Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MN Solved Example 3
Загружено:
Calin AlexandruАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MN Solved Example 3
Загружено:
Calin AlexandruАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
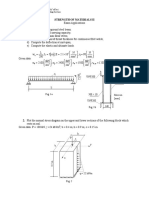
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
Consider the following stepped beam:
a) Determine the free nodal displacements;
b) Determine the reactive forces;
c) Determine the bending moments and the shear forces at the nodes;
d) Plot the shear force and bending moment diagrams.
kN
q 10
m
L 4 m
Given data:
kN
E 2.1108 2
m
I 1.29 103 m 4
y
q L2
M
8
D1 = v1
D2 = 1
1
qL
2
EIy
D3 = v2 D5 = v3
D4 = 2 D6 = 3
2
3
2EIy
R1
0.5L
Step 1:
Input data (units are kN and m):
ORIGIN 1
q 10
8
E 2.110
I 1.2910
Page 1 of 10
R2
R3
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
E I
2 E I
EIy
q L
12
q L
M
Step 2:
Write the finite element force-displacement relations:
Element 1:
1
F1 0
M 0 EI
1
1
1
F fn k1 d n 1 3y
L1
F2 0
M 2
0
6L1
12
6L
4L21
1
12 6L1
2
6L1 2L1
i 1
12 6 Li
6 L 4 L 2
i
i
EIy
i 12 6 L
i
6 L 2 L 2
i i
k1
2
6 L 2 L
i
i
12 6 L
i
2
6 L 4 L
i
i
12
6 L
Li3
5.079 104
5
1.016 10
k1
4
5.079 10
1.016 105
0
0
fn1
0
0
5
5
5
2.709 10 1.016 10 1.355 10
5
4
5
1.016 10 5.079 10 1.016 10
5
5
5
1.355 10 1.016 10 2.709 10
5
1.016 10
5.079 10
1.016 10
Page 2 of 10
12
6L1
12
6L1
6L1 v1
2L21 1
6L1 v 2
4L21 2
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
Element 2:
qL
4
2
F2 q L2
M
2
48 2EI y
k2 d n 2
3
F
q
L
L2
3
M 3 4
2
q L
48
2
F fn
2
6L 2
12
6L
4L22
2
12 6L 2
2
6L 2 2L 2
i 2
12 6 Li
6 L 4 L 2
i
i
EIy
i 12 6 L
i
6 L 2 L 2
i i
k2
2
6 L 2 L
i
i
12 6 L
i
2
6 L 4 L
i
i
12
6 L
Li3
8.127 105
5
8.127 10
k2
5
8.127 10
8.127 105
q L2
2
q L 2
2
12
fn2
q L2
2
q L 2
2
12
6
5
5
1.084 10 8.127 10 5.418 10
5
5
5
8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
6
5.418 10 8.127 10 1.084 10
5
8.127 10
8.127 10
8.127 10
10
3.333
fn2
10
3.333
Page 3 of 10
12
6L 2
12
6L 2
6L 2 v 2
2L22 2
6L 2 v3
4L22 3
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
Step 3:
Determine the assembled structural stiffness matrix and write the structural force-displacement relation:
0
0
R1
v1 R1 q L
D1
qL
0 0
1 0 4
2
1
2
2
2
Q
v v Q
D
F f n K D 0 q L K 12 22 q L K 3
48
M
2 2 M 48
D4
R2 q L
v3 R 2 q L
D5
R 3
3 R 3 4
D6
q L2
q L2
48
48
ii 1 6
jj 1 6
i 1 4
iijj
iijj
j 1 4
5.079 104
1.016 105
4
k1exp 5.079 10
1.016 105
k2exp
k1exp
0
0
0
k2exp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
k1exp
i j
1.016 10
2.709 10
1.016 10
k1
i j
5.079 10
1.016 10
5.079 10
1.016 10
1.355 10
1.016 10
0 0
0
0
1.355 10
1.016 10
2.709 10
k2exp
i 2 j 2
k2
i j
5
5
5
5
8.127 10
8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
6
5
5
8.127 10
1.084 10 8.127 10 5.418 10
5
5
5
5
8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
5
6
8.127 10
5.418 10 8.127 10 1.084 10
0
K k1exp k2exp
Page 4 of 10
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
5.079 104
1.016 105
5.079 104
K
1.016 105
5
5
5
2.709 10 1.016 10 1.355 10
0
0
5
5
5
5
5
1.016 10 8.635 10
7.111 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
6
5
5
1.355 10
7.111 10
1.355 10 8.127 10 5.418 10
5
5
5
5
0
8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
5
6
0
8.127 10
5.418 10 8.127 10 1.084 10
5
1.016 10
5.079 10
1.016 10
fn1exp stack (fn1 00)
0
0
0
fn1exp
0
0
0
fn2exp stack (00fn2 )
0
0
10
fn2exp
3.333
10
3.333
fnexp fn1exp fn2exp
0
0
10
fnexp
3.333
10
3.333
Step 4:
Rearrange and perform the partition of the structural force-displacement relation.
