Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Work 1 English
Загружено:
rgcsm88Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Work 1 English
Загружено:
rgcsm88Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
PHYSICS COURSE (AIEEE/PET/PMT-2013) SARASWATI
WORK -1
December 8, 2014
EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTE
w -1
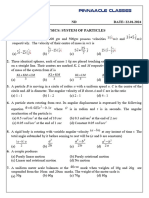
1.
A body of mass m is moving in a circle of radius r
with a constant speed v. The force on the body is
mv2
r
(a) Its velocity is constant (b) Its acceleration is constant
(c)Its kinetic energy is constant(d)It moves in a straight line
10.
and is directed towards the centre. What is the
work done by this force in moving the body over
half the circumference of the circle [NCERT 1977]
mv2
mv2
2.
r 2
mv2
(a) r (b)Zero
(c) r (d)
A man pushes a wall and fails to displace it. He does
2
g
4.
3.
11.
12.
5.
A body of mass m kg is lifted by a man to a height of
one metre in 30 sec. Another man lifts the same
mass to the same height in 60 sec. The work done by
them are in the ratio
[MP PMT 1993]
14.
6.
8.
9.
4:1
A body of mass 10 kg is dropped to the ground from
a height of 10 metres. The work done by the
gravitational force is
7.
2 : 1(d)
(g 9.8 m / sec2)
[SCRA 1994]
d
4
3Mg
d
4
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Mgd
A body moves a distance of 10 m along a straight
line under the action of a force of 5 N. If the work
done is 50 joules, the angle which the force makes
with the direction of motion of the body is[NCERT 1980;
60(d)
90
A body of mass 10 kg is dropped to the ground from
a height of 20 metres. The work done by the
gravitational force is
(a) 2kj(b)+ 2kj(c)
13.
: 1(c)
3Mg
(a) 0(b)30(c)
You lift a heavy book from the floor of the room and keep it in the
book-shelf having a height 2 m. In this process you take 5 seconds.
The work done by you will depend upon[MP PET 1993]
(a) Mass of the book and time taken
(b) Weight of the book and height of the book-shelf
(c) Height of the book-shelf and time taken
(d) Mass of the book, height of the book-shelf and time taken
1 : 2 (b)1
d
4
JIPMER 1997; CBSE PMT 1999;BHU 2000; RPMT 2000; Orissa JEE
4.
(a)
Work done by the cord on the block is [CPMT 1972]
Mg
[CPMT 1992]
(a) Negative work
(b) Positive but not maximum work
(c) No work at all(d) Maximum work
A body moves a distance of 10 m along a straight
line under the action of a force of 5 N. If the work
done is 25 joules, the angle which the force makes
with the direction of motion of the body is
(a) 0(b)30(c)
60(d)
90
A cord is used to lower vertically a block of mass M
by a distance d with constant downward acceleration
(g 9.8 m / sec2)
1kj(d)
[SCRA 1994]
+ 1kj
A body of mass 5 kg is placed at the origin, and can
move only on the x-axis. A force of 10 N is acting on
it in a direction making an angle of 60o with the xaxis and displaces it along the x-axis by 10 metres.
The work done by the force is
[MP PET 2003]
(a) 2.5 J(b)7.25 J(c) 50 J(d)
100 J
A cord is used to lower vertically a block of mass M
by a distance d with constant downward acceleration
g
4.
Work done by the gravitational force on the
block is
[CPMT 1972]
Mg
d
4
3Mg
d
4
3Mg
d
4
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Mgd
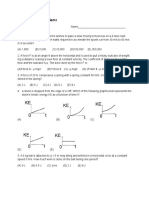
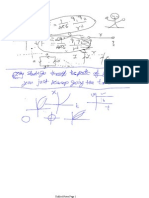
15. in given figure object moved at a distance 10 m .
