Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
New Grammar's Content
Загружено:
Heidi AbbottАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
New Grammar's Content
Загружено:
Heidi AbbottАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
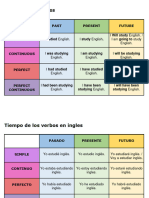
for/since, just, yet, and already
Use this tense to emphasize that something not only
happened but is still true.
English Grammar Review
Nouns, adjectives and adverbs
me
yo
u
yo
u
he
hi
m
sh
e
he
r
it
we
it
us
yo
u
yo
u
they
the
m
Reflexive pronouns
Shall I/we; Will he/she/it/you/they.
Possessive adjectives and pronouns
VERB FORMATIONS
The passive
noun/pronoun + to be + past participle
Someone washes the car every week
The car is washed every week
The definite article the
Comparatives and superlatives
Comparatives: er; Superlatives: the + adj. + est.
too, enough + to
It's too cold to swim today.
(We can't swim today - it's too cold.)
It isn't warm enough to go to the beach.
(We can't go to the beach - it's not warm enough.)
Adverbs of manner
Regulars (add ly): quick > quickly; polite > politely.
Irregulars: good > well; hard > hard; fast > fast;
early > early; late > late; loud > loud or loudly.
Verbs
THE PRESENT TENSE
Present Simple and Present Continuous
THE PAST TENSE
Past Simple and Past Continuous
Past Continuous
I had had some unhappy times, and then I met your
mother.
Use this tense to emphasize that something happened but
is not true anymore.
Present Perfect
used to
I used to work at night.
(I often worked at night, some time ago)
I'm used to working at night.
(It is normal for me to do this)
The indefinite article a
the is used when a word is used a second time, when only
one object exists, before the places we visit in a town,
before names of seas, rivers, groups of islands or
mountains, kingdoms, republics, deserts and plural
names of countries and with musical instruments when
we talk about playing them or listening to them.
Future Perfect
Use this tense to emphasize that something has not
happened but it will happen.
a is used with countable nouns to indicate one or when
talking about cost, speed or how often we do something..
when + Present Simple to describe the future
Ill phone you when/as soon as//after I see him.
No articles
No article before names of academic subjects, languages,
sports, meals, villages, towns, streets, cities, countries or
continents.
THE FUTURE TENSE
Present Continuous + time word
going to
Future Simple
The object is the same person or thing as the subject.
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself,
ourselves, yourselves, themselves
The possessive adjective is always followed by its noun
and the possessive pronoun is never followed by its noun.
hi
it
my
your
her
our your their
s
s
min
your hi her
our your their
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
Present Perfect Continuous
I've been studying English since I was a child.
'You look tired.' 'Yes, I've been working all night.'
Subject and object pronouns
I
The imperative
Conditionals
The first conditional
If she works harder, she will pass the exams.
Neutral condition: might happen, might not.
The second conditional
If she worked harder, she would pass the exams.
Unlikely, hypothetical: probably will not happen.
The third conditional
If she had worked, she would have passed the exams.
She didnt pass the exams because she didnt work.
Zero conditional
if has the same meaning as when
Modals
Modals
Shouldn't we stay? Should we not stay?
can, could
may, might
may is occasionally used to mean to be allowed to
should, must
have + to + infinitive
Gerunds and infinitives
The gerund
The gerund is used like a noun.
When a verb follows a preposition, it takes the gerund.
The infinitive
Certain verbs take the infinitive.
Can express purpose: to + infinitive, in order to +
infinitive and so as to + infinitive.
Reported speech
DIRECT SPEECH
Writing direct speech
He said, 'I'm going home.'
'I'm going home,' he said.
say, tell
tell has a personal direct object (e.g. me, hint, her, etc)
and say never has a personal direct object.
INDIRECT SPEECH
Reported statements with no change of tense
Reporting verb in present, present perfect, or future.
Reported statements with a change of tense
Reporting verb in past tense.
