Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Gen 06
Загружено:
rourkela123Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Gen 06
Загружено:
rourkela123Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
General
Thermocouple Material Specifications
The thermocouple element materials listed below are those most commonly found in process applications. Selection
of the proper thermocouple type for a particular application is determined by temperature expectations and by the
environment in which the sensor will be placed. The following temperature and application tables are intended to aid
in this selection. The thermocouples are listed by ASTM letter designations per thermocouple type.
Letter Designated Thermocouples
TYPE
J
E230
Iron (+)
Copper - 45% Nickel (Constantan) (-)
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
APPLICATION INFORMATION
(0 to 760) C
[32 to 1400] F
Suitable for vacuum, reducing, or inert atmospheres, oxidizing
atmosphere with reduced life. Iron oxidizes rapidly above 538 C
[1000 F] so only heavy gauge wire is recommended for high
temperature. Bare elements should not be exposed to sulphurous
atmospheres above 538 C [1000 F].
K
E230
Nickel - 10% Chromium (+)
Nickel - 2% Aluminum, 2% Manganese,
1% Silicon (-)
(0 to 1260) C
[32 to 2300] F
Recommended for continuous oxidizing or neutral atmospheres.
Mostly used above 538 C [1000 F]. Subject to failure if exposed to
sulphur. Preferential oxidation of chromium in positive leg at certain
low oxygen concentrations causes 'green rot' and large negative
calibration drifts most serious in the (816 to 1038) C
[1500 to 1900] F range. Ventilation or inert-sealing of the protection
tube can prevent this.
N
E230
Nickel - 14% Chromium, 1 1/2% Silicon (+)
Nickel - 4 1/2% Silicon - 1/10% Magnesium (-)
(0 to 1260) C
[32 to 2300] F
Can be used in applications where Type K elements have shorter
life and stability problems due to oxidation and the development of
'green rot'.
T
E230
Copper (+)
Copper - 45% Nickel (Constantan) (-)
(-200 to 370) C
[-328 to 700] F
Useable in oxidizing, reducing, or inert atmospheres as well as
vacuum. Not subject to corrosion in moist atmospheres. Limits of
error published for sub-zero temperature ranges.
E
E230
Nickel - 10% Chromium (+)
Copper - 45% Nickel (Constantan) (-)
(0 to 870) C
[32 to 1600] F
Recommended for continuously oxidizing or inert atmospheres.
Sub-zero limits of error not established. Highest thermoelectric
output of common calibrations.
R
E230
Platinum - 13% Rhodium (+)
Platinum (-)
S
E230
Platinum - 10% Rhodium (+)
Platinum (-)
(538 to 1482) C
[1000 to 2700] F
Recommended for high temperature. Must be protected with
non-metallic protection tube and ceramic insulators. Continued
high temperature usage causes grain growth which can lead to
mechanical failure. Negative calibration drift caused by Rhodium
diffusion to pure leg as well as from Rhodium volatilization.
Type R is used in industry; Type S in the laboratory.
B
E230
Platinum - 30% Rhodium (+)
Platinum - 6% Rhodium (-)
(871 to 1704) C
[1600 to 3100] F
Same as R & S but output is lower. Also less susceptible to grain
growth and drift.
C
E230
95% Tungsten - 5% Rhenium (+)
74% Tungsten - 26% Rhenium (-)
(0 to 2315) C
[32 to 4200] F
Very high temperature applications in inert or vacuum. Preferred
over Tungsten/Tungsten-26% Rhenium because it is less brittle at
low temperatures.
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Non-Letter Designated Thermocouples
TYPE
M
E1751
Nickel - 18% Molybdenum (+)
Nickel - 0.8% Cobalt (-)
(-50 to 1410) C
[-58 to 2570] F
High temperature applications in inert or vacuum atmosphere.
Useful in many hydrogen applications. Continuous cycling causes
excessive grain growth.
P
E1751
Platinel II
Platinel 5355 (+)
Platinel 7674 (-)
(0 to 1395) C
[32 to 2543] F
Noble metal combination which approximates Type K curve but has
much improved oxidation resistance. Should be treated as any noble
metal calibration.
Platinel is a registered trademark of BASF Catalysts.
