Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ortfolio Oncepts: Variance of 2-Asset Portfolio
Загружено:
ankitahandaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ortfolio Oncepts: Variance of 2-Asset Portfolio
Загружено:
ankitahandaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
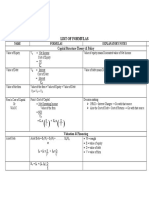
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
Expected return on Two-Asset Portfolio
E(RP) = w1E(R1) + w2E(R2)
E(R1) = expected return on Asset 1
E(R2) = expected return on Asset 2
w1 = weight of Asset 1 in the portfolio
w2 = weight of Asset 2 in the portfolio
Variance of 2-asset portfolio:
s2P = w12s21 + w22s22 + 2w1w2r1, 2s1s2
s1= the standard deviation of return on Asset 1
s2= the standard deviation of return on Asset 2
r1, 2= the correlation between the two assets returns
Variance of 2-asset portfolio:
sP2 = w12s21 + w22s22 + 2w1w2Cov1,2
Cov1,2 = r1, 2s1s2
Expected Return and Standard Deviation for a Three-Asset Portfolio
Expected return on 3-asset portfolio:
E(RP) = w1E(R1) + w2E(R2) + w3E(R3)
Variance of 3-asset portfolio:
sP2 = w12s12 + w22s22 + w32s23 + 2w1w2r1, 2s1s2 + 2w1w3r1, 3s1s3 + 2w2w3r2, 3s2s3
Variance of 3-asset portfolio:
sP2 = w12s12 + w22s22 + w32s23 + 2w1w2Cov1, 2 + 2w1w3Cov1, 3 + 2w2w3Cov2, 3
2014 ELAN GUIDES
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
Expected Return and Variance of the Portfolio
For a portfolio of n assets, the expected return on the portfolio is calculated as:
n
E(RP) =
S w E(R )
j=1
The variance of the portfolio is calculated as:
s2P =
i=1
j=1
S S w w Cov(R ,R )
i
Variance of an Equally-weighted Portfolio
sP2 =
1 2 n-1
s +
Cov
n
n
s2P = s2
1-r
n
+r
Expected Return for a Portfolio Containing a Risky Asset and the Risk-Free Asset
E(RP) = RFR + sP
[E(Ri) - RFR]
si
Standard Deviation of a Portfolio Containing a Risky Asset and the Risk-Free Asset
sP = wisi
2014 ELAN GUIDES
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
CML
Expected return on portfolios that lie on CML:
E(RP) = w1Rf + (1 - w1)E(Rm)
Variance of portfolios that lie on CML:
s2 = w12sf2 + (1 - w1)2sm2 + 2w1(1 - w1)Cov(Rf , Rm)
Equation of CML:
E(RP) = Rf +
E(Rm) - Rf
sP
sm
Calculation and Interpretation of Beta
bi =
Cov(Ri,Rm)
sm2
ri,msi,sm
sm2
ri,msi
sm
The Capital Asset Pricing Model
E(Ri) = Rf + bi[E(Rm) Rf ]
The Decision to Add an Investment to an Existing Portfolio
E(Rnew) - RF
E(Rp) - RF
>
Corr(Rnew,Rp)
sp
snew
Market Model Estimates
Ri = ai + bi RM + ei
Ri = Return on asset i
RM = Return on the market portfolio
ai = Average return on asset i unrelated to the market return
bi = Sensitivity of the return on asset i to the return on the market portfolio
ei = An error term
bi is the slope in the market model. It represents the increase in the return on asset i if
the market return increases by one percentage point.
ai is the intercept term. It represents the predicted return on asset i if the return on the
market equals 0.
Expected return on asset i
E(Ri) = ai + biE(RM)
2014 ELAN GUIDES
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
Variance of the return on asset i
2
Var(Ri) = b2i sM
+ se2i
Covariance of the returns on asset i and asset j
Cov(Ri,Rj) = bibjs2
Correlation of returns between assets i and j
Corr(Ri,Rj) =
2
bibjsM
2
2
(b2i sM
+ se2i )1/2 (b2j sM
+ se2j )1/2
Market Model Estimates: Adjusted Beta
Adjusted beta = 0.333 + 0.667 (Historical beta)
Macroeconomic Factor Models
Ri = ai + bi1FINT + bi2FGDP + ei
Ri = the return to stock i
ai = the expected return to stock i
FINT = the surprise in interest rates
FGDP = the surprise in GDP growth
bi1 = the sensitivity of the return on stock i to surprises in interest rates.
bi2 = the sensitivity of the return on stock i to surprises in GDP growth.
ei = an error term with a zero mean that represents the portion of the return to stock i
that is not explained by the factor model.
