Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
#6 Bai Yamin Paper2
Загружено:
mersiumАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
#6 Bai Yamin Paper2
Загружено:
mersiumАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Analyses of Typical Fault on Stator End-Windings of Turbine-Generator and
Available Countermeasures
Bai Yamin
North China Electric Power Research Institute, China
byamin@cj.net.cn
Abstract--The fastening system loosening is a frequently
typical fault on stator end-windings of turbine-generators, the
faults or failures related to it including fastening bolts, nuts and
washers loosening, insulation worn-out, strands rupture, short
circuit between phase to phase or to the earth, and so on which
have a severe danger to insulation system so that is a huge
menace to machine operation safety. This paper presents some
instances with the faults in China and introduces analyses for
causes and offers some recommendations on the effective
countermeasures with successful practices.
Key words-Turbine-Generator Stator End-Windings Fault
I. INTRODUCTION
uring generator operation normally the stator endwindings are continuously vibrating under alternating
electromagnetic forces with double fundamental frequency.
Because stator end-windings of generator are similar to the
cantilever, especially turbine-generator with longer end parts,
it is very important in design, construction and operation for
avoiding end-windings damaged by vibration. Due to the
electromagnetic forces directly proportional to square current,
so the greater is capacity of generator, the more serious is
vibration problem. Experiences indicate that fastening system
loosening on stator end-windings is a frequently typical fault
for modern great generators. Appearance of the fault might
has variety, e.g. local insulation worn-out on end-windings,
some fixed component loosening and epoxy mud occurred on
the end areas, as to some bolts or nuts dropped down and so
on, which one or more can be discovered during overhaul.
Because the fault should raise vibration amplitude of endwindings, it can little by little worsen and speed up so that
eventually become a serious failure disaster if have no any
treatment in time.
Today a generator with advantage technology ought to
have many reliable measures avoiding vibration excess on
end-windings, e.g. for preventing resonance with
electromagnetic force that natural frequencies of end parts
should avoid double fundamental frequency (100 Hz) and
modal shape of end-windings should not be elliptical shape;
for releasing heat stress and ensuring fastness of end
construction that the end construction should be flexible on
axis direction, and so on. However the vibration state of endwindings actually is changeable under electromagnetic force
and heat stress for a long time in addition to micro-shrinkage
or worn-out of insulation or local loosening. The change of
natural frequencies and modal shapes may make they put in
the dangerous resonance region with 100 Hz even if the
Iris Rotating Machine Conference
June 2007, San Antonio, TX
original had no problem. Unfortunately this change can not
be monitored by normally electrical monitor or mechanical
monitor out of machine so that it is difficult to avoid failure at
all on end-windings. Therefore it is necessary for avoiding
failure to regulate some countermeasures during installation
or overhaul, e.g. detail inspecting to end-windings and doing
dynamic characteristic test and so on.
Actually it is necessary and possible for safety operation to
directly monitor vibration amplitude of end-windings of
stator. The monitor vibration on end-windings also has
special significance to the generator with end part problem
i.e. elliptical modal shape with 100 Hz more or less. It is
difficult to handling the machine because the modal shape of
end-windings is hardly changed by simply modify to end
constructions. If reforming the end-windings entirely the cost
will very expensive and maybe have no certainty of full
success relied on existing technology. Meanwhile the
generator might have already operated for a long time without
any fault, which indicates the end construction is quite
fastening, but it is evident that no body can ensure it in good
condition forever. For the generators with vibration problem,
an economic, reliable and simple treatment method is to
install monitor system to vibration, which can realize warning
of early faults so that effectively avoid sudden failure.
The Author will commence from some fault instances, and
then introduces our efforts against the faults including
experiment methods, available countermeasures and some
successful instances in China.
II. FAULT INSTANCES
A. Fault from End Construction Problem
On Sept. of 1998, a turbine-generator with 500 MW by
Russian made happened a trouble that much hydrogen leaking
from inner-cooling-water tank of the stator windings up to
full scales of type AT 0012 Gas Meter (4% by density) so
that had to stop the machine and to take out the rotor for
examining the fault. Some abnormal phenomena were
discovered with water pressure test e.g. there were a lot of
epoxy mud and some watermarks on end windings of
excitation side, also several insulation pieces dropped out and
worn out. Further examination indicates partial insulation of
several bars was seriously worn out or even copper was bared
out and some hollow strands have cracks. Figure out that 12
support spots became relaxation, 22 binding insulation pieces
dropped out and 8 bars were worn out. Please show pictures
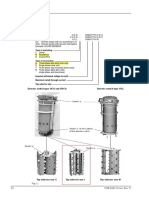
about the fault objects in Fig. 1.
