Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1
Загружено:
Gerardo BocanegraИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1
Загружено:
Gerardo BocanegraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Instituto Tecnolgico de Celaya
Departamento de ingeniera mecnica
Catedrtico: Jos Alberto Zavala Bustos
DISEO MECNICO 1, programa ingeniera mecnica, Grupo FJ21/A
Problemario correspondiente a la primera competencia.
Instrucciones: Resuelve, presenta, expresa o determina, segn el caso, lo que se pide.
Rbrica:
En hojas blancas tamao carta
A mano
Utilizar tinta no lpiz
Presentar diagrama de cuerpo libre o diagrama en su caso
Planteamiento: ecuaciones y/o principios a emplear
Hasta Aqu valor del 90%
Operaciones y resultado
Integrar a su carpeta de evidencias, entregar el da del examen, hora de clase, saln de clase.
Resto valor del 10%
Entregar un juego por equipo de 5 integrantes
1. Electrical strain gauges were applied to a notched specimen to determine the stresses in the
notch. The results were x 0.0021 and y 0 0.00067 . Find x and y if the material
is carbon steel.
2. The state of stress at a point is x 2 , y 6 , z 4 , xy 3 , yz 2 , and zx 5
kpsi. Determine the principal stresses, draw a complete Mohrs three-circle diagram, labeling
all points of interest, and report the maximum shear stress for this case.
3. In the figure, shaft AB is rotating at 1000 rev/min and transmits 10 hp to shaft CD through a
set of bevel gears contacting at point E. The contact force at E on the gear of shaft CD
is determined to be FE CD 92.8 i 362.8 j 808.0k lbf. For shaft CD:
(a) draw a free-body diagram and determine the reactions at C and D assuming simple
supports (assume also that bearing C is a thrust bearing),
(b) draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams, and
(c) assuming that the shaft diameter is 1.25 in, determine the maximum tensile and
shear stresses in the beam.
Instituto Tecnolgico de Celaya
Departamento de ingeniera mecnica
Catedrtico: Jos Alberto Zavala Bustos
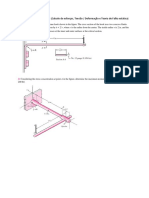
4. Illustrated in the gure 4 is a 1 1/2 in-diameter steel countershaft that supports two pulleys.
Pulley A delivers power to a machine causing a tension of 600 lbf in the tight side of the belt
and 80 lbf in the loose side, as indicated. Pulley B receives power from a motor. The belt
tensions on pulley B have the relation T1 = 0.125T2 . Find the deection of the shaft in the z
direction at pulleys A and B. Determine the maximum tensile and shear stresses in the beam.
Assume that the bearings constitute simple supports.
5.
The gure shows a steel countershaft that supports two pulleys. Pulley C receives power from a
motor producing the belt tensions shown. Pulley A transmits this power to another
machine through the belt tensions T1 and T2 such that T1 = 8T2.
(a) Find the deection of the overhanging end of the shaft, assuming simple supports at
the bearings.
(b) Determine the maximum tensile and shear stresses in the beam.
Instituto Tecnolgico de Celaya
Departamento de ingeniera mecnica
Catedrtico: Jos Alberto Zavala Bustos
6. Among the decisions a designer must make is selection of the failure criteria that is applicable
to the material and its static loading. A 1020 hot-rolled steel has the following properties: Sy
= 42 kpsi, Su t = 66.2 kpsi, and true strain at fracture f = 0.90. Plot the failure locus and, for
the static stress states at the critical locations listed below, plot the load line and estimate the
fac-tor of safety analytically and graphically.
(a) x = 9 kpsi, y = 5 kpsi.
(b) x = 12 kpsi, x y = 3 kpsi ccw.
(c) x = 4 kpsi, y = 9 kpsi, x y = 5 kpsi cw.
(d) x = 11 kpsi, y = 4 kpsi, x y = 1 kpsi cw.
7.
