Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biochem Exam 3 - 2013
Загружено:
Jenna ReynoldsОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biochem Exam 3 - 2013
Загружено:
Jenna ReynoldsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
020.
305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
Biochemistry Exam 3
Biology 020.305
November 13, 2013
Instructions for examination:
1. BEFORE YOU BEGIN, clearly print your name and JHED ID ON THE TALLY PAGE. Failure to
write your JHED ID will cost 2 points. Please also write your name on the front of every page in case
the pages get separated.
2. There are a total of 14 pages including: 1 cover page, 10 question pages 2-11, 1 tally page 12, 1
metabolism pathway diagram page 13 and 1 scratch page 14. If there are any pages missing, obtain a
new exam. No excuses will be accepted for missing pages.
3. Write answers clearly and concisely in the space provided. Anything written on the back of the
exam is not graded. Extra space for doodling is found on the last page of the exam. If you desire
credit for anything that is NOT in the answer space provided, you must clearly indicate where we
should look for that information.
4. For multiple choice questions with multiple possible correct answers (i.e. Circle all that apply), you
will get full credit for selecting all correct answers only. Points may be deducted for selecting incorrect
answers with a minimum score of 0.
5. Exams not written in blue or black permanent ink or containing white-out will not be regraded.
6. Calculators are not necessary and their use is not allowed.
7. This exam is closed note and closed book. Books, notes, phones, computers etc., are to be
placed out of sight before the beginning of the exam and are not to be referred to during the exam.
Talking or looking at other exams during the test is prohibited.
8. If you have any questions, raise your hand and a TA or instructor will come to you. If there is
anything about the exam room that is negatively affecting your ability to focus on the exam, it is your
responsibility to notify a TA or instructor.
9. You will be allowed 65 minutes to take this exam. Once time is called you must stop writing. Any
writing after time is called will result in the loss of points and may be reported as an ethics violation.
10. When you are done with the exam, please show your ID to a proctor who will accept your exam.
Then sign out by marking your test number on the roster.
11. Ethics Pledge: Please make the following commitment by signing and dating underneath the
following pledge: I agree to complete this exam without unauthorized assistance from any person,
materials, or device. I will not alter my answers in any way after receipt of the graded exam. Your
signature here indicates that you have read and understood items 1 -10. Tests not signed may not be
handed back or regraded.
___________________________________
Good Luck!
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
1. 19 points total. Fermentation and Respiration. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis can be used
for fermentation or for cellular respiration. When oxygen is supplied, pyruvate produced from
glycolysis is converted to acetyl coenzyme A for cellular respiration.
A. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, which converts pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A, is tightly regulated at
multiple levels. If the ratio of NADH to NAD+ in the mitochondria is elevated (more NADH), pyruvate
dehydrogenase activity will: INCREASE or DECREASE (circle one). 1
B. When pyruvate produced from glycolysis is used for cellular respiration, how many molecules of
ATP will be produced per each pyruvate consumed? Assume that mitochondrial NADH and FADH2
are equivalent to 2.5 and 1.5 molecules of ATP, respectively. _______ 2
Answer: 4 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 ATP = 10 + 1.5 +1 = 12.5 ATP.
1pt for 10
When oxygen is absent, pyruvate produced from glycolysis is used for fermentation to lactate.
C. What is the cofactor required for the fermentation of pyruvate to lactate? ____________ NADH 2
D. How many molecules of ATP will be produced by fermentation of pyruvate to produce lactate?
Assume that mitochondrial NADH and FADH2 are equivalent to 2.5 and 1.5 molecules of ATP,
respectively. _____0 (2)
E. If fermentation is occurring in muscle cells during exercise, lactate produced from glycolysis needs
to be transported out of cells so that glycolysis can continue. The transporter of lactate requires one
additional substrate in addition to lactate. 2
i. What is the additional substrate? _________ proton
ii. In which direction is this additional substrate transported?