Fundamental Factor Models
Ri = ai + bi1FDY + bi2FPE + ei
Ri = the return to stock i
ai = intercept
FDY = return associated with the dividend yield factor
FPE = return associated with the P-E factor
bi1 = the sensitivity of the return on stock i to the dividend yield factor.
bi2 = the sensitivity of the return on stock i to the P-E factor.
ei = an error term
Standardized sensitivities are computed as follows:
bij =
Assets is attribute value - Average attribute value
s(Attribute values)
2014 ELAN GUIDES
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
Arbitrage Pricing Theory and the Factor Model
E(RP) = RF + l1bp,1 + ... + lKbp,K
E(Rp) = Expected return on the portfolio p
RF = Risk-free rate
l j = Risk premium for factor j
bp,j = Sensitivity of the portfolio to factor j
K = Number of factors
Active Risk
TE = s(Rp - RB)
Active risk squared = s2(Rp - RB)
Active risk squared = Active factor risk + Active specific risk
n
Active specific risk =
Sw s
i=1
a 2
i ei
Where:
wia= The ith assets active weight in the portfolio (i.e., the difference between the assets weight
in the portfolio and its weight in the benchmark).
se2 = The residual risk of the ith asset (i.e., the variance of the ith assets returns that is not explained
i
by the factors).
Active factor risk = Active risk squared Active specific risk.
Active Return
Active return = Rp RB
Active return = Return from fctor tilts + Return from asset selection
K
Active return =
S[(Portfolio sensitivity) - (Benchmark sensitivity) ] (Factor return) + Asset selection
j=1
2014 ELAN GUIDES
PORTFOLIO CONCEPTS
Factors Marginal Contribution to Active Risk Squared (FMCAR)
K
baj
FMCARj =
FMCARj =
S b Cov(F ,F )
i=1
a
i
Active risk squared
Active factor risk
Active risk squared
where:
baj = The portfolios active exposure to factor j
K
baj
S b Cov(F ,F ) = The active factor risk for factor j
i=1
a
i
The Information Ratio
IR =
Rp - RB
s(Rp - RB)
2014 ELAN GUIDES
THE PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND THE INVESTMENT POLICY STATEMENT
THE PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND THE INVESTMENT POLICY
STATEMENT
Risk Tolerance
Willingness to Take Risk
Below Average
Above Average
Ability to Take Risk
Above Average
Below Average
Resolution needed
Below-average risk tolerance
Above-average risk tolerance
Resolution needed
Return Requirements and Risk Tolerances of Various Investors
Type of Investor
Return Requirement
Risk Tolerance
Individual
Depends on stage of life,
circumstances, and obligations
Varies
Pension Plans (Defined
Benefit)
The return that will adequately
fund liabilities on an inflationadjusted basis
Depends on plan and
sponsor characteristics,
plan features, funding status,
and workforce characteristics
Pension Plans (Defined
Contribution)
Depends on stage of life of
individual participants
Varies with the risk
tolerance of individual
participants
Foundations and
Endowments
The return that will cover
annual spending, investment
expenses, and expected inflation
Determined by amount of
assets relative to needs, but
generally above- average
or average
Life Insurance
Companies
Determined by rates used to
determine policyholder reserves
Below average due to factors
such as regulatory constraints
Non-Life- Insurance
Companies
Determined by the need to price
policies competitively and by
financial needs
Below average due to factors
such as regulatory constraints
Banks
Determined by cost of funds
Varies
2014 ELAN GUIDES
Вам также может понравиться
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionОт EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- CFA Level I Formula SheetДокумент27 страницCFA Level I Formula SheetAnonymous P1xUTHstHT100% (4)
- Capital Allocation Between The Risky and The Risk-Free AssetДокумент20 страницCapital Allocation Between The Risky and The Risk-Free AssetlecturerОценок пока нет
- Ch12 ArbitrageДокумент18 страницCh12 Arbitragejence85Оценок пока нет
- Minggu 2-4: Analisis Investasi & PortopolioДокумент34 страницыMinggu 2-4: Analisis Investasi & PortopolioFANNY KRISTIANTIОценок пока нет
- MBA 643 - NotesДокумент1 страницаMBA 643 - NotesSandeepОценок пока нет
- Portfolio Theory PresentationДокумент50 страницPortfolio Theory PresentationAkshatОценок пока нет
