Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Power Electronics Project
Загружено:
noumanscorpionИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Power Electronics Project
Загружено:
noumanscorpionАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Single Phase Half-wave Controlled Rectifier with Inductive Load
Abdullah Nisar#1, Farooq Kamal#2, Jawad Shaikh#3, M. Danish Yousuf#3, Nouman Khan#3
Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Topi, Pakistan
1u2010010@giki.edu.pk
2u2010104@giki.edu.pk
3u2010148@giki.edu.pk
3u2010202@giki.edu.pk
3u2010281@giki.edu.pk
Abstract The objective of this document is to give a description
on the project, the main aim of which was to implement a single
phase half-wave controlled rectifier module with inductive load,
as a lab project for the partial fulfilment of EE434 Power
Electronics Course. Simulations was done on Multisim
Educational Edition Version 11.0.
IV. CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION
Keywords Controlled rectifier, single phase, half-wave
I. INTRODUCTION
To build a controlled rectifier or a phase-controlled rectifier,
diodes in the commonly used uncontrolled rectifier circuits are
replaced by SCRs. These circuits produce a variable DC
output voltage whose magnitude is varied by phase control,
that is, by controlling the duration of the conduction period by
varying the point at which a gate signal is applied to the SCR.
This project is the implementation of one such controlled
rectifier i.e. single phase half-wave controlled rectifier. Single
phase indicates that there is only one AC input while halfwave indicates that the circuit flattens only the positive or
negative side of the AC input. The module is made with the
phase control functionality and an inductive load has been
installed for the testing and observation purposes.
II. COMPONENTS USED
Components Name
SCR Transistor
Inductor
Resistors
Box Casing
Banana Plugs
Specifications
Fig. 2 Circuit Implementation.
V. DESCRIPTION
Fig 3 and 4 show the circuit diagram and the waveforms of a
single phase fully controlled half-wave rectifier supplying a
resistive inductive load.
29H
Variable Values
Internal diameter = 1cm
III. SCHEMATIC
Fig 3. Circuit Diagram Single Phase Half-wave Controlled
Rectifier with RL Load
Fig. 1. Schematic (Multisim Education Edition Version 11.0).
Fig 3. Waveforms of Single Phase Half-wave Controlled
Rectifier with RL Load
As in the case of a resistive load, the thyristor T becomes
forward biased when the supply voltage becomes positive at
t = 0. However, it does not start conduction until a gate pulse
is applied at t = . As the thyristor turns ON at t = the
input voltage appears across the load and the load current
starts building up. However, unlike a resistive load, the load
current does not become zero at t = , instead it continues to
flow through the thyristor and the negative supply voltage
appears across the load forcing the load current to decrease.
Finally, at t = ( > ) the load current becomes zero and
the thyristor undergoes reverse recovery. From this point
onwards the thyristor starts blocking the supply voltage and
the load voltage remains zero until the thyristor is turned ON
again in the next cycle. It is to be noted that the value of
depends on the load parameters. Therefore, unlike the resistive
load the average and RMS output voltage depends on the load
parameters. Since the thyristors does not conduct over the
entire input supply cycle this mode of operation is called the
discontinuous conduction mode.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to thank our course instructor Mr. Faisal Khan
and store Keeper Mr. Gul Hanif for their help and guidance
throughout the project.
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
Ashfaq Ahmed, Power Electronics for Technology
P. C. Sen, Power Electronics
Вам также может понравиться
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Ac To DC Converter Project ReportДокумент75 страницAc To DC Converter Project ReportPranav Tripathi79% (14)
- Ac To DC Converter Project Report PDFДокумент75 страницAc To DC Converter Project Report PDFVishal Bhadalda100% (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesОт EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesОценок пока нет
- Wenzel ISH09Документ6 страницWenzel ISH09Long LeoОценок пока нет
- PE Lecture No 03Документ12 страницPE Lecture No 03Getnet YilfuОценок пока нет
- Generation of Energy Usig MagnetsДокумент26 страницGeneration of Energy Usig MagnetsSridhar PatilОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 DJM 40103 Psim 2Документ23 страницыLab 1 DJM 40103 Psim 2aiman.haziq2913Оценок пока нет
- Lab 5Документ16 страницLab 5msania654Оценок пока нет
- ZVSДокумент28 страницZVS12BACAUОценок пока нет
- Inverter Commutation CircuitsДокумент7 страницInverter Commutation Circuitskanor1991Оценок пока нет
- M9 - Pulsed Power PDFДокумент4 страницыM9 - Pulsed Power PDFSyar ArifОценок пока нет
