Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Handout Endocrine System KEY
Загружено:
Edwin YanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Handout Endocrine System KEY
Загружено:
Edwin YanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
TABLE 1: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ORGANS
Structure
Location
Description/Function
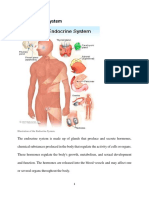
Endocrine System
Pineal Gland, Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland, Thyroid,
Parathyroids, Thymus, Pancreas, Adrenals, and Gonads
(Figure 28.1)
Ductless secretion - secretions (hormones) of the endocrine
system enter the interstitial fluid and then travel by blood
vessels.
Hormones
Synthesized in the organs and tissues of the endocrine
system (traditionally)
chemical messengers that are transported by the
bloodstream and stimulate physiological responses in cells
of another tissue or organ, often a considerable distance
away
Exocrine Glands
Throughout body
Glands that secrete material in tubules or ducts (such as
sweat and salivary glands) or directly to a surface (ovary).
Target Cells
Organs or tissues throughout the body
Areas receptive to hormones
Pineal Gland
Located in the mid-brain - attached to roof of third ventricle
beneath the posterior end of corpus callosum.
Fig. 28.1 - secretes melatonin
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
Located below the Hypothalamus in the sells turcica of the
sphenoid bone
Fig. 28.1 and 28.2 - divided into lobes
Anterior Lobe (adenohypophysis)
Originates from the roof of the oral cavity.
Produces TSH, GH, PRL, FSH, LH, and ACTH
Posterior Lobe (neurohypophysis)
Composed of nervous tissue from the base of the brain.
Hormones released from the posterior pituitary are
synthesized by the hypothalamus and flow through axons to
be stored in the posterior pituitary. Secretes ADH and
oxytocin
Infundibulum
Stalk attached to the hypothalamus from which the pituitary
gland is suspended
Thyroid Gland
Located in the anterior aspect of the neck, inferior to the
thyroid cartilage and superior to the trachea
Lateral lobes
Make up the thyroid gland along with the medial isthmus
Medial isthmus
Connects the two lateral lobes
Follicle Cells
In the Thyroid gland, follicle cells surround the colloid
Fig. 28.7 These cells absorb iodide ions for use in production
of thyroid hormones
Colloid
In the Thyroid gland, surrounded by follicle cells
Fig. 28.7 Storage region for thyroid hormones, primarily
thyroglobulin
Fig. 28.6 Has two lateral lobes and a medial isthmus that
connects the two lobes. Secretes Thyroxine (T4),
Triiodothyronine (T3), and Calcitonin
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
Parafollicular Cells
In the Thyroid gland, in the spaces between the follicles
Fig. 28.7 Secrete Calcitonin
Parathyroid Glands
Attached to the posterior portion of each of the lateral lobes
of the thyroid gland.
Fig. 28.8 typically two pairs of these gland, two attached to
the posterior of each of the lateral lobos of the thyroid.
Chief cells
In the Parathyroid gland
Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Thymus
Located anterior and superior to the heart
Fig. 28.9 Active in young individuals, plays an important part
in immunocompetency
Pancreas
Located between the stomach and small intestine
Fig. 28.1 and 28.10 Mixed gland - has both endocrine and
exocrine function.