then work done is
100 N
600
(a) 490 J(b)+ 490 J(c) 980 J(d) + 980 J
A body of mass 5 kg is placed at the origin, and can
move only on the x-axis. A force of 10 N is acting on
it in a direction making an angle of 60o with the x(a)500j (b)100j (c)1000j (d)10j
axis and displaces it along the x-axis by 4 metres. 16. Given figure object moved at a distance 10 m and
The work done by the force is
[MP PET 2003]
applied force 100N and coefficient of friction is 0.5
(a) 2.5 J(b)7.25 J(c) 40 J(d)
20 J
then work done by the friction force is
A 50kg man with 20kg load on his head climbs up 20
(a) -500j (b)+500j (c)1000j (d)10j
steps of 0.25m height each. The work done in
10kg
climbing is
[JIPMER 2002]
(a) 5 J(b)350 J(c)
100 J(d)
3430 J
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant
magnitude which is always perpendicular to the 17. Given figure object moved at a distance 10 m and
applied force 100N and coefficient of friction is 0.5
velocity of the particle, the motion of the particle
then total work done
takes place in a plane. It follows that [AIEEE 2004]
(a) -500j (b)+500j (c)1000j (d)10j
10kg
18.
A uniform chain of length 3m is kept on a table such that a
length of 60cm hangs freely from the edge of the table. The
total mass of the chain is 4kg. What is the work done in
pulling the entire chain on the table
[AIEEE 2004]
(a) 7.2 J(b)3.6 J
(c) 120 J(d)
1200 J
19.
A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a
smooth table and one third of its length is hanging vertically
down over the edge of the table. If g is acceleration due to
gravity, the work required to pull the hanging part on to the
table is
[IIT 1985; MNR 1990; AIEEE 2002;
2kg
(a) MgL(b)MgL/3(c)
MgL/9(d)
MgL/18
10m
20. on frictionless inclined plane surface2kgthe work done by gravity
300
25. Above question
(a)work done by P is -ive
(b) work done by P is +ive
(c) work done by P is zero
(d) none
26. Above question
(a)total work done by is -ive (b) total work done by is +ive
(c)total work done by P is zero (d) none
27. Work done done by gravity is non-zero
(a) Orbital motion of satellite in circular path
(b) Freely falling object
(b) motion of block on plane surface
(d) none
28.
300
(a)-200j
(b)+100j
10m
(c)+200j
(d)10j
21.
A uniform chain of length 3m is kept on a table such that a
length of 50cm hangs freely from the edge of the table. The
total mass of the chain is 6kg. What is the work done in
pulling the entire chain on the table
[AIEEE 2004]
(a) 7 J(b)3.6 J(c)
on
2kg
inclined plane object is pulling then work done by applied
force in 400j then work done by friction is
29.
30.
22. on inclined plane object is pulling then work done by applied
force in 400j then work done by gravity
(a)-200j (b)+100j
(c)+200j (d)300j
180 J
A uniform chain of length 3m is kept on a table such that a
hangs freely from the edge of the table. The total mass of
the chain is 6kg. What is the work done in pulling the entire
chain on the table
[AIEEE 2004]
(a) 7.2 J(b)3.6 J(c)
(a)-200j (b)+100j
(c)+200j (d)300j
90 J(d)
90 J(d)
180 J
A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a
smooth table and one half of its length is hanging vertically
down over the edge of the table. If g is acceleration due to
gravity, the work required to pull the hanging part on to the
table is
[IIT 1985; MNR 1990; AIEEE 2002;
(a) MgL(b)MgL/8(c)
MgL/2(d)
MgL/4
31. The work done to displace A TO D by the gravitational force is
D
(c) mgh
(d)
mgH
23. The object moving with constant velocity on
H
(b) mg(H-h)
frictionless surface then total work done is
A
(d) mg(h-H)
(a)-ive (b)+ive (c)zero (d) none
h
24.
