Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Adj N Adv Clause
Загружено:
Sabrina Umi Khabibah0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыenglish literature
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документenglish literature
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыAdj N Adv Clause
Загружено:
Sabrina Umi Khabibahenglish literature
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
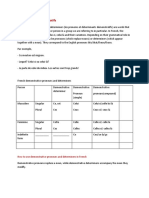
Adjective Clause, Noun Clause and Adverbial Clause
Adjective Clause/Relative Clause
Noun Clause
Adverbial Clause
It is a dependent clause that modifies noun. It It is a dependent clause which is used as a
describes, identifies, or gives further subject or an object.
information about a noun.
The noun clause has its own subject and verb.
An adjective clause closely follows the noun it
modifies.
Noun Clause as Subject:
Where she went is none of your business.
The adjective clause pronouns/relative clause (It is none of your business)
pronouns: who, whom, which, that, whose, Why they left the country is a secret.
where and when.
(That is a secret)
Who-for people
What we are doing in class is easy.
Which-for things
(This is easy)
That-for both people and things
Whether the team wins or loses is not
Where-place
important.
When -time
(It is not important)
It is a dependent clause which shows cause and
effect, contrast, conditions, and time.
Adjective clause pronouns used as the subject:
Conditions
If it rains tomorrow, I will take my umbrella.
Whether it is cold or not, I am going to go
swimming tomorrow.
Even if the weather is cold, Im going to go
swimming.
Ill be at my uncles house in case you need to
reach me.
Ill go swimming tomorrow unless its cold.
(unless = if not)
Only if it rains will the picnic be cancelled.
Only in my hometown do I feel at ease.
(the use of only at the beginning of a sentence
requires Subject-Verb inversion in the main
clause)
I thanked the woman. She helped me.
I thanked the woman who helped me.
Noun Clause as Object.
Do you know whose pen this is?
(Do you know it?)
Please tell me where you live.
The book is mine. It is on the table.
(Please tell me something)
The book which is on the table is mine.
I dont know how old he is.
(I dont know that)
The taxi driver was friendly.
I wonder if she will come or not.
He took me to the airport.
(I wonder something)
The taxi driver who took me to the airport was He always says whatever comes into his mind.
friendly.
(He always says anything)
She can go wherever she wants to go.
(She can go anywhere)
Cause and Effect
Because he was sleepy, he went to bed.
Now that the semester is over, Im going to rest
a few days and then take a trip.
Since youre a good cook and I am not, you
should cook the dinner.
Contrast
Even though I wasnt tired, I went to bed.
Some people are tall, whereas others are short.
While some parts of the world get an abundance
of rain, others get little or none.
Adjective clause pronoun used as the object of a
verb:
The people were very nice.
We visited them yesterday.
The people whom we visited yesterday were
very nice.
The movie wasnt very good.
We saw it last night.
The movie which /that/ 0 we saw last night
wasnt very good.
She is the woman. I told you about her.
She is the woman about whom I told you.
She is the woman whom I told you about.
She is the woman that/ 0 I told you about.
That is the author. I read his book.
That is the author whose book I read.
Mrs. Catt has a painting. Its value is
inestimable.
Mrs. Catt has a painting whose value is
inestimable.
That is the drawer. I keep my jewelry there.
That is the drawer where I keep my jewelry.
They cried the day. They left on that day.
They cried the day when they left.
Time
After, before, when, while, as soon as, until, by
the time, whenever, the first time that, the last
time that, as long as, every time that.