Sentence structure
WORD ORDER
Direct object and indirect object
Frequency adverbs with the Present Simple
Link words: and, but, so, then, before, after,
because
Link words: because, as, since
both ... and, neither... nor
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Making questions
Who asked you? Who did you ask?: question
words as subject or object
Short responses using so, neither, nor
Short responses: / think so, I hope so
RELATIVE CLAUSES
Relative clauses with who and that
Prepositions
PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE
at in, on
Prepositions of movement
Prepositions of position and movement
Prepositions of position and movement
Certain verbs with to or at
PREPOSITIONS OF TIME
at, in, on
until
until, before, after
Prepositions of time
Phrasal Verbs
Some common phrasal verbs
More phrasal verbs
Phrasal verbs that don't take an object
Phrasal verbs that take an object: separable
Phrasal verbs that take an object but do not
separate
Вам также может понравиться
- Grammatica Inglese 2Документ9 страницGrammatica Inglese 2Cristina BonansingaОценок пока нет
- Traditiile Romei AnticeДокумент13 страницTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauОценок пока нет
- E3 Act6.2 LanguageInformationДокумент31 страницаE3 Act6.2 LanguageInformationFRIDA LILIANA GONZALEZ REYESОценок пока нет
- English Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiДокумент11 страницEnglish Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiFaris ArifiansyahОценок пока нет
- Verbs Explained: Kinds, Tenses, Forms & MoreДокумент27 страницVerbs Explained: Kinds, Tenses, Forms & MoreJeff LacasandileОценок пока нет
- Grammar Tenses ReportДокумент13 страницGrammar Tenses ReportAlberto Emiliano Montoya OlivoОценок пока нет
- I Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolДокумент11 страницI Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolEmil FejzagićОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech BreakdownДокумент9 страницParts of Speech BreakdownqwertyphonesОценок пока нет
- 5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICAДокумент11 страниц5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICAShalomPC SystemsОценок пока нет
- Articles and Pronouns GuideДокумент8 страницArticles and Pronouns GuideAdzimah ZullОценок пока нет
- Simple Present and Past TensesДокумент12 страницSimple Present and Past Tensesاحمد حسين مجيد رستمОценок пока нет
- 12 Verb Tenses in English ExplainedДокумент10 страниц12 Verb Tenses in English ExplainedAl HopkinsОценок пока нет
- Tenses of Verb Pre-DemoДокумент31 страницаTenses of Verb Pre-DemoMaridel DiamsayОценок пока нет
- Words TypesДокумент23 страницыWords TypesAlejandro RochaОценок пока нет
- Basic Grammar and ConversationДокумент56 страницBasic Grammar and ConversationAfaf Mahmoud50% (2)
- Verbs 100820034257 Phpapp02Документ27 страницVerbs 100820034257 Phpapp02Vanessa BanderaОценок пока нет
- Present PerfectДокумент59 страницPresent PerfectAlejandro PrezaОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Oxford Learn 4HAVOДокумент25 страницEnglish Grammar Oxford Learn 4HAVOThijs van der KleinОценок пока нет
- English Grammar GuideДокумент25 страницEnglish Grammar GuideThijs van der KleinОценок пока нет
- Special BeginnerДокумент15 страницSpecial BeginnerabdulhakimОценок пока нет
- Chocó Technology UniversityДокумент43 страницыChocó Technology UniversityIvonne Aguilar MosqueraОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Oxford Learn 4HAVOДокумент25 страницEnglish Grammar Oxford Learn 4HAVOThijs van der KleinОценок пока нет
- TESOL2Документ8 страницTESOL2Kerri GastonОценок пока нет
- Comparing Adverbs: Worse, More EasilyДокумент9 страницComparing Adverbs: Worse, More EasilyFABIAN FIENGOОценок пока нет
- Adverb Spelling Notes: Give Me That Tape, PleaseДокумент12 страницAdverb Spelling Notes: Give Me That Tape, PleaseBeaux BambieОценок пока нет
- Present Simple vs Continuous and Simple PastДокумент15 страницPresent Simple vs Continuous and Simple PastIvo Luciano Aboo SarifoОценок пока нет
- Adverbs of Manner and Other TypesДокумент30 страницAdverbs of Manner and Other TypesOlga VainaliОценок пока нет
