Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Female Reproductive Anatomy Guide
Загружено:
arzeManzanoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Female Reproductive Anatomy Guide
Загружено:
arzeManzanoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
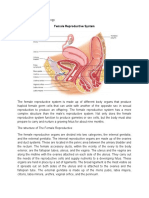
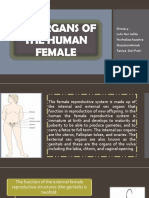
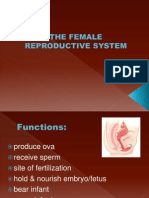
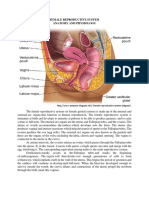
The anatomy and physiology of FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGAN
The female reproductive organs consist of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, external
genitalia, and mammary glands
Ovaries- the two ovaries are small organs suspended in the pelvic cavity by ligaments. Ovaries
are the female reproductive glands where the 400,000 ova or egg cells are stored. The outer part
of the ovary is made up of dense connective tissue and contains ovarian follicles.
Fallopian tubes- the uterine tubes extend from the area of the ovaries to the uterus. They open
directly into the peritoneal cavity near each ovary and receive the oocyte. The opening of each
uterine tube is surrounded by long, thin processes called fimbrae. It is a 4 inches long from
each side of the uterus. It transports the mature ova from the ovaries to the uterus and provide a
place for fertilization of the ova by the sperm in its outer 3rd or outer half.
Uterus- The uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear, with a thick lining and muscular walls.
Located near the floor of the pelvic cavity, it is hollow to allow a blastocyte, or fertilized egg, to
implant and grow. It also allows for the inner lining of the uterus to build up until a fertilized egg
is implanted, or it is sloughed off during menses.
The uterus contains some of the strongest muscles in the female body. These muscles are able to
expand and contract to accommodate a growing fetus and then help push the baby out during
labor. These muscles also contract rhythmically during an orgasm in a wave like action. It is
thought that this is to help push or guide the sperm up the uterus to the fallopian tubes where
fertilization may be possible.
Vagina- is a female organ of copulation and functions to receive the penis during intercourse. It
allows menstrual flow and childbirth. The superior portion of the vagina is attached to the sides
of the cervix so that a part of the cervix extends into the vagina.
External genitalia- also called vulva or pudendum of the vestibule and its surrounding
structures. The vestibule is the space into which the vagina and urethra open. The vestibule is
bordered by a pair of thin, longitudinal skin folds called the labia minora. A small erectile
structure called clitoris. The two labia minora unite over the clitoris to form a fold skin called the
prepuce. Lateral to the labia minora are two prominent, rounded folds skin called labia majora.
The space between the labia majora is called the pudendal
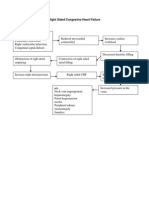
Pathophysiology of Ectopic pregnancy
Predisposing Factors
-Lifestyle(smoking)
-Age (below 18 and above 35 years old)
-Race(black)
Precipitating Factors
-Renal disease or transplant
-History of pelvic inflammatory disesase
-Endometriosis
-Uterine curettage
Matured ovum release from ovary ready for fertilization
Matured egg pick-up by fallopian tube
Division of cells
Sperm cells enter to uterine cavity and migrate to fallopian tube
Only one best and healthiest sperm will reach the ovum
Cluster of cell
Morula
Blocks movement of fertilized egg to the uterus
Fertilized egg attaches and implants in the fallopian tube
Distention and irritation of fallopian tube
-Moderate amount dark red vaginal bleeding
-Abdominal pain
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Вам также может понравиться
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент5 страницFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemДокумент54 страницыPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System Functions and AnatomyДокумент67 страницFemale Reproductive System Functions and AnatomyPaul AndersonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemДокумент67 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Документ49 страницAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)HumrazОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System: External Generative OrgansДокумент28 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System: External Generative OrgansAlmira Gamao100% (1)
- Unit XДокумент18 страницUnit XPreeti ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент5 страницAnatomy and Physiologychinchin ramosОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент11 страницFemale Reproductive SystemArianna Jasmine MabungaОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMДокумент127 страницScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemДокумент6 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemFarlyn Real MoralesОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology HmoleДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology HmoleEunice CasaclangОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology: Female External GenitaliaДокумент85 страницAnatomy and Physiology: Female External GenitaliaJonah Rei BeatoОценок пока нет
- Sex Organs of The Human FemaleДокумент17 страницSex Organs of The Human FemaleTaniya DwiputriОценок пока нет
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewДокумент49 страницREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaОценок пока нет