Вам также может понравиться
- Panneerselvam2016 PDFДокумент11 страницPanneerselvam2016 PDFSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- Accepted Manuscript: Sensors and Actuators BДокумент29 страницAccepted Manuscript: Sensors and Actuators BSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- Campbell2018 PDFДокумент21 страницаCampbell2018 PDFSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- An Unusual Case of Highly False-Positive Breath-Alcohol Test in A Motor Vehicle DriverДокумент4 страницыAn Unusual Case of Highly False-Positive Breath-Alcohol Test in A Motor Vehicle DriverSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- Indole PurineДокумент18 страницIndole PurineRamling PatrakarОценок пока нет
- IELTS Sample Writing General Task 1 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыIELTS Sample Writing General Task 1 1 PDFAditya WadeeОценок пока нет
- Dragendorf Test in AlkaloidДокумент7 страницDragendorf Test in AlkaloidSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- CulturingДокумент3 страницыCulturingSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- Field Guide Psilocybin Complete - GhouledДокумент20 страницField Guide Psilocybin Complete - GhouledSabrina Umi Khabibah100% (1)
- Terre Des HommesДокумент40 страницTerre Des HommesSabrina Umi KhabibahОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Seminar Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыSeminar Lesson Planapi-238297343Оценок пока нет
- Yuvaan 23 RuleBookДокумент29 страницYuvaan 23 RuleBookasОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: A I M S TI MI N GДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan: A I M S TI MI N GMihaela PetreciucОценок пока нет
- Delphi Informant Magazine (1995-2001)Документ40 страницDelphi Informant Magazine (1995-2001)reader-647470Оценок пока нет
- Adaptive2 CYCBDДокумент18 страницAdaptive2 CYCBD于明杰Оценок пока нет
- Supplement+to+Mounce+Chs.26 27Документ6 страницSupplement+to+Mounce+Chs.26 27טימותיוסבִּנדִּיОценок пока нет
- FasciДокумент11 страницFasciLiza Dahan Andea-SaayoОценок пока нет
- Dma ControllerДокумент28 страницDma ControllerVEL TECHОценок пока нет
- Unit 5Документ19 страницUnit 5isara_ariesОценок пока нет
- Tempos Var HaydnДокумент9 страницTempos Var HaydnElision06Оценок пока нет
- Shine On 4 Worksheet SolutionДокумент2 страницыShine On 4 Worksheet SolutionJoze LwyzОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map TleДокумент2 страницыCurriculum Map TleReynalyn Mercado Pineda-CarabocОценок пока нет
- Administration Guide Open Bee Scan (En)Документ45 страницAdministration Guide Open Bee Scan (En)peka76Оценок пока нет
- Les Pronoms dém-WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыLes Pronoms dém-WPS OfficeEdirinОценок пока нет
- Error While Connecting Dremio Through PaxataДокумент22 страницыError While Connecting Dremio Through PaxataDiptam DuttaОценок пока нет
- Gre VocabsДокумент11 страницGre VocabsSaidur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Building Scalable Web Architectures: Aaron BannertДокумент75 страницBuilding Scalable Web Architectures: Aaron BannertshardullavandeОценок пока нет
- Indian LogicДокумент30 страницIndian Logicmr mr100% (1)
- Grade 6 Entrep and Ict Tle Q1WK3 1Документ33 страницыGrade 6 Entrep and Ict Tle Q1WK3 1Empress KheiОценок пока нет
- Jean Mark Mutumbo 5 Fallen Angels The Progenitors of Hybrid Races and Promulgators of Dark KnowledgeДокумент12 страницJean Mark Mutumbo 5 Fallen Angels The Progenitors of Hybrid Races and Promulgators of Dark KnowledgeisaacdsapiОценок пока нет
- Secondary Primary SourcesДокумент4 страницыSecondary Primary SourcesVinMoroCiprianoОценок пока нет
- Ads Unit - 5Документ7 страницAds Unit - 5MonicaОценок пока нет
- Chinese LiteratureДокумент25 страницChinese LiteratureQueenie Anne Barroga AspirasОценок пока нет
- Absence REST UserDocumentationДокумент9 страницAbsence REST UserDocumentationYonny Isidro RendonОценок пока нет
- Official SAT Study Guide Practice Test 9 - March 13, 2022Документ8 страницOfficial SAT Study Guide Practice Test 9 - March 13, 2022Phan Bảo NgọcОценок пока нет
- PEÑUELA-PINEDA, Jahisber (2019) - Sanctuary-Temple in Genesis 1-3, A Reevaluation of The Biblical Evidence. Tesis Doctoral. Andrews University PDFДокумент325 страницPEÑUELA-PINEDA, Jahisber (2019) - Sanctuary-Temple in Genesis 1-3, A Reevaluation of The Biblical Evidence. Tesis Doctoral. Andrews University PDFHumberto José Cardoza MorenoОценок пока нет
- Tarot and The Hebrew Alphabet PDFДокумент8 страницTarot and The Hebrew Alphabet PDFRemus BabeuОценок пока нет
- 4.2 TEST 2 KeysДокумент4 страницы4.2 TEST 2 KeysThu GiangОценок пока нет
- LP 19 Pythagorean TriplesДокумент10 страницLP 19 Pythagorean TriplesJack BuhaweОценок пока нет
- English CG 1-10Документ334 страницыEnglish CG 1-10Jan Aguilar Estefani100% (1)