1
Fig. 1 Worn out of Insulation of Bars due to End Construction Loosening
Analyses of the fault indicate the direct cause is the
construction of the stator end windings and manufacture
technology not good, which the binding ropes are too thin
and insulation piece edges are too sharp. Besides it maybe has
resonance at 100 Hz on stator end windings. In 1997 during
the first overhaul, similar phenomena that the support
looseness and the insulation pieces dropping out also were
discovered so did special treatment. For further analyzing the
fault we measured the natural frequencies and the modal
shapes on the stator end windings. Owing to some support
components taken down before test, the test results should not
be full same as the machine stopping before. But also the test
results indicate many bars on excitation side have natural
frequencies near by 100 Hz and have a irregular modal shape
at 108 Hz, meanwhile on the turbine side have ellipse modal
shape at 115 Hz. Experience and theory research indicates the
natural frequencies of bars should drop down 2 Hz ~ 10 Hz
due to heating during generator operating. Therefore basically
it was confirmed that the resonance sped up and aggravated
vibration effects to end winding construction.
The generator went on overhaul immediately and replaced
all bars in stator result in halted 118 days.
B. Fault from Current Surge Failure
On May of 2002, a turbine-generator with 500 MW in
North China happened a large trouble from a mistake
operation of field regulator that caused generator lost
excitation and oscillated with power system, which generator
absorb reactive power up to 444 Mavrs in the first oscillating
cycle and next then oscillation of active power between 290
MW and 450 MW and of reactive power between -278 Mavrs
and -666 Mavrs, meanwhile of frequency between 49.9 Hz
and 51.0 Hz and of IA between 9 kA and 29.5 kA, which
oscillation lasted 4 minutes and 10 seconds and oscillation
cycle is 5.2 seconds. After the failure the examination of
generator construction did not find out any abnormal spot so
it continues operation[1]. On January of 2003 during overhaul
many evident fault spots of loosening and worn-out on endwindings of stator were recovered which the most serious
fault is insulation worn-out up to 3 mm ~4 mm so that it may
develop to become disastrous short circuit failure at any
moment if the machine had run again continually.
Iris Rotating Machine Conference
June 2007, San Antonio, TX
According the fault analysis it is the oscillation failure
happened 8 months ago that made the end fastening
construction some degree damage by current surge with many
times even though it looked like no abnormal at that time.
The manufacturer undertook restoration job in addition to
partial reinforcement. However the works cannot assure that
generator restores original condition so we are also anxious
about loosening fault appearing again in the future.
In recent years there also were several generators in China
that happened the serious troubles cause by end-winding
vibration problem, e.g. insulation worn-out, fatigue fracture
or water leakage of hollow conductors in nose-end, or even
short circuit failure between phase to phase or to earth. The
failures of the kinds caused by the faults on end-windings
have a feature of emergency and hardly any simple repair so
the economic losses with the failures are very huge, so that it
is very necessary to pay attention particularly to the faults.
III. PREVENTIVES FOR STATOR BAR INSULATION WORN-OUT
A. Design and Technology on End Winding Construction
The most problems of design and technology belonged to
manufacturers should be cleared up in manufactories. Up to
date Chinese manufacturers have been adopting some new
technologies and standards about end winding construction,
e.g. axial flexible support construction and natural
frequencies avoiding 100 Hz as far as possible. Now Industry
Standard[2] of China about measuring modal shapes and
natural frequencies on stator end windings of turbinegenerators provides that the generators with 300 MW and
over should permit no the natural frequencies between 94 Hz
~ 115 Hz and no elliptic modal shape before leaving from
manufactory. In recent years our manufacture quality has had
evident improvement but also there are some problems need
to resolve, e.g. hope the natural frequency avoiding region
can further to expand.
