Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Visit The History of Making Electricity
Загружено:
schlemielzОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Visit The History of Making Electricity
Загружено:
schlemielzАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Alternating current
electric current that reverses direction many times per second
this is the type of electricity that's used in your home
often abbreviated as AC
Amps
the unit for measuring electric current
named after French physicist Andr-Marie Ampre who played a role in discovering electroma
Visit the History of Making Electricity section for more information.
Atom
the smallest particle of an element
everything is made up of tiny atoms
Battery
a device that stores energy and makes it available as electricity
Biomass
renewable source of energy that uses organic waste to produce electricity
for example, wood by-products, plants, crops, and animal waste are used instead of fossil fuels
this resource is considered clean because it can be used over and over again without any negat
environment.
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Blackout
a total power failure over a large area, usually caused by a breakdown at a power plant or large
Brownout
a small, temporary reduction of voltage and/or power
usually caused by the utility company trying to conserve power during heavy periods of use
often causes lights to dim
Cell
a device that delivers an electric current as the result of a chemical reaction (i.e. a battery)
Charge
the amount of electricity an object contains
Circuit
an electric device that provides a path for electric current to flow
Coal
a fossil fuel that's burned in the large boilers.
the burning coal heats water in a boiler and this produces steam, which spins a turbine engine a
this is a non-renewable energy source
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Conductor
a substance that allows electric current to pass through it
Current
the flow of electricity in an electric circuit
it's measured in amps
Carbon dioxide
a colourless gas that has no smell
also known as CO2, it's present in the Earth's atmosphere and is produced when fossil fuels are
Direct Current
a type of electric energy that travels in one direction
often abbreviated as DC
batteries produce a direct current
Dynamo
an electric generator that produces a direct current
Electricity
a form of energy that's produced by the flow of electrons
provides power for lighting, appliances, and other electric devices in our homes and businesses
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Electric Shock
the physical reaction caused when electricity flows through the body
it can occur when your body comes in contact with any source of voltage high enough to send
muscles or hair
may cause tissue damage or a heart attack if the current is high enough
Electrolysis
chemical changes produced by passing a current through a water solution
Electromagnet
a magnet formed when an electric current flows through a wire or other conductor
Electromagnetic
when an object is made magnetic by an electric current
Electron
a basic particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom
the flow of electrons produces electricity
Energy
the ability to do work
people get energy from food, but things like your iPod, a video game player, or a cell phone ge
electricity
Energy efficiency
using energy wisely and not wasting it
ENERGY STAR qualified
a product that uses less energy, saves money, and helps protect the environment
Environmentally friendly
any thing or any action that is not harmful or damaging to the environment
Fossil fuel
any kind of fuel that is found under the ground, like coal, oil, or gas
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Fuel cell
a device that converts the energy of a fuel - such as hydrogen - into electricity or heat
Fuse
a protective device that's designed to melt or break when the current flowing through it becom
a fuse helps protect against fire
Generator
a machine that produces electricity by converting mechanical energy into electric energy
Geothermal energy
using heat from below the Earth's surface to create electricity
it's a renewable source of energy
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Ground
a connection between an electric device and the earth
Grid
a network of electric power lines and connections that delivers electricity to our homes and bu
Hydroelectricity
also known as water power, this renewable energy source uses water from a river or dam to ge
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Insulator
a material that does not allow the flow of electricity to pass through it
Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO)
an organization that was established in 1999
responsible for the day-to-day operation of Ontario's electrical system
Kilowatt (kW)
the unit used to measure electric energy
there are 1,000 watts in one kilowatt
Kilowatt hour (kWh)
this measurement refers to the use of 1,000 watts of electricity in one hour
o 1kWh = ten 100 watt bulbs all burning at the same time for one hour
o
10 bulbs x 100 watts each hour x 1 hour = 1,000 watts hours or 1kWh
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED)
developed in 1994, this program encourages building homes and structures that are environme
efficient
certification program for the design, construction and operation of high-performance green bui
Lightning
an electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to the earth
it is accompanied by a flash of light
Load
the amount of electricity consumed by an electric device, such as a video game or an appliance
Local (Electricity) Distribution Company (LDC)
these companies take power from high-voltage transmission lines, transform the electricity to a
provide it to local companies
they monitor the electricity distribution system, which is important for all electricity consumer
Magnet
an object that is surrounded by a magnetic field
it has the natural power to attract objects made of iron or steel
Magnetic field
the area around a magnet in which objects are attracted or repelled
Mechanical energy
the energy of an object in motion
Megawatt
a unit of electricity equivalent to 1000kW or 1 million watts (MW)
Meter
a device that measures the levels of customers' electricity and gas use
Motor
a machine that converts energy to motion or power
Nuclear power
the energy generated in a nuclear power plant
it's produced by splitting atoms in a nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
part of a nuclear power plant where atoms break into many parts and power is generated
Non-renewable energy
fuels that cannot be made easily and take millions of years to form
oil, coal, and gas are examples of non-renewable energy
Ohm
the basic unit for measuring resistance to an electric current
it was named after German physicist Georg Ohm, who researched the relationship between vol
resistance
Visit the History of Making Electricity section for more information.
