Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Microsoft Word Chapter 9 Stability
Загружено:
Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Microsoft Word Chapter 9 Stability
Загружено:
Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Science Form 2 note
Teacher zaidi@maher
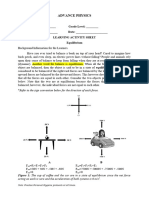
CHAPTER 9: STABILITY
CENTRE OF GRAVITY OF OBJECTS
http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/cg.html
http://www2.umist.ac.uk/construction/intranet/teaching/ul222/exp/cogex.htm
1. When an object is stationary or at rest, it is said to be in
equilibrium.
2. The centre of gravity is the exact point where an object
can be balanced.
3. The point at which an object can be balanced horizontally
is called the centre of gravity of the object.
4. The equilibrium point of an object is also its centre of
gravity.
Balanced at the point of equilibrium
Lukis rajah 9.1 m/s 80 textbook volume 2
5. When the ruler is balanced at its centre, its remains in its
position.
6. However, when the ruler is balanced at some other point
away from its centre, it will become unbalanced and tilt
to one side.
Point of equilibrium
Ruler is not balanced
Science Form 2 note
Teacher zaidi@maher
http://www.exloratorium.edu/snacks/center_of_gravity.html
Lukis rajah 9.2 m/s 81 textbook volume 2
7. The point of equilibrium in regular-shaped objects, such
as the ruler in the diagram above, is usually at its centre.
8. The point of equilibrium in a triangle or a rectangle is the
intersection of diagonal lines drawn from the corners.
centre of gravity is
The point where the
Lines meet.
9. An object with a higher centre of gravity is less stable.
10.
An object with a larger base area is more stable.
11.
When two objects have the same shape and size, the
heavier object is more stable.
Relationship Between Centre of Gravity and Stability.
1. When an object is in equilibrium, its supported either at
its centre of gravity or at a point vertically above or below
its centre of gravity.
2. Stability refers to an objects ability to remain in its
original position.
3. The stability of an object is its ability to return to its
original position when the object is moved or tilted
slightly.
4. Its is unstable equilibrium if it continues to move further
from its original position after being displaced and then
released.
5. Its in neutral equilibrium if remains in its displaced
position.
Science Form 2 note
Teacher zaidi@maher
6. Figure below shows three type of equilibrium;
Stable
Equilibrium
unstable
equilibrium
neutral
equilibrium
EXPERIMENT
Lukis rajah 9.7 m/s 83 textbook volume 2
Questions (underline the answer)
1. Is an object more stable or less stable when its centre of
gravity is raised? (more stable / less stable)
2. Is the stability of an object increased or decreased when
its base area is smaller? (increased / decreased)
Factors that affect stability.
1. The position of the centre of gravity.
A lower centre of gravity gives more stability to an object.
2. The size of the base area.
An object with a large base has better support and more
stability compared to an object with a smaller base.
3. The weight of the object.
A heavier object is more stable than a lighter one. If an
object has different densities, the heavier part of it will
have a lower centre of gravity.
Science Form 2 note
Teacher zaidi@maher
THE IMPORTANCE OF STABILITY IN OUR DAILY LIFE.
1. Racing cars are made more stable by having most of their
weight as low down as possible. This ensures a low
centre of gravity for the cars. Their wheels are also kept
far apart to give them a wide base.
2. A weight lifter bends his leg and keeps them wide apart.
3. The passengers of a double-decker bus are not allowed
to stand on the upper deck.
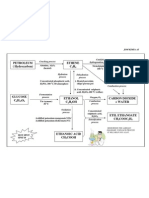
STABILITY
APPLICATIONS
IN OUR DAILY
LIFE
FACTORS
THE CENTRE
OF GRAVITY
BASE
AREA
The stability of
object is increased
lowering its centre
gravity or increasing
base area.
THE
CONTRUCTION
OF RACING CARS
AND BOATS
SPORTS SUCH AS
WRESTLING,
DIFFERENT ARTS OF
SELF DEFENCE
an
by
of
its
other reference books add one more factor that
affect the stability is the weight of the object.