Page 5 of 10
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
0
qL
D1
R1 4
D
R
2
5
2 q L
R 3 48
D6 Fr f r K rr
K2
0 0
D 2 Fn f n K nr
Q q L
D3
D 4
M 4
q L2
48
K rn Dr
K nn Dn
K1 stack (submatrix(K1116) submatrix(K5616) submatrix(K2416))
K2 augment (submatrix(K11611) submatrix(K11656) submatrix(K11624))
5.079 104
0
K2
1.016 105
4
5.079 10
5
1.016 10
5
5
5
5
8.127 10 8.127 10
0
8.127 10 8.127 10
5
6
5
5
8.127 10 1.084 10
0
8.127 10
5.418 10
5
5
5
0
0
2.709 10 1.016 10 1.355 10
5
5
5
5
5
8.127 10 8.127 10 1.016 10 8.635 10
7.111 10
5
5
5
5
6
8.127 10 5.418 10
1.355 10
7.111 10
1.355 10
0
1.016 10
5.079 10
Krr submatrix(K21313)
5.079 104
0
0
5
5
Krr
0
8.127 10 8.127 10
5
6
0
8.127 10 1.084 10
Krn submatrix(K21346)
1.016 105 5.079 104 1.016 105
5
5
Krn
0
8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
0
8.127 10
5.418 10
Knr submatrix(K24613)
Page 6 of 10
1.016 10
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
1.016 105
0
0
4
5
5
Knr 5.079 10 8.127 10 8.127 10
5
5
5
1.016 10 8.127 10 5.418 10
Knn submatrix(K24646)
2.709 105 1.016 105 1.355 105
5
5
5
Knn 1.016 10 8.635 10 7.111 10
5
5
6
1.355 10 7.111 10 1.355 10
fn submatrix(fnexp 2411)
0
fn 10
3.333
fr stack (submatrix(fnexp 1111) submatrix(fnexp 5611))
0
fr 10
3.333
0
Fn Q
M
0
Fn 20
20
Step 5:
Determine the free nodal displacements and the reactive forces according to the support conditions:
Fr
f r
K rr
Fn
f n
K nr
K rn Dr Fr f r K rr Dr K rn Dn
K nn Dn Fn f n K nr Dr K nn Dn
0
Fr K rn K nn 1 Fn f n f r
Fr f r K rn Dn
Since D r 0
1
Dn K nn Fn f n
Fn f n K nn Dn
Page 7 of 10
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
Dn lsolve(Knn Fn fn )
1.995 10 5
5
Dn 4.324 10
6
7.471 10
or:
Dn Knn
(Fn fn )
1.995 10 5
5
Dn 4.324 10
6
7.471 10
Fr fr Krn Dn
0.929
Fr 39.071
34.429
qL
2
q L2
M
8
EIy
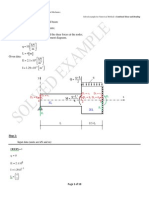
R3 = 34.429 kNm
x
2
3
2EIy
R1 = 0.929 kN
0.5L
Checking up the support reactions:
Page 8 of 10
R2 = 39.071 kN
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
15
Fr Q q L Fr 7.105 10
1
Fr L L
1
2
Fr 0
2 2
3
M Q L q L
2
Step 6:
Determine the bending moments and the shear forces at the nodes:
Node 1:
Vz1 0.929
Vz1 Fr
My1 0
Node 2:
Vz2left 0.929
Vz2left Fr
My2left 3.714
My2left Fr L
1 1
Vz2right 19.071
Vz2right Fr Q
1
My2right Fr L M
1 1
My2right 23.714
Node 3:
Vz3 Fr
Vz3 39.071
My3 Fr
My3 34.429
IN SUMMARY:
1.995 105 D2
a) D n 4.324 105 D3
7.471106 D
R1 0.929
b) Fr R 2 39.071
R 34.429
3
Page 9 of 10
Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Structural Mechanics
Solved example for Numerical Methods Combined Shear and Bending
d)
y
qL
2
q L2
M
8
EIy
R3 = 34.429 kNm
x
2
3
R2 = 39.071 kN
2EIy
R1 = 0.929 kN
0.5L
0.929 kN
Vz
+
-
19.071 kN
39.071 kN
34.429 kNm
My
3.714 kNm
+
23.714 kNm
Page 10 of 10
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Serviceability Limit States (SLS)Документ62 страницыServiceability Limit States (SLS)Calin Alexandru100% (2)
- PH4211 Statistical Mechanics: RS T UV W BGBGДокумент11 страницPH4211 Statistical Mechanics: RS T UV W BGBGRoy Vesey100% (1)
- Drawing 2Документ1 страницаDrawing 2Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Fibre Reinforced Concrete FRCДокумент23 страницыFibre Reinforced Concrete FRCCalin Alexandru0% (1)
- Examen RM 2 v2Документ2 страницыExamen RM 2 v2Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Foundation Beam: Figure 5.1 - Plan View 0,00Документ2 страницыFoundation Beam: Figure 5.1 - Plan View 0,00Macovei AlinОценок пока нет
