Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aldo Ster One
Загружено:
ZiedTrikiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aldo Ster One
Загружено:
ZiedTrikiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aldosterone
21
12
19
2
3
HO
1
4
11
24
22
17
15
26
Mineralocorticoids
25
23
16
14
10
20
18
13
O
OH
HO
17,20 lyase
HO
OH
OH
OH
11-deoxycortisol
OH
O
OH
HO
Androstenedione
17-HSD
OH
Estrone
HO
OH
Testosterone
O
s)
on
arb
8c
s (1
en
og
Dihydrotestosterone
H
(21 carbons)
OH
OH
Estriol
HO
Estradiol
HO
tr
Es
O
Glucocorticoids
OH
Cellular location
of enzymes
Mitochondria
Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
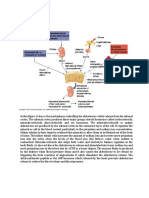
Steroidogenesis, showing aldosterone synthesis at upper-right
corner
1.1 Stimulation
Aldosterone synthesis is stimulated by several factors:
It was rst isolated by Simpson and Tait in 1953.[3]
OH
5-reductase
Drugs that interfere with the secretion or action of aldosterone are in use as antihypertensives, like lisinopril,
which lowers blood pressure by blocking the angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE), leading to lower aldosterone
secretion. The net eect of these drugs is to reduce
sodium and water retention but increase retention of
potassium. Aldosterone is part of the renin-angiotensin
system. Another example is spironolactone, a potassiumsparing diuretic, which decreases blood pressure by releasing uid from the body while retaining potassium.
Corticosterone
Cortisol
Androstenediol
HO
OH
O
HO
(liver and placenta)
Dehydroepiandrosterone
17-hydroxy
progesterone
Aromatase
Androgens (19 carbons)
Aldosterone
synthase
OH
DeoxyO
corticosterone
21-hydroxylase
17-hydroxy
pregnenolone
3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3-HSD)
Progestagens (21 carbons)
Pregnenolone
17-hydroxylase
Aldosterone
Progesterone O
OH
HO
Cholesterol
Cholesterol side-chain
cleavage enzyme
HO
O O
(21 carbons)
27
11-hydroxylase
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone (mineralocorticoid
family) produced by the outer section (zona glomerulosa)
of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland.[1][2] It plays
a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly
by acting on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the
nephron, increasing reabsorption of ions and water in the
kidney, to cause the conservation of sodium, secretion
of potassium, increase in water retention, and increase
in blood pressure and blood volume.[1] When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the
development and progression of cardiovascular and renal
disease.[2] Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function
of the atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart.[1]
increase in the plasma concentration of angiotensin
III, a metabolite of angiotensin II
increase in plasma angiotensin II, ACTH, or
potassium levels, which are present in proportion to
plasma sodium deciencies. (The increased potassium level works to regulate aldosterone synthesis
by depolarizing the cells in the zona glomerulosa,
which opens the voltage-dependent calcium channels.) The level of angiotensin II is regulated by
angiotensin I, which is in turn regulated by renin,
an enzyme secreted in the kidneys. Potassium levels
are the most sensitive stimulator of aldosterone.
Synthesis
The corticosteroids are synthesized from cholesterol
within the zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex. Most
steroidogenic reactions are catalysed by enzymes of the
cytochrome P450 family. They are located within the
mitochondria and require adrenodoxin as a cofactor (except 21-hydroxylase and 17-hydroxylase).
Aldosterone and corticosterone share the rst part of their
biosynthetic pathways. The last parts are mediated either by the aldosterone synthase (for aldosterone) or by
the 11-hydroxylase (for corticosterone). These enzymes
are nearly identical (they share 11-hydroxylation and 18hydroxylation functions), but aldosterone synthase is also
able to perform an 18-oxidation. Moreover, aldosterone
synthase is found within the zona glomerulosa at the outer
edge of the adrenal cortex; 11-hydroxylase is found in
the zona fasciculata and reticularis.
the ACTH stimulation test, which is sometimes used
to stimulate the production of aldosterone along
with cortisol to determine whether primary or secondary adrenal insuciency is present. However,
ACTH has only a minor role in regulating aldosterone production; with hypopituitarism there is no
atrophy of the zona glomerulosa.
Note: aldosterone synthase is absent in other sections of
the adrenal gland.
the stretch receptors located in the atria of the heart.
If decreased blood pressure is detected, the adrenal
plasma acidosis
4 CONTROL OF ALDOSTERONE RELEASE FROM THE ADRENAL CORTEX
gland is stimulated by these stretch receptors to re- Aldosterone, probably acting through mineralocorticoid
lease aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorp- receptors, may positively inuence neurogenesis in the
tion from the urine, sweat, and the gut. This causes dentate gyrus.[9]
increased osmolarity in the extracellular uid, which
will eventually return blood pressure toward normal.
