+derivationskhushiОценок пока нет
- Physics 1.3 SolutionsДокумент4 страницыPhysics 1.3 SolutionsHin Wa LeungОценок пока нет
- Experimento # 8-1Документ4 страницыExperimento # 8-1GodVegeta 28 TorresОценок пока нет
- Review/Diagnostic Homework, Physics 4304, Dr. Charles W. MylesДокумент5 страницReview/Diagnostic Homework, Physics 4304, Dr. Charles W. MylesNur SyahirahОценок пока нет
- Angular Momentum ThesisДокумент4 страницыAngular Momentum Thesisrwzhdtief100% (2)
- Ch4 Conceptual QuestionsДокумент5 страницCh4 Conceptual QuestionsTheresa Matthews100% (1)
- MHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Документ31 страницаMHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Klaus Danjolli100% (1)
- REV12020 PhysicsДокумент4 страницыREV12020 Physicshari kroviОценок пока нет
- Physics Study GuideДокумент12 страницPhysics Study Guidebmack21Оценок пока нет
- 1ST Year Physics Guess PaperДокумент8 страниц1ST Year Physics Guess Papermubashar khokharОценок пока нет
- Rotating Frame - Pseudo ForcesДокумент5 страницRotating Frame - Pseudo ForcesHarishОценок пока нет
- Physics 4A Chapter 5: Force and Motion - I: Reading: OutlineДокумент8 страницPhysics 4A Chapter 5: Force and Motion - I: Reading: OutlineHasan MehediОценок пока нет
- 1301 Lab 7Документ30 страниц1301 Lab 7stacyyyОценок пока нет
- Ap1 Lab Phet Hookes LawДокумент5 страницAp1 Lab Phet Hookes LawDaniel AmmarОценок пока нет
- Effect.: Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierДокумент8 страницEffect.: Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierRashard AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Newtons Laws Learning GuideДокумент13 страницNewtons Laws Learning GuideRana MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Juniorinter Physics Questions em 4 PDFДокумент13 страницJuniorinter Physics Questions em 4 PDFnasreenrai7991Оценок пока нет
- Ch4newtonsslaws 101013161156 Phpapp02Документ94 страницыCh4newtonsslaws 101013161156 Phpapp02Reynante Dap-ogОценок пока нет
- Ch04 Homework SolutionsДокумент88 страницCh04 Homework SolutionsOsama Maher100% (1)
- 11 Phy Systemofparticlesandrotationalmotion Tp01Документ6 страниц11 Phy Systemofparticlesandrotationalmotion Tp01Fennix AGОценок пока нет
- JR InterДокумент4 страницыJR InterAswani Kumar67% (3)
- AP Physics 1 Hooke's Law Take-Home Simulation LabДокумент3 страницыAP Physics 1 Hooke's Law Take-Home Simulation LabLaura AlhammadОценок пока нет
- Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Lab ReportДокумент16 страницElastic and Inelastic Collisions Lab ReportDelfina FariasОценок пока нет
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions Manual Full DownloadДокумент8 страницPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions Manual Full Downloadchristinehallpkadrcnjxs100% (36)
- Lab 1 - Statistical Analysis LabДокумент7 страницLab 1 - Statistical Analysis Labdibia collinsОценок пока нет
- 1101 Lab 7 - EquilibriumДокумент8 страниц1101 Lab 7 - EquilibriumrajesaravindОценок пока нет
- Rotation Learning GuideДокумент12 страницRotation Learning GuideRana MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Particle Dynamics (QB)Документ28 страницParticle Dynamics (QB)Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- PC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersДокумент19 страницPC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersMikael Lee0% (3)
- Advance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumДокумент27 страницAdvance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumMilcah Shane Niones SarenОценок пока нет
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Документ4 страницыVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Jagadeesh KarriОценок пока нет
- Imp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18Документ5 страницImp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18akash kalraОценок пока нет
- Physics Chapters 5 HomeworkДокумент6 страницPhysics Chapters 5 HomeworkRuža KukićОценок пока нет
- Class IX Ch. Laws of Motion Assertion & Reasoning QuestionДокумент2 страницыClass IX Ch. Laws of Motion Assertion & Reasoning Questionrudranilm2008Оценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент53 страницыPhysicsIwana Rademaekers100% (1)
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- General Relativity - Benjamin CrowellДокумент273 страницыGeneral Relativity - Benjamin CrowellpanteraindacoОценок пока нет
- Motion and Forces - SindhДокумент5 страницMotion and Forces - SindhMuhammad Ibrahim MubashirОценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент60 страницNewton's Laws of MotionSherif Yehia Al Maraghy100% (1)
- Newton's Second Law of MotionДокумент7 страницNewton's Second Law of MotionZeroseveen SeveenОценок пока нет
- MEE214 แผนการเรียนДокумент3 страницыMEE214 แผนการเรียนT KongcharoenОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechancis Manoj K Harbola-IIT Knapur .PDF Filename UTF-8''Engineering Mechancis (Manoj K Harbola-IIT Knapur)Документ272 страницыEngineering Mechancis Manoj K Harbola-IIT Knapur .PDF Filename UTF-8''Engineering Mechancis (Manoj K Harbola-IIT Knapur)Abhinav MishraОценок пока нет
- Kinetic of ParticleДокумент58 страницKinetic of ParticlegholamrezaОценок пока нет
- CMP T1Документ261 страницаCMP T1Aditi KaradeОценок пока нет
- Module 7 Rectilinear Motion and Free FallingДокумент10 страницModule 7 Rectilinear Motion and Free FallingJay LopezОценок пока нет
- Physics 02-01 Newton's Laws LabДокумент3 страницыPhysics 02-01 Newton's Laws Labtonisupriadi100% (1)
- Advanced Level Physics Teaching SchemesДокумент29 страницAdvanced Level Physics Teaching SchemesBeaugar MaxwellОценок пока нет
- Physics Forces PDFДокумент5 страницPhysics Forces PDFObed Alonso LlagunoОценок пока нет
- Stand-Alone Senior High SchoolДокумент4 страницыStand-Alone Senior High SchoolRei ChanОценок пока нет
- Unit I - Module Ii - Oral CommunicationДокумент4 страницыUnit I - Module Ii - Oral CommunicationCAROLINA MORENO CARDONAОценок пока нет
- Wa0006.Документ66 страницWa0006.shaunjali21Оценок пока нет
- Newtons LawsДокумент110 страницNewtons LawsTenisha CastilloОценок пока нет
- Law of MotionДокумент4 страницыLaw of MotionRose GilaОценок пока нет
- Motion and Machines Unit Part III - Download .PPT atДокумент257 страницMotion and Machines Unit Part III - Download .PPT atRyan MurphyОценок пока нет
- Long Test 1.1-Grade 8 ScienceДокумент3 страницыLong Test 1.1-Grade 8 ScienceBernadeth Bagnes HernandezОценок пока нет
- Physics For Remedial Program Lectures NoteДокумент201 страницаPhysics For Remedial Program Lectures NoteNesredin Teshome100% (5)
- Sample Pages: Physics Toolkit Module 1: Kinematics Module 2: DynamicsДокумент20 страницSample Pages: Physics Toolkit Module 1: Kinematics Module 2: DynamicsNam NguyenОценок пока нет
- Phy130 Textbook College PhysicsДокумент2 страницыPhy130 Textbook College PhysicsHisyammudin RoslanОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes On Basic Physics: Compiled By: Chibuikem N. OkekeДокумент12 страницLecture Notes On Basic Physics: Compiled By: Chibuikem N. OkekeCHIBUIKEM OKEKEOGUEGBEОценок пока нет