- Past Vs Future: The Past Simple Tense, Also Called The Simple Past, Is Used For Past ActionsДокумент4 страницыPast Vs Future: The Past Simple Tense, Also Called The Simple Past, Is Used For Past ActionsfiorellaОценок пока нет
- InglesДокумент20 страницInglesJesús RamsésОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect TenseДокумент9 страницPresent Perfect TenseHizkiel SembiringОценок пока нет
- Parts of speech, conditional sentences, and adverb rulesДокумент10 страницParts of speech, conditional sentences, and adverb rulesBalach M. TheboОценок пока нет
- AdverbsДокумент13 страницAdverbsDelia CatrinaОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Guide - Articles, Nouns, Verbs & MoreДокумент5 страницEnglish Grammar Guide - Articles, Nouns, Verbs & MoreAngela Cristi LimОценок пока нет
- Easy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishОт EverandEasy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Grammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFДокумент85 страницGrammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFKarma Kuenzang WangdiОценок пока нет
- Simple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningДокумент16 страницSimple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningyanieggОценок пока нет
- GROUP 1-Nouns and PronounДокумент29 страницGROUP 1-Nouns and PronounAMA MUTTAHIZI AHADAN AUHANОценок пока нет
- English Grammar FinalДокумент47 страницEnglish Grammar Finalanjaani13100% (1)
- AdjectiveДокумент4 страницыAdjectiveKristine Joy GuaroОценок пока нет
- Simple Present and Future TensesДокумент8 страницSimple Present and Future TensesFlorencia MaccaroneОценок пока нет
- Unit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Документ14 страницUnit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Johana CamposОценок пока нет
- Present Continuous and Simple Present TensesДокумент17 страницPresent Continuous and Simple Present TensessherinaОценок пока нет
- Tense and TimeДокумент6 страницTense and TimeSatarupa SenОценок пока нет
- Final Assignment of English: Pysiotherapy Academi of St. Lukas Tomohon 2010Документ12 страницFinal Assignment of English: Pysiotherapy Academi of St. Lukas Tomohon 2010cbxfОценок пока нет
- Grammar FundamentalsДокумент12 страницGrammar FundamentalsCilok CakepОценок пока нет
- FELn TenseДокумент8 страницFELn TenseMohammedselam MdОценок пока нет
- Suport Curs Gramatica Sem 1 2012Документ19 страницSuport Curs Gramatica Sem 1 2012Alexandru CraciunescuОценок пока нет
- TENSE-ASPECT SYSTEM (Villasis - Orlanes)Документ18 страницTENSE-ASPECT SYSTEM (Villasis - Orlanes)Christine Joy VillasisОценок пока нет
- Economic Verbs and Tenses for Business EnglishДокумент48 страницEconomic Verbs and Tenses for Business EnglishCristina AlexeОценок пока нет
- Verb Tenses - NewДокумент16 страницVerb Tenses - NewSai AmruthaОценок пока нет
- + Gerund: Will, Going ToДокумент7 страниц+ Gerund: Will, Going ToTeresa De Jesús Juárez GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- Some Points About English Language: M.N.SamavatiДокумент20 страницSome Points About English Language: M.N.SamavatiMaryamОценок пока нет
- Adverbs 21Документ20 страницAdverbs 21Carola TorrealbaОценок пока нет
- 16tens HukumДокумент42 страницы16tens Hukumlathif zdayОценок пока нет
- Spanish III H Study Guide Created by Easy-NotesДокумент11 страницSpanish III H Study Guide Created by Easy-NotesawarmwalrusОценок пока нет
- Homophones: Words that Sound AlikeДокумент4 страницыHomophones: Words that Sound AlikeWinnie Bautista MercadoОценок пока нет
- Presentation 24Документ14 страницPresentation 24Thurein Lin ThantОценок пока нет
- Webster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageОт EverandWebster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageОценок пока нет
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОт EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОценок пока нет
- Conversion Rule in ALEДокумент7 страницConversion Rule in ALEHeidi AbbottОценок пока нет
- Como Criar Function Module EXIT in SAP ABAP With TutorialДокумент3 страницыComo Criar Function Module EXIT in SAP ABAP With TutorialHeidi AbbottОценок пока нет
- Vpnclient SetupДокумент1 страницаVpnclient SetupPaul WhiteleyОценок пока нет
- VPNClient Removal ManuallyДокумент5 страницVPNClient Removal ManuallyHeidi AbbottОценок пока нет