3 Location of receptors
adrenoglomerulotropin, a lipid factor, obtained from
pineal extracts. It selectively stimulates secretion of
Steroid receptors are intracellular. The aldosterone minaldosterone.[4]
eralcorticoid receptor complex binds on the DNA to specic hormone response element, which leads to gene speThe secretion of aldosterone has a diurnal rhythm.[5]
cic transcription.
Some of the transcribed genes are crucial for transepithelial sodium transport, including the three subunits of the
2 Function
epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), the Na+ /K+ pumps
and their regulatory proteins serum and glucocorticoidAldosterone is the primary of several endogenous mem- induced kinase, and channel-inducing factor, respecbers of the class of mineralocorticoids in humans. tively.
Deoxycorticosterone is another important member of this
class. Aldosterone tends to promote Na+ and water reten- The mineralcorticoid receptor is stimulated by both altion, and lower plasma K+ concentration by the following dosterone and cortisol, but a mechanism protects the
body from excess aldosterone receptor stimulation by
mechanisms:
glucocorticoids (such as cortisol), which happen to be
present at much higher concentrations than mineralcorti1. Acting on the nuclear mineralocorticoid receptors
coids in the healthy individual. The mechanism consists
(MR) within the principal cells of the distal tubule
of an enzyme called 11 -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
and the collecting duct of the kidney nephron, it
+
+ (11 -HSD). This enzyme co-localizes with intracellular
upregulates and activates the basolateral Na /K
adrenal steroid receptors and converts cortisol into cortipumps, which pumps three sodium ions out of the
sone, a relatively inactive metabolite with little anity for
cell, into the interstitial uid and two potassium ions
the MR. Liquorice, which contains glycyrrhetinic acid,
into the cell from the interstitial uid. This crecan inhibit 11 -HSD and lead to a mineralcorticoid exates a concentration gradient which results in reabcess syndrome.
+
sorption of sodium (Na ) ions and water (which follows sodium) into the blood, and secreting potassium (K+ ) ions into the urine (lumen of collecting
4 Control of aldosterone release
duct).
2. Aldosterone upregulates epithelial sodium channels
(ENaCs), increasing apical membrane permeability
for Na+ .
4.1
from the adrenal cortex
Major regulators
3. Cl is reabsorbed in conjunction with sodium
cations to maintain the systems electrochemical bal- 4.1.1 The role of the renin-angiotensin system
ance.
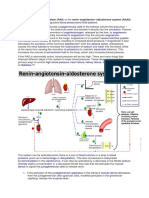
Angiotensin is involved in regulating aldosterone and is
4. Aldosterone stimulates the secretion of K+ into the the core regulation.[11] Angiotensin II acts synergistically
tubular lumen.[6]
with potassium, and the potassium feedback is virtually inoperative when no angiotensin II is present.[12] A
5. Aldosterone stimulates Na+ and water reabsorption
small portion of the regulation resulting from angiotensin
from the gut, salivary and sweat glands in exchange
II must take place indirectly from decreased blood ow
for K+ .
through the liver due to constriction of capillaries.[13]
6. Aldosterone stimulates secretion of H+ in exchange When the blood ow decreases so does the destruction
for K+ in the intercalated cells of the cortical collect- of aldosterone by liver enzymes.
ing tubules, regulating plasma bicarbonate (HCO3 ) Although sustained production of aldosterone requires
levels and its acid/base balance.[7]
persistent calcium entry through low-voltage-activated
Ca2+ channels, isolated zona glomerulosa cells are considAldosterone is responsible for the reabsorption of about ered nonexcitable, with recorded membrane voltages that
2% of ltered sodium in the kidneys, which is nearly are too hyperpolarized to permit Ca2+ channels entry.[2]
equal to the entire sodium content in human blood un- However, mouse zona glomerulosa cells within adrenal
slices spontaneously generate membrane potential osder normal glomerular ltration rates.[8]
4.3
Aldosterone feedback
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
4.2.1 The role of sympathetic nerves
Hypothalamus of brain
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
Pituitary gland
Thirst
Antidiuretic hormone
+
+
ACTH
Vasoconstriction of
blood vessels
Effective +
circulating
volume
Angiotensin II
ACE
in lungs
Extracellular
fluid +
volume
High plasma K
Blood +
pressure
Liver
Adrenals
Aldosterone
Kidneys
H O excretion K excretion +
4.2.2 The role of baroreceptors
Na+ excretion
2
Angiotensinogen
Angiotensin I
Renin
The renin-angiotensin system, showing role of aldosterone between the adrenal glands and the kidneys[10]
cillations of low periodicity; this innate electrical excitability of zona glomerulosa cells provides a platform
for the production of a recurrent Ca2+ channels signal
that can be controlled by angiotensin II and extracellular potassium, the 2 major regulators of aldosterone
production.[2] Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels have been detected in the zona glomerulosa of the human adrenal,
which suggests that Ca2+ channel blockers may directly
inuence the adrenocortical biosynthesis of aldosterone
in vivo. [14]
4.1.2
The aldosterone production is also aected to one extent
or another by nervous control, which integrates the inverse of carotid artery pressure,[17] pain, posture,[21] and
probably emotion (anxiety, fear, and hostility)[24] (including surgical stress).[25] Anxiety increases aldosterone,[24]
which must have evolved because of the time delay involved in migration of aldosterone into the cell
nucleus.[26] Thus, there is an advantage to an animals anticipating a future need from interaction with a predator,
since too high a serum content of potassium has very adverse eects on nervous transmission.