..the end
Science Form 2 note
Teacher zaidi@maher
DICTIONARY
Base area
Pulley
Topple
Tilt
Centre of gravity
Equilibrium
Pivot
Stationary
Due
Incline
Blows
Sails
Beat
Opponent
Regular
Irregular
Edge
Intersection
Hip
Equidistance
Spinning
luas tapak
takal
tumbang
condong
pusat gravity
keseimbangan
pangsi
pegun
Вам также может понравиться
- Balance and Stability PowerpointДокумент36 страницBalance and Stability PowerpointCzarina Amor CabilleteОценок пока нет
- Centre of Gravity, Stability & EquilibriumДокумент6 страницCentre of Gravity, Stability & EquilibriumA BarrettОценок пока нет
- Center of Gravity 3Документ1 страницаCenter of Gravity 3gorgeouslypoisonedОценок пока нет
- Advance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumДокумент27 страницAdvance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumMilcah Shane Niones SarenОценок пока нет
- 2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFДокумент3 страницы2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFPhilip Moore100% (1)
- InertiaДокумент10 страницInertiaZalini AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Moment Notes and WorksheetДокумент10 страницMoment Notes and WorksheetarjaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2Документ42 страницыLesson 2Tr. PrincessОценок пока нет
- Center of Gravity1Документ28 страницCenter of Gravity1Leon LawnОценок пока нет
- Center of Gravity Lab ReportДокумент3 страницыCenter of Gravity Lab ReportHarlynn Joy Salmeo13% (8)
- Center of GravityДокумент28 страницCenter of GravityLeon LawnОценок пока нет
- Center of GravityДокумент21 страницаCenter of GravityIra AgcaoiliОценок пока нет
- Center of Gravity and Moment of ForceДокумент17 страницCenter of Gravity and Moment of ForceLeonidas RocksОценок пока нет
- Lab No-14Документ13 страницLab No-14ShahZaib AnwarОценок пока нет
- Center of GravityДокумент38 страницCenter of GravityYonathan EnggarОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент19 страницPhysics Projectayeaye50% (2)
- Group 2 Individual Report SuerteДокумент2 страницыGroup 2 Individual Report SuerteHnut hinorОценок пока нет
- Science G8 TG FINAL PDFДокумент230 страницScience G8 TG FINAL PDFNicole Eve Pelaez-AbarrientosОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE Q3 WK 1-2 LASДокумент24 страницыSCIENCE Q3 WK 1-2 LASAnaLizaD.SebastianОценок пока нет
- Physics Form 4: Force & Motion 1Документ55 страницPhysics Form 4: Force & Motion 1NORSHAZLINDA BINTI ROSLI MoeОценок пока нет
- Centre of Gravity and StabilityДокумент32 страницыCentre of Gravity and Stabilitylorry lamОценок пока нет
- Quarter 1 - Hybrid Module 3 Potential and Kinetic Energy Week 3Документ19 страницQuarter 1 - Hybrid Module 3 Potential and Kinetic Energy Week 3Rasty VillamorОценок пока нет
- Physics 10 - 12Документ28 страницPhysics 10 - 12jieeniola1Оценок пока нет
- Science-8 Q1 Week-3Документ19 страницScience-8 Q1 Week-3Rasty VillamorОценок пока нет
- Science TG Grade 8Документ225 страницScience TG Grade 8Aabdu Zhaif Andal100% (1)
- Science 8 Q1 M3 W3Документ19 страницScience 8 Q1 M3 W3Jason GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Centre of Gravity and Stability of An Object: GCSE PhysicsДокумент29 страницCentre of Gravity and Stability of An Object: GCSE PhysicsQuinella TuitionОценок пока нет
- Centre of Gravity and Stability PDFДокумент29 страницCentre of Gravity and Stability PDFkonincoОценок пока нет
- Notes Chapter 9 - Stability PDFДокумент18 страницNotes Chapter 9 - Stability PDFledanirudhОценок пока нет
- Centre PF GravityДокумент3 страницыCentre PF GravityAshley JagdeshОценок пока нет
- Inbound 3065761028398401936Документ21 страницаInbound 3065761028398401936Eric Alvarado SaludaresОценок пока нет
- 4 Copies Each Collated 80grДокумент41 страница4 Copies Each Collated 80grمصطفىمرجانОценок пока нет
- FORCESДокумент4 страницыFORCESRishi GovindaHarryОценок пока нет
- SLEM GRADE 8 Week3Документ7 страницSLEM GRADE 8 Week3aquino.136536120539Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityДокумент18 страницUnit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Base - p6Документ5 страницBase - p6darleneyvettebaseeeОценок пока нет
- Centre of GravityДокумент4 страницыCentre of GravityAvish GunnuckОценок пока нет