B. Pay Attention to Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Every maintenance and overhaul should in detail examine
stator end winding construction, particularly pay attention to
the marks of insulation worn out. If the looseness on end
construction is discovered must go on modal test of vibration
so that confirm resonance problem. The related Industry
Standard[3] provides that the generators with 200 MW and
over should carry out modal test during overhaul and the
limits as the above. According to test results can determine
repair program and check up the repair effects. In 2000 we
took a modal test for a generator with 300 MW that was
discovered seriously looseness existing i.e. 4 bolts on support
dropped down, 12 bolts were loosened and 6 spots on
insulation system were worn out. The test results indicate the
generator has modal shape with 7-petal at 101 Hz (modal
damping 1.58%) and modal shape with 8-petal at 112 Hz
(modal damping 1.88%), therefore can confirm the looseness
related to resonance at a contain extent. It is interesting that
the test again going on after repair with restoring insulation
and end construction indicates no modal frequencies between
89.5 Hz ~137.9 Hz and modal damping increased up to
4.45% and over. Since the tests proved repair effects and
provided with safe data for operation.
This instance also shows the natural frequencies maybe
change after a long time of operation, and particularly the
change will occur following the looseness. Therefore it is
necessary for regularly carrying on modal test. From 1998 we
have done the tests about 50 times and obtained many test
data that are useful to evaluate generator operation.
If a generator happened a huge surge of stator current, e.g.
single phase or three-phase short circuit, serious oscillation
fallen out step etc. it ought to be inspected and treated for
fastening constructions of stator end-windings as soon as
possible. If no defect it can continue operation but should be
examined again in one year. Generally a long time of several
months passed may reveal the latent defects of fastening
problem on stator end-windings so the treatment in time will
effectively avoid it developing to become a serious failure.
C. Monitor Generator Operation with Advanced Technology
1) Monitor Vibration on Stator End Windings
Amplitude of vibration on stator end windings during
operation can directly indicate the condition of vibration. If
the looseness or the worn-out appears the amplitude of
vibration will increase quickly and even go beyond the limit.
This time should be ideal right time to stop and examine the
machine for avoiding damage.
Our practices indeed prove that the condition maintenance
with monitoring vibration on end-windings of stator is very
effective measures to ensure safety operation of generator.
Particularly it is a key link for avoiding failure as the machine
having vibration problems on end-windings by modal test
confirming.
Because of the characters of generator inner with high
potential, strong electromagnetic field etc. it is very important
for choice of devices of monitor system in reliability and
availability. We consider that the optical fiber system
monitoring vibration has an evident advantage in safety and
ought to firstly select it even price higher.
Because of limitation of monitor spots the monitor system
cannot absolutely avoid the entire end winding faults. For
example, on June of 1998 a generator with 667 MW in China
took place a failure of short circuit on a leading wire of stator
end windings to earth. The generator has a monitor vibration
system by ALSTHOM, but the fault spot has no detector. The
specially measured value at same spot on another generator
with same type in this power plant indicates the amplitude of
vibration up to 930 m, but the alarm set only at 500 m by
manufacturer.
2) Monitor Hydrogen Leaking from Inner-Cooling Water
Tank of Stator Windings
Due to hydrogen pressure higher then water pressure, if
there is gas leaking from inner-cooling water tank of stator
Iris Rotating Machine Conference
June 2007, San Antonio, TX
windings which should indicate leaking problem existed on
inner-cooling water system, including seal of water joint
becoming invalid, welding seams splitting, insulation
manifolds damage or inner-cooling strands damage etc.,
which each one can bring on serious short circuit failure.
Therefore it is important for monitoring hydrogen leaking
from the water tank. The instance on the A of section II of
this paper also shows that the first alarm is gas leakage from
the water tank for bars worn out. As early as the nineties a
hydrogen detector for turbine-generator has been developed
by us that adopted Pd-gate MOS as hydrogen-sensitive
element and can measure hydrogen percentage concentration
from 0%~4%. Up to date the hydrogen detectors have been
installed on above 20 generators only in North China Power
Network [4].
IV. OUR PRACTICE OF MONITOR VIBRATION OF STATOR ENDWINDINGS
We have been doing some works on monitoring vibration
on stator end windings in recent years. The vibration monitor
systems installed on stator end-windings of turbinegenerators are either acceleration sensors of optical fiber or
piezoelectric crystal type or both.
A. Application Instance
There is a 200 MW turbine generator with type QFQS200-2 made in China went operation in 1986, which up to
date took place 4 time failures of insulation damage of stator
bars in its history. Except for poor manufacture quality the
direct cause is vibration character of end-windings not good.
