Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bar Stock or Round Bar
Загружено:
P Sandana NaraАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bar Stock or Round Bar
Загружено:
P Sandana NaraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bar stock or Round Bar
Process and types
Most metal produced by a steel mill or aluminium plant is formed (via rolling or extrusion) into
long continuous strips of various size and shape. These strips are cut at regular intervals and
allowed to cool, each segment becoming a piece of bar stock. A good analogy is pasta-making, in
which lumps of dough are extruded into various cross-sectional shapes; cut into lengths; and then
dried in that form. The cross-sectional shapes of pasta vary from simple bar or tube shapes (such
as linguine or penne) to more elaborate extrusions (such as rotelle, fiori, or rotini). The same is
true of metal bar stock. The most common shapes are round bar (also called rod), rectangular
bar (including square bar, the special case of equal sides), and hexagonal bar (usually called
hex bar for short). Tube and pipe are similar, but have hollow centers and are traditionally not
called "bar" in industrial usage. (However, a product called hollow bar, essentially tube but with
custom-orderable OD and ID and thus custom wall thickness, is marketed for lathe bar work
which can benefit from obviation of drilling and rough boring.) Also similar in concept, but not
called "bar", are the common structural shapes such as angle stock and channel stock. These are
commonly available in steel and aluminum; the names "angle iron" and "channel iron" are still
commonly used (informally) even though their literal namesake, wrought iron, has been replaced
by steel and aluminum for most uses.
In a machine shop, bar stock and plate are often called billet, although in a rolling mill, that word
refers to a piece of metal that has not yet been rolled into bar.
Rolling
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one
or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness and to make the thickness uniform. The concept is
similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal
rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process
is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature,
the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than
any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold
working processes.[1][2] Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills
that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams,
angle stock, channel stock, and so on), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mills have rolling mill
divisions that convert the semi-finished casting products into finished products.
There are many types of rolling processes, including ring rolling, roll bending, roll forming,
profile rolling, and controlled rolling.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_stock
Вам также может понравиться
- Traceability List: ProjectДокумент16 страницTraceability List: ProjectP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- Quality Manual for Machining, Fabrication and Testing ServicesДокумент76 страницQuality Manual for Machining, Fabrication and Testing ServicesP Sandana Nara100% (2)
- Remove The Welder No Remove and Put As "Refer To The Attached Drawing"Документ4 страницыRemove The Welder No Remove and Put As "Refer To The Attached Drawing"P Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- Arc Gouging Process GuideДокумент6 страницArc Gouging Process GuideP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- No Smoking PolicyДокумент1 страницаNo Smoking PolicyP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- MR No Team Part No Item No Type Grade Standard Specification 140447-01,02, 140462-01-01 Cameron 235672-27/01 N/A Metal A36/S275JRASTM N/AДокумент3 страницыMR No Team Part No Item No Type Grade Standard Specification 140447-01,02, 140462-01-01 Cameron 235672-27/01 N/A Metal A36/S275JRASTM N/AP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- Approved SMDL Copy of Worksheetin4500541788-40-Smdlrev00 - 20130911043508.141 - XДокумент2 страницыApproved SMDL Copy of Worksheetin4500541788-40-Smdlrev00 - 20130911043508.141 - XP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- MR No Team Part No Item No Type Grade Standard Specification 140447-01,02, 140462-01-01 Cameron 235672-27/01 N/A Metal A36/S275JRASTM N/AДокумент3 страницыMR No Team Part No Item No Type Grade Standard Specification 140447-01,02, 140462-01-01 Cameron 235672-27/01 N/A Metal A36/S275JRASTM N/AP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
