Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Industrial Plant Processes - Proposal
Загружено:
PK PeredaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Industrial Plant Processes - Proposal
Загружено:
PK PeredaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Project Summary
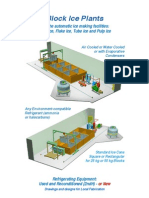
Ice plant is the production and storage of ice; it is a unit that converts water
into ice together with the associating refrigeration machinery, harvesting and
storage equipment, and the building. Ice plant is usually classified by the type of ice
they produce; hence there are block ice plant, flake ice plants, tube, and slice or
plate ice plants and so on. Ice plants may be further subdivided into those that
make dry or wet ice. Dry ice here means ice at a temperature low enough to
prevent the particles becoming moist; the term does not refer in this note to solid
carbon dioxide. In general; dry sub-cooled ice is made in plants that mechanically
remove the ice from the cooling surface; most flake ice plants are of this type. When
the cooling surface of an icemaker is warmed by a defrost mechanism to release the
ice, the surface of the ice is wet and, unless the ice is then sub-cooled below 0C,
remains wet in storage; tube ice and plate ice plants are of this type.
The type of icemaker that will be used will produce a Block ice. It will have a
tapered rectangular cans filled with water which will be immersed in a tank
containing refrigerated sodium chloride brine. The dimensions of the can and the
temperature of the brine are usually selected to give a 24 hour production time, and
batches of cans are emptied and refilled in sequence during that period. Ice block
weight can range from 12 150 kg depending on requirements; 150 kg is regarded
as the largest size of block one man cans conveniently handle. A block ice plant
requires continuous attention and labor intensive.
The proposed space of the plant has a foot area of 190 m 2 and a proposed
height of 4 m. Average power and peak power requirements will depend on the type
of icemaker, operating temperature, make-up water temperature, cooling water
temperature, air temperature, size of plant, utilization of plant, and method of
refrigeration. In addition to water for ice making, water may be required for cooling,
as in a refrigeration plant condenser, or for heating, as in a warm water defrosting
system. The amount of water required for making ice is roughly equal to the amount
of ice being produced plus some allowance for wastage and for prevention of buildup of solids in the water circulating system.
Law of Supply and Demand
It is rarely possible to match production to demand; therefore some ice
storage is still required. However, since the capacity of both the icemaker and the
refrigeration machinery is lower in warmer weather, the size of the plant should be
selected for warm weather operation, when demand for ice is also likely to be
greatest.
Also manufacture of ice can seldom be matched to meet immediate demand;
therefore storage is used to cater for peak demand and to allow the icemaker to be
operated continuously. Storage also acts as a buffer against interruption of
production due to breakdown or routine maintenance.
Вам также может понравиться
- Refits, More Ways to Make Your Boat Better.: Cruising Boats, How to Select, Equip and Maintain, #5От EverandRefits, More Ways to Make Your Boat Better.: Cruising Boats, How to Select, Equip and Maintain, #5Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- 3classification of Ice PlantsДокумент11 страниц3classification of Ice PlantsPaulo GalleraОценок пока нет
- How to Use and Enjoy Your New Frigidaire RefrigeratorОт EverandHow to Use and Enjoy Your New Frigidaire RefrigeratorОценок пока нет
- Mini Ice Plant ReportДокумент40 страницMini Ice Plant ReportLeyzer MalumayОценок пока нет
- Mini Ice Plant ReportДокумент40 страницMini Ice Plant ReportCherry Obias100% (1)
- Ice Plant & Cold StorageДокумент4 страницыIce Plant & Cold Storageakaitotheawesome0% (1)
- Lab 11Документ10 страницLab 11Famero Franz AikenОценок пока нет
- An Introduction to Thermogeology: Ground Source Heating and CoolingОт EverandAn Introduction to Thermogeology: Ground Source Heating and CoolingОценок пока нет
- Icemaking PlantДокумент10 страницIcemaking PlantAshokОценок пока нет
- Performance Test of A Mini Ice Plant (Lecture)Документ9 страницPerformance Test of A Mini Ice Plant (Lecture)Alfred100% (1)
- Mini Ice PlantДокумент28 страницMini Ice PlantCharlie RamirezОценок пока нет
- Ice Slurry Brochure PDFДокумент8 страницIce Slurry Brochure PDFmattiturboОценок пока нет
- Ice Slurry Brochure PDFДокумент8 страницIce Slurry Brochure PDFMattia ParentiОценок пока нет
- Eastern Visayas State University Tacloban CityДокумент7 страницEastern Visayas State University Tacloban CityRonaldОценок пока нет
- Ice Plants SLMДокумент28 страницIce Plants SLMMonuj BorahОценок пока нет