- 2 4foundation-DesignДокумент11 страниц2 4foundation-DesignCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Pags Levels Distance Between Pags (CM) Cumulated Distance (CM)Документ1 страницаPags Levels Distance Between Pags (CM) Cumulated Distance (CM)Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- New Text DocumentДокумент1 страницаNew Text DocumentCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- RalДокумент295 страницRalCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- MasonryДокумент44 страницыMasonryCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- New Text DocumentДокумент1 страницаNew Text DocumentCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Examen RM 2 v2Документ2 страницыExamen RM 2 v2Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Aei Rental VibratorsДокумент2 страницыAei Rental VibratorsCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials Ii: Q UNP200 500 × 10Документ2 страницыStrength of Materials Ii: Q UNP200 500 × 10Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Casanova: GeometryДокумент11 страницCasanova: GeometryCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Geotehnica SubiecteДокумент9 страницGeotehnica SubiecteBobaru MariusОценок пока нет
- Concrete Vibrators: Focused Innovation, Concrete ReputationДокумент2 страницыConcrete Vibrators: Focused Innovation, Concrete ReputationCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Work 2Документ17 страницWork 2Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Borehole RecordДокумент2 страницы1.1 Borehole RecordCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Work 1Документ31 страницаWork 1Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Example: Gravity Retaining Wall: 1.8 M Surcharge, Q 20 KpaДокумент5 страницExample: Gravity Retaining Wall: 1.8 M Surcharge, Q 20 KpaMadhu KumarОценок пока нет
- 2 Specific Thermal Adjust 2Документ2 страницы2 Specific Thermal Adjust 2Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Ural Evaluation 3Документ8 страницUral Evaluation 3Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Topic - Connections - Design IssuesДокумент128 страницTopic - Connections - Design IssuesCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Assignment NoДокумент4 страницыAssignment NoCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- MN Solved Example 3Документ10 страницMN Solved Example 3Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Spanning of The Floor BeamsДокумент3 страницыSpanning of The Floor BeamsCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Standard FormsДокумент4 страницы1.2 Standard FormsCalin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- TC 1Документ1 страницаTC 1Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 0Документ2 страницы0Calin AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 02 Time Value of MoneyДокумент50 страниц02 Time Value of MoneyFauziah Husin HaizufОценок пока нет
- BCA First Year SubjectsДокумент4 страницыBCA First Year SubjectsKamatchi KartheebanОценок пока нет
- Link State RoutingДокумент11 страницLink State RoutingPav TechnicalsОценок пока нет
- Melody Generation Using An Interactive Evolutionary AlgorithmДокумент6 страницMelody Generation Using An Interactive Evolutionary AlgorithmOmar Lopez-RinconОценок пока нет
- CS-13410 Introduction To Machine Learning: Lecture # 17Документ11 страницCS-13410 Introduction To Machine Learning: Lecture # 17fake TigerОценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ34 страницыUnit 3Mahesh ThallapelliОценок пока нет
- Floyd - Warshall Algorithm: J, K) in Terms of The Following Recursive FormulaДокумент5 страницFloyd - Warshall Algorithm: J, K) in Terms of The Following Recursive FormulavivekОценок пока нет