- MGT201 Assignment SolutionДокумент3 страницыMGT201 Assignment SolutionMuhammad Najeebullah KhanОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetДокумент4 страницыCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- Exam Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыExam Formula SheetYeji KimОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheets-GDBA505 – must be returned after exam < 40Документ3 страницыFormula Sheets-GDBA505 – must be returned after exam < 40FLOREAROMEOОценок пока нет
- Chapter-10 Return & RiskДокумент19 страницChapter-10 Return & Riskaparajita promaОценок пока нет
- Formula For Financial Market TheoryДокумент6 страницFormula For Financial Market TheoryHansОценок пока нет
- Portifolio Theory & Asset Pricing ModelsДокумент39 страницPortifolio Theory & Asset Pricing ModelszivainyaudeОценок пока нет
- CMU Portfolio Risk and Return AnalysisДокумент18 страницCMU Portfolio Risk and Return AnalysisHugo PagolaОценок пока нет
- Risk and ReturnДокумент52 страницыRisk and ReturnSrinivas NuluОценок пока нет
- Important financial formulasДокумент5 страницImportant financial formulasKhalil AkramОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Portfolio TheoryДокумент44 страницыChapter 7 Portfolio Theorysharktale2828100% (1)
- Fin All Formula - Docx 1Документ9 страницFin All Formula - Docx 1Marcus HollowayОценок пока нет
- Risk and Return: Understanding the RelationshipДокумент54 страницыRisk and Return: Understanding the RelationshipMega capitalmarket100% (1)
- Portfolio Theory: Risk, Return and Efficient FrontierДокумент71 страницаPortfolio Theory: Risk, Return and Efficient FrontierCEA130089 StudentОценок пока нет
- Finance NoteДокумент19 страницFinance NoteHui YiОценок пока нет
- Financial Management FormulasДокумент5 страницFinancial Management Formulasrera zeoОценок пока нет
- Portfolio Math CFA ReviewДокумент3 страницыPortfolio Math CFA ReviewDionizioОценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыFormula SheetEdithОценок пока нет
- Alternative View of Risk and Return: Arbitrage Pricing TheoryДокумент50 страницAlternative View of Risk and Return: Arbitrage Pricing TheoryANKIT AGARWALОценок пока нет
- Foundations of Finance MidtermДокумент2 страницыFoundations of Finance MidtermVamsee JastiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10: Risk-Return and Asset Pricing ModelsДокумент22 страницыChapter 10: Risk-Return and Asset Pricing Modelstjarnob13Оценок пока нет
- CH 02Документ48 страницCH 02Harsh DhawanОценок пока нет
- Risk and Return: The Basics: Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsДокумент4 страницыRisk and Return: The Basics: Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsFatikchhari USOОценок пока нет
- FORMULASДокумент5 страницFORMULASNurul AsyiqinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ61 страницаChapter 2Meseret HailemichaelОценок пока нет
- Session 9-02-07-2020 Portfolio Return and Risk: Arithmetic Versus Geometric AveragesДокумент7 страницSession 9-02-07-2020 Portfolio Return and Risk: Arithmetic Versus Geometric AveragesVineetha Chowdary Gude100% (1)
- Risk and Return: Past and PrologueДокумент39 страницRisk and Return: Past and ProloguerrОценок пока нет
- EMBA Chapter5Документ38 страницEMBA Chapter5Mehrab RehmanОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Portfolio Theory: The Benefits of DiversificationДокумент13 страницUnit 2 Portfolio Theory: The Benefits of DiversificationHarshk JainОценок пока нет
- List of Corporate Finance FormulasДокумент9 страницList of Corporate Finance FormulasYoungRedОценок пока нет
- International Portfolio DiversificationДокумент34 страницыInternational Portfolio DiversificationGaurav KumarОценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент7 страницFormula SheetAbraham RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Risk & Return: Risk of A Portfolio-Uncertainty Main View Two AspectsДокумент36 страницRisk & Return: Risk of A Portfolio-Uncertainty Main View Two AspectsAminul Islam AmuОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Portfolio ManagementДокумент2 страницыIntroduction To Portfolio ManagementKatieYoungОценок пока нет
- FM FormulasДокумент9 страницFM FormulasrafishogunОценок пока нет
- 10 Risk and Return - Student VersionДокумент59 страниц10 Risk and Return - Student VersionKalyani GogoiОценок пока нет