Ontario Energy Board (OEB)
a corporation that's responsible for managing natural gas and electricity utilities in Ontario
part of its responsibility includes setting the price of gas and power
Ontario Energy Network (OEN)
an association that's formed to allow information to be shared between organizations within th
Ontario Power Generation
a public company that's owned by the government of Ontario
it is Canada's largest owner and operator of nuclear power plants, as well as some alternative e
Photovoltaic
a solar power technology that converts the sun's light into electricity
Power
the energy used to do work
Radio
a technology that allows the transmission of sound or other signals by electromagnetic waves t
Renewable energy
fuels that do not run out and can generate electricity cleanly
examples include solar power, wind power, and hydroelectricity
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Resistance
this is the degree to which a substance resists, or opposes, an electric current
Socket
the opening that a light bulb screws into
Solar energy
this is energy that's created directly from the light or heat of the sun
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Static electricity
a charge of electricity that's generated by the friction between two objects
Switch
a mechanical device used to turn a current on or off in an electric circuit
Thermal
a word used to mean "heat"
a thermal power station uses heat to produce electricity
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
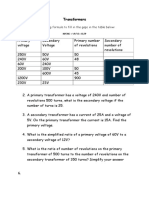
Transformer
an electric device that is used to raise or lower the voltage of electricity
voltage is increased at a transformer so it can be transmitted over long distances and then it is d
transformer so it can be distributed to customers
To learn more, visit the What is Electricity section
Volt
a unit of measurement for electricity
it indicates how much pressure there is on an electric current
named after Alessandro Volta, who invented the first battery
Watt
unit for measuring electric power
it was named after Scottish inventor James Watt, who made improvements to the steam engine
Visit the History for Making Electricity section for more information.
Water power
also known as hydroelectricity, this renewable energy source uses water from a river or dam to
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Wind turbine
a rotating machine that converts the energy of wind into mechanical energy
this energy turns a rotating generator shaft, converting it into electricity
this is a renewable energy source
To learn more, visit The Ins and Outs of Making Electricity section
Вам также может понравиться
- Computer Graphics MCQ 01Документ10 страницComputer Graphics MCQ 01schlemielzОценок пока нет
- Schroeter R - 91 Smoker's BookletДокумент21 страницаSchroeter R - 91 Smoker's BookletFrankPapa100% (2)
- Wireman PDFДокумент29 страницWireman PDFMALAYALA MANTRA YANTRA TANTRA100% (4)
- Service Service Manual Manual: Generator SetДокумент54 страницыService Service Manual Manual: Generator Setemildoykov4046100% (1)
- 7 DC Machimes - DC MotorsДокумент31 страница7 DC Machimes - DC MotorsIan VillaseñorОценок пока нет
- Sci ReviewerДокумент5 страницSci ReviewerCRAIG MIKEL P YUОценок пока нет
- Physics-Energy and Electricity: 1) Radiation Is Energy Carried by Electromagnetic WavesДокумент14 страницPhysics-Energy and Electricity: 1) Radiation Is Energy Carried by Electromagnetic WavesilalithОценок пока нет
- 9th Elect NotesДокумент13 страниц9th Elect NotesHI-FIОценок пока нет
- BU2 - ElectricityДокумент11 страницBU2 - Electricityjona serranoОценок пока нет
- Unit III NotesДокумент22 страницыUnit III NotesArun prakashОценок пока нет
- Reviewer For EesДокумент6 страницReviewer For EesShanne ColleraОценок пока нет
- Intelligent BuildingsДокумент11 страницIntelligent BuildingsJumeirahlyn TutaanОценок пока нет
- Fau Cep-Interview NotesДокумент14 страницFau Cep-Interview Noteschmuh110Оценок пока нет
- Toyol EnergyДокумент1 страницаToyol EnergyzinilОценок пока нет