Alpha cells
In the pancreas, occur in clusters called pancreatic islets
Fig. 28.10 Glucagon is produced in the these specialized
cells
Pancreatic islets
In the pancreas
Fig. 28.10 Produce insulin, also called islets of Langerhans
Beta Cells
In the pancreas, within the pancreatic islets
Fig. 28.10 Produce insulin, also called islets of Langerhans
Delta Cells
In the pancreas, within the pancreatic islets
Fig. 28.10 Secretes somatostatin
Adrenal Glands
Located superior to the kidneys
Fig. 28.11 Composed of an outer cortex and an inner
medulla
Outer Cortex
Outer part of the Adrenal Glands
Secretes corticosteroid hormones
Inner Medulla
Inner part of the Adrenal Glands
Zona Glomerulosa
Outermost layer of the Cortex of the Adrenal Gland
Fig. 28.12 Clusters of cells that secrete mineralocorticoids
(aldosterone)
Zona Fasciculata
Middle layer of the Cortex of the Adrenal Gland
Fig. 28.12 Consists of parallel bundles of cells that secrete
glucocorticoids (Cortisol/hydrocortisone)
Zona Reticularis
Innermost layer of the Cortex of the Adrenal Gland
Fig. 28.12 Consists of a branched pattern of cells that
produce both glucocorticoids and sex hormones
Testes
Male reproductive organ
Where spermatogenesis occurs, secrete testosterone and
inhibin, also has exocrine function
Seminiferous Tubules
Within the testes
Fig. 28.13 where meiosis occurs (spermatogenesis)
Interstitial Cells
Found between the seminiferous tubules of the testes
Fig. 28.13 produce testosterone
Ovaries
Female reproductive organ
Figure 28.14 Where oogenesis occurs, secretes estrogen
and progesterone, also has exocrine function
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
TABLE 2: HORMONES AND THIER EFFECTS
Organ
Hormones Produced
Effect of Hormones
Melatonin
hormone of darkness !
role not completely understood!
Implicated in Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)!
Stimulates production of sex cells!
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulates ovaries to produce other hormones
thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) (TSH)
Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Controls hormone production in the adrenal cortex
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulates mammary glands to begin the production of
milk
Growth Hormone (GH)
Promotes growth of most of the cells and tissues of the
body
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Stimulates the reabsorption and retention of water by the
kidneys
Oxytocin
Stimulates the contraction of the cells of the mammary
glands, resulting in the release of milk, and causes uterine
contractions.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
increases basal metabolic rate and ATP production
Thyroxine (T4)
the major form of the thyroid hormone, less active,
converted to T3
Calcitonin
Decreases blood calcium levels
Parathyroid Gland
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Increases calcium levels in the blood
Thymus
Thymosin
Causes maturation of T cells
Pancreas
Insulin
Decreases blood sugar levels by accelerating!
glucose uptake and glycogenesis
Glucagon
Converts glycogen to glucose
Pineal Gland
Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis)
Pituitary Gland (Neuropophysis)
Thyroid Gland (Colloid)
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
Somatostatin
Secreted after ingestion of a meal and inhibits the
secretion of insulin and glucagons
Adrenal Gland (cortex)
Corticosteroid Hormones
Regulate water and electrolyte balance in the body
Adrenal Gland (zona glomerulosa)
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Regulate water and electrolyte balance in the body
Adrenal Gland (zona fasciculata)
Glucocorticoids (cortisol/hydrocortisone)
Regulate protein and fat catabolism and gluconeogenesis
Adrenal Gland (zona reticularis)
Glucocorticoids (cortisol/hydrocortisone)
Regulate protein and fat catabolism and gluconeogenesis
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
Secreted by the Adrenal glands and converted into
estrogen or testosterone in other tissues
Epinephrine
Increase heart rate and prepares the body for fight or
flight reactions
Norepinephrine
Increase heart rate and prepares the body for fight or
flight reactions
Testosterone
Responsible for development of male secondary sex
characteristics
Inhibin
Regulates production of testosterone
Estrogen
Responsible for development of female secondary sex
characteristics
Progesterone
Responsible for development of female secondary sex
characteristics
Inhibin
Regulates production of estrogen and progesterone
Adrenal Gland (Medulla)
Testes
Ovaries
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
1. What is the general name for the types of organs that produce hormones?!
Ans: The general name for organs that produce hormones are endocrine glands. !
2. What name is given to cells or tissues receptive to hormones?!
Ans: Regions that are receptive to hormones are called target areas (target cells). !
3. Melatonin is secreted by what gland?!
Ans: Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland. !
4. Where is ADH stored?!
Ans: The hormone ADH is produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. !
5. What is the effect of TSH, and where is it produced?!
Ans: TSH is an anterior pituitary hormone and it stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). !
6. What connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland?!
Ans: The isthmus connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland.!
7. Does parathormone increase or decrease calcium levels in the blood?!
Ans: Parathormone increases calcium levels in the blood. !
8. What does glucagon do as a hormone, and where is it produced?!
Ans: Glucagon increases blood sugar levels by converting glycogen to glucose and it is found in the pancreatic islets. !
