Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Partsofspeechandtenses
Загружено:
CinthyaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Partsofspeechandtenses
Загружено:
CinthyaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Parts of Speech
Noun
A naming word. It names a person, place, thing, idea, living creature, quality, or action.
Examples: cowboy, theatre, box, thought, tree, kindness, arrival
Verb
A word which describes an action (doing something) or a state (being something).
Examples: walk, talk, think, believe, live, like, want
Adjective
A word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun.
Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important
Adverb
A word which can describe verbs and adjectives. It tells you how something is done. It may also tell
you when or where something happened. Why?, how?, when? where? how much?
Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere
Pronoun
Used instead of a noun, to avoid repeating the noun.
Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
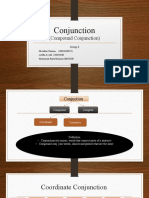
Joins words, phrases or clauses together.
Conjunction Examples: for, and, nor, but, or, yet (coordinating) - after, although, as, because, if, since, when, while
(subordinating). A subordinating conjunction introduces a dependent clause.
Preposition
Usually comes before a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. It joins the noun to some other part of the
sentence.
Examples: on, in, by, with, under, through, at
An unusual kind of word, because it often stands alone. Interjections are words which express emotion
Interjection or surprise, and they are usually followed by exclamation marks.
Examples: Ouch!, Hello!, Hurray!, Oh no!, Ha!
Article
Used to introduce a noun.
Examples: the, a, an
http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/parts.htm
The verb
The noun
The pronoun
The proper noun
The adjective
The adverb
The preposition
The conjunction
The interjection.
Clauses
eat, dance, play, work, study
He is always under the big tree, but not today
floor, computer, table, sky, shoes She sometimes dances amazingly on the floor
he, she, it, I, you, they, we
He always is in the beautiful park.
John, Costa Rica, Maria, Cenfotec I study at Cenfotec.
amazing, pretty, smart, big, red
Amanda plays with her new computer everyday
always, likely, many, first, quickly Angie was running quickly on the pretty beach
under, to, for, on, at
Wow, Alex is probably the best liar in the world
but, and, or, so, because
Paola was quietly reading a scary book, but she fell asleep.
ouch, wow, oh my god, ahh,
Oh no, I suddenly felt the earth shake.
Independent: A group of words with subject and verb (predicate). An independent clause is a sentence. One can join
independent clauses with a period (.), semicolon (;), or a conjunction.
I like to ride my bike. It is fun.
Dependent: A group of words with a subject and verb, but does not express a complete though. It depends on an
independent clause. One uses a comma (,) to join a dependent and independent clause.
When I ride my bike, I go to the park.
http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/598/01/
SVO: Subject + verb + object
The object: a word or phrase in a sentence referring to the person or thing receiving the action.
I like apples
Subject complement with verb to be. That is a car
Tenses
Past
Simple Past: Subject + past verb.
Do: Did + subject + verb?
Subject + did
Be: Was/were + subject...?
Subject + was/were
Present Perfect: Has/have + subject + past participle?
Subject + has/have + past participle
Past continuous: Subject + was/were + verb-ing.
Present Perfect Continuous: Subject + has/have + been + verb-ing
Past Perfect: Subject + had +past participle
Had + subject + past participle?
I walked.
Did Gwen walk?
Yes, she did.
Was Gwen at the party?
Yes, she was.
Has Gwen eaten?
No, she has not.
She was dancing, and then she fell.
Gwen has been eating.
I had already eaten.
Had you already eaten?
o What are some past time expressions? A few years ago In the past In the nineteenth century in the 60s
Present
Simple Present: Subject + verb
Do: Do/does + subject + verb?
Subject + do/does
Be: Be + subject+...?
Subject + be
Present continuous: Be + subject + present participle?
Subject + be + present participle
Bryan sings.
Does Bryan sing?
Yes, he does.
Is Bryan in the bathroom?
No, he is not.
Are Bryan and Tao fighting?
No, they are not.
o What are some present time expressions? These days Today Nowadays This year
Future
Will: Will + subject + verb?
Subject + will + verb
Be: Be + subject+ going to?
Subject + be + going to.
Will Felix eat?
Yes, he will.
Is Felix going to eat?
Yes, he is going to eat.
o What are some future time expressions? Soon In twenty years In the future In a year in twenty years.
Modal verbs: can, must, may, might, will, would, should. Auxiliary verbs used to be polite or formal. They can express
ability, obligation, possibility, and give advice. They do not need an additional auxiliary in negatives or questions. For
example: Must I come? (Do I must come?), or: He shouldn't smoke (He doesn't should smoke).. http://esl.fis.edu/
grammar/rules/modal.htm
Verbals
Gerund: verb + ing (noun)
Playing is fun.