An ASTM cast iron, grade 30 (see Table A24), carries static loading resulting in the stress
state listed below at the critical locations. Choose the appropriate failure locus, plot it
and the load lines, and estimate the factors of safety analytically and graphically.
(a) A = 20 kpsi, B = 20 kpsi.
(b) x y = 15 kpsi.
(c) A = B = 80 kpsi.
(d) A = 15 kpsi, B = 25 kpsi.
8. The gure is a schematic drawing of a countershaft that supports two V-belt pulleys.
For each pulley, the belt tensions are parallel. For pulley A consider the loose belt tension is 15
percent of the tension on the tight side. A cold-drawn UNS G10180 steel shaft of uniform
diameter is to be selected for this application. For a static analysis with a factor of safety
of 3.0, determine the minimum preferred size diameter. Use the distortion-energy theory.
Instituto Tecnolgico de Celaya
Departamento de ingeniera mecnica
Catedrtico: Jos Alberto Zavala Bustos
9. The gure shows a shaft mounted in bearings at A and D and having pulleys at B and C. The
forces shown acting on the pulley surfaces represent the belt tensions. The shaft is to be made
of ASTM grade 25 cast iron using a design factor nd = 2.8. What diameter should be used for
the shaft?
10. A 2-in-diameter solid steel shaft has a gear with ASTM grade 20 cast-iron hub (E = 14.5 Mpsi)
shrink-tted to it. The specications for the shaft are
The hole in the hub is sized at 1.999 0.0004 in with an OD of 4.00 1/ 32 in. Using the
midrange values and the modied Mohr theory, estimate the factor of safety guarding against
fracture in the gear hub due to the shrink t.
Вам также может понравиться
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)Документ2 страницыAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartДокумент2 страницыStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevОценок пока нет
- 10CV/EV33: Strength of MaterialsДокумент2 страницы10CV/EV33: Strength of MaterialsnvnrevОценок пока нет
- ME 370 Elements of Mechanical Design Assignment #1: Problem 1Документ6 страницME 370 Elements of Mechanical Design Assignment #1: Problem 1Nick RoselliОценок пока нет
- 10CV33 Dec2012Документ2 страницы10CV33 Dec2012nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartДокумент2 страницыStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityДокумент2 страницыTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaОценок пока нет
- T 06Документ8 страницT 06baskoroediОценок пока нет
- FEM 18ME73 AssignmentsДокумент10 страницFEM 18ME73 AssignmentsFOODIE USОценок пока нет
- Question Paper ME1-FДокумент3 страницыQuestion Paper ME1-FbrainmanthansОценок пока нет
- BME - MOD I QuestionsДокумент4 страницыBME - MOD I QuestionsGaurav ThakareОценок пока нет
- Model Questions For PracticeДокумент4 страницыModel Questions For PracticeRohan SahanaОценок пока нет
- Theory of PlasticityДокумент10 страницTheory of Plasticitybabu1434100% (1)
- Mid Sem 2021 MDD Date 02 March 2021Документ3 страницыMid Sem 2021 MDD Date 02 March 2021Mohit JaniОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Документ3 страницыQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics of StructureДокумент4 страницыMechanics of StructurePrakash JoshiОценок пока нет
- Paper Summer Camp Final Term MOS-IIДокумент2 страницыPaper Summer Camp Final Term MOS-IIZohaibShoukatBalochОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Документ4 страницыQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Keesanth Geetha ChandrasekaranОценок пока нет
- Me218 Fa15 W3 HoДокумент10 страницMe218 Fa15 W3 HonhiuОценок пока нет
- Binder 1Документ4 страницыBinder 1Muhammad Rizqi RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Solid Mechanics - DM23801Документ41 страницаSolid Mechanics - DM23801Michael MeashoОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Документ3 страницыTutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Kiat HauОценок пока нет