The object moving with constant velocity on
frictionless surface then
P
v
10kg
(a)work done by F is -ive (b) work done by F is +ive
(c) work done by F is zero (d) none
32. The work done to displace C TO D by the gravitational force is
(a)mgh(b)mgH (c)mg(H-h)(d) mg(h-H)
33. The work done to displace B TO C by the gravitational force is
(a)mgh(b)mgH (c) mg(H-h)(d) mg(h-H)
34. The work done to displace A TO B by the gravitational force is
(a)mgh(b)-mgh (c) mg(H-h)(d) mg(h-H)
Вам также может понравиться
- Work Done by Constant Force-MCQДокумент10 страницWork Done by Constant Force-MCQvishal_kalraОценок пока нет
- Work, Power, Energy-Practice ProblemДокумент18 страницWork, Power, Energy-Practice ProblemApex Institute0% (1)
- 07) Wpe 11 Aiims 24 Dec Answer KeyДокумент10 страниц07) Wpe 11 Aiims 24 Dec Answer Keyshaikhhafsa1802Оценок пока нет
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Work Power and Energy MCQs TestДокумент26 страницWork Power and Energy MCQs Testrizal123100% (1)
- Wpe ExerciseДокумент19 страницWpe ExerciseMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- DPP WpeДокумент6 страницDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedОценок пока нет
- WEP Exercise 1 To 3Документ20 страницWEP Exercise 1 To 3Rakesh Singh kushwahaОценок пока нет
- Wpe ComДокумент18 страницWpe ComShreyas AtreОценок пока нет
- Immin111 6007Документ4 страницыImmin111 6007Shreyas ShankerОценок пока нет
- Work, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Документ7 страницWork, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Abhimanyu BhasinОценок пока нет
- Part 02 Question (274 - 299)Документ30 страницPart 02 Question (274 - 299)RОценок пока нет
- Work Energy and Power: NEET QuestionsДокумент3 страницыWork Energy and Power: NEET QuestionsGanesh MogaveeraОценок пока нет
- MCQ CH 5 & 6Документ3 страницыMCQ CH 5 & 6Shaku JoshiОценок пока нет
- 5 - NLM Practice Assignment @JEEAdvanced - 2024Документ5 страниц5 - NLM Practice Assignment @JEEAdvanced - 2024Vineet SierraОценок пока нет
- Level-1: Laws of Motion + Kirchoff Laws Maximum Marks: 100Документ2 страницыLevel-1: Laws of Motion + Kirchoff Laws Maximum Marks: 100Sombir AhlawatОценок пока нет
- Diwali Assignment Enthuse JEE (M A)Документ73 страницыDiwali Assignment Enthuse JEE (M A)Harsh GuptaОценок пока нет
- 003 Newtons LawsДокумент5 страниц003 Newtons LawsRanjit KumarОценок пока нет
- 05 - Work, Energy and PowerДокумент6 страниц05 - Work, Energy and PowerAñîkët KãmãlОценок пока нет
- Phy PaperДокумент6 страницPhy PaperCrazy BrainОценок пока нет
- 1 Work Energy and PowerДокумент13 страниц1 Work Energy and PowerWilliam VaughnОценок пока нет
- CH 7 Questn (Updated)Документ1 страницаCH 7 Questn (Updated)raffia mahakОценок пока нет
- Engg Mech Unit 3Документ4 страницыEngg Mech Unit 3Piyush BhandariОценок пока нет
- Question Bank (S.C)Документ54 страницыQuestion Bank (S.C)Mohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- CLASS: 11 (PCM) : (Jee Main Mock Test)Документ11 страницCLASS: 11 (PCM) : (Jee Main Mock Test)Hirdesh Sehgal50% (2)
- MCQ CH 5 & 6Документ3 страницыMCQ CH 5 & 6Aadil ShakulОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Physics Chap 5 6Документ3 страницыWorksheet Physics Chap 5 6Aadil ShakulОценок пока нет
- Lows of MotionДокумент20 страницLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaОценок пока нет
- WPE AssignmentДокумент14 страницWPE AssignmentSuraj KumarОценок пока нет
- SMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Документ13 страницSMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Souseiseki ChromeОценок пока нет
- Work and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Документ13 страницWork and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Mansoor Al TunijiОценок пока нет
- IIT (M+A) & JEE MAINS ONLY - Diwali Assignment - XIIДокумент73 страницыIIT (M+A) & JEE MAINS ONLY - Diwali Assignment - XIIPremesh the greatОценок пока нет
- Physics Work Energy Power MCQДокумент6 страницPhysics Work Energy Power MCQMmonster GirirajОценок пока нет
- Impo. WpeДокумент24 страницыImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaОценок пока нет
- Problems Based On Centre of MassДокумент11 страницProblems Based On Centre of Massrgurvareddy100% (2)
- PC1431 Term Test 2012Документ10 страницPC1431 Term Test 2012MrshuaiОценок пока нет
- Module Mock Test - 2 (JEE Main)Документ11 страницModule Mock Test - 2 (JEE Main)ALI RIZVIОценок пока нет
- Newton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009Документ4 страницыNewton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009shiva ram prasad pulagamОценок пока нет