Circle one: Same direction as lactate
Opposite direction from lactate
F. The accumulation of lactate secreted into the blood can be lethal if it is not removed. Liver is the
major organ that removes lactate from the blood. Name two possible metabolic pathways that could
use lactate in the liver. Explain how lactate enters the pathway naming key intermediates. 4
Pathway 1: gluconeogenesis, TCA, fatty acid synthesis, pentose phosphate, cholesterol synthesis,
alanine synthesis
Explain: via conversion to pyruvate and or acetyl CoA, OAA ok for gluconeogenesis
Pathway 2:
Explain:
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
1. continued
G. The production of lactate by muscle cells and uptake of lactate by liver cells is part of the Cori cycle.
In the Cori cycle, how many molecules of ATP are consumed per cycle? ___4 ATP 2
H. When cells are depleted of oxygen and, thus, electron transfer chain is not functional, cells do not
normally convert pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A. If cells did convert pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A
and if the acetyl coenzyme A is used for citric acid cycle, how many molecules of ATP will be
produced from a molecule of pyruvate consumed? _1 ATP ____ 2
I. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA for use in the citric acid cycle is energetically favorable even
in the absence of oxygen. However, normal muscle cells do not use respiration in the absence of
oxygen. Respiration is likely inhibited due to the accumulation of NADH in mitochondria in the
absence of oxygen. How can NADH accumulation in mitochondria inhibit respiration? 2
Answer: NADH inhibits TCA cycle, specifically pyruvate dehydrogenase, isocitrate dehydrogenase,
and succinyl CoA synthase.
2. 22 points total. Cellular compartmentalization of metabolic pathways and Gluconeogenesis.
A. Yeast cells are eukaryotes and they normally have mitochondria. However, some yeast cells called
rhoo have almost no mitochondrial functions but are still viable. Please select all metabolic processes
rhoo cannot do. Select all that apply. 3
i. glycolysis
ii. citric acid cycle
iii. oxidative phosphorylation
iv. fatty acid oxidation
v. cholesterol synthesis
vi. pentose phosphate pathway
vii. nucleotide biosynthesis
viii. fatty acid synthesis
In comparison to some of the metabolic pathways above, gluconeogenesis requires multiple
subcellular organelles/compartments.
B. The first step of gluconeogenesis is the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, where ATP is
consumed. This step occurs in: Select one answer. 2
i. mitochondrial inner membrane
ii. cytoplasm
iii. endoplasmic reticulum
iv. plasma membrane
v. mitochondrial matrix
vi. mitochondrial outer membrane
vii. mitochondrial intermembrane space
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
2 continued
The second step of gluconeogenesis is the conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate,
where GTP is consumed. For this reaction, oxaloacetate produced in the mitochondria needs to be
transported to the cytosol.
C. Fill in the blanks. Oxaloacetate is first converted to ____________ using ____________ as a cosubstrate. The product of this reaction is transported to the cytosol, then converted back to
oxaloacetate using ___________________ as a co-substrate. 3
Answer: malate, NADH or NADH + H+, NAD+.
D. How many molecules of ATP or GTP should be hydrolyzed to make one molecule of glucose from
pyruvate? ______ Answer: 6 ATP or GTP. 2
1 point for 3 ATP
The conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate is not simply the reverse of
glycolysis and requires the enzyme (F6BPase). F6BPase is inhibited by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
(F2,6BP) and activated by citrate.
E. Is FBPase stimulated or suppressed when ATP citrate lyase becomes hyperactive?
Circle One:
Stimulated
or
suppressed 1
The molecule shown below (PFKFB) catalyzes both the conversion of F6BP to F2,6BP (PFK2) and
F2,6BP to F6BP (FBPase2). The figure shows the reciprocal regulation of the enzyme by
phosphorylation.
F. When liver cells are stimulated with glucagon:
Circle the correct words of each underlined pair to correctly complete each sentence. 5
i. (Circle one: PKA or phosphoprotein phosphatase) will be (Circle one: activated or inhibited).
ii. PFKB will be (Circle one: phosphorylated or dephosphorylated).
iii. F26BP levels will (Circle one: increase or decrease).
iv. Blood glucose levels will (Circle one: increase or decrease).
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
2 continued
The last step of gluconeogenesis is the hydrolysis of glucose-6-phosphate to
glucose and inorganic phosphate by glucose-6-phosphatase. Breakdown of
glycogen generates glucose-6-phosphate which can also be a substrate for
Glucose-6-phosphatase.