- LECTUERE 6 E 1530 High Voltage EngineeringДокумент30 страницLECTUERE 6 E 1530 High Voltage Engineeringahmed372416Оценок пока нет
- Report 1 Power eДокумент12 страницReport 1 Power eMuhd HafizzudinОценок пока нет
- DC ChopperДокумент37 страницDC ChopperAnuroopОценок пока нет
- DC Chopper PDFДокумент37 страницDC Chopper PDFmadhubalagangapureОценок пока нет
- High Power Factor Soft SwitchedДокумент7 страницHigh Power Factor Soft SwitchedMohan KrishnaОценок пока нет
- EES612 Lab2Документ19 страницEES612 Lab2kombat13_708353334Оценок пока нет
- 2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiДокумент59 страниц2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiSaranya. M SNSОценок пока нет
- Yog Patil - Expt. No. 3Документ8 страницYog Patil - Expt. No. 3Yog PatilОценок пока нет
- Lab1 EPS FinaДокумент13 страницLab1 EPS FinaJorge Nelson75% (4)
- 1 Phase Controlled RectifierДокумент34 страницы1 Phase Controlled RectifierAfiq BobbyОценок пока нет
- Lab Report: Bangladesh University of Business and Technology (BUBT)Документ5 страницLab Report: Bangladesh University of Business and Technology (BUBT)23 - 017 - Md. Imran HossainОценок пока нет
- Manual Ee IVДокумент56 страницManual Ee IVAkhilesh Kumar MishraОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 NotesДокумент30 страницUnit 2 Notesganesh ganeshОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics 15-LabsДокумент63 страницыPower Electronics 15-LabsKrishna v.mОценок пока нет
- Sunday2 PDFДокумент6 страницSunday2 PDFيوسف سامي عبد هاديОценок пока нет
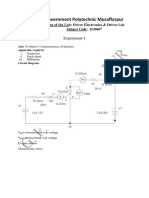
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesДокумент18 страницGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarОценок пока нет
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesДокумент18 страницGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DОценок пока нет
- CVTДокумент4 страницыCVTscribdkkkОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringДокумент42 страницыBasic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringSourav SahooОценок пока нет
- Family of Soft-Switching PWMДокумент7 страницFamily of Soft-Switching PWMMohan KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Single Stage Inverter Topology For Renewable Resources: Jeena Mary Abraham, M.S.P. Subathra, Senraj. RДокумент5 страницSingle Stage Inverter Topology For Renewable Resources: Jeena Mary Abraham, M.S.P. Subathra, Senraj. RskrtamilОценок пока нет
- EE254 1 IntroductionДокумент47 страницEE254 1 IntroductionClint GengosОценок пока нет
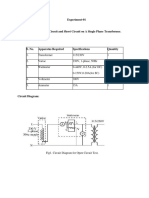
- Open Circuit & Short Open Circuit & Short Circuit Test Single Phase Transformer Tests of RmerДокумент14 страницOpen Circuit & Short Open Circuit & Short Circuit Test Single Phase Transformer Tests of Rmersameerpatel15770Оценок пока нет
- DC-DC Boost Converter With Constant Output Voltage For Grid Connected Photovoltaic Application SystemДокумент5 страницDC-DC Boost Converter With Constant Output Voltage For Grid Connected Photovoltaic Application SystemMuhammad Adli RizqullohОценок пока нет
- Phase Controlled RectifiersДокумент59 страницPhase Controlled RectifiersAravindh EnggОценок пока нет
- Machine LabДокумент7 страницMachine LabNurjahan-Ara StudentОценок пока нет
- Print Close: Time-Dependent Pulse TrainДокумент10 страницPrint Close: Time-Dependent Pulse TrainLeo_MaxОценок пока нет
- Answers of Power Electronics NewДокумент9 страницAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahОценок пока нет
- Split Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Документ3 страницыSplit Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Miz AelyfhaОценок пока нет
- PEC Lecture Slide Inverter TurkceДокумент43 страницыPEC Lecture Slide Inverter Turkcemdur67Оценок пока нет
- PEL Lab ManualДокумент127 страницPEL Lab Manualmksamy2021Оценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Lab 6Документ13 страницPower Electronics Lab 6muzzamilfarid47Оценок пока нет
- Effect of Source InductanceДокумент10 страницEffect of Source Inductancemeeravali_snОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshiДокумент67 страницLaboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshipriyaОценок пока нет
- Pe Unit 5 PDFДокумент8 страницPe Unit 5 PDFmjrsudhakarОценок пока нет
- IJEDRCP1402017Документ4 страницыIJEDRCP1402017anas maraabaОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.5 Thevenin's Theorem: 1.1 ObjectiveДокумент5 страницExperiment No.5 Thevenin's Theorem: 1.1 ObjectiveNAJMUL HASSAN SARKARОценок пока нет
- Lec2 Transformers IIДокумент17 страницLec2 Transformers IIMohammed Dyhia AliОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshДокумент13 страницASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshHemkeshОценок пока нет
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualДокумент64 страницы17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaОценок пока нет
- Shunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsДокумент14 страницShunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsJames Ernes Llacza Carmelo100% (1)
- Magnetic Saturation PDFДокумент6 страницMagnetic Saturation PDFDaniel MemijeОценок пока нет
- Dire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyДокумент49 страницDire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyAsed ZakirОценок пока нет
- DC-DC Converter SimulationДокумент3 страницыDC-DC Converter SimulationMThe StrokesОценок пока нет
- Fly-Back Mode 150wДокумент17 страницFly-Back Mode 150wanon_4880132Оценок пока нет
- A Single Stage Flyback Power Supply Unit For LED Lighting ApplicationsДокумент5 страницA Single Stage Flyback Power Supply Unit For LED Lighting ApplicationsPhạm Văn TưởngОценок пока нет
- 501 Sentence Completion QuestionsДокумент194 страницы501 Sentence Completion QuestionsSapna Ludhani100% (4)
- Data AnalysisДокумент88 страницData AnalysisnoumanscorpionОценок пока нет
- Tutorial On Fuzzy LogicДокумент20 страницTutorial On Fuzzy LogicnsadnanОценок пока нет
- ECE402 Quadcopter Final PaperДокумент41 страницаECE402 Quadcopter Final Papernoumanscorpion100% (1)
- An Insight Into Human PhilosophyДокумент2 страницыAn Insight Into Human PhilosophynoumanscorpionОценок пока нет
- Thumb Rules For Civil Engineers PDFДокумент4 страницыThumb Rules For Civil Engineers PDFA KОценок пока нет
- STR ReportДокумент30 страницSTR ReportrahulОценок пока нет
- Shaft Alignment: Your Photo HereДокумент75 страницShaft Alignment: Your Photo HereMahmoud Elghandour0% (1)
- BMTC 132Документ16 страницBMTC 132Deepak Chaudhary JaatОценок пока нет
- Sesam and Bladed - Efficient Coupled Analyses - Webinar Presentation - tcm8-102589 PDFДокумент31 страницаSesam and Bladed - Efficient Coupled Analyses - Webinar Presentation - tcm8-102589 PDFsamiransmitaОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Equation - MATH IS FUNДокумент8 страницQuadratic Equation - MATH IS FUNChanchan LebumfacilОценок пока нет
- Slides Prepared by John S. Loucks St. Edward's University: 1 Slide © 2003 Thomson/South-WesternДокумент34 страницыSlides Prepared by John S. Loucks St. Edward's University: 1 Slide © 2003 Thomson/South-WesternHRish BhimberОценок пока нет
- Ap T240 13Документ92 страницыAp T240 13mehdiОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Energy Recovery SystemДокумент2 страницыKinetic Energy Recovery SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Work 1 Computation of Metrics of Productivity of Computer SystemДокумент12 страницLaboratory Work 1 Computation of Metrics of Productivity of Computer SystemHhhhhh75% (4)
- EE TermsДокумент25 страницEE TermsKerr AgotОценок пока нет
- Supercritical CO2: Properties and Technological Applications - A ReviewДокумент38 страницSupercritical CO2: Properties and Technological Applications - A ReviewXuân ĐứcОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Statistial Process Control (SPC)Документ22 страницыChapter 4 Statistial Process Control (SPC)Yousab CreatorОценок пока нет
- Random Numbers in PythonДокумент3 страницыRandom Numbers in PythonShubham RawatОценок пока нет
- Guest WiFi With MikroTik RoutersДокумент1 страницаGuest WiFi With MikroTik Routersmahad3vaОценок пока нет
- TM 9-4110-241-23PДокумент41 страницаTM 9-4110-241-23PwwwsurvivalebookscomОценок пока нет
- Shape of Water in Rotating Bucket - Physics Stack ExchangeДокумент3 страницыShape of Water in Rotating Bucket - Physics Stack ExchangeHector TrianaОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент10 страницProjectabdul basitОценок пока нет
- Prime Number FactorizationДокумент10 страницPrime Number FactorizationedithaenriquezОценок пока нет
- Rodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowДокумент20 страницRodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowShara MotaОценок пока нет
- Delamination With AbaqusДокумент13 страницDelamination With AbaqusSchmetterling TraurigОценок пока нет
- Changeling - The Dreaming 20th Anniversary Edition 9Документ1 страницаChangeling - The Dreaming 20th Anniversary Edition 9André Vieira0% (1)
- OSHA Module 3Документ17 страницOSHA Module 3Varsha GОценок пока нет
- V-RAY 2.0 Option Editor Overview (SketchUp)Документ14 страницV-RAY 2.0 Option Editor Overview (SketchUp)thonethoneОценок пока нет
- MDM Heiana Nadia Hamzah: Prepared byДокумент50 страницMDM Heiana Nadia Hamzah: Prepared bySyarfa FurzanneОценок пока нет
- LRL 1220 DДокумент6 страницLRL 1220 DDEShifОценок пока нет
- Science July Assignment Grade 8Документ3 страницыScience July Assignment Grade 8G PОценок пока нет
- Differential EquationДокумент17 страницDifferential EquationAashika DhareОценок пока нет
- Immediate Settlement Analysis Using Finite Element Analysis Models of Fb-MultipierДокумент22 страницыImmediate Settlement Analysis Using Finite Element Analysis Models of Fb-MultipierRaaf RifandiОценок пока нет
- 02 Sub-Surface Exploration 01Документ24 страницы02 Sub-Surface Exploration 01kabir AhmedОценок пока нет