- Technology and Livelihood EducationДокумент63 страницыTechnology and Livelihood EducationNo RiОценок пока нет
- Power PlantsДокумент20 страницPower Plantsjvharsha.sОценок пока нет
- Industrial Arts Group 2Документ5 страницIndustrial Arts Group 2Xyril buenaventuraОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Energy2Документ80 страницIntroduction To Energy2Javier RojasОценок пока нет
- Energy and The EnvironmentДокумент65 страницEnergy and The EnvironmentJavonie ScottОценок пока нет
- Gener Ation: Electr IcityДокумент29 страницGener Ation: Electr IcityMohammed AliОценок пока нет
- Electrical PowerДокумент36 страницElectrical PowerMorley MuseОценок пока нет
- Electricity PrintДокумент14 страницElectricity PrintSirna Santosh KumarОценок пока нет
- All About VolcanoesДокумент36 страницAll About VolcanoesBless beljОценок пока нет
- Unit - 3: Building Services - IДокумент30 страницUnit - 3: Building Services - IYoesof HilabyОценок пока нет
- Electrical Safety, Electrical Devices, Electric Potential, Capacitance, Sources of Energy and ScientistsДокумент11 страницElectrical Safety, Electrical Devices, Electric Potential, Capacitance, Sources of Energy and ScientistsJhayrald SilangОценок пока нет
- Sources of Electricity Generation and SupplyДокумент32 страницыSources of Electricity Generation and SupplyNidhi JindalОценок пока нет
- Unit 7Документ6 страницUnit 7Samreen KhanОценок пока нет
- TLE ModuleДокумент73 страницыTLE ModuleDexter Bola100% (1)
- ElectricityДокумент19 страницElectricityAdie Alie PumpОценок пока нет
- Document 1Документ14 страницDocument 1chinnamadesh58Оценок пока нет
- Geothermal PlantДокумент4 страницыGeothermal PlantJamandre, Joseph M.Оценок пока нет
- ElectricityДокумент21 страницаElectricityChidambar S DudgikarОценок пока нет
- GST 122Документ6 страницGST 122SylviaОценок пока нет
- Poe 1 2 Key TermsДокумент2 страницыPoe 1 2 Key Termsapi-260948905100% (2)
- 1 2 KeytermsДокумент2 страницы1 2 Keytermsapi-275474011Оценок пока нет
- Electrical EnergyДокумент4 страницыElectrical EnergyCabal Traders100% (1)
- Sosurces of ElectricityДокумент5 страницSosurces of Electricityaustin otienoОценок пока нет
- Notes EnergyДокумент7 страницNotes EnergyRasha GhabbounОценок пока нет
- Importance of Electricity in Our Daily LifeДокумент4 страницыImportance of Electricity in Our Daily LifeArnaut DianaОценок пока нет
- Power Generation by Stair CaseДокумент26 страницPower Generation by Stair CaseMayur Madhukar MankarОценок пока нет
- 1 2 KeytermsДокумент2 страницы1 2 Keytermsapi-275559543Оценок пока нет
- Electricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryДокумент11 страницElectricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryMarie GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Types of Power Plants - 2018 PDFДокумент71 страницаTypes of Power Plants - 2018 PDFJeff Justine GeragaОценок пока нет
- Power Plants 3cДокумент32 страницыPower Plants 3cOLATZ VACASОценок пока нет
- Psa Quiz 1 ReviewerДокумент4 страницыPsa Quiz 1 ReviewerJhonloyd Rosete LittauaОценок пока нет
- ELECTRICAL THEORY - Group 2 - 085619Документ51 страницаELECTRICAL THEORY - Group 2 - 085619BASITO, CHRISTIAN PAUL B.Оценок пока нет
- L3 - Non-Conventional Power GenerationДокумент29 страницL3 - Non-Conventional Power GenerationSwapnilОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT-DEFINITION-OF-TERMS Power PlantДокумент4 страницыASSIGNMENT-DEFINITION-OF-TERMS Power PlantAmiel Ohween AnayОценок пока нет
- Nces Module 1&2Документ113 страницNces Module 1&2Naveen S BasandiОценок пока нет
- CHAP 1, Lecture 1-A Fundamental's of Power SystemДокумент54 страницыCHAP 1, Lecture 1-A Fundamental's of Power SystemBiruk DawitОценок пока нет
- M4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFДокумент5 страницM4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFMujeeb KhanОценок пока нет
- Electrical Circuit&MechineДокумент96 страницElectrical Circuit&MechineDipendra Bahadur SinghОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ5 страницAssignment 2RalphNicholaiApostolUlepОценок пока нет
