Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
House Wiring Circuits
Загружено:
uzair12345Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
House Wiring Circuits
Загружено:
uzair12345Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
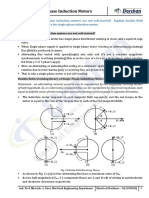
AC single-phase induction motors
Single-coil AC induction motors
AC induction motors usually use two or more coils to generate a rotating magnetic field, which produces
torque on the rotor. When a single coil is used, it will generate a pulsating magnetic field, which is enough
to sustain rotation, but not sufficient to start the motor from a standstill. Motors with a single coil have to
be started by using an external force.
Start capacitor AC induction motors
One way to improve on the single coil design is by using an auxiliary coil in series with a motor starting
capacitor. The auxiliary winding (coil), also called starting winding, is used to create an initial rotating
magnetic field. In order to create a rotating magnetic field, the current flowing through the main winding
must be out of phase in respect to the current flowing through the auxiliary winding. The role of the
starting capacitor is to lag the current in the auxiliary winding, bringing these two currents out of phase.
When the rotor reaches sufficient speed, the auxiliary coil is disconnected from the circuit by means of a
centrifugal switch, and the motor remains powered by a single coil creating a pulsating magnetic field.
Start/run capacitor AC induction motors
Another way to further improve on the single-coil single-phase induction motor design is to introduce an
auxiliary coil, which remains powered not only during the motor startup phase, but also during normal
operation. As opposed to an AC motor using only a motor start capacitor, which creates a pulsating
magnetic field during normal operation, AC motors using a motor start capacitor and a motor run capacitor
create a rotating magnetic field during normal operation. The function of the motor start capacitor remains
the same as in the previous case it gets disconnected from the circuit after the rotor reaches a
predetermined speed by means of a centrifugal switch. After that point, the auxiliary winding remains
powered through a motor run capacitor.
A centrifugal switch is an electric switch that operates using the centrifugal force created from a rotating
shaft, most commonly that of an electric motor. The switch is designed to activate or de-activate as a
function of the rotational speed of the shaft.
The iron-core electromagnetic ballast consists of a magnetic core of laminated transformer steel around
which is wound a coil of insulated copper or aluminium wire use to limit the arc current. Electronic ballasts
are energy-efficient electromagnetic ballasts with added electronic circuitry which cuts off current to the
lamp filaments once the gas discharge has been established. Using this type of ballast with the same lamps
as the previous example, the ballast loss would typically be only 5% of the input power.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Fluorescent Tube light
A fluorescent light does not have the usual glowing filament of an incandescent bulb, but instead contains a
mercury vapour that gives off ultraviolet light when ionized. The ultraviolet light makes particles that coat
the inside of the tube, and these particles glow or fluoresce.
Fluorescent starters are there to help the lamp light. When voltage is applied to the fluorescent lamp, here's
what happens:
1. The starter (simply a timed switch) allows current to flow through the filaments at the ends of the tube.
2. The current causes the starter's contacts to heat up and open, thus interrupting the flow of current.
3. Since the lighted fluorescent tube has a low resistance, the ballast now serves as a current limiter.
When you turn on a fluorescent tube, the starter is a closed switch. The filaments at the ends of the tube are
heated by electricity, and they create a cloud of electrons inside the tube. The fluorescent starter is a timedelay switch that opens after a second or two. When it opens, the voltage across the tube allows a stream of
electrons to flow across the tube and ionize the mercury vapour.
Without the starter, a steady stream of electrons is never created between the two filaments, and the lamp
flickers. Without the ballast, the arc is a short circuit between the filaments, and this short circuit contains a
lot of current. The current either vaporizes the filaments or causes the bulb to explode.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Hajj GuideДокумент22 страницыHajj Guideuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Industrial Automated Systems Instrumentation and Motion Control 1st EditionДокумент9 страницSolution Manual For Industrial Automated Systems Instrumentation and Motion Control 1st Editionclementchang3iur0% (1)
- AC Generator Simulation Using FEMM and LuaДокумент6 страницAC Generator Simulation Using FEMM and LuaSushant ChhotrayОценок пока нет
- Microgrids Architectures and CДокумент1 страницаMicrogrids Architectures and Cuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Sitting ArrangementsДокумент1 страницаSitting Arrangementsuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Zyarat e QuboorДокумент1 страницаZyarat e Qubooruzair12345Оценок пока нет
- 8 Machine Learning Algorithms in PythonДокумент16 страниц8 Machine Learning Algorithms in Pythonuzair12345100% (2)