9. Which hormones in the adrenal gland control water and electrolyte balance?!
Ans: Corticosteroid hormones in the adrenal gland control water and electrolyte balance. !
10. What is the primary gland that secretes epinephrine?!
Ans: The primary gland that secretes epinephrine is the medulla of the adrenal gland. !
11. Where is growth hormone produced?!
Ans: Growth hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary !
12. What is another name for T3?!
Ans: Another name for T3 is triiodothyronine. !
13. Label the endocrine glands indicated in the following illustration. !
Ans:!
a. pineal gland!
b. hypothalamus!
c. pituitary gland !
CBIO 2210L - Endocrine System Key
d. thyroid gland!
e. thymus!
f. adrenal gland!
g. pancreas!
h. parathyroid gland! !
i. ovaries!
j. testes!
!
!
14.!
Identify the parts of the pituitary as seen in the following illustration and label two hormones located in each.!
Ans: a. (anterior pituitary - any two of the following)!
growth hormone!
!
!
luteinizing hormone! !
!
thyroid stimulating hormone! !
follicle stimulating hormone!
prolactin!
!
!
!
adrenocorticotropin !
b. posterior pituitary! !
1. oxytocin! !
!
2. antidiuretic hormone!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
15.!
Identify the three layers of the adrenal cortex as illustrated and list the hormones produced by each layer.!
Ans: !
a. zona reticularis!
!
glucocorticoids & sex hormones!
b. zona fasciculata! !
glucocorticoids!
c. zona glomerulosa! !
mineralocorticoids!
!
!
16.!
Interstitial cells produce which hormone?!
Ans: Testosterone!
17. What structures are responsible for the production of estrogen?!
Ans: The ovaries are responsible for producing estrogen.
Вам также может понравиться
- Lesson 7 - Nervous, Endocrine, Reproductive, Urinary SystemДокумент37 страницLesson 7 - Nervous, Endocrine, Reproductive, Urinary SystemAlejandro GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Review of Endocrine SystemДокумент32 страницыReview of Endocrine SystemJames FОценок пока нет
- CNS RosettesДокумент5 страницCNS RosettesSick DuckОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System Study GuideДокумент5 страницEndocrine System Study GuideClaudia SanchezОценок пока нет
- Study Guide QuestionsДокумент4 страницыStudy Guide QuestionszaidaОценок пока нет
- Chapter25 Urinary SystemДокумент9 страницChapter25 Urinary Systemkikajet23Оценок пока нет
- Diencephalon-Ppt For BioДокумент7 страницDiencephalon-Ppt For BioLipi UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Nonvisual Photoreceptors of The PinealДокумент36 страницNonvisual Photoreceptors of The Pinealrambo_style19Оценок пока нет
- Endocrine System 2017Документ28 страницEndocrine System 2017cyber sec100% (1)
- Comparative Analysis Reveals The Underlying Mechanism of Vertebrate Seasonal ReproductionДокумент5 страницComparative Analysis Reveals The Underlying Mechanism of Vertebrate Seasonal ReproductionJosiana Gonçalves RibeiroОценок пока нет
- The Human Body A Nutrition PerspectiveДокумент50 страницThe Human Body A Nutrition PerspectiveRichard GelmanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParДокумент64 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson FrankОценок пока нет
- 5-17 Endocrine HandoutДокумент10 страниц5-17 Endocrine HandoutJohn Lawrence YbanezОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System NotesДокумент8 страницEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoОценок пока нет
- Nervous SYSTESTДокумент19 страницNervous SYSTESTedwalk1250% (2)
- S07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainДокумент40 страницS07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainRobert MartinОценок пока нет
- The Human Nervous Syste1Документ10 страницThe Human Nervous Syste1taytay321Оценок пока нет
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletДокумент5 страницEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionДокумент62 страницыPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionWilliam C Chisha100% (1)
- 21 - Peripheral Nervous SystemДокумент16 страниц21 - Peripheral Nervous Systembhavikrao7605Оценок пока нет
- Comparative Account of Brain in Vertebrates Dr. Younus Ah PDFДокумент14 страницComparative Account of Brain in Vertebrates Dr. Younus Ah PDFIsmart PraveenОценок пока нет