In 1998 during overhaul the modal shapes of end-windings of
stator both turbine side and excitation side were confirmed
being elliptical modal shape with natural frequency about 107
Hz by modal test. According to Chinese Standard[3] the test
result indicates the fastening constructions of stator end have
a serious vibration problem. For avoiding failure some
measures can be adopted to stator end-windings are either
thoroughly reforming the end constructions for natural
frequency change or installing monitor system for vibration.
In view of the machine has been operating without any fault
for a long time, particularly no evident worn-out and
loosening cases on the end-windings, that indicates either
modal damp is bigger so that restraining the vibration
amplitude or oscillation frequency band is very narrow so that
have no resonation even though near by the oscillation
frequency yet. This operation condition maybe can maintain a
very long time or not, eventually with operation time
extending the danger of end-winding damage will appear
more and more due to the fastening constructions might
gradually become poor with vibration. We consider the good
choice is to install monitor system for vibration because of
the investment less and realizing early warning to the end part
faults for operation safety.
B. Selection and Installation of Monitor System
By integrated survey for supply, prices and achievement etc.
we chose an optical fiber system by VibroSystM Inc. of
Canada made specially for monitoring vibration of stator endwindings, which the acceleration sensor is called FOA-100
type and data treatment and display device is called PCU-100
type. We installed 6 sensors separately on excitation side and
turbine side.
In order to compare we also installed 6 acceleration
sensors with piezoelectric crystal type at low electrical
potential spots on same sides of the generator.
C. Operation Condition of Monitor Systems
Since summer of 1999 installed the monitor systems both
the generator and the monitor devices have been operating
normally. The optical fiber monitor system is real time work
on line and can display vibration amplitude with automatic
alarm and data record function. The piezoelectric crystal
measurement system needs routine sampling so total took 3
times after installation and eventually had been token out
during a minor overhaul.
We set the alarm at 150 m of amplitude or by a sudden
change over 50 m, and if the amplitude over 250 m should
stop the machine to examine.
Because the two systems have different sampling spots the
results cannot compare directly with each other, however also
have certain comparable i.e. all data displayed are within
allowed limits. Now the generator is steadily operating
usually under 100 m of amplitude. The maximum of
amplitude recorded by the optical fiber monitor system is 178
m also less then the limit of machine stop.
On November of 2000, the vibration amplitude of the 43rd
bar increased 75 m suddenly and lasted about 10 days then it
also went back to original value 40 m or so. During a next
minor overhaul the end part was inspected particularly to the
43rd bar and near region, and so the support bolt loosening
between 44th bar and 45th bar was discovered and was treated
in time.
The monitored results indicate the machine condition is
normal and vibration amplitude is within limit values even
though it has elliptical modal shapes with frequencies nearby
100 Hz. Therefore it can run continue under monitoring for
vibration and it not necessary to reform end construction for
change natural frequency so that saved over 3,000,000 of
reforming expense and avoided economic losses by kWh up
to several hundred millions owing to outage for 80 days
according to original reforming schedule, meanwhile also
increased availability ratio and reliability level of the
generation unit. So the power plant obtains good economic
benefit from it.
constructions on stator end-windings is a typical common
fault or failure in turbine generators. This paper introduces
and analyzes several fault instances in China, then presents
some available countermeasures to the faults.
Practice indicates the above fault may grow to short circuit
failure between phase to phase or to earth and the dynamic
condition of end-windings during operation cannot be known
well by mean of regular methods e.g. monitoring out machine
or off-line test. In order to avoid generator failure, firstly
ought to improve design and technology quality including to
make fastening system of end-windings stronger and more
perfect, i.e. the natural frequencies avoiding double
fundamental frequency and vibration amplitude as smaller as
possible, meanwhile can endure larger current surge without
recessively harmful deformation; secondly ought to enhance
inspection during overhaul, particularly carry out modal test
to stator end-windings for mastering its history, current
situation and trend in the future for end vibration condition.
Practices prove that the monitoring vibration on stator endwindings is very effective measures to ensure safety operation
of generator. Particularly the monitoring vibrating amplitude
is a key link for avoiding failure as the machine having
vibration problems on end-windings. Because of the
characters of generator inner with high voltage, strong
electromagnetic field etc. it is very important for monitor
system choice in reliability and availability. We consider that
the optical fiber system monitoring vibration has an evident
advantage in safety and ought to firstly select it even price
higher.
This paper presents a successful instance of optical fiber
system monitoring vibration for a turbine-generator with 200
MW and the actual beneficial results obtained.