The plasma concentration of potassium
Pressure-sensitive baroreceptors are found in the vessel
walls of nearly all large arteries in the thorax and neck,
but are particularly plentiful in the sinuses of the carotid
arteries and in the arch of the aorta. These specialized receptors are sensitive to changes in mean arterial pressure.
An increase in sensed pressure results in an increased rate
of ring by the baroreceptors and a negative feedback response, lowering systemic arterial pressure. Aldosterone
release causes sodium and water retention, which causes
increased blood volume, and a subsequent increase in
blood pressure, which is sensed by the baroreceptors.[27]
To maintain normal homeostasis these receptors also detect low blood pressure or low blood volume, causing aldosterone to be released. This results in sodium retention
in the kidney, leading to water retention and increased
blood volume.[28]
4.2.3 The plasma concentration of sodium
Aldosterone is a function of the inverse of the sodium intake as sensed via osmotic pressure.[29] The slope of the
The amount of aldosterone secreted is a direct function response of aldosterone to serum potassium is almost inof the serum potassium[15][16] as probably determined by dependent of sodium intake.[30] Aldosterone is much insensors in the carotid artery.[17][18]
creased at low sodium intakes, but the rate of increase of
plasma aldosterone as potassium rises in the serum is not
much lower at high sodium intakes than it is at low. Thus,
4.1.3 ACTH
the potassium is strongly regulated at all sodium intakes
by aldosterone when the supply of potassium is adequate,
ACTH, a pituitary peptide, also has some stimuwhich it usually is in primitive diets.
lating eect on aldosterone, probably by stimulating the formation of deoxycorticosterone, a precursor
of aldosterone.[19] Aldosterone is increased by blood
loss,[20] pregnancy,[21] and possibly by other circum4.3 Aldosterone feedback
stances such as physical exertion, endotoxin shock, and
burns.[22][23]
Feedback by aldosterone concentration itself is of a nonmorphological character (that is, other than changes in
the cells number or structure) and is poor, so the elec4.2 Miscellaneous regulators
trolyte feedbacks predominate, short term.[22]
Associated clinical conditions
Hyperaldosteronism is abnormally increased levels of aldosterone, while hypoaldosteronism is abnormally decreased levels of aldosterone.
A measurement of aldosterone in blood may be termed
a plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC), which may
be compared to plasma renin activity (PRA) as an
aldosterone-to-renin ratio.
5.1
Hyperaldosteronism
Primary aldosteronism, also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, is characterized by the overproduction of aldosterone by the adrenal glands,[31] when not a result of
excessive renin secretion. It leads to arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) associated with hypokalemia,
usually a diagnostic clue. Secondary hyperaldosteronism,
on the other hand, is due to overactivity of the reninangiotensin system.
REFERENCES
122 (6): 20462053. doi:10.1172/JCI61996. PMID
22546854.
[3] Williams JS, Williams GH (June 2003). 50th anniversary of aldosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88
(6): 236472. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030490. PMID
12788829.
[4] Farrell G (May 1960). Adrenoglomerulotropin. Circulation 21 (5): 100915. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.21.5.1009.
PMID 13821632.
[5] Hurwitz S, Cohen RJ, Williams GH (April 2004).
Diurnal variation of aldosterone and plasma renin activity: timing relation to melatonin and cortisol and consistency after prolonged bed rest. J App Physiol 96 (4):
140614. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00611.2003. PMID
14660513.
[6] Palmer, LG; Frindt, G (2000). Aldosterone and potassium secretion by the cortical collecting duct. Kidney international 57 (4): 13248. doi:10.1046/j.15231755.2000.00970.x. PMID 10760062.
Conns syndrome is primary hyperaldosteronism caused
by an aldosterone-producing adenoma.
[7] Rector, Floyd C.; Brenner, Barry M. (2004). Brenner
& Rectors the kidney. Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 07216-0164-2. OCLC 51838812.
Depending on cause and other factors, hyperaldosteronism can be treated by surgery and/or medically, such as
by aldosterone antagonists.
[8] Sherwood, Lauralee (2001). Human physiology: from
cells to systems. Pacic Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole. ISBN
0-534-56826-2. OCLC 43702042.
5.2
Hypoaldosteronism
[9] Fischer AK, von Rosenstiel P, Fuchs E, Goula D, Almeida
OF, Czh B (August 2002). The prototypic mineralocorticoid receptor agonist aldosterone inuences neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adrenalectomized
rat. Brain Res. 947 (2): 2903. doi:10.1016/S00068993(02)03042-1. PMID 12176172.