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Документ3 страницыEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126Документ7 страницAssignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126MOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356Оценок пока нет
- StressДокумент5 страницStressmessel2013Оценок пока нет
- AE May 2013 98 Civ A2Документ3 страницыAE May 2013 98 Civ A2NikhilBennyОценок пока нет
- Istability of A Column - LAB MENUДокумент3 страницыIstability of A Column - LAB MENUAlan LeungОценок пока нет
- PMO Department - Engineering Test:: Name: Nationality: Visa Status: Current Salary/package: Family Status: Notice PeriodДокумент8 страницPMO Department - Engineering Test:: Name: Nationality: Visa Status: Current Salary/package: Family Status: Notice PeriodMohamed Gamal100% (1)
- LE1 Problem Set PDFДокумент14 страницLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapОценок пока нет
- Machine Design Model PaperДокумент2 страницыMachine Design Model PaperVinay Karanam100% (1)
- Mechanics of MaterialДокумент3 страницыMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela - 769 008Документ2 страницыNational Institute of Technology, Rourkela - 769 008Tarun KumarОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFДокумент8 страницMechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFSumeet TiwariОценок пока нет
- Mech 260-Final ExamДокумент3 страницыMech 260-Final ExamwerewaroОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaОценок пока нет
- Machine Design Autumn 2012Документ7 страницMachine Design Autumn 2012stansilawОценок пока нет
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisДокумент4 страницыMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranОценок пока нет
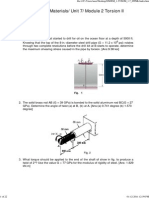
- Strength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem SetДокумент22 страницыStrength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem Setneeru143Оценок пока нет
- Objective GATE QuestionsДокумент24 страницыObjective GATE QuestionsAshwani GoelОценок пока нет
- Mec 323 FinalДокумент7 страницMec 323 FinalJihadHejaziОценок пока нет
- Mechanics of Solids Question PapersДокумент10 страницMechanics of Solids Question PapersNandu Sreekumar SОценок пока нет
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsДокумент9 страницDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Exercícios Elementos de MáquinasДокумент8 страницExercícios Elementos de MáquinasThomas AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsДокумент4 страницы9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Take Home QuizДокумент8 страницTake Home QuizAshley SimmonsОценок пока нет
- Design of Machine ElementsДокумент2 страницыDesign of Machine ElementsSoumava SamantaОценок пока нет
- PEC ERyRM I PDFДокумент11 страницPEC ERyRM I PDFAlejandro serrano pozoОценок пока нет
- Advanced Structural AnalysisДокумент3 страницыAdvanced Structural AnalysisAmit ThoriyaОценок пока нет
- Assignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointДокумент4 страницыAssignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointRitesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Lista Exercicios PDFДокумент8 страницLista Exercicios PDFLeonardo NecoОценок пока нет
- Solid Mechanics BCS Previous Year Questions PDFДокумент3 страницыSolid Mechanics BCS Previous Year Questions PDFjjoe joliОценок пока нет
- answer The Followings: (20 Points) What Is Local Buckling CouldДокумент4 страницыanswer The Followings: (20 Points) What Is Local Buckling CouldAhmed Pshtiwan AhmedОценок пока нет
- Exam 2 Machine Design Auburn UniversityДокумент6 страницExam 2 Machine Design Auburn UniversityNathan AndersonОценок пока нет
- American University of Beirut: Mechanics of Materials (Mech320) QUIZ 2 - (Spring 2011) - 2HДокумент10 страницAmerican University of Beirut: Mechanics of Materials (Mech320) QUIZ 2 - (Spring 2011) - 2HChanjoh RexsonОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3 - LoadStressAnalysisДокумент2 страницыTutorial 3 - LoadStressAnalysisSanthosh AmaraОценок пока нет