G. In which subcellular location does this step occur? Select one answer. 2
i. mitochondria inner membrane
ii. cytoplasm
iii. endoplasmic reticulum
iv. plasma membrane
v. mitochondrial matrix
H. How is this gluconeogenic reaction different than the conversion of glucose to glucose-6phosphate during glycolysis? Select all that apply. 2
i. the gluconeogenic reaction occurs in different cellular location
ii. the gluconeogenic reaction generates ATP instead of using ATP
iii. the gluconeogenic reaction occurs regardless of the concentration of substrates
iv. the glucogenogenic reaction is thermodynamically unfavorable
I. The reaction is regulated by transporting the substrate and products in and out of the subcellular
organelle. If the transport of inorganic phosphate out of the subcellular organelle were inhibited, which
of the following would be true? Select one answer. 2 1 pt for selecting 2/3 answers
i. the reaction will be inhibited
ii. gluconeogenesis will be inhibited
iii. glycogen breakdown will be decreased
iv. all of the above
v. none of the above
3. 10 points total. Pentose phosphate pathway and nucleotide biosynthesis. In the pentose
phosphate pathway, glucose-6-phosphate is converted to ribose-5-phosphate. Glucose-6-phosphate
is an intermediate of metabolic processes.
A. Which metabolic processes produce glucose-6-phosphate? Select all correct ones. 2
i. glycolysis
ii. gluconeogenesis
iii. fatty acid synthesis
iv. fatty acid oxidation
v. citric acid cycle
B. How many molecules of ATP are generated by the conversion of 4 glucose-6-phosphate
molecules to pyruvate during glycolysis (ignore fermentation/respiration)? _____ 2
Answer: straight through glycolysis 3 ATP each x 4 = 12 ATP; 1 point for 3, 1 point for 8
Instead, the 4 glucose-6-phosphate molecules can enter the pentose phosphate pathway to produce
2 fructose-6-phosphate molecules, 1 ribose-phosphate, and 1 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
C. In this case, how many molecules of ATP will be generated from the combination of pentose
phosphate pathway and glycolysis (ignore fermentation/respiration)? ____ 2
through pentose phosphate: 2 F6P x 3 ATP + 1 GAP x 2 ATP = 8 ATP.
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
3 continued
D. How many molecules of NADP+ are reduced from the 4 molecules of glucose-6-phosphate? _____
2 Answer: 2 NAD PH per glucose-6-phosphate x 4 glucose -6-phosphate = 8 NADPH,
E. If all of the NADPH generated from 4 molecules of glucose-6phosphate (answer above) are used for the synthesis of a fatty
acid called hexanoic acid (C5H11CO2H), how many molecules of
the fatty acid can be produced? _______ 2
Answer: for each synthesis of hexanoic acid, 2 cycles of fatty acid synthesis is required. Each
cycle consumes 2 NADPH. Thus 4 NADPH are consumed. Therefore, the NADPH produced from C is
sufficient to make 2 hexanoic acids
4. 16 points total. Fatty acid metabolism.
A family of molecules found in coffee called coffee polyphenols
(CPP) have been shown to affect mice that have been fed a high-fat
diet. Specifically, mice on the high-fat diet who were given CPP
showed lower triglyceride levels compared to mice on the same
high-fat diet with no CPP.
A. Triglyceride obtained from food that enters the bloodstream can
be used for immediate energy or storage. 2
i. Name one type of cell that will use triglcyerides immediately for
energy. ____ muscle
ii. Name one type of cell that will store triglcyerides. ____ liver, adiopcyte
Researchers decided to measure both fatty acid synthesis and -oxidation to determine the
mechanism of CPP function.
B. Both fatty acid synthesis and breakdown (beta-oxidation) require shuttles for critical molecules to
cross the inner mitochondrial membrane at the beginning of the processes. Select one of these
shuttles and answer the following questions. 3
Select one:
Carnitine shuttle
Citrate shuttle
i. Which metabolic Pathway requires this shuttle?
Circle one: Fatty acid synthesis
or Beta-oxidation
ii. Name the key molecule transported that will continue in the pathway. _____________
iii. Is the molecule transported into or out of the mitochondrial matrix?