An ACTH stimulation test for aldosterone can help in determining the cause of hypoaldosteronism, with a low aldosterone response indicating a primary hypoaldosteronism of the adrenals, while a large response indicating a [10] Page 866-867 (Integration of Salt and Water Balance) and
1059 (The Adrenal Gland) in: Walter F., PhD. Boron
secondary hypoaldosteronism.
Additional images
Corticosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rat
Corticosterone
See also
Mineralocorticoid
References
[1] Marieb Human Anatomy & Physiology 9th edition, chapter:16, page:629, question number:14
[2] Hu C, Rusin CG, Tan Z, Guagliardo NA, Barrett PQ (June
2012). Zona glomerulosa cells of the mouse adrenal
cortex are intrinsic electricaloscillators.. J Clin Invest.
(2003). Medical Physiology: A Cellular And Molecular
Approaoch. Elsevier/Saunders. p. 1300. ISBN 1-41602328-3.
[11] Williams GH, Dluhy RG (November 1972). Aldosterone
biosynthesis. Interrelationship of regulatory factors.
Am J Med 53 (5): 595605.
doi:10.1016/00029343(72)90156-8. PMID 4342886.
[12] Pratt JH (September 1982). Role of angiotensin II
in potassium-mediated stimulation of aldosterone secretion in the dog. J Clin Invest. 70 (3): 66772.
doi:10.1172/JCI110661. PMC 370270. PMID 6286729.
[13] Messerli FH, Nowaczynski W, Honda M, et al. (February
1977). Eects of angiotensin II on steroid metabolism
and hepatic blood ow in man. Circulation Research
40 (2): 2047. doi:10.1161/01.RES.40.2.204. PMID
844145.
[14] Felizola SJA, Maekawa T, Nakamura Y, Satoh F, Ono
Y, Kikuchi K, Aritomi S, Ikeda K, Yoshimura M, Tojo
K, Sasano H. (2014). Voltage-gated calcium channels in the human adrenal and primary aldosteronism..
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 144 (part B): 410416.
doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.08.012. PMID 25151951.
[15] Bauer JH, Gauntner WC (March 1979). Eect of potassium chloride on plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone during sodium restriction in normal man. Kidney Int. 15 (3): 28693. doi:10.1038/ki.1979.37. PMID
513492.
[30] Dluhy RG, Axelrod L, Underwood RH, Williams GH
(August 1972). Studies of the control of plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man: II. Eect of dietary
potassium and acute potassium infusion. J Clin Invest.
51 (8): 19507. doi:10.1172/JCI107001. PMC 292351.
PMID 5054456.
[16] Linas SL, Peterson LN, Anderson RJ, Aisenbrey GA, Simon FR, Berl T (June 1979). Mechanism of renal potassium conservation in the rat. Kidney Int. 15 (6): 60111.
doi:10.1038/ki.1979.79. PMID 222934.
[31] Conn JW, Louis LH (1955). Primary aldosteronism: a
new clinical entity. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 68:
21531; discussion, 2313. PMID 13299331.
[17] Gann DS Mills IH Bartter 1960 On the hemodynamic parameter mediating increase in aldosterone secretion in the
dog. Fed. Proceedings 19; 605610.
9 External links
[18] Gann DS, Cruz JF, Casper AG, Bartter FC (May 1962).
Mechanism by which potassium increases aldosterone
secretion in the dog. Am J Physiol. 202: 9916. PMID
13896654.
[19] Brown RD, Strott CA, Liddle GW (June 1972). Site
of stimulation of aldosterone biosynthesis by angiotensin
and potassium. J Clin Invest. 51 (6): 14138.
doi:10.1172/JCI106937. PMC 292278. PMID 4336939.
[20] Ruch TC Fulton JF 1960 Medical Physiology and Biophysics. W.B. Saunders and Co., Phijl & London. On
p1099.
[21] Farrell G (October 1958). Regulation of aldosterone secretion. Physiological Reviews 38 (4): 70928. PMID
13590935.
[22] Vecsei, Pl; Glz, Edith (1971). Aldosterone. New York:
Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-013368-1. OCLC 186705.
[23] Farrell GL, Rauschkolb EW (November 1956). Evidence for diencephalic regulation of aldosterone secretion. Endocrinology 59 (5): 52631. doi:10.1210/endo59-5-526. PMID 13375573. on 529
[24] Venning EH, DyrenfurthY I, Beck JC (August 1957).
Eect of anxiety upon aldosterone excretion in
man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 17 (8): 10058.
doi:10.1210/jcem-17-8-1005. PMID 13449153.
[25] Elman R, Shatz BA, Keating RE, Weichselbaum TE (July
1952). Intracellular and Extracellular Potassium Decits
in Surgical Patients. Annals of surgery 136 (1): 111
31. doi:10.1097/00000658-195208000-00013. PMC
1802239. PMID 14934025.
[26] Sharp GUG Leaf A 1966 in; Recent Progress in Hormone
Research.(Pincus G, ed.