- Part Five - The Youth Camp in Theory and Practice - TG by Dr. Hisham AltalibДокумент47 страницPart Five - The Youth Camp in Theory and Practice - TG by Dr. Hisham Altalibuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Zakatal FitrДокумент1 страницаZakatal Fitruzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Electrical Power ManualДокумент1 страницаElectrical Power Manualuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Caring For An OrphanДокумент1 страницаCaring For An Orphanuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Power DistributionДокумент1 страницаPower Distributionuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- World Orphans DayДокумент1 страницаWorld Orphans Dayuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Power Utilization TechДокумент1 страницаPower Utilization Techuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Automated Web Testing Using SeleniumДокумент10 страницAutomated Web Testing Using SeleniumFaceme TesterОценок пока нет
- Course Outline of Functional English & Communication SkillsДокумент2 страницыCourse Outline of Functional English & Communication Skillsuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Bin Qasim Power PLant MapДокумент1 страницаBin Qasim Power PLant Mapuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- CEC Accreditation DesignДокумент20 страницCEC Accreditation Designuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Effective Comm at WorkplaceДокумент60 страницEffective Comm at Workplaceuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Linear Combination: 3.4 Linear Dependence and Span P. DanzigerДокумент14 страницLinear Combination: 3.4 Linear Dependence and Span P. DanzigerzjnsrbtОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Power Distribution and UtilizationДокумент53 страницыLab Manual Power Distribution and Utilizationuzair12345100% (4)
- University Lesson Planner TipsДокумент1 страницаUniversity Lesson Planner Tipsuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Pakistan Engineering Council Registration FormДокумент6 страницPakistan Engineering Council Registration FormZeeshan HaiderОценок пока нет
- IEC Voltage ClassificationДокумент1 страницаIEC Voltage Classificationuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Swift CodesДокумент3 страницыSwift Codesuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Active Pool SupervisionДокумент1 страницаActive Pool Supervisionuzair12345Оценок пока нет
- 2G 3G RF Drive Tesing Tems Genex Actix RF Optimization GSM RF PlanningДокумент1 страница2G 3G RF Drive Tesing Tems Genex Actix RF Optimization GSM RF Planninguzair12345Оценок пока нет
- Outdoor - Units - MOU 12HDN1 - MOUB 36HDN1 R220075500920 - MOUB 48HDN1 R220075700690 - MOUD 60HDN1 R - MOUA 60HRDN1Документ48 страницOutdoor - Units - MOU 12HDN1 - MOUB 36HDN1 R220075500920 - MOUB 48HDN1 R220075700690 - MOUD 60HDN1 R - MOUA 60HRDN1Muhidin KozicaОценок пока нет
- Variable Speed TechnologyДокумент10 страницVariable Speed Technologyashumishra007Оценок пока нет
- Basic Motor TheoryДокумент26 страницBasic Motor TheoryRoberth Salsr LpzОценок пока нет
- Product Catalog: Electric Propulsion Systems and AccessoriesДокумент40 страницProduct Catalog: Electric Propulsion Systems and AccessoriesMarc MPОценок пока нет
- Summer Training Report PDFДокумент53 страницыSummer Training Report PDFAnjali VermaОценок пока нет
- PROJECT On Power Saving System For LeatheДокумент20 страницPROJECT On Power Saving System For LeatheHi-Bye MarketОценок пока нет
- Materi Motor Listrik (MCSA)Документ207 страницMateri Motor Listrik (MCSA)Nur Muhammad FatkhurrohmanОценок пока нет
- Guide To Low Voltage Motor Testing - 2012-431 - enДокумент44 страницыGuide To Low Voltage Motor Testing - 2012-431 - enNga VũОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Week 7: Assignment 7Документ9 страницUnit 10 - Week 7: Assignment 7venkatОценок пока нет
- DC and AC Motor ControlДокумент6 страницDC and AC Motor Controldes tosОценок пока нет
- Mech 03Документ28 страницMech 03Sahil ThakurОценок пока нет
- Ee 2nd PDFДокумент67 страницEe 2nd PDFbharath sОценок пока нет
- AC MotorДокумент71 страницаAC Motorstallone21Оценок пока нет
- Inverter TrainerДокумент2 страницыInverter TrainerBudhi PrasetiyoОценок пока нет
- Firoz Alam Resume 1Документ5 страницFiroz Alam Resume 1Tahir ArshadОценок пока нет
- Introduction Electrical MotorДокумент36 страницIntroduction Electrical MotorYajidОценок пока нет
- Week1 Introduction PDFДокумент33 страницыWeek1 Introduction PDFMohammad A AlawneОценок пока нет
- BE420002 P2.x ATEXДокумент67 страницBE420002 P2.x ATEXSantiago Hernandez MoralesОценок пока нет
- Dasar Listrik Arus Bolak-BalikДокумент35 страницDasar Listrik Arus Bolak-BalikAri AsriyantoОценок пока нет
- 3GAA091002 ASE Ac Motor M2aa90l 2 2kw PDFДокумент2 страницы3GAA091002 ASE Ac Motor M2aa90l 2 2kw PDFDuilio Matias GonçalvesОценок пока нет
- Fristam FSP-PM-PMV enДокумент15 страницFristam FSP-PM-PMV enAzisОценок пока нет
- Single Phase Motor Schematics and WorkingДокумент4 страницыSingle Phase Motor Schematics and WorkingRajesh TipnisОценок пока нет
- Automatic Side Stand For Two WheelerДокумент84 страницыAutomatic Side Stand For Two Wheelercoolhari0825% (4)
- The Use of Electric Motors For The Propulsion of Seagoing VesselsДокумент23 страницыThe Use of Electric Motors For The Propulsion of Seagoing Vesselspal_malayОценок пока нет
- NEMA MG1-1998 Revision 2002Документ596 страницNEMA MG1-1998 Revision 2002jose manuelОценок пока нет
- Basic Training: Motors, Gears & DrivesДокумент80 страницBasic Training: Motors, Gears & DrivesDANIZACH50% (2)
- PrinciplesДокумент5 страницPrinciplesSachin RohillaОценок пока нет
- Ans.-01 Why Single-Phase Induction Motors Are Not Self-Started?Документ16 страницAns.-01 Why Single-Phase Induction Motors Are Not Self-Started?DharamОценок пока нет