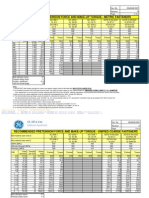
- GE Oil & Gas Subsea Systems Torque and Tension RecommendationsДокумент2 страницыGE Oil & Gas Subsea Systems Torque and Tension RecommendationsP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- Material TestДокумент9 страницMaterial TestP Sandana NaraОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- BlockStack Top 21 Trends in Web3 1676290935Документ9 страницBlockStack Top 21 Trends in Web3 1676290935Ahmed BachaОценок пока нет
- Using Accelerometers in A Data Acquisition SystemДокумент10 страницUsing Accelerometers in A Data Acquisition SystemueidaqОценок пока нет
- Writing Patterns NotesДокумент2 страницыWriting Patterns NoteslwitsfadontОценок пока нет
- Arduino Project: Smart Irrigation SystemДокумент13 страницArduino Project: Smart Irrigation SystemAleeza AnjumОценок пока нет
- Doctrina PNP Mayer LotДокумент23 страницыDoctrina PNP Mayer LotWilson Francisco Saldarriaga CruzОценок пока нет
- Study Guide For Kawabata's "Of Birds and Beasts"Документ3 страницыStudy Guide For Kawabata's "Of Birds and Beasts"BeholdmyswarthyfaceОценок пока нет
- Family Values, Livelihood Resources and PracticesДокумент285 страницFamily Values, Livelihood Resources and PracticesRogelio LadieroОценок пока нет
- CCTV Effectiveness in Reducing CrimeДокумент31 страницаCCTV Effectiveness in Reducing CrimeNeil Adonis UsaragaОценок пока нет
- Interventional Radiology & AngiographyДокумент45 страницInterventional Radiology & AngiographyRyBone95Оценок пока нет
- Intrrogative: Untuk Memenuhi Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris DasarДокумент9 страницIntrrogative: Untuk Memenuhi Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris DasarRachvitaОценок пока нет
- 12soal Uas - K.99 - Raditya - Bahasa Inggris Hukum (1) - 1Документ3 страницы12soal Uas - K.99 - Raditya - Bahasa Inggris Hukum (1) - 1Brielle LavanyaОценок пока нет
- Quarter 4 English 3 DLL Week 1Документ8 страницQuarter 4 English 3 DLL Week 1Mary Rose P. RiveraОценок пока нет
- Guidance On Energy AuditsДокумент6 страницGuidance On Energy AuditsTesfahun Girma100% (1)
- Neotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideДокумент21 страницаNeotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideRamesh PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 20 ASL Circular-1 PDFДокумент3 страницы20 ASL Circular-1 PDFAlagu MurugesanОценок пока нет
- JAG Energy Case StudyДокумент52 страницыJAG Energy Case StudyRei JelОценок пока нет
- System ThinkingДокумент18 страницSystem Thinkingpptam50% (2)
- Curriculum Design and Development Part IДокумент18 страницCurriculum Design and Development Part IAngel LimboОценок пока нет
- Teaching Arts in ElementaryДокумент21 страницаTeaching Arts in ElementaryJackaii Waniwan IIОценок пока нет
- Detect3D Fire and Gas Mapping Report SAMPLEДокумент29 страницDetect3D Fire and Gas Mapping Report SAMPLEAnurag BholeОценок пока нет
- 1950's or The Golden Age of TechnologyДокумент15 страниц1950's or The Golden Age of TechnologyFausta ŽurauskaitėОценок пока нет
- Falcon Nir Online AnalyzerДокумент4 страницыFalcon Nir Online AnalyzerCesc MezaОценок пока нет
- HandwritingДокумент25 страницHandwritingajeshtnОценок пока нет
- Metamorphic differentiation explainedДокумент2 страницыMetamorphic differentiation explainedDanis Khan100% (1)
- Model HA-310A: Citizens BandДокумент9 страницModel HA-310A: Citizens BandluisОценок пока нет
- The Heart of Arabia - A Record of Travel & ExplorationДокумент503 страницыThe Heart of Arabia - A Record of Travel & ExplorationAltug100% (1)
- Test 1: (Units 1-2)Документ59 страницTest 1: (Units 1-2)Elena MH100% (1)
- No. of Periods UNIT - 1: Antenna FundamentalsДокумент8 страницNo. of Periods UNIT - 1: Antenna Fundamentalsbotla yogiОценок пока нет
- MySQL Backups Go Near-ContinuousДокумент43 страницыMySQL Backups Go Near-ContinuousOleksiy KovyrinОценок пока нет
- Lineshaft Turbine Pump 1800 RPM 60 HZДокумент156 страницLineshaft Turbine Pump 1800 RPM 60 HZFayez Al-ahmadiОценок пока нет