- Strength of Material 2Документ6 страницStrength of Material 2viv_1971Оценок пока нет
- Final ExamSOMFinal 2016 FinalДокумент11 страницFinal ExamSOMFinal 2016 Finalkhalil alhatabОценок пока нет
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Lesson 5 332acДокумент12 страницLesson 5 332acSrinivasa Rao DОценок пока нет
- Structural Analysis 7 Edition in SI Units: Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment DistributionДокумент47 страницStructural Analysis 7 Edition in SI Units: Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment DistributionAbdul Wali KhanОценок пока нет
- Buckling of Woven Fabric - NewДокумент27 страницBuckling of Woven Fabric - NewShovan Das100% (3)
- Torque 1Документ1 страницаTorque 1Li JefferyОценок пока нет
- Cooling BladesДокумент35 страницCooling BladesdbОценок пока нет
- Jam 14Документ12 страницJam 14Udaibir PradhanОценок пока нет
- Weight of Block + Weight Added vs. Weight of Pan + Weight AddedДокумент1 страницаWeight of Block + Weight Added vs. Weight of Pan + Weight AddedJohnoricks Ace Camarillo CatlingОценок пока нет
- GasesДокумент34 страницыGasesPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezОценок пока нет
- Phase Analysis: Making Vibration Analysis Easier: Tony DematteoДокумент11 страницPhase Analysis: Making Vibration Analysis Easier: Tony DematteoSrinivas BudatiОценок пока нет
- UNIT III Properties of Steam and Steam Power CycleДокумент8 страницUNIT III Properties of Steam and Steam Power CycleamdevaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6 - Energy - and - MomentumДокумент1 страницаWorksheet 6 - Energy - and - MomentumJNZSeriesОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Manufacturing Processes For Engineering Materials 6Th Edition Kalpakjian Schmid 0134290550 9780134290553 Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницSolution Manual For Manufacturing Processes For Engineering Materials 6Th Edition Kalpakjian Schmid 0134290550 9780134290553 Full Chapter PDFnick.fleming516100% (17)
- BSAP 2018 Revised CurriculumДокумент2 страницыBSAP 2018 Revised Curriculumrobles.migszanderОценок пока нет
- Scientific Computation: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GMBHДокумент354 страницыScientific Computation: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GMBHGalliano CantarelliОценок пока нет
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionДокумент11 страницUniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionEricka Pallon CamayudoОценок пока нет
- Fracture Lecture of AbaqusДокумент552 страницыFracture Lecture of AbaqusMohammed Abu Sufian71% (7)
- Fatigue Ch12Документ87 страницFatigue Ch12mkumar_234155Оценок пока нет
- Maxima 1Документ125 страницMaxima 1Chris LumyОценок пока нет
- Day 3 CoachingДокумент14 страницDay 3 CoachingMilton Dels RosaОценок пока нет
- Gauss Law 2 PDFДокумент41 страницаGauss Law 2 PDFAbdiyah AmudiОценок пока нет
- HERFLEX HF-50-180 - EnglishДокумент2 страницыHERFLEX HF-50-180 - Englishlaroussi aymenОценок пока нет
- Physics Bits For Fluid Dynamic PDFДокумент40 страницPhysics Bits For Fluid Dynamic PDFMALLA DOLAОценок пока нет
- Figure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityДокумент9 страницFigure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityPAULA ANDREA CARO BAEZОценок пока нет
- Coefficient of Active Earth Pressure at RestДокумент1 страницаCoefficient of Active Earth Pressure at RestAnkush PendhariОценок пока нет
- Design, Fabrication and Performance of AДокумент12 страницDesign, Fabrication and Performance of AnaveenОценок пока нет
- Question EngaaДокумент32 страницыQuestion EngaaxingchenОценок пока нет
- Dog Leg SeverityДокумент7 страницDog Leg Severitymadonnite3781Оценок пока нет
- Trosy Basel 2013aДокумент109 страницTrosy Basel 2013aRigel_TОценок пока нет
- LNG Cooldown Stresses PipeДокумент10 страницLNG Cooldown Stresses Pipechemsac2100% (2)