- Solar Inverter 1 & 2Документ38 страницSolar Inverter 1 & 2kalu chimdiОценок пока нет
- EnergíaДокумент7 страницEnergíaJorge MuñozОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент29 страницUntitledLovely Quevedo ʚĩɞОценок пока нет
- Different Kind of Electric Generation Powerplants: Nuclear Power PlantsДокумент14 страницDifferent Kind of Electric Generation Powerplants: Nuclear Power PlantsluffyОценок пока нет
- What Is ElectricityДокумент24 страницыWhat Is ElectricityAlbeno Saleh AhmadОценок пока нет
- Tidal Power PlantДокумент13 страницTidal Power Plantmujeeb17100% (1)
- Hydro PowerДокумент24 страницыHydro Powermaximelus243Оценок пока нет
- How Electricity Is MadeДокумент2 страницыHow Electricity Is MadeŠärâh ĞhērŕîОценок пока нет
- Photovoltaic Design and Installation: Bucknell University Solar Scholars ProgramДокумент112 страницPhotovoltaic Design and Installation: Bucknell University Solar Scholars ProgramVinay BabuОценок пока нет
- 2.4. Electric CircuitsДокумент12 страниц2.4. Electric CircuitsschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Resistor NetworksДокумент15 страницResistor NetworksThomas SmithОценок пока нет
- DC CircuitsДокумент16 страницDC CircuitsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 2.4. Electric CircuitsДокумент12 страниц2.4. Electric CircuitsschlemielzОценок пока нет
- 2.4 Internal Resistance PDFДокумент16 страниц2.4 Internal Resistance PDFschlemielzОценок пока нет
- 2.3 DC Circuits MS PDFДокумент5 страниц2.3 DC Circuits MS PDFNur Hafizah MukhtarОценок пока нет
- 4.4.1 Electric Fields ...Документ16 страниц4.4.1 Electric Fields ...NiazHaqueОценок пока нет
- Current A LevelДокумент9 страницCurrent A Levelnazran68Оценок пока нет
- Physics Revision Booklet Year 12Документ5 страницPhysics Revision Booklet Year 12schlemielzОценок пока нет
- Uses of RadiationДокумент6 страницUses of RadiationschlemielzОценок пока нет
- TransformersДокумент2 страницыTransformersschlemielz0% (1)
- Effect of Nuclear Radiation On Living CellsДокумент1 страницаEffect of Nuclear Radiation On Living CellsschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Cosmic Anniversary: 'Big Bang Echo' Discovered 50 Years Ago TodayДокумент3 страницыCosmic Anniversary: 'Big Bang Echo' Discovered 50 Years Ago TodayschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Problems in A-Level PhysicsДокумент201 страницаProblems in A-Level Physicsweews97% (36)
- Television Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?Документ2 страницыTelevision Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?schlemielzОценок пока нет
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismДокумент82 страницыMagnetism and ElectromagnetismschlemielzОценок пока нет
- BashuДокумент5 страницBashuschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Final Coal For Web1Документ39 страницFinal Coal For Web1schlemielzОценок пока нет
- Television Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?Документ2 страницыTelevision Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?schlemielzОценок пока нет
- 4PH0 1P Que 20160119 PDFДокумент28 страниц4PH0 1P Que 20160119 PDFschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Economy in Numbers-The Beijing Olympics by The NumbersДокумент3 страницыEconomy in Numbers-The Beijing Olympics by The NumbersschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Television Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?Документ2 страницыTelevision Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?schlemielzОценок пока нет
- A Summary Guide To The Structure and Naming-Organic ChemistryДокумент15 страницA Summary Guide To The Structure and Naming-Organic ChemistryschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Television Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?Документ2 страницыTelevision Commercial (TVC) : What Does TVC Mean?schlemielzОценок пока нет