- VPN Client 5007Документ16 страницVPN Client 5007aldo1980Оценок пока нет
- VPNClient Removal ManuallyДокумент5 страницVPNClient Removal ManuallyHeidi AbbottОценок пока нет
- ABAP01Документ76 страницABAP01Luiz O. GiordaniОценок пока нет
- TND PDC Handbook 2010-1Документ162 страницыTND PDC Handbook 2010-1Sherilyn Powell100% (2)
- 5 Senses Taste and Hear SkittlesДокумент5 страниц5 Senses Taste and Hear Skittlesapi-569849927Оценок пока нет
- DSM-5-TR Neurocognitive-Disorders-Supplement 2022 APA PublishingДокумент66 страницDSM-5-TR Neurocognitive-Disorders-Supplement 2022 APA Publishing574Suvie Fatimah AzzearaОценок пока нет
- Rundown Workshop Inovasi Dan Improvement-1279299 PDFДокумент1 страницаRundown Workshop Inovasi Dan Improvement-1279299 PDFSyiffaОценок пока нет
- Cu 31924081220968Документ176 страницCu 31924081220968Jerrin GeorgeОценок пока нет
- 0386Документ239 страниц0386Mohsin RazaОценок пока нет
- T-Tess GoalsДокумент2 страницыT-Tess Goalsapi-414999095Оценок пока нет
- Crumple and ShootДокумент24 страницыCrumple and ShootDianne MasapolОценок пока нет
- Theories of Language Evolution and DefinitionsДокумент6 страницTheories of Language Evolution and DefinitionsHaleema KhalidОценок пока нет
- Intentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating 9Th Edition Ivey Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент34 страницыIntentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating 9Th Edition Ivey Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevahuynh4vn8d100% (8)
- Reviewer Midterm Fola 0313 Basic SpanishДокумент5 страницReviewer Midterm Fola 0313 Basic SpanishAngelyn JacintoОценок пока нет
- PH 104 NotesДокумент12 страницPH 104 NotesJOSE GABRIEL MALLARIОценок пока нет
- Why Is Modus Tollens A Valid Form of ArgumentДокумент3 страницыWhy Is Modus Tollens A Valid Form of ArgumentACCIStudentОценок пока нет
- G 6, ServicescapeДокумент15 страницG 6, ServicescapeDolores H. RichmanОценок пока нет
- Thesis Statement On Technology and EducationДокумент8 страницThesis Statement On Technology and Educationmichellejohnsoncharleston100% (2)
- Hypnotherapy From A To Z Manual PDFДокумент446 страницHypnotherapy From A To Z Manual PDFjohannes2212100% (2)
- Self - Check - PatalitaДокумент3 страницыSelf - Check - PatalitaJourdyllene Prince PatalitaОценок пока нет
- Workshop..oral ComДокумент5 страницWorkshop..oral ComDana Althea AlgabreОценок пока нет
- Language and Linguist Compass - 2007 - Romaine - Preserving Endangered LanguagesДокумент18 страницLanguage and Linguist Compass - 2007 - Romaine - Preserving Endangered LanguagesConstanza MuñozОценок пока нет
- Katia Sachoute Ead 523 Clinical Field Experience A Professional Development ProgramДокумент6 страницKatia Sachoute Ead 523 Clinical Field Experience A Professional Development Programapi-639561119Оценок пока нет
- KS3 - English - Punctuation - Avoiding - Comma - Splicing - 01 Homework PDFДокумент4 страницыKS3 - English - Punctuation - Avoiding - Comma - Splicing - 01 Homework PDFRania FarranОценок пока нет
- Syl Log IsmsДокумент22 страницыSyl Log IsmsjiashengroxОценок пока нет
- A Study in Personal OntologyДокумент6 страницA Study in Personal OntologyÖmer OsmanoğluОценок пока нет
- Effective Time Management For High Performance in An OrganizationДокумент4 страницыEffective Time Management For High Performance in An OrganizationHiteshОценок пока нет
- Sleep, Dreams, & More (: Exploring Consciousness)Документ46 страницSleep, Dreams, & More (: Exploring Consciousness)Sheila G. DolipasОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Global Supply Chain Management 2022Документ21 страницаSyllabus Global Supply Chain Management 2022Ya YaОценок пока нет
- 13 Habits That Hinder Critical ThinkingДокумент17 страниц13 Habits That Hinder Critical ThinkingArina ShahirahОценок пока нет
- Theories, Frameworks, and ModelsДокумент34 страницыTheories, Frameworks, and Modelsgctv049182% (11)
- The Power of Language - How Words Shape People, CultureДокумент8 страницThe Power of Language - How Words Shape People, CultureludipovaОценок пока нет
- Child and Adolescent Development PrinciplesДокумент5 страницChild and Adolescent Development PrinciplesCiara Janine Meregildo100% (3)