Circle one: Into matrix
or
Out of matrix
Carnitine shuttle: beta oxidation, acyl-CoA, into matrix
Citrate shuttle: fatty acid synthesis, acetyl-CoA, out of matrix
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
4 continued
C. This graph shows that mice on a high fat diet have lower levels of
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity when treated with CPP. What
conclusions about the effects of CPP are consistent with this
observation? Select all that apply. 2
i. suppresses fatty acid synthesis
ii. increases malonyl-CoA levels
iii. decreases acetyl-CoA levels
iv. suppresses beta oxidation
v. promotes cancer cell survival
D.The following molecules are regulators of ACC activity that might be affected by CPP. Which
molecules normally inhibit ACC activity? Select all that apply. 3
i. AMP-activated kinase (AMPK)
ii. citrate
iii. long chain fatty acids
iv. insulin
v. glucagon
E.The graph shows the oxygen consumption of control
mice on a normal diet (Cont), mice on a high fat diet (HF),
and mice on a high fat diet supplemented with CPP (HF +
1.0% CPP). What is the best conclusion can you make
from this data? Select one. 4
i. a high fat diet increases ATP synthesis
ii. a high fat diet decreases fatty acid -oxidation
iii. CPP stimulates aerobic fermentation
iv. CPP increases fatty acid -oxidation
v. CPP decreases ATP synthesis
Explain your reasoning:
More O2 is consumed, so the ETC is active. This means the TCA cycle is active and the likely source
of acetylCoA is from fatty acid breakdown.
It cannot be the high fat diet alone because the HF mice use the same amount of oxygen as the
control mice.
F. The data showed that, in addition to fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis is affected. Fatty
acids synthesis and cholesterol synthesis both: Select all that apply. 2
i. use NADH.
ii. can be synthesized from acetyl CoA.
iii. require HMG-CoA reductase.
iv. require Acyl carrier protein (ACP).
v. can be regulated by SREBP.
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
5. 9 points total. Metabolism and Cancer
Metabolic pathways of cancer cells are often observed to be different than normal cells.
A. The Warburg effect is characterized by an increase in: (Select all that apply). 2
i. fatty acid synthesis
ii. glycolysis
iii. oxidative phosphorylation
iv. gluconeogenesis
v. aerobic fermentation
vi. anaerobic fermentation
vii. nucleotide synthesis
The citric acid cycle is also altered in cancer cells. In some cancer cells, Isocitrate dehydrogenase
(IDH) converts isocitrate to -ketoglutarate and another mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase additionally
converts reduces -ketoglutarate to 2-hydroxyglutarate using NADH.
B. If every -ketoglutarate generated by TCA is immediately converted to 2-hydroxyglutarate (and
excess oxaloacetate is available), how many molecules of ATP will be produced from each molecule
of acetyl coenzyme A in this particular case? ______0 ATP. 2
Another alteration of the TCA cycle observed in cancer cells is the conversion of isocitrate to
glyoxylate. Glyoxylate can react with acetyl-CoA to form malate, bypassing several steps of the TCA
cycle.
C. Compared to normal cells, cancer cells using the glyoxylate pathway will have which of the
following? Select all that apply. 1
i. higher oxaloacetate levels
ii. higher succinyl-CoA levels
iii. lower isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) levels
iv. lower ratio of citrate to malate
v. higher ratio of isocitrate to -ketogluterate
D. Name one advantage that bypassing specific steps of the TCA cycle potentially provides to cancer
cells. 2
Advantage: able to use pyruvate without being regulated by IDH and alpha-ketogluterate
dehydrogenase
E. How might the glyoxylate pathway contribute to increased glycolysis in cancer cells? 2
Possible answers include glyoxylate pathway provides malate and oxaloacetate that can be used to
consume cytoplasmic NADH, it can be used to convert pyruvate to other biological materialsetc
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
6. 12 points total. Signaling and Diabetes
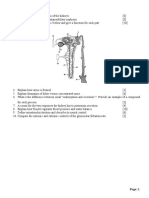
The insulin signaling pathway is diagrammed in the image above. To summarize, insulin binding to
the receptor leads to activation of the kinase Akt. Active Akt affects the cell in several ways including
causing an increase in the amount of the glucose transporter GLUT4 on the cell surface.
A. Which of the following is true about insulin signaling? Select all that apply.2
i. Insulin is secreted by liver cells
ii. Insulin is secreted by pancreas cells
iii. Insulin signaling leads to increased uptake of glucose from the blood
iv. When insulin is secreted, blood glucagon concentration is elevated.
B. Which pathways are stimulated by insulin signaling? Select all that apply. 3
i. glycolysis
ii. gluconeogenesis
iii. breakdown of glycogen
iv. synthesis of glycogen
v. beta-oxidation
vi. fatty acid synthesis
Type II diabetes is often called insulin-resistant diabetes, meaning that insulin is properly secreted,
but other cells do not respond to insulin properly.