- Xii Neet Physics Question (Xi TH Full Portion) (1) (1) 4651.47530Документ8 страницXii Neet Physics Question (Xi TH Full Portion) (1) (1) 4651.47530vijiramraj786Оценок пока нет
- E8 QuestionsДокумент11 страницE8 Questionsmail2sgarg_841221144Оценок пока нет
- DPP - 20 (Work-Energy Theorem)Документ4 страницыDPP - 20 (Work-Energy Theorem)Peter JermayОценок пока нет
- (A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) IДокумент10 страниц(A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) Ikush jindalОценок пока нет
- Xi ND Phy NeetДокумент7 страницXi ND Phy NeetDeena chemistОценок пока нет
- AIEEE Work Energy and PowerДокумент4 страницыAIEEE Work Energy and PowerVansh SinghОценок пока нет
- Question 412291Документ8 страницQuestion 412291Nikhil PanigrahiОценок пока нет
- 17-09-23 Neet Ans.-1Документ6 страниц17-09-23 Neet Ans.-1yxfjmv862qОценок пока нет
- Review Questions: 3. The Cyclist Has A Mass of 50 KG and Is Accelerating at 0.9 M/sДокумент8 страницReview Questions: 3. The Cyclist Has A Mass of 50 KG and Is Accelerating at 0.9 M/sMohamedОценок пока нет
- Sheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Документ11 страницSheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Gaurav KumarОценок пока нет
- 15P08Q Circular Motion by Inu BansalДокумент9 страниц15P08Q Circular Motion by Inu BansalSaurabh LadОценок пока нет
- Shiv Nadar School Gurgaon Class 11 - Physics: Chapter Test - Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент3 страницыShiv Nadar School Gurgaon Class 11 - Physics: Chapter Test - Newton's Laws of MotionVarun SethОценок пока нет
- Laws of Motion and ForcesДокумент5 страницLaws of Motion and ForcesUJJVAL GAHOI100% (1)
- Laws of MotionДокумент5 страницLaws of MotionPakhi MauryaОценок пока нет
- Work Energy & Power - DPP 01 - DPP-01 - WPE - JEE Ultimate Crash CourseДокумент3 страницыWork Energy & Power - DPP 01 - DPP-01 - WPE - JEE Ultimate Crash CourseArnav AdarshОценок пока нет
- Phys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2Документ19 страницPhys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2SawarSagwalОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 FinalДокумент14 страницUnit 4 FinalmansikakaniОценок пока нет
- QP HYE 23 Physics FinalДокумент6 страницQP HYE 23 Physics Finalmrdevil1.2007Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet-5 ENERGY Answer KeyДокумент16 страницWorksheet-5 ENERGY Answer KeyAnas SaadОценок пока нет
- Centre of Mass QUESTIONДокумент12 страницCentre of Mass QUESTIONrgcsm88100% (1)
- Target: Pre-Medical 2014 Major Test # 04: Leader CourseДокумент3 страницыTarget: Pre-Medical 2014 Major Test # 04: Leader Coursergcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Sec M/ Sec M Sec M: (C) - MV (D)Документ2 страницыSec M/ Sec M Sec M: (C) - MV (D)rgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- City Home TuterДокумент1 страницаCity Home Tuterrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Code P Solution HindiДокумент50 страницCode P Solution Hindirgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Digital Gaiit Jeete en 1 NewДокумент4 страницыDigital Gaiit Jeete en 1 Newrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- IIT-JEE 2003 ScreeningДокумент32 страницыIIT-JEE 2003 Screeningrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Fluid Dynamics PDFДокумент11 страницFluid Dynamics PDFrgcsm88100% (1)
- Test Review Hindi WorkДокумент4 страницыTest Review Hindi Workrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Friction Test-2 WaДокумент3 страницыFriction Test-2 Wargcsm88Оценок пока нет
- PGDCA Syllabus 2005Документ9 страницPGDCA Syllabus 2005rgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- c1 Notes HindiДокумент1 страницаc1 Notes Hindirgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Force 2Документ7 страницForce 2rgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Physics Aieee AnalyisДокумент1 страницаPhysics Aieee Analyisrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Physics NotesДокумент1 страницаPhysics Notesrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент2 страницыThermodynamicsrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Mba1 Am Dec07Документ4 страницыMba1 Am Dec07rgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- Leadership Is Action, Not PositionДокумент59 страницLeadership Is Action, Not Positionrgcsm88Оценок пока нет
- 14 Partial Derivatives 2Документ23 страницы14 Partial Derivatives 2Thanh Thiên Phúc NguyễnОценок пока нет