- Mass and WeightДокумент29 страницMass and WeightVinay KorekarОценок пока нет
- M7 Uniform Circular Motion Stability Center of Gravity and Equilibrium of ForcesДокумент16 страницM7 Uniform Circular Motion Stability Center of Gravity and Equilibrium of ForcesLawrence AguilosОценок пока нет
- Science Form2 - Chapter9Документ18 страницScience Form2 - Chapter9Beevy GB100% (6)
- M4-Kinematics in One-DimensionДокумент14 страницM4-Kinematics in One-Dimensionggt9zfhsjvОценок пока нет
- 1st Quarter - SCIENCE 8-WEEK 1-2Документ6 страниц1st Quarter - SCIENCE 8-WEEK 1-2MICAH NORADAОценок пока нет
- Body MechanicsДокумент7 страницBody MechanicsJanelle LasalaОценок пока нет
- Kinetic & Potential Energy: Prepared By: Marissel A. LimДокумент43 страницыKinetic & Potential Energy: Prepared By: Marissel A. LimangeliОценок пока нет
- Body Mechanics ChecklistДокумент7 страницBody Mechanics ChecklistPrincess ZantuaОценок пока нет
- General Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaДокумент42 страницыGeneral Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaLADY SUZETTE LANDICHOОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan - Balance PhysicsДокумент8 страницLesson Plan - Balance PhysicsCzarina Amor CabilleteОценок пока нет
- Science 6 DLP 37 - Kinds of EnergyДокумент8 страницScience 6 DLP 37 - Kinds of EnergyBerlyn JoyОценок пока нет
- Science-4 Quarterly Examination Reviewer:: Step by Step Procedure in Conducting The ExperimentДокумент3 страницыScience-4 Quarterly Examination Reviewer:: Step by Step Procedure in Conducting The ExperimentUnknown GeekОценок пока нет
- Scf2c9 - Answer (Rafida)Документ4 страницыScf2c9 - Answer (Rafida)JeanShuenОценок пока нет
- Science Grade 1 Forces and MotionДокумент21 страницаScience Grade 1 Forces and Motionbahjatiqbal100% (1)
- Force and Laws of Motion: Shake Its BranchДокумент4 страницыForce and Laws of Motion: Shake Its Branchtara tuitionОценок пока нет
- Science 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonДокумент14 страницScience 6 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbОценок пока нет
- Notes of Force and Laws of Motion Upto InertiaДокумент5 страницNotes of Force and Laws of Motion Upto InertiaSyed NeeshaanОценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Документ4 страницы3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Michael Edward De VillaОценок пока нет
- Force Lesson Plan 7Документ5 страницForce Lesson Plan 7Juan Miguel Sapad AlpañoОценок пока нет
- Joyful Physics Volume II: Learning by Experiencing - Momentum, Gravitational Force, and Weight WorkbookОт EverandJoyful Physics Volume II: Learning by Experiencing - Momentum, Gravitational Force, and Weight WorkbookОценок пока нет
- Open 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulДокумент1 страницаOpen 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- E Waris Paper 2 PPT f4 PDFДокумент17 страницE Waris Paper 2 PPT f4 PDFHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionДокумент32 страницыElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- I'D Like Your Permission To Sell A Photo You'Re in On Eyeem. Please Could You Fill Out This Quick Form?Документ1 страницаI'D Like Your Permission To Sell A Photo You'Re in On Eyeem. Please Could You Fill Out This Quick Form?Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- IT Chem F4 Final Year Examination (BL)Документ13 страницIT Chem F4 Final Year Examination (BL)Bayane Awang100% (1)
- Johor Trial P3 MS 2008Документ13 страницJohor Trial P3 MS 2008Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Документ14 страницIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Buku Latihan Kimia f5Документ50 страницBuku Latihan Kimia f5Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Soalan Gerakgempur Kimia Kertas 1Документ30 страницSoalan Gerakgempur Kimia Kertas 1Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Chem Topical Test (Answer)Документ19 страницForm 4 Chem Topical Test (Answer)Gee LengОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis Molten Sodium ChlorideДокумент2 страницыElectrolysis Molten Sodium ChlorideHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- IT Chemistry F5 