[27] Copstead, E. C. & Banasik, J. L. (2010.) Pathophysiology. (4th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Saunders Elsevier.
[28] Marieb, E. N. (2004) Human anatomy and physiology
(6th ed) San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
[29] Schneider EG, Radke KJ, Ulderich DA, Taylor RE (April
1985). Eect of osmolality on aldosterone secretion.
Endocrinology 116 (4): 16216. doi:10.1210/endo-1164-1621. PMID 3971930.
Aldosterone at Lab Tests Online
10
10
10.1
TEXT AND IMAGE SOURCES, CONTRIBUTORS, AND LICENSES
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
Text
Aldosterone Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosterone?oldid=643623106 Contributors: AxelBoldt, Bryan Derksen, Andre Engels, Mac, Ugen64, Emperorbma, Whcernan, Robbot, Altenmann, Yelyos, Stewartadcock, Fuelbottle, Diberri, Giftlite, Ksheka, SoCal,
Michael Devore, Bensaccount, Jfdwol, Antandrus, Mr Bound, Rich Farmbrough, Petersam, Bobo192, Wood Thrush, Arcadian, HasharBot, Alansohn, Benjah-bmm27, Drbreznjev, Dan100, Bignoter, Eleassar777, Rjwilmsi, The wub, FlaBot, Margosbot, Physchim62, Benlisquare, Karsten Adam, Bubbachuck, YurikBot, RussBot, Princessamoeba, Spaully, Hede2000, Shaddack, Wimt, , Razol2,
Epipelagic, Theda, KnightRider, Unschool, Edgar181, Chris the speller, RDBrown, Adun12, Uthbrian, UberMD, Gregnz, HansThane,
Drphilharmonic, Jabronimus, FrozenMan, Beetstra, Cajolingwilhelm, Brianf711, Courcelles, Tawkerbot2, Fvasconcellos, Tpjv86b, Anthonyhcole, Thijs!bot, Peter morrell, CopperKettle, N5iln, Codsears, Xerophon, AntiVandalBot, Settersr, Spencer, JAnDbot, MER-C,
Triviaa, Hamsterlopithecus, Bsehn, Isoptera, Mbc362, Ling.Nut, Rich257, WhatamIdoing, AdoreMila, MartinBot, Nono64, Leyo, Nbauman, Faldizzle, Woochiao, Mikael Hggstrm, SS1981, Lanternix, Jepoirrier, Eshywiki, Mowtown philippe, Idioma-bot, VolkovBot,
DancingMan, Philip Trueman, TXiKiBoT, Spuntyb, Sintaku, BotMultichill, Gerakibot, Chrisgj, Mike2vil, Bogwhistle, Chem-awb, Animeronin, ClueBot, Cab.jones, A3camero, Sarindam7, DerBorg, DumZiBoT, Captain108, Vanished 45kd09la13, Facts707, MystBot, Addbot, AkhtaBot, Diptanshu.D, Orlandoturner, Shakiestone, Kisbesbot, Ambience3, Ssschhh, Epop fr, Frehley, Luckas-bot, Vedran12,
Yobot, CheMoBot, Amirobot, Anypodetos, Citation bot, Xqbot, Thatfeel, OlaIsacsson, FrescoBot, Jonesey95, Orenburg1, TobeBot, John
of Reading, Dcirovic, ZroBot, , DemonicPartyHat, Louisajb, ClueBot NG, H12321, Pashihiko, Widr, BG19bot, Sahara4u, MusikAnimal, Meclee, Dr Bilal Alshareef, Rob Hurt, KugelaP, Jeremy112233, Luckydhaliwal, Graphium, Herizora, Csmith0434, Arripay, Brainiacal, Monkbot, Odd Hglund (SLU), TheFunkyHobo, Medgirl131 and Anonymous: 135
10.2
Images
File:Aldosterone-2D-skeletal.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ea/Aldosterone-2D-skeletal.svg License:
Public domain Contributors: Vector version of Image:Aldosterone-2D-skeletal.png. Original artist: Image:Aldosterone-2D-skeletal.png
by Ben Mills, vectorized by Fvasconcellos (talk contribs)
File:Renin-angiotensin_system_in_man_shadow.svg
Source:
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7c/
Renin-angiotensin_system_in_man_shadow.svg License: Public domain Contributors: All used images are in public domain. Original artist: Mikael Hggstrm
File:Steroidogenesis.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/13/Steroidogenesis.svg License: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Contributors: Self-made using bkchem and inkscape Original artist: David Richeld (User:Slashme) and Mikael Hggstrm. Derived
from previous version by Homeier and Settersr.
File:X_mark.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a2/X_mark.svg License: Public domain Contributors: Own
work Original artist: User:Gmaxwell
File:Yes_check.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/fb/Yes_check.svg License: ? Contributors: ? Original artist: ?