Infinitive: to + verb (noun, adverb, adjective)
To play is fun. He left to go home. He has a game to play.
Participles (adjective):
The crying baby is tired.
Present: verb + ing
Past: verb + ed (or irregular) The tired baby is crying.
http://www.towson.edu/ows/verbals.html
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Revision Decisions Talking Through Sentences and Beyond PDFДокумент201 страницаRevision Decisions Talking Through Sentences and Beyond PDFkarimhisham100% (4)
- Autonomy in Second Language Learning Managing The ResourcesДокумент220 страницAutonomy in Second Language Learning Managing The Resourcesmyhoopoe100% (6)
- Compound ConjunctionДокумент10 страницCompound ConjunctionMusliFatur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Pasado Simple REvisionДокумент2 страницыPasado Simple REvisionSelene Landaverde0% (1)
- PT4 Grammar Lessons Unit 5 Passive VoiceДокумент4 страницыPT4 Grammar Lessons Unit 5 Passive VoiceCarlos Daniel Taveras LiranzoОценок пока нет
- Elementary Unit 8bДокумент2 страницыElementary Unit 8bladislaoОценок пока нет
- Practice Exercises Unit 7Документ4 страницыPractice Exercises Unit 7Sheryll Joan SolanoОценок пока нет
- Defining Relative Clauses Non-Defining Relative ClausesДокумент1 страницаDefining Relative Clauses Non-Defining Relative ClausesSashidhar BaralОценок пока нет
- Verbs Using ÊTRE in Past Tense A Cup of FrenchДокумент12 страницVerbs Using ÊTRE in Past Tense A Cup of FrenchJEAN JOSUE RAKOTOARIMANANAОценок пока нет
- Mini Vocab Englis Camp 2020Документ8 страницMini Vocab Englis Camp 2020Muhammad ZainuriОценок пока нет
- Narrative TensesДокумент5 страницNarrative Tensesdakooles1Оценок пока нет
- Paraphrasing Steps HandoutДокумент1 страницаParaphrasing Steps HandoutRandy RebmanОценок пока нет
- Pre IntermediateДокумент84 страницыPre IntermediateAlejandra AsencioОценок пока нет
- Advanced Grammar: Subject and Verb InversionДокумент5 страницAdvanced Grammar: Subject and Verb InversionNisrin AdelynaОценок пока нет
- What We Know About Human LanguageДокумент2 страницыWhat We Know About Human LanguageMegan KennedyОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Test Questions Grade 10 English (Quarter 3)Документ2 страницыDepartment of Education: Test Questions Grade 10 English (Quarter 3)Jonah BucoyОценок пока нет
- Theory of Computation: Computer ScienceДокумент134 страницыTheory of Computation: Computer ScienceBijay NagОценок пока нет
- Top-Down Parsing TechniquesДокумент10 страницTop-Down Parsing TechniquesDechasa ShimelsОценок пока нет
- DOCUMENTApproved Yearly Plan for the 7th GradeДокумент2 страницыDOCUMENTApproved Yearly Plan for the 7th GradeБаатар Бат-ЭрдэнэОценок пока нет
- Actvities Under Listening SkillДокумент16 страницActvities Under Listening Skillhannah goldОценок пока нет
- CAT 1999 Paper Answers and ExplanationsДокумент23 страницыCAT 1999 Paper Answers and Explanationsrai19Оценок пока нет
- Đáp Án Chương 5Документ5 страницĐáp Án Chương 5Huỳnh Bảo NgọcОценок пока нет
- Ballad of A Mother's HeartДокумент6 страницBallad of A Mother's HeartRazel Resula100% (1)
- CDS-II 2016 English Solutions - pdf-77Документ10 страницCDS-II 2016 English Solutions - pdf-77pranav KumarОценок пока нет
- Cat Forklift t30d Spare Parts ManualДокумент22 страницыCat Forklift t30d Spare Parts Manualchristineferguson190889rtw100% (111)
- Test Bank For Business Communication 2nd EditionДокумент6 страницTest Bank For Business Communication 2nd Editionturbanthappily7k9stОценок пока нет
- Junior Explorer" 5, PodręcznikДокумент25 страницJunior Explorer" 5, PodręcznikKlaudia JankowskaОценок пока нет
- Test of Present TenseДокумент3 страницыTest of Present TenseWachida RizkiОценок пока нет
- The Writing Center - Choosing The Correct Word Form - GuidesДокумент9 страницThe Writing Center - Choosing The Correct Word Form - GuidesChalee YanaОценок пока нет
- Bhanu SS Arjundhara 77Документ2 страницыBhanu SS Arjundhara 77Shyam Dahal100% (1)