- DPP 1 PhysicsДокумент3 страницыDPP 1 PhysicsSanjay Verma100% (1)
- Engenering Agriculture PerryДокумент423 страницыEngenering Agriculture PerryDaniel López100% (1)
- P-MECH312 - REMEDIALS RevisedДокумент18 страницP-MECH312 - REMEDIALS RevisedKelly SisonОценок пока нет
- Ch.3 Collisions PDFДокумент22 страницыCh.3 Collisions PDFClarence LimОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry ModuleДокумент367 страницGeneral Chemistry ModuleBirhaanu TolesaОценок пока нет
- N. N. Ghosh-Coaching at Home - Physics (For JEE-IIT and Other Entrance Examinations) (Lesson 1-12) - Bharati Bhawan (2003) PDFДокумент261 страницаN. N. Ghosh-Coaching at Home - Physics (For JEE-IIT and Other Entrance Examinations) (Lesson 1-12) - Bharati Bhawan (2003) PDFAmjith Khan.S71% (7)
- Mcq-Chp-1-Electrostatics Class 12Документ8 страницMcq-Chp-1-Electrostatics Class 12domahe7121100% (2)
- The Planck LengthДокумент1 страницаThe Planck LengthZárate Solano RodrigoОценок пока нет
- PHY10 ReviewerДокумент4 страницыPHY10 ReviewerAngelo Montelibano PatronОценок пока нет
- Galilean RelativityДокумент29 страницGalilean Relativitysamuel_okenyОценок пока нет
- Rotation Analysis of Rigid Diaphragm Based On 2018 IBC / 2019 CBCДокумент5 страницRotation Analysis of Rigid Diaphragm Based On 2018 IBC / 2019 CBCciptastrada japek selatanОценок пока нет
- Audels Engineers and Machinists Guide Vol1 PDFДокумент486 страницAudels Engineers and Machinists Guide Vol1 PDFloosenutОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Fluid Statics BuoyancyДокумент9 страницFluid Mechanics Fluid Statics BuoyancyJey MidayОценок пока нет
- Motion in A Straight Line: by Shahzada Khan (M.SC in Physics)Документ15 страницMotion in A Straight Line: by Shahzada Khan (M.SC in Physics)Vision Academy100% (1)
- PolynomialsДокумент10 страницPolynomialshoneyyadavОценок пока нет
- Bolaji Ojekunle - Collisions Lab - 4823034Документ3 страницыBolaji Ojekunle - Collisions Lab - 4823034John DoeОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE GRADE 6 - ST1-4 Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыSCIENCE GRADE 6 - ST1-4 Answer KeyJill Maguddayao100% (7)
- Lakhmir Singh Gravitation Solve Examples Class 9Документ35 страницLakhmir Singh Gravitation Solve Examples Class 9UDAI DASОценок пока нет
- Physics-As Level (Formulae & Relationships)Документ4 страницыPhysics-As Level (Formulae & Relationships)RAMAN KUMARОценок пока нет
- Problem # 1: Hint and AnswerДокумент10 страницProblem # 1: Hint and Answerpk2varmaОценок пока нет
- MCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetДокумент3 страницыMCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber0971% (7)
- Phys 12th Grade - Final - NOkeyДокумент3 страницыPhys 12th Grade - Final - NOkeyOliver VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Exam Style Answers 24 Asal Physics CBДокумент2 страницыExam Style Answers 24 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahОценок пока нет
- Lecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionДокумент55 страницLecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionRazan AlmuairfiОценок пока нет
- MA1506Документ70 страницMA1506ernie123219405Оценок пока нет
- 4.content - Electricity and MagnetismДокумент6 страниц4.content - Electricity and MagnetismbhavikОценок пока нет
- Section 4.6 Vertical Motion Under GravityДокумент26 страницSection 4.6 Vertical Motion Under Gravitytwy11350% (2)
- Physical ScienceДокумент468 страницPhysical Sciencesergiovelasquezg93% (15)
- Design LabДокумент76 страницDesign LabRajath AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceОт EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОт EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОценок пока нет
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (157)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishОт EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (410)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОценок пока нет
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceОт EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityОт EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (78)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionОт EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseОт EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeОт EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeОценок пока нет
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeОт EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)