AnswerДокумент18 страницIT Chemistry F5 AnswerHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- AR3011 Bluetooth Users GD PCДокумент74 страницыAR3011 Bluetooth Users GD PCHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Group 17, HalogenДокумент30 страницGroup 17, HalogenHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Molar Mass For ChemistryДокумент31 страницаMolar Mass For ChemistryHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Ethene C H Petroleum (Hydrocarbon) Ethane C H: Jom Kimia AiДокумент1 страницаEthene C H Petroleum (Hydrocarbon) Ethane C H: Jom Kimia AiHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Exp 4.1 For Group 1Документ8 страницExp 4.1 For Group 1Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- RPT: Science Form 3Документ14 страницRPT: Science Form 3Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Wild West DBQДокумент10 страницWild West DBQTatic SenadОценок пока нет
- FS-6525MFP-6530MFP SM PDFДокумент345 страницFS-6525MFP-6530MFP SM PDFReneeОценок пока нет
- Ôn ThiДокумент4 страницыÔn ThiKim Ánh ĐàoОценок пока нет
- Results: Fleet Optimization For Productivity ImprovementДокумент1 страницаResults: Fleet Optimization For Productivity ImprovementdileepОценок пока нет
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor: Opportunities and Challenges For PakistanДокумент17 страницChina-Pakistan Economic Corridor: Opportunities and Challenges For Pakistanوقاص صارمОценок пока нет
- NYSDOT Construction Opportunities ListДокумент71 страницаNYSDOT Construction Opportunities ListgeorgeptacОценок пока нет
- Chapter III - Chartering and CharterpartiesДокумент1 страницаChapter III - Chartering and CharterpartiesMithunОценок пока нет
- Feasibility Study On Choice of Transportation Mode: Kiran Bharat DhobaleДокумент60 страницFeasibility Study On Choice of Transportation Mode: Kiran Bharat DhobaleNikhil desaiОценок пока нет
- Airbus A380: Not Much Information Introduced in 2013Документ5 страницAirbus A380: Not Much Information Introduced in 2013DeepSinghОценок пока нет
- Tractors FiatДокумент523 страницыTractors Fiatomni_parts100% (2)
- 58.concrete Dispatch SlipДокумент1 страница58.concrete Dispatch SlipSoundar PachiappanОценок пока нет
- Gr5 Wk5 Active Passive Transport PDFДокумент2 страницыGr5 Wk5 Active Passive Transport PDFMonina Tojon OrbeОценок пока нет
- Police Chase Results InvestigationДокумент44 страницыPolice Chase Results InvestigationLas Vegas Review-JournalОценок пока нет
- HowStuffWorks - How Bridges WorkДокумент6 страницHowStuffWorks - How Bridges WorkomuletzzОценок пока нет
- Contents.: The New BMW M4 GTSДокумент31 страницаContents.: The New BMW M4 GTSturbojloОценок пока нет
- Hyundai RotemДокумент12 страницHyundai RotemFazila KhanОценок пока нет
- Plant CropsДокумент40 страницPlant CropsAmeer Jaffar A. LabanОценок пока нет
- Town PlanningДокумент31 страницаTown PlanningAviraj SawanОценок пока нет
- Volvo B13R: A Solid Base For AДокумент5 страницVolvo B13R: A Solid Base For APhilippine Bus Enthusiasts SocietyОценок пока нет
- Marx Drive Gears and The Locomotives They LoveДокумент2 страницыMarx Drive Gears and The Locomotives They LoveBill SayreОценок пока нет
- Vizio Vw32l Hdtv10a Service ManualДокумент136 страницVizio Vw32l Hdtv10a Service ManualClarence Huang100% (1)
- Diamond PileДокумент19 страницDiamond PileRamesh K Karuppannan100% (2)
- 2020-10-01 Practical Boat OwnerДокумент92 страницы2020-10-01 Practical Boat OwnerAnantoly KoretskyОценок пока нет
- Malta PresentationДокумент36 страницMalta PresentationGaurav TehlanОценок пока нет
- Gard AS - Case Study No 17 - Hot WorkДокумент2 страницыGard AS - Case Study No 17 - Hot WorkmolmolОценок пока нет
- D2.2 - Construction Site Machineries - Cranes - ElevДокумент79 страницD2.2 - Construction Site Machineries - Cranes - ElevDJОценок пока нет
- Xillinx-Zynq-based Development Plarform For ADASДокумент8 страницXillinx-Zynq-based Development Plarform For ADASSatishОценок пока нет
- Cokaliong Shipping Lines v. UCPBДокумент16 страницCokaliong Shipping Lines v. UCPBMonica Bolado-AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Wbs of Cmbt-Layout1Документ1 страницаWbs of Cmbt-Layout1Gunjan UttamchandaniОценок пока нет