C. Which of the following scenarios would likely cause an insulin-resistant phenotype? Select all that
apply. 2
i. An insulin receptor that constantly phosphorylates its substrates
ii. A version of Phopsphoinositide 3 kinase that does not localize to the cell plasma membrane
iii. A version of PDK1 that cannot bind PIP3
iv. A version of Atk that is constantly phosphorylated
v. A cell membrane with excessively high levels of PIP3 in the absence of PI3K activity
D. Select one of the answers you chose in part B above and briefly (2 sentences or fewer) describe
how this would lead to the type II diabetes phenotype.
3
ii: If PI3K were not at the membrane, it would be slow to find its substrate (which is part of the
membrane), PIP3 would not be made efficiently, PDK would not activate Akt and Akt would not cause
GLUT4 to be in the membrane, so blood glucose would not be imported leaving blood glucose levels
high.
iii. If PDK1 does not bind PIP3, it will not be activated, will not activate Akt, and Akt would not cause
GLUT4 to be in the membrane, so blood glucose would not be imported leaving blood glucose levels
high.
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
6 continued
E. Individuals with type II diabetes are likely to also have defects in glucagon signaling. 2
Is this statement true or false? Circle one: True
False
Explain your reasoning:
If False: Glucagon signals through a completely different mechanism including a different receptor
(beta adrenergic) and signaling molecules including cAMP.
If TRUE: an explanation might be that these individuals have overactive glucagon signaling that
causes liver cells to undergo gluconeogenesis constitutively, thus moving glucose into the blood,
elevating glucose levels)
7. 12 points. ETC and ATP Synthase
A. On the diagram of the electron transport chain above, what molecule is represented by D?
______ 1
Cytochrome C
The table lists 3 inhibitors of the electron transport chain.
Inhibitor
Demerol
Carboxin
Antimycin
A
Step
inhibited
complex
I
complex
II
Q
cycle
B. Compare the effects of these three drugs on the following: 6
Delivery of electrons from NADH and FADH2:
Demerol inhibits delivery of electrons from NADH
Carboxin inhibits delivery of electrons from FADH2
Antimycin A inhibits both. Credit was given if the answer states that ActA has no direct effect on
electrons being delivered to Q QH2
Proton Gradient:
Demerol suppress all proton gradient from NADH but not from FADH2
Carboxin inhibits all proton pumping from FADH2 (which includes the protons normally pumped from
complexes III and IV) but not from NADH
Antimycin A inhibits proton pumping from both NADH and FADH2 (partial credit if one notes antimycin
A still produces 4H+ per NADH)
ATP synthesis:
All three reduce ATP synthesis. Actimycin A results in the least protons pumped, so reduces ATP
synthesis the most. Demerol causes a moderate decrease in ATP synthesis, and carboxin has the
smallest effect. These effects are directly related to the number of protons that can be pumped in the
presence of each drug.
10
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
7 continued.
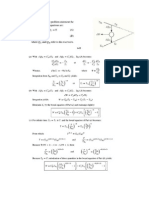
C. In the c subunit of F1 F0 ATP synthase, there is a conserved aspartate residue that binds to H+. If
the aspartate is mutated to a non-natural amino acid of equal size with a primary amine side chain,
what will happen to the rotation of the F0 subunit? 1
i. still rotate
ii. stop rotating
iii. rotate in the other direction
D. Electrons from NADH produced in the cytosol are transported to the mitochondria indirectly by the
malate-aspartate shuttle or the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle. 2
i. Why might the malate-asparate shuttle be preferred? (One sentence limit). More ATP
more efficient, NADH conserved
ii. Why is this shuttle not used by all cells? (One sentence limit). Reversible- it only works
when cytosolic NADH/NAD+ ratio is higher than mitochondrial NADH/NAD+ ratio.
Typical F1 F0 ATP synthase contains 12 c subunits and mitochondrial NADH adds 10 protons to the
gradient. Imagine that there is an organism that has 3 c subunits instead of 12.
E. In this organism, how many ATP can be produced from NADH oxidation? Please take into
account that the transport of ADP from cytoplasm to mitochondrial matrix consumes 1 H+.