- Ice Making Plant Visit ReportДокумент8 страницIce Making Plant Visit ReportAnis Badshah33% (3)
- Myat Noe KhinДокумент42 страницыMyat Noe KhinThaungShanHtet PalatarОценок пока нет
- Yu Ki Ko KoДокумент54 страницыYu Ki Ko KoThaungShanHtet PalatarОценок пока нет
- The Concrete Producer Article PDF - Comparing The Options For Cooling ConcreteДокумент4 страницыThe Concrete Producer Article PDF - Comparing The Options For Cooling Concretearangar1100% (1)
- CH 06Документ11 страницCH 06lakshmi heat treatmentОценок пока нет
- Ice Plant ProcesДокумент3 страницыIce Plant ProcesCedie Refuerzo100% (1)
- AG-414-4 Hydrocooling - NCSU BAE PDFДокумент14 страницAG-414-4 Hydrocooling - NCSU BAE PDFcarlos342asdОценок пока нет
- Design of Ice Manufacturing Plant 2000 LBДокумент5 страницDesign of Ice Manufacturing Plant 2000 LBEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- Yu Ki Myat NoeДокумент26 страницYu Ki Myat NoeThaungShanHtet PalatarОценок пока нет
- Ministory of Education: West Yangon Technological University Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент30 страницMinistory of Education: West Yangon Technological University Department of Mechanical EngineeringThaungShanHtet PalatarОценок пока нет
- REVICED RAC Practical Lab Jan 2021Документ52 страницыREVICED RAC Practical Lab Jan 2021Archana MaskeОценок пока нет
- Article 3 Brine Circulated SystemsДокумент46 страницArticle 3 Brine Circulated Systemsmdalt9180Оценок пока нет
- Rainwater Collection in Cold EnvironmentsДокумент19 страницRainwater Collection in Cold EnvironmentsGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- ICE PLANT Proposal in Sablayan MindoroДокумент34 страницыICE PLANT Proposal in Sablayan MindoroMarcelino Sanico100% (1)
- Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramodaya Vishwavidyalaya: Topic:-Ice Manufacturing ProcessesДокумент15 страницMahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramodaya Vishwavidyalaya: Topic:-Ice Manufacturing Processesanimesh100% (1)
- 1 Ref Intro 3rd Term June 2016Документ15 страниц1 Ref Intro 3rd Term June 2016Nicolai CeloОценок пока нет
- Ice Slurry Applications PDFДокумент15 страницIce Slurry Applications PDFmattiturboОценок пока нет
- Concrete CoolingДокумент19 страницConcrete CoolingAbdulrahman AlnagarОценок пока нет
- Block Ice Plants: and The Automatic Ice Making Facilities: Plate Ice, Flake Ice, Tube Ice and Pulp IceДокумент6 страницBlock Ice Plants: and The Automatic Ice Making Facilities: Plate Ice, Flake Ice, Tube Ice and Pulp Icetiaan12345Оценок пока нет
- Evaporator TubeДокумент3 страницыEvaporator TubeWiro SablengОценок пока нет
- Cooling Technology - Cooling TowersДокумент2 страницыCooling Technology - Cooling TowerstaghdirimОценок пока нет
- Performance Test of A: Mini Ice PlantДокумент14 страницPerformance Test of A: Mini Ice PlantBrian TuazonОценок пока нет
- Vending Machine RefrigerationДокумент1 страницаVending Machine RefrigerationxenohjbОценок пока нет
- ManojДокумент13 страницManojpranavОценок пока нет
- Food Technology Assignment 3Документ7 страницFood Technology Assignment 3bhavya modiОценок пока нет
- Acitivity 1 (Daga, Kristan O'Neal C.)Документ9 страницAcitivity 1 (Daga, Kristan O'Neal C.)Kristan Oneal DagaОценок пока нет
- M14 - Jurnal Prof KauffeldДокумент15 страницM14 - Jurnal Prof KauffeldMark SandyОценок пока нет
- Defrosting of Air Coolers - Dec 2012Документ6 страницDefrosting of Air Coolers - Dec 2012Captain hopiОценок пока нет
- Ice Making Plant FactoryДокумент7 страницIce Making Plant FactoryKifayat UllahОценок пока нет
- Role in Human Activities: CoolingДокумент6 страницRole in Human Activities: CoolingAshis MingalaОценок пока нет
- MEBS6008 ThermalДокумент81 страницаMEBS6008 ThermalHaymanot BaynesagnОценок пока нет
- Experiment 6 Ref SystemДокумент6 страницExperiment 6 Ref SystemRenroseОценок пока нет
- 0 0 07 May 2015 1300032071ProjectProfile0001Документ6 страниц0 0 07 May 2015 1300032071ProjectProfile0001B.A HОценок пока нет
- 0 0 07 May 2015 1300032071ProjectProfile0001Документ6 страниц0 0 07 May 2015 1300032071ProjectProfile0001basel alezziОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Cold StoragreДокумент16 страницModule 4 Cold StoragreRecoil SОценок пока нет
- Curso de Fabricadores de Hielo de NeveraДокумент42 страницыCurso de Fabricadores de Hielo de NeveraJOSE CAMPOSОценок пока нет
- MElab Mini Ice PlantДокумент8 страницMElab Mini Ice PlantKent NabzОценок пока нет
- Ground FreezingДокумент17 страницGround FreezingSparsh ShukalОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurship Project: Ice PlantДокумент5 страницEntrepreneurship Project: Ice PlantsujadОценок пока нет
- Operating Cooling Towers in Freezing Weather: SubjectДокумент8 страницOperating Cooling Towers in Freezing Weather: Subjectdijana387Оценок пока нет
- MSL Technical Guide 1 The Ice Point: LiquidДокумент2 страницыMSL Technical Guide 1 The Ice Point: LiquidVictorSanchezОценок пока нет
- Cold Weather Operation of Cooling Towers: ForwardДокумент8 страницCold Weather Operation of Cooling Towers: ForwardChris VarugheseОценок пока нет