- Of Time and The MindДокумент18 страницOf Time and The MindAntonio LanotОценок пока нет
- Lect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54Документ74 страницыLect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54nopporn2520Оценок пока нет
- Nervous SYSTEM: by Animal Physiology StaffДокумент37 страницNervous SYSTEM: by Animal Physiology StaffSyifarhОценок пока нет
- Ncert Biology Chapter 22Документ13 страницNcert Biology Chapter 22sai arunОценок пока нет
- Principia DiscordiaДокумент85 страницPrincipia DiscordiaAbraham OgdenОценок пока нет
- Review 4 Chap 12-16Документ21 страницаReview 4 Chap 12-16j_docsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 28 The Reproductive SystemДокумент40 страницChapter 28 The Reproductive SystemRushaida AminullaОценок пока нет
- فسلجة الحيوان PDFДокумент9 страницفسلجة الحيوان PDFelhamОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент6 страницEndocrine SystemChechan AmbaОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент22 страницыNervous SystemAltaf Hussain Khan50% (2)
- The Peripheral Nervous SystemДокумент80 страницThe Peripheral Nervous SystemDanitra B AlexanderОценок пока нет
- List of Organs of The Human BodyДокумент10 страницList of Organs of The Human BodyAdeniyi AleseОценок пока нет
- RenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Документ49 страницRenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhОценок пока нет
- Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemДокумент33 страницыDrugs Acting On The Immune SystemAnonymous iG0DCOf100% (1)
- Endocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology DictionaryДокумент7 страницEndocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionaryrania khanОценок пока нет
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationДокумент3 страницыCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUОценок пока нет
- Autonomic Nervous SystemДокумент16 страницAutonomic Nervous SystemmogibsfОценок пока нет
- Lab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemДокумент7 страницLab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemJohn Louis AguilaОценок пока нет
- New Study - Reproduction and Electromagnetic Field ExposureДокумент9 страницNew Study - Reproduction and Electromagnetic Field ExposureEMFsafetyОценок пока нет
- Chap OutlineДокумент8 страницChap OutlinedurrieОценок пока нет
- Histo - Pituitary GlandДокумент22 страницыHisto - Pituitary GlandRessam Nazir100% (1)
- Nervous SystemДокумент26 страницNervous Systemhanimunch0% (1)
- The Endocrine System Study GuideДокумент4 страницыThe Endocrine System Study Guideapi-2776680980% (1)
- Illustration of The Endocrine SystemДокумент7 страницIllustration of The Endocrine SystemMohammed MohammedОценок пока нет
- Unit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisДокумент16 страницUnit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisaclumutОценок пока нет
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandДокумент39 страницHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandGish KioiОценок пока нет
- General Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyДокумент4 страницыGeneral Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyChristine Rose EmОценок пока нет
- Human Physiology: The Nervous SystemДокумент29 страницHuman Physiology: The Nervous Systemzandrex delunaОценок пока нет
- Classification of Endocrine GlandsДокумент3 страницыClassification of Endocrine GlandsReine100% (1)
- Endocrine System Workbook 2015Документ8 страницEndocrine System Workbook 2015api-298277560100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics Theory and Applications PDFДокумент22 страницыQuantum Mechanics Theory and Applications PDFVladimir AnticapitalistkiОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент30 страницNervous SystemkenОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент21 страницаEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutОценок пока нет
- Urinary SystemДокумент7 страницUrinary SystemShelley CobbОценок пока нет
- Clinton Hackney Anatomy & Physiology II BctcsДокумент65 страницClinton Hackney Anatomy & Physiology II BctcsJack HolthouseОценок пока нет