VI. REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
Li Xinyou and Ren Yibin, Effect of Excitation System Failure in 500
MW Generator on Power System, North China Electric Power, pp. 3134, No. 11, 2002, Nov. 2002
Modal Test Analyses and Natural Frequency Measurement Methods of
Large Turbo-Generators on Stator End Windings and Evaluation
Criteria, Chinese Engineering Industry Standard JB/T 8990-1999, Jan.
2000
Measurement and Evaluation of the Dynamic Characteristic on Stator
End Windings of the Large Turbo-Generator, Chinese Power Industry
Standard, DL/T 735-2000, Jan. 2001
Xu Yongxiang, Bai Yamin and Lu Ming, Development and
Application of Generator Hydrogen Leakage Monitor, Electrical
Equipment, pp 71-73, Vol. 1, No. 3-4, Dec. 2000
V. CONCLUSION
Insulation worn-out caused by loosening of fastening
Iris Rotating Machine Conference
June 2007, San Antonio, TX
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Welding Electrode Classifications 123Документ2 страницыWelding Electrode Classifications 123Unnikrishnan RajanОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation Notes by Alamgir RahimДокумент66 страницInstrumentation Notes by Alamgir RahimmersiumОценок пока нет
- Valves and ActuatorsДокумент129 страницValves and Actuatorsmhmd100% (1)
- Shaft AlignmentДокумент20 страницShaft AlignmentmersiumОценок пока нет
- Pages From 1ZSE 5492-116 en Rev 11 (Installation and Commissioning Guide)Документ1 страницаPages From 1ZSE 5492-116 en Rev 11 (Installation and Commissioning Guide)mersiumОценок пока нет
- Stefan M Hoek Omicron PDFДокумент7 страницStefan M Hoek Omicron PDFmersiumОценок пока нет
- Ga 55 PDFДокумент50 страницGa 55 PDFTareq Murshed Biplab88% (8)
- Motor Protection Application GuideДокумент28 страницMotor Protection Application Guidemersium100% (1)
- 14 04 08 Referenslista Turbo (SE En)Документ11 страниц14 04 08 Referenslista Turbo (SE En)mersiumОценок пока нет
- Lecture 07 Prof - Dr.ing. Peter WerleДокумент19 страницLecture 07 Prof - Dr.ing. Peter WerlemersiumОценок пока нет
- Creating A World That Doesnt BreakdownДокумент23 страницыCreating A World That Doesnt BreakdownmersiumОценок пока нет
- CP 05-12 En-2Документ2 страницыCP 05-12 En-2mersiumОценок пока нет
- Price ListДокумент2 страницыPrice ListMalik ZunairОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Motor Current UnbalanceДокумент3 страницыThree-Phase Motor Current UnbalancejoabaarОценок пока нет
- DUVR110RY5M: Product Data SheetДокумент2 страницыDUVR110RY5M: Product Data SheetmersiumОценок пока нет
- Maintenance - Technical Seminar For Cathodic Protection To GOGC DesignДокумент9 страницMaintenance - Technical Seminar For Cathodic Protection To GOGC DesignmersiumОценок пока нет
- Understanding Accuracy Specifications Technical Note B211482ENДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding Accuracy Specifications Technical Note B211482ENparam540Оценок пока нет
- Plant Valves PDFДокумент49 страницPlant Valves PDFmersiumОценок пока нет
- Cathodic Protection - Maintenance - of - SystemsДокумент15 страницCathodic Protection - Maintenance - of - Systemscadtil100% (1)
- BusTrac User ManualДокумент62 страницыBusTrac User ManualmersiumОценок пока нет
- HPT High Speed Boiler Feedwater PumpsДокумент49 страницHPT High Speed Boiler Feedwater PumpsvijeyimusОценок пока нет
- Gaskets 111Документ32 страницыGaskets 111mersiumОценок пока нет
- Jurgen SchwarzДокумент6 страницJurgen SchwarzmersiumОценок пока нет
- Advanced Gas Path BrochureДокумент8 страницAdvanced Gas Path BrochuremersiumОценок пока нет
- Machinery Alignment: Prepared by WAДокумент23 страницыMachinery Alignment: Prepared by WAmersiumОценок пока нет
- AlignmentДокумент14 страницAlignmentmersiumОценок пока нет
- 1 Crankshaft AlignmentДокумент6 страниц1 Crankshaft AlignmentmersiumОценок пока нет
- SiemensPowerAcademy 2012catalogДокумент40 страницSiemensPowerAcademy 2012catalogmersiumОценок пока нет