- Vibrocontrol 1500: Operating InstructionsДокумент12 страницVibrocontrol 1500: Operating InstructionsBudhi Prasetya HakimОценок пока нет
- Selection Output 30RB039SДокумент1 страницаSelection Output 30RB039SSinggih KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2-3 - Introduction To Aerodynamics & FundamentalsДокумент15 страницLecture 2-3 - Introduction To Aerodynamics & FundamentalsAli RazaОценок пока нет
- Energy Piles and Other Thermo-Active Ground-Source Systems: Heinz BrandlДокумент22 страницыEnergy Piles and Other Thermo-Active Ground-Source Systems: Heinz BrandlwongtianhuiОценок пока нет
- Me6404 Te Even QBДокумент32 страницыMe6404 Te Even QBBala NarayanasamyОценок пока нет
- Amende 2007Документ6 страницAmende 2007Warren PuthОценок пока нет
- The Maxwell-Boltzmann DistributionДокумент9 страницThe Maxwell-Boltzmann Distributiondiego espinozaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Triple Pressure Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorДокумент7 страницThermodynamic Analysis of Triple Pressure Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorIJIRSTОценок пока нет
- Catalogue RAC Mitsubishi ElectricДокумент10 страницCatalogue RAC Mitsubishi ElectricYizhar Bechamel MestokoОценок пока нет
- Re92105 01 X b2 - 2017 08Документ56 страницRe92105 01 X b2 - 2017 08cln100% (1)
- Science 08 atДокумент4 страницыScience 08 atJoel Opciar CuribОценок пока нет
- Workshop Survival GuideДокумент172 страницыWorkshop Survival Guidezenview2000Оценок пока нет
- Ketron® Peek HPV - Ficha TécnicaДокумент1 страницаKetron® Peek HPV - Ficha TécnicaDerson OliveiraОценок пока нет
- CSEC Physics June 2015Документ7 страницCSEC Physics June 2015Clendon Donai25% (4)
- Activity 3 Weather and ClimateДокумент7 страницActivity 3 Weather and ClimateJR ParkОценок пока нет
- Pet Bottle FaultsДокумент40 страницPet Bottle FaultsPiyalarp Ludeelerd100% (2)
- Concrete Against Explosion2Документ145 страницConcrete Against Explosion2usama anterОценок пока нет
- G.I. DuctingДокумент20 страницG.I. Ductingawsafasif100% (1)
- Discussion and ConclusionДокумент3 страницыDiscussion and ConclusionFadhli HashimОценок пока нет
- 20180906101631-b SC Hons Chemistry PDFДокумент72 страницы20180906101631-b SC Hons Chemistry PDFAnshul JayantОценок пока нет
- 14 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Encounter The PhenomenonДокумент5 страниц14 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Encounter The PhenomenonvaraprasadОценок пока нет
- Sheet 7Документ1 страницаSheet 7mkkОценок пока нет
- E106: Specific Heat Capacity E107: Latent Heat of Fusion: June N. Lantacon Results and DiscussionДокумент4 страницыE106: Specific Heat Capacity E107: Latent Heat of Fusion: June N. Lantacon Results and DiscussionJune LantaconОценок пока нет
- Part A 1 Heat TransferДокумент10 страницPart A 1 Heat TransferPrasanthОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Gen - Chem 1Документ7 страницFinal Exam Gen - Chem 1Ricardo VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Physics Thermal ExpansionДокумент5 страницPhysics Thermal ExpansionMarielleyОценок пока нет
- Refrigeration Test RigДокумент10 страницRefrigeration Test Rigakshayarora1909Оценок пока нет
- Pi Dxfkaptpk GBRДокумент42 страницыPi Dxfkaptpk GBRProfОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in PowerpointДокумент53 страницыChapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in Powerpointbrayan CortezОценок пока нет
- Selection Output 30XW0902PДокумент1 страницаSelection Output 30XW0902PLuffyVeraAghestyОценок пока нет
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОт EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОценок пока нет
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorОт EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (137)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsОт EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutОт EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (142)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldОт EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessОт EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (254)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsОт EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (65)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsОт EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (223)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeОт EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (19)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogОт EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsОт EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1424)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignОт EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsОт EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (3)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (397)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (35)