10.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Вам также может понравиться
- Mineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SДокумент42 страницыMineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SShajeer SalimОценок пока нет
- Mineralocorticoid - AldosteoneДокумент17 страницMineralocorticoid - AldosteoneExplore Life ScienceОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanДокумент18 страницAdrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDrFarah Emad Ali100% (1)
- Mineral o CorticoidsДокумент20 страницMineral o CorticoidsAayush AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Pi Is 1548559517301222Документ7 страницPi Is 1548559517301222Obito AkatsukiОценок пока нет
- Adrenal GlandДокумент46 страницAdrenal GlandhSANОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesДокумент21 страницаAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjОценок пока нет
- Water Reabsorption and Blood Pressure Regulation via ADH and Renin-Angiotensin Pathways (39Документ13 страницWater Reabsorption and Blood Pressure Regulation via ADH and Renin-Angiotensin Pathways (39rajeshОценок пока нет
- ADRENAL GLAND X.PPTX - 1Документ23 страницыADRENAL GLAND X.PPTX - 1b29jcqnfn9Оценок пока нет
- Regulation of Aldosterone Secretion: Scott M. Mackenzie, Josie C. Van Kralingen, Eleanor DaviesДокумент23 страницыRegulation of Aldosterone Secretion: Scott M. Mackenzie, Josie C. Van Kralingen, Eleanor DaviesRaisa MeloОценок пока нет
- Hormones of The Adrenal Cortex 1-13Документ47 страницHormones of The Adrenal Cortex 1-13abstabs50% (2)
- Adrenal Cortex Functions & Disorders GuideДокумент80 страницAdrenal Cortex Functions & Disorders Guidevihang146Оценок пока нет
- Kid and 2 CatsДокумент33 страницыKid and 2 Catsastrid shabrinaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceДокумент5 страницChapter 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDawlat SalamaОценок пока нет
- Questions From Exam 08.09.22Документ12 страницQuestions From Exam 08.09.22Ismo SОценок пока нет
- KidneyДокумент14 страницKidneypromisearinzechi4Оценок пока нет
- Renal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GДокумент55 страницRenal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GAmanuel DinaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 20 Notes 2018Документ6 страницLecture 20 Notes 2018Omed ZarifiОценок пока нет
- Homeostatic mechanisms that regulate temperature, blood glucose, blood gases, blood oxygen, and arterial blood pressure in humansДокумент8 страницHomeostatic mechanisms that regulate temperature, blood glucose, blood gases, blood oxygen, and arterial blood pressure in humansT SeriesОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland by Dr. Rajnee IInd PartДокумент30 страницAdrenal Gland by Dr. Rajnee IInd Part9460106212Оценок пока нет
- Aldo Ster OneДокумент2 страницыAldo Ster OneAimmi Champ'sОценок пока нет
- DocumentДокумент1 страницаDocumentJOSHUA TALLORINОценок пока нет
- SiadhДокумент16 страницSiadhGokul Rajan100% (1)
- Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Hyperkalemia PDFДокумент9 страницPathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Hyperkalemia PDFJbarrianОценок пока нет
- Part 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryДокумент34 страницыPart 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryFarah Bashar Al-RawachyОценок пока нет
- 25.9 Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxДокумент4 страницы25.9 Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforОценок пока нет
- NADPH Oxidase-Derived H2O2 Contributes To Angiotensin II-Induced Aldosterone Synthesis in Human and Rat Adrenal Cortical CellsДокумент15 страницNADPH Oxidase-Derived H2O2 Contributes To Angiotensin II-Induced Aldosterone Synthesis in Human and Rat Adrenal Cortical CellsSENTHILKUMAR B RAJAMOHANОценок пока нет
- General Principles of Tubular ReabsorptionДокумент54 страницыGeneral Principles of Tubular ReabsorptionRalph JacintoОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland Structure and Hormone FunctionsДокумент16 страницAdrenal Gland Structure and Hormone FunctionsSalman KhanОценок пока нет
- Renal System PPT (Pharmacology)Документ100 страницRenal System PPT (Pharmacology)Cheska DillupacОценок пока нет
- Adrenocortical HormonesДокумент5 страницAdrenocortical HormonesHala RezaОценок пока нет
- Adrenocortical HormonesДокумент77 страницAdrenocortical HormonesMaxamed Faarax XaashiОценок пока нет
- Body Fluids: M. Alif Prizarky 04011381419173 GammaДокумент7 страницBody Fluids: M. Alif Prizarky 04011381419173 GammaAlviss RmidОценок пока нет
- 1 DiurethicsДокумент8 страниц1 DiurethicsMoataz TrabehОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент6 страницAssignmentleone shikukuОценок пока нет
- 101 OHara PDFДокумент11 страниц101 OHara PDFAntonio Lopez HernandezОценок пока нет
- Physiology RAASДокумент3 страницыPhysiology RAASAulia Mahya FaradisaОценок пока нет
- Renal Extra Notes: Total Body Water (TBW) 0.6 X Body WeightДокумент3 страницыRenal Extra Notes: Total Body Water (TBW) 0.6 X Body WeightKhaing26Оценок пока нет
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент17 страницOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorОценок пока нет