- SMAI StateSpaceSearchДокумент88 страницSMAI StateSpaceSearchcacaОценок пока нет
- ISYE 6420 SyllabusДокумент1 страницаISYE 6420 SyllabusYasin Çagatay GültekinОценок пока нет
- Lat5 - AlproSa01 (1322001, 1322005, 1322011, 1322015, 1322021, 1322026)Документ9 страницLat5 - AlproSa01 (1322001, 1322005, 1322011, 1322015, 1322021, 1322026)Hikmal Ananta PutraОценок пока нет
- Function & ITF (Ph-4) (Sol)Документ5 страницFunction & ITF (Ph-4) (Sol)Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- Indian Forest Service (IFoS-IFS) Mains Exam Maths Optional Linear Algebra Previous Year Questions (PYQs) From 2020 To 2009Документ9 страницIndian Forest Service (IFoS-IFS) Mains Exam Maths Optional Linear Algebra Previous Year Questions (PYQs) From 2020 To 2009hshejejОценок пока нет
- Cyclic Redundancy CheckДокумент9 страницCyclic Redundancy CheckBabaiОценок пока нет
- 1697mining Web Graphs For RecommendationsДокумент12 страниц1697mining Web Graphs For RecommendationsPurushothama ReddyОценок пока нет
- AA A Are Any N Events Associated With A Random Experiment, Prove That PA A A PA PA PAДокумент3 страницыAA A Are Any N Events Associated With A Random Experiment, Prove That PA A A PA PA PARamesh AkulaОценок пока нет
- Calculating Ultra-Strong and Extended Solutions For Nine Men's Morris, Morabaraba, and Lasker MorrisДокумент12 страницCalculating Ultra-Strong and Extended Solutions For Nine Men's Morris, Morabaraba, and Lasker MorrisMayank JoshiОценок пока нет
- Computer Control of Process 2UPsДокумент134 страницыComputer Control of Process 2UPskarthiveeraОценок пока нет
- Week 14 - Frobenius MethodДокумент20 страницWeek 14 - Frobenius MethodHanee Farzana HizaddinОценок пока нет
- Similarity Measures For Categorical DataДокумент12 страницSimilarity Measures For Categorical DataNeti SuherawatiОценок пока нет
- It6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulДокумент1 страницаIt6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulVanathi AnandavelОценок пока нет
- Jeyaraj, Nadar - 2018 - Computer-Assisted Medical Image Classification For Early Diagnosis of Oral Cancer Employing Deep Learning AlgoriДокумент9 страницJeyaraj, Nadar - 2018 - Computer-Assisted Medical Image Classification For Early Diagnosis of Oral Cancer Employing Deep Learning AlgoriCarlos Henrique LemosОценок пока нет
- Multi Rate DSPДокумент41 страницаMulti Rate DSPrekhakasiraman100% (2)
- Unit-3 TOCДокумент42 страницыUnit-3 TOCsageranimesh20Оценок пока нет
- Multi-Head Self-Attention Transformer For Dogecoin Price PredictionДокумент6 страницMulti-Head Self-Attention Transformer For Dogecoin Price PredictionThu GiangОценок пока нет
- Hrvoje Jasak PH DДокумент394 страницыHrvoje Jasak PH DJemeneОценок пока нет
- Compare and Contrast An Algorithmic and Convolution Reverb. Demonstrate The Difference and The Important Features in Both Types of Reverb.Документ5 страницCompare and Contrast An Algorithmic and Convolution Reverb. Demonstrate The Difference and The Important Features in Both Types of Reverb.Miguel PeñaОценок пока нет
- Sampling Distribution Exam HelpДокумент9 страницSampling Distribution Exam HelpStatistics Exam HelpОценок пока нет
- Gain Margin, Phase Margin, and Crossover Frequencies - MATLAB MarginДокумент3 страницыGain Margin, Phase Margin, and Crossover Frequencies - MATLAB Margintipo_de_incognitoОценок пока нет
- Ahmed Hassan Ismail - BESE-9B - 237897 - NS Lab 5Документ15 страницAhmed Hassan Ismail - BESE-9B - 237897 - NS Lab 5Hasan AhmedОценок пока нет