2006 Pyromation, Inc.
GEN-6
Phone (260) 484-2580 FAX (260) 482-6805 or (800) 837-6805 www.pyromation.com
26-8
Вам также может понравиться
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- 01 Introduction To Manufacturing and MachiningДокумент10 страниц01 Introduction To Manufacturing and MachiningTarun MehtaОценок пока нет
- TE-Thermocouple Materials PaperДокумент20 страницTE-Thermocouple Materials Paperrourkela123Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- GK Power Capsule (April 2014)Документ7 страницGK Power Capsule (April 2014)SunilChaudharyОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Current Affairs IES 2012Документ26 страницCurrent Affairs IES 2012Rishav RoyОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Std12 Phy Vol 1Документ237 страницStd12 Phy Vol 1Aaron Merrill50% (2)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Thermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedДокумент265 страницThermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedRavinder Antil90% (40)
- NCERT Physics Inter Ist YearДокумент217 страницNCERT Physics Inter Ist Yearmalleshpage100% (9)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Current Affairs IES 2012Документ26 страницCurrent Affairs IES 2012Rishav RoyОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Catálogo PCV-9614 MR98H - SC150212Документ40 страницCatálogo PCV-9614 MR98H - SC150212Marcos PauloОценок пока нет
- Realization Phase of Model in Terms of EcodesignДокумент7 страницRealization Phase of Model in Terms of EcodesignZvonimir MajićОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- Tests for Organic MoleculesДокумент7 страницTests for Organic MoleculesICAMisterPОценок пока нет
- Bpharmacy 1 Sem Pharmaceutics 1 Set P 2018Документ3 страницыBpharmacy 1 Sem Pharmaceutics 1 Set P 2018Mandlik PritiОценок пока нет
- Compendium OIV Vol1Документ539 страницCompendium OIV Vol1Daniela MenegatОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- SuspensionДокумент31 страницаSuspensionSakandar TalibОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- 11.VIA Group ElementsДокумент3 страницы11.VIA Group ElementsANIL KumarОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Atividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Документ3 страницыAtividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Maria ClaraОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- XPS de AluminioДокумент6 страницXPS de AluminioBeatriz BrachettiОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- 15.1 Dispersion of LightДокумент16 страниц15.1 Dispersion of LightRecky LasutОценок пока нет
- Coagulation of Natural Rubber Latex with Hydrochloric AcidДокумент6 страницCoagulation of Natural Rubber Latex with Hydrochloric Acidchaminda nayanajithОценок пока нет
- Is 2951 1 1965 PDFДокумент28 страницIs 2951 1 1965 PDFlagnajit dasОценок пока нет
- 301 Lab2Документ9 страниц301 Lab2Ryan BaleОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-7 SET-1 Chapter-14Документ6 страницCLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-7 SET-1 Chapter-14Sanchit PREDATORОценок пока нет
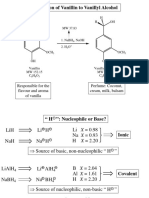
- Síntesis de Alcohol VainillílicoДокумент6 страницSíntesis de Alcohol VainillílicoYago L100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Nano World A. DefinitionДокумент6 страницThe Nano World A. DefinitionSavy CruzОценок пока нет
- ECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021Документ10 страницECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021supinya bieОценок пока нет
- P131 Problem Set 1Документ2 страницыP131 Problem Set 1TyОценок пока нет
- Oxford English Dictionary: Physical GeographyДокумент1 страницаOxford English Dictionary: Physical GeographyCatalin BucurОценок пока нет
- Ion DipoleДокумент18 страницIon DipoleblessyramasamillanoОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Benzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationДокумент7 страницBenzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationXiang Yu100% (7)
- Chemistry and LithographyДокумент878 страницChemistry and LithographyAna Violeta Girão83% (6)
- PH Ysicsguide: Basic Concepts of Statistical MechanicsДокумент14 страницPH Ysicsguide: Basic Concepts of Statistical MechanicsMОценок пока нет
- Titration CurveДокумент12 страницTitration Curveoguztop10Оценок пока нет
- Ozone Layer & Greenhouse EffectДокумент29 страницOzone Layer & Greenhouse EffectIlyas A HuqqaniОценок пока нет
- 02 Assignments MECДокумент22 страницы02 Assignments MECWillis ChekovОценок пока нет
- Galvanic Test Panels For Accelerated Corrosion Testing of Coated Al Alloys: Part 2-Measurement of Galvanic InteractionДокумент13 страницGalvanic Test Panels For Accelerated Corrosion Testing of Coated Al Alloys: Part 2-Measurement of Galvanic InteractionwhathОценок пока нет
- Heat 1Документ36 страницHeat 1ZainabОценок пока нет