- The Reproductive SystemДокумент17 страницThe Reproductive SystemRye ManosОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент6 страницFemale Reproductive SystemAlyanna L. ArquillanoОценок пока нет
- 10FRSДокумент27 страниц10FRSWakanda ForeverОценок пока нет
- Female Reproduction Anatomy PhysiologyДокумент15 страницFemale Reproduction Anatomy PhysiologyMhiahLine TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Organ in MammalsДокумент11 страницReproductive Organ in MammalstajudeenabdullahaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of the Female Reproductive OrgansДокумент2 страницыAnatomy of the Female Reproductive OrgansJahn Dela RosaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент8 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyAironne ManguilimotanОценок пока нет
- Document (17) XXДокумент45 страницDocument (17) XXShafiq SaweraОценок пока нет
- Gender & Society Lo4Документ6 страницGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Human Reproduction: Prepared By: Kriti BanstolaДокумент78 страницUnit 1: Human Reproduction: Prepared By: Kriti BanstolaKriti BanstolaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive AnatomyДокумент34 страницыFemale Reproductive AnatomyAswin Dwi PrayudiОценок пока нет
- Understanding Hysterectomy: A Guide to the Surgical ProcedureДокумент22 страницыUnderstanding Hysterectomy: A Guide to the Surgical ProcedureGinger Enireht HTaibОценок пока нет
- Female RSsystem 2Документ90 страницFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент25 страницFemale Reproductive SystemJay PornelaОценок пока нет
- ANATOMY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM - RamosДокумент4 страницыANATOMY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM - RamosLouwella RamosОценок пока нет
- 12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionДокумент16 страниц12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionNishant ShahОценок пока нет
- REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGYДокумент17 страницREPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGYBobby Dwi PutraОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGYДокумент6 страницBIOLOGYCLANSIE BUXTON CHIKUMBEОценок пока нет
- Dana AssignmentДокумент10 страницDana AssignmentDana khalidОценок пока нет
- GEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Документ9 страницGEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Hannah Lee LumosbogОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System in Human - DocxenjelДокумент35 страницFemale Reproductive System in Human - DocxenjelAyusofilla ChipzzОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент43 страницыReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuerteОценок пока нет
- The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент48 страницThe Female Reproductive SystemLiezel CauilanОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System (Human)Документ21 страницаFemale Reproductive System (Human)RiazAhmedОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент6 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsОценок пока нет
- Reproductive System ReportДокумент18 страницReproductive System ReportminnieОценок пока нет
- Gynecologic Disorder Case ReportДокумент30 страницGynecologic Disorder Case ReportlhedavenОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System PDFДокумент48 страницFemale Reproductive System PDFTeppy the GreatОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology - EctopicДокумент4 страницыAnatomy and Physiology - EctopicReyzelinОценок пока нет
- Inbound 7864817067318640141Документ55 страницInbound 7864817067318640141Rijane Mae Castillo GabaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент7 страницFemale Reproductive SystemjonaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Women's Health: An Overview of the Female Reproductive System and Menstrual CycleДокумент47 страницIntroduction to Women's Health: An Overview of the Female Reproductive System and Menstrual CycleDarren LimОценок пока нет
- Notes On The Human Female Reproductive SystemДокумент10 страницNotes On The Human Female Reproductive Systemfichte121Оценок пока нет
- Human Body Flat Design Presentation Pink VariantДокумент16 страницHuman Body Flat Design Presentation Pink VariantAngie MejaritoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology CompleteДокумент9 страницAnatomy and Physiology CompleteJohn BretanaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive Anatomy in <40 CharactersДокумент7 страницFemale Reproductive Anatomy in <40 CharactersEdDa LaIne TotillaОценок пока нет
- Female RSystemДокумент71 страницаFemale RSystemicliftonguytonОценок пока нет
- C CCCCC CCCC C C CC C C C C C CCCCCCCCCCCC CCC CC CCCCCCCCCCC CCCC!CC"CCC C C CCCCC CCCCCCCC CC C CCCCCC#CCCCC CC C CCCCC CCCCC C C C CC CCCC#C C CCCCCC C $CCCCC C %C C&C 'CCCДокумент4 страницыC CCCCC CCCC C C CC C C C C C CCCCCCCCCCCC CCC CC CCCCCCCCCCC CCCC!CC"CCC C C CCCCC CCCCCCCC CC C CCCCCC#CCCCC CC C CCCCC CCCCC C C C CC CCCC#C C CCCCCC C $CCCCC C %C C&C 'CCCJona Phie Domingo MonteroОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент69 страницFemale Reproductive Systemenam professorОценок пока нет
- ModuleДокумент8 страницModuleKarnina MagbuhosОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент5 страницFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyGeevee Naganag VentulaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Документ36 страницFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithОценок пока нет