- Formula For Financial Market Theory AMENDEDДокумент7 страницFormula For Financial Market Theory AMENDEDHansОценок пока нет
- Formulas and ConceptsДокумент7 страницFormulas and Conceptscolen.anneОценок пока нет
- Presentation 04 - Risk and Return 2012.11.15Документ54 страницыPresentation 04 - Risk and Return 2012.11.15SantaAgataОценок пока нет
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceДокумент6 страницFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemОценок пока нет
- Financial Statement Analysis RatiosДокумент4 страницыFinancial Statement Analysis RatiosSumeet DekateОценок пока нет
- Formulas For Chapter 8Документ2 страницыFormulas For Chapter 8RaaОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet FIMДокумент4 страницыFormula Sheet FIMYОценок пока нет
- R) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVДокумент9 страницR) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVAgnes LoОценок пока нет
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetДокумент9 страницCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Portfolio TheoryДокумент41 страницаChapter 7 Portfolio TheoryRupesh DhindeОценок пока нет
- Capm and AptДокумент10 страницCapm and AptRajkumar35Оценок пока нет
- Calculate fair share price using dividend discount modelДокумент9 страницCalculate fair share price using dividend discount modelTannao100% (1)
- Risk and Return Theories ExplainedДокумент24 страницыRisk and Return Theories ExplainedMarselinus Aditya Hartanto TjungadiОценок пока нет
- Capital Market Theory: An OverviewДокумент41 страницаCapital Market Theory: An OverviewAmjad IqbalОценок пока нет
- Equations From DamodaranДокумент6 страницEquations From DamodaranhimaggОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionОт EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Business Writing - SCQAДокумент6 страницBusiness Writing - SCQAankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Tricks - Read MeДокумент5 страницTricks - Read MeankitahandaОценок пока нет
- 2 Mechanized Grain Handling and Storage Unit at PortДокумент16 страниц2 Mechanized Grain Handling and Storage Unit at PortankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Idiom List PDFДокумент1 страницаIdiom List PDFankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Aristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeДокумент30 страницAristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeKrishnendu GhoshОценок пока нет
- File 372 PDFДокумент1 240 страницFile 372 PDFAkula VeerrajuОценок пока нет
- 15 BeingДокумент7 страниц15 BeingMayank PareekОценок пока нет
- GMAT Quant Topic 1 (General Arithmetic) SolutionsДокумент120 страницGMAT Quant Topic 1 (General Arithmetic) SolutionsAyush PorwalОценок пока нет
- Statement of PurposeДокумент17 страницStatement of PurposestanayОценок пока нет
- GMAT Quant Topic 7 - P and C SolДокумент14 страницGMAT Quant Topic 7 - P and C SolPrasanna IyerОценок пока нет
- GMAT Flashcards v7 PDFДокумент120 страницGMAT Flashcards v7 PDFVidit GuptaОценок пока нет
- AdaniДокумент14 страницAdaniankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Cost StatementДокумент24 страницыCost StatementankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Tamil NaduДокумент6 страницTamil NaduankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Indian Logistics Industry Gaining The TractionДокумент8 страницIndian Logistics Industry Gaining The TractionankitahandaОценок пока нет
- When Supply is of Public Interest: Roche and Tamiflu Case StudyДокумент16 страницWhen Supply is of Public Interest: Roche and Tamiflu Case StudyankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Popcorn JudgementДокумент2 страницыAnalysis of Popcorn JudgementankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Mgt. AccountingДокумент2 страницыMgt. AccountingankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Excel Sheet AIFS HWДокумент6 страницExcel Sheet AIFS HWankitahanda25% (4)
- Cost SheetДокумент6 страницCost SheetAishwary Sakalle100% (1)
- Cet121160515 PDFДокумент274 страницыCet121160515 PDFankitahandaОценок пока нет
- 8.introduction To Management AccountingДокумент10 страниц8.introduction To Management AccountingeddamartОценок пока нет