- Visualising Energy LevelsДокумент9 страницVisualising Energy LevelsschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Документ28 страницEdexcel Igcse January 2017 Physics p1Kriti0% (1)
- To Fight Climate Change We Must Fight CapitalismДокумент6 страницTo Fight Climate Change We Must Fight CapitalismschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Definitions of Terms in Practical QuestionsДокумент7 страницDefinitions of Terms in Practical QuestionsschlemielzОценок пока нет
- 4PM0 02 Que 20160125 PDFДокумент36 страниц4PM0 02 Que 20160125 PDFschlemielzОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Electrical Machines Subject Code: Ele-405 L T P: 2 1 0 Credits: 03Документ3 страницыSyllabus Electrical Machines Subject Code: Ele-405 L T P: 2 1 0 Credits: 03Nitin PalОценок пока нет
- Section 1 Standby Generator - Lift StationДокумент26 страницSection 1 Standby Generator - Lift StationSebastian CantilloОценок пока нет
- Ewg 2Документ23 страницыEwg 2syamsudin4077Оценок пока нет
- Isolation and Protection of The Motor-Generator Pair System For Fault Ride-Through of Renewable Energy Generation SystemsДокумент20 страницIsolation and Protection of The Motor-Generator Pair System For Fault Ride-Through of Renewable Energy Generation SystemsUmesh GowdaОценок пока нет
- BE8261 - BEEIE Lab Manual For II Sem Mech/ AeroДокумент123 страницыBE8261 - BEEIE Lab Manual For II Sem Mech/ AeroRAJARAJAN RОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineers Just Have The Right SparkДокумент4 страницыElectrical Engineers Just Have The Right SparkShreta MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- AEM Dessau Production FluxДокумент24 страницыAEM Dessau Production FluxRadu BabauОценок пока нет
- Insulation Resistance Monitor For Shipboard Electrical Motors and GeneratorsДокумент3 страницыInsulation Resistance Monitor For Shipboard Electrical Motors and GeneratorsPhong ThanhОценок пока нет
- Aeolos-H 10kw BrochureДокумент23 страницыAeolos-H 10kw BrochureAyan MajiОценок пока нет
- EE 3111 SyllabusДокумент25 страницEE 3111 SyllabusKenОценок пока нет
- Lessons Learned From Wind Integration StudiesДокумент109 страницLessons Learned From Wind Integration StudiesjeffguitarОценок пока нет
- VFD Solar Pump Controller User ManualДокумент45 страницVFD Solar Pump Controller User ManualMuhammad SalmanОценок пока нет
- X1 Air Install ManualДокумент18 страницX1 Air Install ManualNeil CzsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Steam TurbineДокумент78 страницChapter 5 Steam TurbineGloria Del Carmen MuñozОценок пока нет
- Ansys Maxwell Brochure 14.0Документ8 страницAnsys Maxwell Brochure 14.0Ramesh NaiduОценок пока нет
- Series Hybrid Car Doc - 3Документ137 страницSeries Hybrid Car Doc - 3mekkararameshОценок пока нет
- PS5000 1Документ2 страницыPS5000 1swarupkumarnayakОценок пока нет
- EA230 Manual Voltage RegulatorДокумент4 страницыEA230 Manual Voltage Regulatorhenryvargas238565Оценок пока нет
- Engine Data Sheet (KTA50 - 1250kVA)Документ6 страницEngine Data Sheet (KTA50 - 1250kVA)Ghulam MujtabaОценок пока нет
- HB959204500 T20 PSS PDFДокумент43 страницыHB959204500 T20 PSS PDFcynaiduОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Electrical Systems FPR A&pДокумент45 страницAircraft Electrical Systems FPR A&pAlaye AkpanaОценок пока нет
- Electrical and Magnetic Materials For Automotive ManufacturingДокумент15 страницElectrical and Magnetic Materials For Automotive ManufacturingdawitОценок пока нет
- Vtu Electricvehecles Module2openelectivepptbydr 221021054719 1293bcdfДокумент64 страницыVtu Electricvehecles Module2openelectivepptbydr 221021054719 1293bcdfprashantkumar chinamalliОценок пока нет
- Vaila Bility: WarningДокумент6 страницVaila Bility: WarningPhillip SmithОценок пока нет
- NOVEMBER 2019 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectoryДокумент716 страницNOVEMBER 2019 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectorySurplus RecordОценок пока нет
- Marimuthu RESUME - Rotating Equipment Specialist - June 2012Документ10 страницMarimuthu RESUME - Rotating Equipment Specialist - June 2012vibmuthu100% (1)