______ 2
Answer: 3 H+ equals 3 ATP in this system. Thus 1 H+ = 1 ATP. And because of ADP transport, 1
more H+ is needed. Total 2 H+ per ATP. NADH=10 protons=5 ATP
REMEMBER TO WRITE YOUR JHED ID ON THE FOLLOWING PAGE
11
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
Tally Page-WRITE YOUR JHED ID ON THIS PAGE
page 2 ______________________ of 13
page 3 ______________________ of 11
page 4 ______________________ of 11
page 5 ______________________ of 12
page 6 ______________________ of 9
page 7 ______________________ of 11
page 8 ______________________ of 9
page 9 _____________________ of 10
page 10 _____________________ of 9
page 11 _____________________ of 5
-2 if no jhed ID ___________________
total _______________________ of 100
12
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
13
020.305 Exam 3 2013 Name _____________________________ jhed ID____________________________
SCRATCH PAGE
14
Вам также может понравиться
- Bach Floral Esoteric Remedies Self Healing WorkbookДокумент99 страницBach Floral Esoteric Remedies Self Healing Workbooksorin100% (9)
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionДокумент69 страницHUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionAyan Sarkar100% (1)
- Matlab Mathworks Data AnalysisДокумент167 страницMatlab Mathworks Data Analysisbob_mirkОценок пока нет
- C9e Answers Active Reading 07Документ7 страницC9e Answers Active Reading 07Daniel DHizzy Hizgilov83% (18)
- Chem 121 Chapter 22. Nucleic AcidsДокумент14 страницChem 121 Chapter 22. Nucleic Acidsnurain IsmailОценок пока нет
- Histology Lab Samplex RationaleДокумент13 страницHistology Lab Samplex RationaleFrances Dei100% (1)
- Renal Physiology Practice QuestionsДокумент4 страницыRenal Physiology Practice QuestionsAndiWilkinsОценок пока нет
- Comparsion of Lipid Profile in Diabetic Hypertensives VS Diabetic NormotensivesДокумент8 страницComparsion of Lipid Profile in Diabetic Hypertensives VS Diabetic NormotensivesIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- 01 Emryology The BeginningДокумент117 страниц01 Emryology The BeginningOsman Saidu SesayОценок пока нет
- Molecular BiologyДокумент54 страницыMolecular BiologyAnonymous GhQ1eIyxunОценок пока нет
- Hematology & Lymphoid System Study Guide - Y1 2025Документ43 страницыHematology & Lymphoid System Study Guide - Y1 2025Wahaj Mujahid100% (1)
- St. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Diagnostic Examination: Anatomy & Physiology December 15, 2018Документ6 страницSt. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Diagnostic Examination: Anatomy & Physiology December 15, 2018JoherОценок пока нет
- MCQ RespirationДокумент28 страницMCQ RespirationBonifacius Budi Nugroho100% (1)
- A. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean OilДокумент8 страницA. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean Oildrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Lect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54Документ74 страницыLect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54nopporn2520Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - QuestionsДокумент6 страницLecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - Questions中华雅思王Оценок пока нет
- Md2024 Physio SamplexДокумент11 страницMd2024 Physio SamplexSHAN-SHAN CHANGОценок пока нет
- As Biochemistry QuizДокумент7 страницAs Biochemistry QuizFati QuaynorОценок пока нет
- Mineral MetabolismДокумент24 страницыMineral Metabolismyasarc365Оценок пока нет
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsДокумент3 страницыSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirОценок пока нет
- Elle Canada 2010-03Документ203 страницыElle Canada 2010-03PontesDebora100% (1)
- 00018Документ92 страницы00018Fernandez-De Ala NicaОценок пока нет
- Past Life Returner - 01!1!150Документ150 страницPast Life Returner - 01!1!150Edgar Estebam Soto EstrellaОценок пока нет
- The Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysДокумент25 страницThe Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysXuân Vi100% (1)
- Physiology questions topic wiseДокумент18 страницPhysiology questions topic wisekoutharapu lasyapriyankaОценок пока нет
- Endicrine MCQ-QuestionsДокумент4 страницыEndicrine MCQ-QuestionsThe White Army100% (1)
- Histology Final ExamДокумент8 страницHistology Final Examliz gamezОценок пока нет