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент17 страницOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorОценок пока нет
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент17 страницOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCОценок пока нет
- 10 Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Документ4 страницы10 Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)saleem9242ssОценок пока нет
- UrinaryДокумент87 страницUrinaryJohn Paolo Dalida SalazarОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of Kidneys and UrineДокумент18 страницBiochemistry of Kidneys and UrineAndrias PutriОценок пока нет
- Renin - Angiotensin System RAS Renin - Angiotensin-Aldosterone System RaasДокумент3 страницыRenin - Angiotensin System RAS Renin - Angiotensin-Aldosterone System RaasReynaKatОценок пока нет
- Adrenocortical HormonesДокумент46 страницAdrenocortical HormoneschayChay gapolОценок пока нет
- Cholesterol: Synthesis and MetabolismДокумент45 страницCholesterol: Synthesis and MetabolismSoffa ShmuelОценок пока нет
- ReninДокумент3 страницыReninAli GalaОценок пока нет
- BSFCR Cardio Case Group 1Документ23 страницыBSFCR Cardio Case Group 1Qurrataini IbanezОценок пока нет
- Aldosterone, A Vasculotoxic Agent-Novel Functions For An Old HormoneДокумент4 страницыAldosterone, A Vasculotoxic Agent-Novel Functions For An Old HormoneNhung NguyenОценок пока нет
- Renin-Angiotensin System: Navigation SearchДокумент5 страницRenin-Angiotensin System: Navigation SearchArchit PatelОценок пока нет
- ADRENOCORTICAL HORMONES PhysiologyДокумент12 страницADRENOCORTICAL HORMONES PhysiologyHameer Saif TalpurОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About DiureticsДокумент48 страницEverything You Need to Know About DiureticsRuturaj DesaiОценок пока нет
- Renal Physiology and FunctionДокумент4 страницыRenal Physiology and FunctionDayledaniel Sorveto100% (1)
- Endocrine 3Документ115 страницEndocrine 3Dessalegn LemmaОценок пока нет
- Control of Extracellular Fluid Volume by The KidneyppДокумент28 страницControl of Extracellular Fluid Volume by The KidneyppLilian EdeniОценок пока нет
- Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Hyperkalemia: Educational ReviewДокумент8 страницPathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Hyperkalemia: Educational ReviewAlvaro FloresОценок пока нет
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansОт EverandAcid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansAngela Randels-ThorpОценок пока нет
- MYD Progressive Cerebellar Ataxia in An Adult DogДокумент5 страницMYD Progressive Cerebellar Ataxia in An Adult DogZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Tumor Suppressor GeneДокумент3 страницыTumor Suppressor GeneZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Tumor Antigen: 1 Mechanism of Tumor AntigenesisДокумент3 страницыTumor Antigen: 1 Mechanism of Tumor AntigenesisZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 7adrenal MedullaДокумент3 страницы7adrenal MedullaZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceДокумент4 страницыElectrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceZiedTriki100% (1)
- 2 Structure: Tumor Protein p53, Also Known As p53, Cellular p53 (p53, Tumor Suppressor p53, Antigen NY-CO-13Документ21 страница2 Structure: Tumor Protein p53, Also Known As p53, Cellular p53 (p53, Tumor Suppressor p53, Antigen NY-CO-13ZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Brca2: 1 FunctionДокумент9 страницBrca2: 1 FunctionZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Hydro Cep Hal UsДокумент8 страницHydro Cep Hal UsZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Adly Diseases and Epidemics) Carmen Ferreiro-Mad Cow Disease-Chelsea House Publishers (2004)Документ125 страницAdly Diseases and Epidemics) Carmen Ferreiro-Mad Cow Disease-Chelsea House Publishers (2004)ZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Vomiting: 1 Complications 2 PathophysiologyДокумент8 страницVomiting: 1 Complications 2 PathophysiologyZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Urinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyДокумент8 страницUrinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Diarrhea: 1 DefinitionДокумент13 страницDiarrhea: 1 DefinitionZiedTriki100% (1)
- Electrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceДокумент4 страницыElectrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceZiedTriki100% (1)