- Functional Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент38 страницFunctional Anatomy and PhysiologyNawalОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisДокумент38 страницIntroduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisAnanta Subedi100% (1)
- The Endocrine System-JULYДокумент40 страницThe Endocrine System-JULYKELVINОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент19 страницEndocrine Systemethel roseОценок пока нет
- Uses of Isotopes in Our Daily LivesДокумент3 страницыUses of Isotopes in Our Daily LivesVibhor Mathur70% (10)
- Diare Pada BalitaДокумент10 страницDiare Pada BalitaYudha ArnandaОценок пока нет
- Relationship of Chronic Disease With Psychososial Problems in Patients in Gunung Jati Hospital CirebonДокумент7 страницRelationship of Chronic Disease With Psychososial Problems in Patients in Gunung Jati Hospital CirebonSitti AuraОценок пока нет
- Masha Sardari Nutrition ResumeДокумент2 страницыMasha Sardari Nutrition Resumeapi-428097674Оценок пока нет
- Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy: Original ArticleДокумент7 страницJournal of Infection and Chemotherapy: Original ArticleNoNWOОценок пока нет
- Dorothy Johnson PosterДокумент1 страницаDorothy Johnson Posterapi-519455077Оценок пока нет
- Aira Noreen Leyva - Resume ReviewДокумент2 страницыAira Noreen Leyva - Resume Reviewapi-447475293Оценок пока нет
- 1.causes For Neonatal Sepsis, Newborn Sepsis, Neonatal Infection, Sepsis TreatmentДокумент12 страниц1.causes For Neonatal Sepsis, Newborn Sepsis, Neonatal Infection, Sepsis TreatmentlardiyahОценок пока нет
- Conflict or Consensus - An Investigation of Stakeholder Concerns DuringДокумент10 страницConflict or Consensus - An Investigation of Stakeholder Concerns DuringhohoexeОценок пока нет
- MDWF 1030 Carter Plugged Duct Mastitis Abscess PGДокумент5 страницMDWF 1030 Carter Plugged Duct Mastitis Abscess PGapi-366292665Оценок пока нет
- Magnetis Polus AmboДокумент4 страницыMagnetis Polus Amboadi.mititean1585Оценок пока нет
- Penlon Absorbedor A200Документ68 страницPenlon Absorbedor A200Manuel FloresОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Nursing - Nurse As ProfessionДокумент7 страницFundamentals of Nursing - Nurse As ProfessionDarryl C. LocañasОценок пока нет
- New Trends in Mechanical VentilationДокумент4 страницыNew Trends in Mechanical Ventilationashley_castro_4Оценок пока нет
- MMG 301 Study Guide For Exam 1Документ14 страницMMG 301 Study Guide For Exam 1Juyeon CheongОценок пока нет
- Contingency PlansДокумент8 страницContingency PlansNoel GalangОценок пока нет
- Microbiology-Disinfectants Lab ReportДокумент2 страницыMicrobiology-Disinfectants Lab Reportsaraebo25% (4)
- 12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistДокумент8 страниц12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistShrey BadrukaОценок пока нет
- Photovoice Paper HLTH 102Документ7 страницPhotovoice Paper HLTH 102api-625678417Оценок пока нет
- 1391 Budget Sent To Parliament - April 10 2012 - CPДокумент79 страниц1391 Budget Sent To Parliament - April 10 2012 - CPJW4688173Оценок пока нет
- Offshore Risk Management - Security Assessment For Offshore Oil PDFДокумент26 страницOffshore Risk Management - Security Assessment For Offshore Oil PDFlightangeldavidОценок пока нет
- Soal Bahasa InggrisДокумент2 страницыSoal Bahasa Inggrisana fauziahОценок пока нет
- Analisis Keberhasilan Implementasi RME Mutu PelayananДокумент8 страницAnalisis Keberhasilan Implementasi RME Mutu PelayananWinda PurbaОценок пока нет
- Practise-Book Reading Set1Документ4 страницыPractise-Book Reading Set1Ketheesaran Lingam100% (1)
- GP 9.7 Brochure 6 5 20 PDFДокумент16 страницGP 9.7 Brochure 6 5 20 PDFDaisy FloresОценок пока нет
- Brand Management of PatanjaliДокумент22 страницыBrand Management of PatanjaliDarshan GohilОценок пока нет
- BP HSE Action PLanДокумент6 страницBP HSE Action PLanbesongОценок пока нет
- Caroline O'Mahony Caroline's Fit PlanДокумент30 страницCaroline O'Mahony Caroline's Fit PlanGizem MutluОценок пока нет
- The Danger of Microwave TechnologyДокумент16 страницThe Danger of Microwave Technologyrey_hadesОценок пока нет
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1Документ10 страницPostpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1erikafebriyanarОценок пока нет