Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Enhanced UL
Загружено:
mydendiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Enhanced UL
Загружено:
mydendiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Enhanced UL
In order to fulfil the need for improvement also for UL packet data, Enhanced UL also called HSUPA was introduced in
3GPP Release 6.
A major difference between DL and UL is that for DL there is ONE transmitter per cell, NodeB, whilst for the UL there might be
MANY transmitters, each UE with an active UL, each moving and sending independently. Hence, the DL physical channels will
all be orthogonal- at least at the point of transmission, having channelization codes from the same code tree, and they will be
sharing the available power in the NodeB. In the UL it is not possible to get perfect orthogonality since the senders, UEs, are
moving independently. Every UE has its own channelization code tree and its own battery. As in R99 long scrambling codes,
with low correlation, are used to separate between channels from different transmitters, i.e. NodeBs DL and UEs UL.
In HSDPA the data to different UEs is carried on a shared channel, while in Enhanced UL the data from different users will be
carried on a dedicated channel; transport channel Enhanced Dedicated Channel (E-DCH) mapped onto the physical channel EDCH-Dedicated Physical Data Channel (E-DPDCH) for high data rates more than one E-DPDCH will be used. The E-DPDCH
can use a channelization code with a minimum value of SF = 2. In Release 6 the maximum channel rate for Enhanced UL is 5.8
Mbps, with a peak data rate of 5.4 Mbps, this value is valid for the MAC layer. For Enhanced UL there are two options for TTI, 2
ms or 10 ms.
For Enhanced UL scheduling is still carried out by the NodeB, now the receiving node, while transport format selection is done
by the scheduled UEs, see figure 6. The NodeB will measure the interference level on the UL and receive information about
buffer status in the UEs, and make a decision about which UEs that are to be scheduled. Information about scheduling decision is
delivered in scheduling grants, which also provides information about how much power the UE(s) may use when transmitting.
The higher the power the higher the bitrate, and the interference! In the DL the shared resources are channelization codes and
power, in the UL the shared resource is contribution to the intra-cell interference.
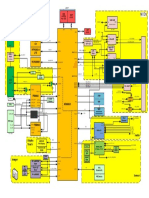
Figure 6 Scheduling, transport format selection and HARQ for Enhanced UL
For Enhanced UL channels soft handover will be used in basically the same way as for R99.
To handle these functions new MAC protocol sublayers are added, MAC-e in NodeB is responsible for scheduling and HARQ,
and MAC-es in RNC to handle reordering of received data from multiple NodeBs in case of soft handover, see figure 7.
Вам также может понравиться
- ACCESSIBILITY OPTIMIZATIONДокумент2 страницыACCESSIBILITY OPTIMIZATIONmydendiОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Problem Related To The Standardizing of The CSSR in Viettel Project in VietnamДокумент2 страницы1.1 Problem Related To The Standardizing of The CSSR in Viettel Project in VietnammydendiОценок пока нет
- Features/Prameters LTE OptimizationДокумент3 страницыFeatures/Prameters LTE OptimizationFuzail Khan50% (2)
- Parameters EricssonДокумент4 страницыParameters Ericssonmydendi100% (1)
- Handover - Event GSMДокумент2 страницыHandover - Event GSMmydendiОценок пока нет
- GSM Neighboring CellsДокумент6 страницGSM Neighboring CellsmydendiОценок пока нет
- Pilot Pollution Analysis AlgorithmДокумент8 страницPilot Pollution Analysis AlgorithmmydendiОценок пока нет
- Missing Neighboring CellsДокумент6 страницMissing Neighboring CellsmydendiОценок пока нет
- Analysis Process and Optimization MethodДокумент3 страницыAnalysis Process and Optimization MethodmydendiОценок пока нет
- Information Feedback: SN Information Remarks PurposeДокумент2 страницыInformation Feedback: SN Information Remarks PurposemydendiОценок пока нет
- Missing Neighboring CellsДокумент3 страницыMissing Neighboring CellsmydendiОценок пока нет