- Welding Electrode Classifications 123Документ2 страницыWelding Electrode Classifications 123Unnikrishnan RajanОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Close Up b1 AnswersДокумент6 страницClose Up b1 Answersmega dragos100% (1)
- Mazada Consortium LimitedДокумент3 страницыMazada Consortium Limitedjowila5377Оценок пока нет
- External InterruptДокумент4 страницыExternal Interruptsiva kumaarОценок пока нет
- Collaboration Proposal FormДокумент4 страницыCollaboration Proposal FormGabriel TecuceanuОценок пока нет
- What Is Situational Coaching and When To Use ItДокумент3 страницыWhat Is Situational Coaching and When To Use ItBrian KamoedОценок пока нет
- Exercises-Consumption Based Planning PDFДокумент4 страницыExercises-Consumption Based Planning PDFfitroniОценок пока нет
- CasДокумент2 страницыCasJamesalbert KingОценок пока нет
- Rizal and The Theory of NationalismДокумент37 страницRizal and The Theory of NationalismLiza Betua Sotelo78% (58)
- Toro 006Документ2 страницыToro 006Eric CОценок пока нет
- MAS500 2011 Vår Masteroppgave Henrik Engedal Per Magne EgelidДокумент130 страницMAS500 2011 Vår Masteroppgave Henrik Engedal Per Magne EgelidPoppy DanielsОценок пока нет
- Aerospace Material Specification: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Moldings General Purpose Grade, As SinteredДокумент8 страницAerospace Material Specification: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Moldings General Purpose Grade, As SinteredMax Salogni50% (2)
- PDF EnglishДокумент36 страницPDF EnglishSanti CheewabantherngОценок пока нет
- 0404 eДокумент80 страниц0404 eFrancisco MisleОценок пока нет
- Excel Tips Tricks e-BookV1.1 PDFДокумент20 страницExcel Tips Tricks e-BookV1.1 PDFSulabhОценок пока нет
- Prima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiДокумент12 страницPrima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiGita GloriaОценок пока нет
- Hypersizer For Composite Bicycle AnalysisДокумент29 страницHypersizer For Composite Bicycle AnalysislawrenceОценок пока нет
- Project 8 - Part 1 - ResumeДокумент2 страницыProject 8 - Part 1 - Resumeapi-275234784Оценок пока нет
- B4 Ethical Problems and Rules of Internet NetiquetteДокумент11 страницB4 Ethical Problems and Rules of Internet NetiquetteTarkan SararОценок пока нет
- 843-Artificial Intelligence-Xi XiiДокумент11 страниц843-Artificial Intelligence-Xi XiiPɾαƙԋყαƚ PαɳԃҽყОценок пока нет
- Indian Standard: Methods of Test For Aggregates For ConcreteДокумент22 страницыIndian Standard: Methods of Test For Aggregates For ConcreteAnuradhaPatraОценок пока нет
- Uvm UnderstandingДокумент8 страницUvm UnderstandingLokesh KumarОценок пока нет
- V0 VSS VDD: Unit PIN Symbol Level Nominal Dimensions Pin Connections Function Mechanical Data ItemДокумент1 страницаV0 VSS VDD: Unit PIN Symbol Level Nominal Dimensions Pin Connections Function Mechanical Data ItemBasir Ahmad NooriОценок пока нет
- MLA 7th Edition Formatting and Style GuideДокумент14 страницMLA 7th Edition Formatting and Style Guideapi-301781586Оценок пока нет
- Instructional Module: IM No.: IM-NSTP 1-1STSEM-2021-2022Документ6 страницInstructional Module: IM No.: IM-NSTP 1-1STSEM-2021-2022Princess DumlaoОценок пока нет
- Pests and Diseases Identification in MangoДокумент4 страницыPests and Diseases Identification in MangoBaino Olpugad Gerald100% (1)
- Oo All MethodДокумент35 страницOo All Methodmeeraselvam19761970Оценок пока нет
- Czujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERДокумент7 страницCzujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERhelp3rОценок пока нет
- Sepction - 3Документ3 страницыSepction - 3k koradiaОценок пока нет
- Excavation and Trenching Implementation PlanДокумент29 страницExcavation and Trenching Implementation Planracing.phreakОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, BaliДокумент58 страницThe Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, Balirachelle agathaОценок пока нет