- Metabolism Lippincott's Q&AДокумент86 страницMetabolism Lippincott's Q&Alina amjadОценок пока нет
- Activity Book 2Документ14 страницActivity Book 2Josune Arévalo75% (4)
- Biopolymers/Natural polymers structure and propertiesДокумент78 страницBiopolymers/Natural polymers structure and propertiesgautamahujaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry - Final Exam Biology 020.305 December 15, 2011 Instructions For ExaminationДокумент11 страницBiochemistry - Final Exam Biology 020.305 December 15, 2011 Instructions For ExaminationJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionДокумент7 страницBiochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionTheo SantoОценок пока нет
- Cell Communication MechanismsДокумент4 страницыCell Communication MechanismsjanetotheohОценок пока нет
- Part I June 2013: 1. 1-The Physiological Dead SpaceДокумент20 страницPart I June 2013: 1. 1-The Physiological Dead SpaceHazim Rhman AliОценок пока нет
- Skeletal System ExamДокумент9 страницSkeletal System ExamBijay Kumar Mahato100% (1)
- Metabolism MCQ AДокумент0 страницMetabolism MCQ ASurajit BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- Cycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CycleДокумент6 страницCycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CyclejayrajsenОценок пока нет
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyДокумент79 страницNerve Muscle Physiologyroychanchal562100% (2)
- Important Seqs of Biochemistry For 1st Year Mbbs StudentsДокумент7 страницImportant Seqs of Biochemistry For 1st Year Mbbs Studentsdr saadia anjum0% (1)
- MCQ On Biochemistr2Документ3 страницыMCQ On Biochemistr2BassamSheryanОценок пока нет
- Biochem Chapter19a ProfДокумент8 страницBiochem Chapter19a ProfAnonymous t5TDwdОценок пока нет
- Complex Lipid MetabolismДокумент46 страницComplex Lipid MetabolismkalloliОценок пока нет
- The Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionДокумент12 страницThe Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionSimón JimenezОценок пока нет
- Basic Structure and Functions of the GI TractДокумент10 страницBasic Structure and Functions of the GI TractDwi Rezky AmaliaОценок пока нет
- MCQSДокумент25 страницMCQSkays30002403Оценок пока нет
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComДокумент74 страницыMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Physiology QB - Human SystemsДокумент1 страницаAnatomy & Physiology QB - Human SystemsmanasОценок пока нет
- Second Year ExamДокумент4 страницыSecond Year ExamSyamil AzharОценок пока нет
- Practice Questions From LectureДокумент4 страницыPractice Questions From LectureJeevikaGoyalОценок пока нет
- 2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTДокумент40 страниц2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTjabirОценок пока нет
- Important Physiology Questions For 2nd Year Mbbs Students by Dr. RoomiДокумент1 страницаImportant Physiology Questions For 2nd Year Mbbs Students by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiОценок пока нет
- Ganong Physiology 21eДокумент1 страницаGanong Physiology 21eprasun_v0% (1)
- Concepts in Biochemistry2Документ38 страницConcepts in Biochemistry2atefmaboodОценок пока нет
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidДокумент9 страницLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarОценок пока нет
- Biochem QbankДокумент16 страницBiochem Qbank786waqar786Оценок пока нет
- Ipsr Biochem Board Question No AnswersДокумент18 страницIpsr Biochem Board Question No AnswersCatherine RiaОценок пока нет
- 054 Physiology MCQ ACEM Primary RenalДокумент1 страница054 Physiology MCQ ACEM Primary RenalYasif AbbasОценок пока нет
- Anatomy-1 PDFДокумент50 страницAnatomy-1 PDFSaransh Ghimire100% (1)
- Quiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYДокумент13 страницQuiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Osmolarity vs OsmolalityДокумент13 страницOsmolarity vs OsmolalityBurhan HameedОценок пока нет
- Human Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 2014Документ5 страницHuman Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 2014api-279830436Оценок пока нет
- PG TRB Zoology Revision Test Unit IV and VДокумент13 страницPG TRB Zoology Revision Test Unit IV and VRoopa Roopavathy100% (1)
- 15 Lecture 3 Endo 2 Tutorial PDFДокумент2 страницы15 Lecture 3 Endo 2 Tutorial PDFFafa MusОценок пока нет
- BIOC 307 Old Exam 1Документ17 страницBIOC 307 Old Exam 1Katie RoseОценок пока нет