- 07 GSM BSS Network KPI (Call Setup Success Rate) Optimization ManualДокумент17 страниц07 GSM BSS Network KPI (Call Setup Success Rate) Optimization ManualMistero_HОценок пока нет
- Optimization CasesДокумент3 страницыOptimization CasesmydendiОценок пока нет
- Definition of The CSSRДокумент3 страницыDefinition of The CSSRmydendiОценок пока нет
- High Speed DataДокумент1 страницаHigh Speed DatamydendiОценок пока нет
- Utran Channels - DCCH Rach FachДокумент2 страницыUtran Channels - DCCH Rach FachmydendiОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Technical Seminar UARTДокумент23 страницыTechnical Seminar UARTcharan467100% (1)
- Rel 15Документ52 страницыRel 15Sateesh ChanderОценок пока нет
- Point To Point SDH-PDH PDFДокумент2 страницыPoint To Point SDH-PDH PDFAfanОценок пока нет
- Heiednhain TNC 155Документ3 страницыHeiednhain TNC 155Danijel KnezevicОценок пока нет
- Codingbox User Specification Rev 1.1Документ5 страницCodingbox User Specification Rev 1.1Антон ЛузгинОценок пока нет
- UMTS Heavy Traffic Precautions and Emergency MeasureДокумент28 страницUMTS Heavy Traffic Precautions and Emergency Measurekara nacimОценок пока нет
- Optix Metro 100 V100R002 System Description V1 20Документ33 страницыOptix Metro 100 V100R002 System Description V1 20Nguyen Minh Tu88% (8)
- DX07SeriesUSBType CConnector (Receptacle)Документ4 страницыDX07SeriesUSBType CConnector (Receptacle)SEHUNОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Moshell Useful Commands and TasksДокумент11 страницIntroduction To Moshell Useful Commands and TasksPrabhat Kumar Singh100% (9)
- European Digital Carrier SystemДокумент2 страницыEuropean Digital Carrier SystemXyОценок пока нет
- Buses - Characteristics, Types & UsesДокумент15 страницBuses - Characteristics, Types & UsesAnmol HamidОценок пока нет
- Diagrama de Bloques ServicellДокумент1 страницаDiagrama de Bloques ServicellJoséViloria100% (1)
- Rtl8367rb CG RealtekДокумент78 страницRtl8367rb CG RealtekNadya Mariela ShamaraОценок пока нет
- Networked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Документ17 страницNetworked Option Pods Operating Instructions July 2023 v1.3Ariel Horta LoeraОценок пока нет
- MIMO LogsДокумент457 страницMIMO LogsPeterParker SpidyОценок пока нет
- ASK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using Functions in MATLABДокумент4 страницыASK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using Functions in MATLABdes tosОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Tellabs 6325 EDGE NodeДокумент2 страницыDatasheet Tellabs 6325 EDGE NodeBoby Rahmadi100% (1)
- ET-7053 PET-7053 ET-7253 PET-7253: FeaturesДокумент2 страницыET-7053 PET-7053 ET-7253 PET-7253: FeaturesYan TronicОценок пока нет
- Dell Latitude 7490 Da240 La-F322 Sbmlk14 - Nonar - MB r20 A01Документ59 страницDell Latitude 7490 Da240 La-F322 Sbmlk14 - Nonar - MB r20 A01Ali AsgharОценок пока нет
- What Are The Differences Between 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G Networks?Документ4 страницыWhat Are The Differences Between 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G Networks?savsen6720Оценок пока нет
- IATEX2012 03 B PN IntroductionДокумент61 страницаIATEX2012 03 B PN Introductionnice hossainОценок пока нет
- Fibras Multimodo Ethernet SM e RF ModulesДокумент11 страницFibras Multimodo Ethernet SM e RF ModulesBJNE01Оценок пока нет
- Familiarization To Lab Equipment and Packet Tracer Software, and Construct Network Cable. (CLO-1, PLO-4)Документ10 страницFamiliarization To Lab Equipment and Packet Tracer Software, and Construct Network Cable. (CLO-1, PLO-4)Hadia RashidОценок пока нет
- (Mgg7) Kajian#2c - MIMO - RevДокумент32 страницы(Mgg7) Kajian#2c - MIMO - RevRaga FilyОценок пока нет
- Standards and Applications of SDHДокумент18 страницStandards and Applications of SDHyogesh_simiffОценок пока нет
- Universal Serial Bus USB ReportДокумент24 страницыUniversal Serial Bus USB ReportshivaОценок пока нет
- Md936 DVR Usb Inst Reva2 RedlineДокумент6 страницMd936 DVR Usb Inst Reva2 RedlineMatias Contreras KöbrichОценок пока нет
- ATC-277MM User's ManualДокумент0 страницATC-277MM User's ManualMaitry ShahОценок пока нет
- Debug 1214Документ4 страницыDebug 1214Dobrán László AttilaОценок пока нет
- WBR 3408 DatasheetДокумент3 страницыWBR 3408 DatasheetGrandeCleitonОценок пока нет