- Intracranial Pressure: 2 Increased ICPДокумент6 страницIntracranial Pressure: 2 Increased ICPZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Intravenous Therapy: 1 Infused SubstancesДокумент10 страницIntravenous Therapy: 1 Infused SubstancesZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Sinus Rhythm: 2 Cardiac Conduction System and PathwayДокумент3 страницыSinus Rhythm: 2 Cardiac Conduction System and PathwayZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Dehydration: 2 Signs and SymptomsДокумент5 страницDehydration: 2 Signs and SymptomsZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia Causes and TreatmentДокумент3 страницыJunctional Ectopic Tachycardia Causes and TreatmentZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 14 CatecholamineДокумент5 страниц14 CatecholamineZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 23coronary Artery DiseaseДокумент10 страниц23coronary Artery DiseaseZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Atrial Utter: 2 PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыAtrial Utter: 2 PathophysiologyZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Adrenergic Receptors: Types, Functions and MechanismsДокумент5 страницAdrenergic Receptors: Types, Functions and MechanismsZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- P-glycoprotein Structure and FunctionДокумент5 страницP-glycoprotein Structure and FunctionZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Classification of Antiarrhythmic AgentsДокумент4 страницыClassification of Antiarrhythmic AgentsZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 18sodium Calcium ExchangerДокумент4 страницы18sodium Calcium ExchangerZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 17atrioventricular NodeДокумент3 страницы17atrioventricular NodeZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 15G Protein-Coupled ReceptorДокумент15 страниц15G Protein-Coupled ReceptorZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 11 HypotensionДокумент5 страниц11 HypotensionZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- 9vascular ResistanceДокумент3 страницы9vascular ResistanceZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- HP4. Endocrine System - 100 - Ethan HelmДокумент17 страницHP4. Endocrine System - 100 - Ethan HelmNorPhea - នភាОценок пока нет
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemДокумент84 страницыDisorders of The Endocrine Systemcy lifeОценок пока нет
- CBL HypertensionДокумент23 страницыCBL HypertensionWan AswanОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland Disorders ExplainedДокумент73 страницыAdrenal Gland Disorders ExplainedReunita ConstantiaОценок пока нет
- PyelonephritisДокумент59 страницPyelonephritisGheyl GabrielОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 Lippincott BiochemistryДокумент62 страницыChapter 18 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System OverviewДокумент9 страницEndocrine System OverviewNicole Ken AgdanaОценок пока нет
- Electrolytes and Related AbnormalitiesДокумент8 страницElectrolytes and Related AbnormalitiesKyla CastilloОценок пока нет
- And Its: Dr. V.PushkarДокумент92 страницыAnd Its: Dr. V.PushkarMudit MisraОценок пока нет
- 2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESДокумент32 страницы2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESGabrielle John HernaezОценок пока нет
- Hypertension Clinical Study PDFДокумент42 страницыHypertension Clinical Study PDFsertti23Оценок пока нет
- Preparation of Uric Acid Standard Stock SolutionДокумент2 страницыPreparation of Uric Acid Standard Stock SolutionAlonso Ornelas GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Hypokalemia: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент17 страницHypokalemia: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and TreatmentIntan NoaОценок пока нет
- Blood Pressure Ranges by Age and SexДокумент15 страницBlood Pressure Ranges by Age and SexGias UddinОценок пока нет
- Body Fluids-1: Fluid Compartments of The Body Fluid and Electrolyte CompositionДокумент33 страницыBody Fluids-1: Fluid Compartments of The Body Fluid and Electrolyte CompositionMan LingОценок пока нет
- ECF & ICF Electrolyte CompositionДокумент33 страницыECF & ICF Electrolyte CompositionDwi SiregarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19Документ6 страницChapter 19Teehee JonesОценок пока нет
- Apbio 45 LectoutДокумент15 страницApbio 45 LectoutSimone Alexis GuinocorОценок пока нет
- Hypokalemia - Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, EtiologyДокумент15 страницHypokalemia - Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, EtiologymirzeroОценок пока нет
- Pex 9 6Документ6 страницPex 9 6Rima Wenisa AinandaОценок пока нет
- CateterixareДокумент4 страницыCateterixareClaudia IrimieОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Cortex Hormones RegulationДокумент19 страницAdrenal Cortex Hormones RegulationsabaОценок пока нет
- Adrenal GlandsДокумент116 страницAdrenal GlandsBrandon AreteОценок пока нет
- PNLE: Maternal and Child Health Nursing Exam 1: Text ModeДокумент47 страницPNLE: Maternal and Child Health Nursing Exam 1: Text ModeAngelica SorianoОценок пока нет
- Dapus 16 PDFДокумент7 страницDapus 16 PDFTiti SulistiowatiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Fluids and Electrolytes - Acid-Base BalanceДокумент8 страницChapter 3 Fluids and Electrolytes - Acid-Base BalanceDiony CruzОценок пока нет
- 3.blood Pressure and Its RegulationДокумент44 страницы3.blood Pressure and Its RegulationNatasha Grace NtembwaОценок пока нет
- Corticosteroids: Prof. Dr. Shah MuradДокумент51 страницаCorticosteroids: Prof. Dr. Shah MuradnehascribdjoshiОценок пока нет
- 21 Hearing Boosting VeggiesДокумент39 страниц21 Hearing Boosting VeggiesMitch Yeoh100% (2)
- 003Документ358 страниц003Gordana UzelacОценок пока нет