- 200L Excitable Tissues & Ans PhysiologyДокумент65 страниц200L Excitable Tissues & Ans PhysiologyAdedolapo bello100% (1)
- Handbook of Endocrine Research TechniquesОт EverandHandbook of Endocrine Research TechniquesFlora de PabloОценок пока нет
- L34 Post Class NotesДокумент3 страницыL34 Post Class NotesJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- 02 Transactions 1Документ61 страница02 Transactions 1Jenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Homework 4 SolutionsДокумент6 страницHomework 4 SolutionsJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Lesson 7Документ1 страницаStudy Guide Lesson 7Jenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Close Open Systems HimmelДокумент2 страницыClose Open Systems HimmelJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- JHU Biochem - Exam 2 - 2013Документ11 страницJHU Biochem - Exam 2 - 2013Jenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Close Open Systems HimmelДокумент2 страницыClose Open Systems HimmelJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Galvanic Cells 2014Документ4 страницыGalvanic Cells 2014Jenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Close Open Systems HimmelДокумент2 страницыClose Open Systems HimmelJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Degree of Freedom AnalysisДокумент1 страницаDegree of Freedom AnalysisJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Mutations in Kir2.1AndersenSyndromeДокумент9 страницMutations in Kir2.1AndersenSyndromeJenna ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Principles of BioassayДокумент17 страницPrinciples of BioassayUmasankar KulandaiveluОценок пока нет
- Apeejay School, Sheikh Sarai-I Holiday Homework - 2016 Class - Xi EnglishДокумент12 страницApeejay School, Sheikh Sarai-I Holiday Homework - 2016 Class - Xi Englishbalamurali_aОценок пока нет
- Humphries Sex DeterminationДокумент34 страницыHumphries Sex DeterminationJhonny Huaraquispe HipolitoОценок пока нет
- DNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapДокумент1 страницаDNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapVibhav SinghОценок пока нет
- Peter Et Al. 1972 - Fiber Types Guinea Pigs&RabbitsДокумент7 страницPeter Et Al. 1972 - Fiber Types Guinea Pigs&RabbitsQuintanaОценок пока нет
- Class 4Документ7 страницClass 4Ajay kuhireОценок пока нет
- Hema II Chapter 3 - Anemiarev - ATДокумент154 страницыHema II Chapter 3 - Anemiarev - AThannigadah7Оценок пока нет
- 02 The Biology of MindДокумент74 страницы02 The Biology of MinderhetzОценок пока нет
- PapersДокумент25 страницPapersMush TОценок пока нет
- THORAXДокумент27 страницTHORAXOleashedОценок пока нет
- Manual of Fisheries Science Part 2Документ67 страницManual of Fisheries Science Part 2daniralОценок пока нет
- Immortality From The Scientific Point of ViewДокумент38 страницImmortality From The Scientific Point of ViewpustoshkinОценок пока нет
- Scicent AB TE U4 eДокумент28 страницScicent AB TE U4 erayckng2Оценок пока нет
- Tsingy de Bemaraha's Limestone Peaks and Rare WildlifeДокумент5 страницTsingy de Bemaraha's Limestone Peaks and Rare Wildlifebharath_mv7-1Оценок пока нет
- City School Science WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCity School Science WorksheetIrram RanaОценок пока нет
- LABORATORY CLASSIFICATIONДокумент5 страницLABORATORY CLASSIFICATIONRoselie Mae GarciaОценок пока нет
- Nevada Sagebrush Archives 03/05/13Документ16 страницNevada Sagebrush Archives 03/05/13The Nevada SagebrushОценок пока нет
- MICROBIAL GROWTH AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIONДокумент43 страницыMICROBIAL GROWTH AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIONMichal VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Cell DivisionДокумент10 страницCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.Оценок пока нет
- Radiometric Dating of Rocks and FossilsДокумент3 страницыRadiometric Dating of Rocks and FossilsDaniel50% (2)
- Activity 2 - Making Venn DiagramДокумент3 страницыActivity 2 - Making Venn DiagramVea Ann CantollasОценок пока нет
- KEY - Experimetnal ScenariosДокумент2 страницыKEY - Experimetnal ScenariosArabellaОценок пока нет
- General Surgery Exam Syllabus BlueprintДокумент59 страницGeneral Surgery Exam Syllabus BlueprintSamiaNazОценок пока нет
- B12 Assay MethodДокумент3 страницыB12 Assay Methodtrs22Оценок пока нет