- CLAT 2014 UG Merit ListДокумент396 страницCLAT 2014 UG Merit ListBar & BenchОценок пока нет
- Hedging Currency RisksДокумент3 страницыHedging Currency RisksankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Abs MBSДокумент1 страницаAbs MBSankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Globalizing Cost of Capital at AESДокумент3 страницыGlobalizing Cost of Capital at AESArpita Gupta100% (1)
- Foreign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General MotorsДокумент6 страницForeign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General MotorsLarry Holmes100% (5)
- QuesДокумент2 страницыQuesankitahandaОценок пока нет
- 2M M Case StudyДокумент4 страницы2M M Case StudyankitahandaОценок пока нет
- Petroleum GeomechanicsДокумент35 страницPetroleum GeomechanicsAnonymous y6UMzakPW100% (1)
- 2 Fourier and Wavelet Transforms: 2.1. Time and Frequency Representation of SignalsДокумент25 страниц2 Fourier and Wavelet Transforms: 2.1. Time and Frequency Representation of SignalszvjpОценок пока нет
- Formation and Evolution of Planetary SystemsДокумент25 страницFormation and Evolution of Planetary SystemsLovelyn Baltonado100% (2)
- Non-Performing Assets: A Comparative Study Ofsbi&Icici Bank From 2014-2017Документ8 страницNon-Performing Assets: A Comparative Study Ofsbi&Icici Bank From 2014-2017Shubham RautОценок пока нет
- State-Of-The-Art CFB Technology For Utility-Scale Biomass Power PlantsДокумент10 страницState-Of-The-Art CFB Technology For Utility-Scale Biomass Power PlantsIrfan OmercausevicОценок пока нет
- Grundfosliterature 5439390Документ108 страницGrundfosliterature 5439390ptlОценок пока нет
- Digital Techniques/Electronic Instrument SystemsДокумент29 страницDigital Techniques/Electronic Instrument SystemsE DОценок пока нет
- Sky Telescope 201304Документ90 страницSky Telescope 201304Haydn BassarathОценок пока нет
- A-019730-1647416754604-137865-W.M.Supun Anjana DSAДокумент175 страницA-019730-1647416754604-137865-W.M.Supun Anjana DSADishan SanjayaОценок пока нет
- Subsurface Remote Sensing of Kelp ForestsДокумент20 страницSubsurface Remote Sensing of Kelp Forestsjpeterson1Оценок пока нет
- Celda Carga - KIS-2BA - 5KNДокумент4 страницыCelda Carga - KIS-2BA - 5KNJosé TimanáОценок пока нет
- Pipe Flow Expert BrochureДокумент2 страницыPipe Flow Expert BrochurecristinelbОценок пока нет
- Cube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning IntroductionДокумент6 страницCube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning Introductionmirali74Оценок пока нет
- Queue PPTДокумент19 страницQueue PPTharshvardhanshinde.2504Оценок пока нет
- Astm E1588.1207649 GSRДокумент5 страницAstm E1588.1207649 GSRjoao carlos100% (1)
- MP Lab3Документ4 страницыMP Lab3kawish420Оценок пока нет
- Discussion Exp 2 Chm674Документ4 страницыDiscussion Exp 2 Chm674Eva Lizwina MatinОценок пока нет
- Report Navigation Prashanth RamadossДокумент1 страницаReport Navigation Prashanth RamadossaustinvishalОценок пока нет
- User's Manual: Electrolyte AnalyzerДокумент25 страницUser's Manual: Electrolyte AnalyzerNghi NguyenОценок пока нет
- 14GMK 6250 TelescopeДокумент13 страниц14GMK 6250 TelescopeВиталий РогожинскийОценок пока нет
- Sumitomo Catalog1Документ17 страницSumitomo Catalog1metalartbielskoОценок пока нет
- Mapping Abap XML PDFДокумент88 страницMapping Abap XML PDFassane2mcsОценок пока нет
- Image ReconstructionДокумент28 страницImage ReconstructionRahul PaulОценок пока нет
- EO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityДокумент62 страницыEO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityZahir KhiraОценок пока нет
- Indigenous Microorganisms Production and The Effect On Composting ProcessДокумент5 страницIndigenous Microorganisms Production and The Effect On Composting ProcessAldrin Baquilid FernandezОценок пока нет
- Manriding Tirfor O-MДокумент16 страницManriding Tirfor O-MPhillip FrencilloОценок пока нет
- Biophoton Light TherapyДокумент1 страницаBiophoton Light TherapyVíctor ValdezОценок пока нет
- Cadillac: Operator'S ManualДокумент63 страницыCadillac: Operator'S ManualRaj jainОценок пока нет
- Perfect Fourths GuitarДокумент8 страницPerfect Fourths Guitarmetaperl6453100% (1)
- COP ImprovementДокумент3 страницыCOP ImprovementMainak PaulОценок пока нет