- Fetal DevelopmentДокумент9 страницFetal DevelopmentarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Neuro Quiz: Key Signs and Symptoms of MeningitisДокумент16 страницNeuro Quiz: Key Signs and Symptoms of MeningitisarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- DB35 - Thyroid PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыDB35 - Thyroid PathophysiologyJainee Canilao TuazonОценок пока нет
- Brand Names: Generic NameДокумент3 страницыBrand Names: Generic NameEzraManzanoОценок пока нет
- Communicable Diseases - ArticlesДокумент4 страницыCommunicable Diseases - ArticlesarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Bring It On: D F G DДокумент1 страницаBring It On: D F G DHernan Josue Nuñez RomoОценок пока нет
- Fetal Circulation Explained: How Blood Flows Before BirthДокумент1 страницаFetal Circulation Explained: How Blood Flows Before BirtharzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Assessment Dengue CaseДокумент4 страницыAssessment Dengue CasearzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Labresult CHFДокумент4 страницыLabresult CHFarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Case Study DM TYPE IIДокумент16 страницCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureДокумент1 страницаRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureEzraManzanoОценок пока нет
- ComДокумент27 страницComarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Family Case AnalysisДокумент91 страницаFamily Case AnalysisarzeManzanoОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Health TeachingДокумент3 страницыPulmonary Tuberculosis Health Teachinggenellemaarte100% (1)
- Lab Activity I: Vaginal Smear in MiceДокумент9 страницLab Activity I: Vaginal Smear in MiceNadhillaHauraWahyudianaОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY SS2 3RD TERM E-NOTES (Reviewed)Документ89 страницBIOLOGY SS2 3RD TERM E-NOTES (Reviewed)kanajoseph2009Оценок пока нет
- Sexual Hookup Culture A ReviewДокумент28 страницSexual Hookup Culture A ReviewBowman lilyОценок пока нет
- Fraternal TwinsДокумент4 страницыFraternal TwinsjovinerОценок пока нет
- Male and Female Radiographic ProceduresДокумент5 страницMale and Female Radiographic ProceduresKaye A. JardinicoОценок пока нет
- Angiosperm Life Cycle StagesДокумент2 страницыAngiosperm Life Cycle StagesAubrey TawandaОценок пока нет
- MARRIENILLA MERCADO Lab Report. Exercise 5. The Structure of A Flower and Seed DevelopmentДокумент12 страницMARRIENILLA MERCADO Lab Report. Exercise 5. The Structure of A Flower and Seed DevelopmentMagisa JosephОценок пока нет
- 18 HR 1Документ5 страниц18 HR 1bingchillingОценок пока нет
- Pros and Cons of InbreedingДокумент8 страницPros and Cons of InbreedingBBОценок пока нет
- Mode of ReproductionДокумент33 страницыMode of ReproductionMd. Rayhan Ali RejviОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент4 страницыPDFmbakpithi0% (1)
- 10th Biology Mcqs NotesДокумент31 страница10th Biology Mcqs Notessupersaad987Оценок пока нет
- Floral Formula: BotanyДокумент7 страницFloral Formula: BotanyzedoksОценок пока нет
- Assessment 1 Unit 2Документ12 страницAssessment 1 Unit 2maya 1DОценок пока нет
- Reproductive System Power Point AckroydДокумент36 страницReproductive System Power Point AckroydMary Grace FacularinОценок пока нет
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1Документ20 страницScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1Kate BatacОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 Mcas ReviewДокумент142 страницыGrade 8 Mcas Reviewapi-294483847Оценок пока нет
- Paschoal & Zara (2020) - AABCДокумент19 страницPaschoal & Zara (2020) - AABCLucas PaschoalОценок пока нет
- Ohana Circle (F4) / Fresh N Dash (F5) Sultanah Bahiyah National Secondary School Form 4Документ7 страницOhana Circle (F4) / Fresh N Dash (F5) Sultanah Bahiyah National Secondary School Form 4Hafizuddin KamarudinОценок пока нет
- Internal and External Fertilization in AnimalДокумент10 страницInternal and External Fertilization in AnimalSerdar AgidОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Sure Short Questions SetДокумент17 страницCBSE Class 12 Biology Sure Short Questions SetJohn SamuelОценок пока нет
- National Public School: SUBJECT-Science (10 (Pre Board Examination)Документ2 страницыNational Public School: SUBJECT-Science (10 (Pre Board Examination)amit kumarОценок пока нет
- Advances and Limitations of in Vitro Embryo Production in Sheep and Goats, Menchaca Et Al., 2016Документ7 страницAdvances and Limitations of in Vitro Embryo Production in Sheep and Goats, Menchaca Et Al., 2016González Mendoza DamielОценок пока нет
- Science QuizДокумент13 страницScience Quizgrethel anne abellanosaОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0007193505800223 MainДокумент12 страниц1 s2.0 S0007193505800223 Mainadamos1945Оценок пока нет
- MaternalДокумент5 страницMaternalStephanie Joy EscalaОценок пока нет
- Recent Advances in The Application of Plant Tissue Culture in DieffenbachiaДокумент10 страницRecent Advances in The Application of Plant Tissue Culture in DieffenbachiaaguilaquecaeОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan in Science (PollinationДокумент4 страницыLesson Plan in Science (PollinationChamille AmahoyОценок пока нет
- The Genetic Foundations of DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыThe Genetic Foundations of Developmentmark bryan roblezaОценок пока нет